The brain is a complex and poorly understood human organ that is difficult to diagnose. However, the brain is the control center responsible for the operation of all systems in the body. Therefore, any pathological processes in it affect the physical and mental health of a person.
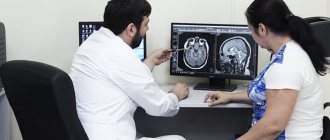
MRI is one of the methods for studying the brain to determine negative conditions in it. Diagnostics is prescribed for adults and children and is a safe examination method.
What it is
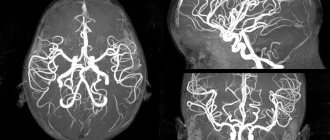
The method refers to a non-invasive examination using radio waves and a magnetic field. During the scanning process, the doctor receives an image showing parts of the brain. Diagnosis is carried out without radiography. The study reveals disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and vascular systems, aneurysms, and tumors.
Also, based on the results of the examination, the level of activity of the cerebral cortex is determined. When using a contrast agent, tissues are better visualized, which helps to more accurately identify pathologies.
Advantages of the method
Advantages of brain tomography:
- the patient does not experience pain during diagnosis;
- During the examination, no foreign substances are introduced into the human body;
- no ionizing radiation;
- clear images help to accurately recognize pathology and prescribe treatment;
- as prescribed by a specialist, an examination of the head and cervical/upper spine is carried out to assess the functional activity of the brain - based on the results, a safe method of surgical intervention is prescribed;
- areas of the brain hidden by the bones of the skull are examined - other methods do not diagnose these areas;
- MRI helps to obtain a complete picture of the brain and vascular system even without the use of a contrast agent;
- tumors and other pathologies are detected in the early stages of development.
Make an appointment now!
Indications for MRI of the brain
Indications for examination are:
- dizziness, fainting, headaches;
- ringing and noise in the ears;
- decreased vision;
- auditory hallucinations;
- problems maintaining balance;
- disturbances of taste and smell;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- complete or partial memory loss.
All of these signs indicate the presence of pathological changes in the nervous or circulatory systems. To find out whether they are related to the condition of the brain, it is necessary to perform magnetic resonance imaging.
Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging are the first trimester of pregnancy, severe cardiac pathologies and the constant presence of metal objects in the body (implants, pacemakers, braces, etc.).
Why is an examination prescribed?
MRI diagnostics helps to recognize pathological changes in the soft tissues of the lining of the brain, inflammatory reactions, and disorders of the central nervous system. Also, with the help of an examination, the conditions of the parts of the head are studied: the visual and occipital lobes, the pituitary gland, the cerebellum, areas of thinking and memory, and the ventricles of the brain.
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes tests, the results of which determine the type of diagnosis. For example, tests showed that the patient had an excess level of the hormone prolactin. The doctor writes a referral for examination of the cerebellum.
Examination of the brain in a magnetic field helps determine the presence of:
- Multiple sclerosis - lesions of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. The diagnosis determines the stage of the disease, the level of damage, after which the doctor prescribes therapy.
- Benign and malignant tumors. Brain scanning is used to identify the affected area, monitor the development of the tumor, as well as the treatment process.
- Disorders in the cerebral cortex - Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease. MRI determines the density of white and gray matter, the presence of pathologies in the subcortex and cortex of the head.
- Ischemic strokes, heart attacks. The images determine the area and density of ischemic lesions, the presence of cortical necrosis, the appearance of edema, and the stage of development of the disease.
- Brain injuries are damage to blood vessels and tissues due to trauma. Diagnostics reveals the first signs of VSD.
- Mental disorders of endogenous and exogenous types. The method helps to identify hereditary pathologies, changes after traumatic brain injury, viral infection, and poisoning with toxic substances. MRI diagnostics determines schizophrenia.
For children, head tomography is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- head injury, concussion after injury, intrauterine infectious processes;
- hypoxia, ischemia and other disruptions in brain development;
- epileptic seizures, cerebral hemorrhage;
- the first stages of multiple sclerosis;
- dangerous diseases such as pituitary adenoma, brain tumors, cysts and suspicions of them;
- a sharp deterioration in vision and hearing, malfunction of the inner ear;
- high intracranial pressure.
Diagnostics helps to study the state of the brain and its parts, identify the causes of headaches in children, and prevent the development of autism.
What does a brain MRI show?
Magnetic resonance imaging helps to see:
- benign and malignant tumors;
- areas of nervous tissue necrosis;
- areas of hemorrhage;
- vascular diseases;
- inflammatory processes of brain tissue;
- dystrophic changes;
- traumatic brain injuries.
Due to its high accuracy, MRI diagnostics can detect even the slightest pathological changes in brain structures.
What diseases can be detected by MRI of the brain?
MRI is used to detect the following diseases:
- ischemic, hemorrhagic stroke;
- thrombosis and vascular aneurysms;
- neoplasms;
- cysts;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- epilepsy;
- atherosclerosis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- inflammatory diseases: meningitis, encephalitis;
- abscesses;
- hemorrhages;
- Parkinson's disease;
- cysts, pituitary adenomas.
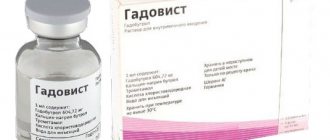
Application of contrast agent
When carrying out MRI diagnostics, contrast can be used, which makes it possible to visualize the deep structures of the brain in more detail, to determine clear boundaries of hemorrhages, neoplasms, and sclerotic changes.
For contrast, drugs containing the chemical element gadolinium are used. The drug is administered intravenously immediately before the study. Carrying through the bloodstream throughout the body, particles of the contrast agent settle in pathologically altered structures, staining them.
Contrasting can be used in the following cases:
- Suspicions of the presence of neoplasms. The contrast agent settles in the tumor tissue, which helps to accurately determine the boundaries and size of the tumor, as well as draw preliminary conclusions about the nature of the tumor. Benign tumors usually have regular sizes and clear boundaries, while malignant tumors grow into surrounding tissues and are irregular in shape with jagged edges.
- Pituitary gland studies. The pituitary gland is very small and is located deep in the structures of the brain. Contrasting allows not only to clearly see the organ itself, but also to identify the presence of pathologies and neoplasms.
- Diagnosis of demyelinating diseases. Contrasting helps to more clearly identify the boundaries and total volume of brain tissue damage.
Brain MRI with contrast
Contrast can be used to diagnose any brain pathologies, because provides a much clearer picture than MRI without contrast.
Contrast drugs are harmless to the body and are excreted through the kidneys. Contraindications for the use of contrast may include renal failure and previously observed allergic reactions.
Differences between MRI and CT scan of the brain
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head differs from other diagnostic methods in the following:
- the examination is performed in 3-4 projections, which provides more information for identifying diseases and choosing treatment methods;
- pathologies are detected in the early stages of development - ischemic changes are detected 2-3 hours after a stroke;
- even minimal changes in the brain that cause multiple sclerosis are determined;
- parts of the brain that are not diagnosed by computed tomography (CT) are studied - the brain stem, the cerebellum.
Who needs to undergo an MRI of the brain?
Most often, a neurologist refers you to magnetic resonance imaging. Indications for research may include:
- regular dizziness and headaches of unspecified nature;
- decreased hearing or vision in the absence of an explanation from an ENT or ophthalmologist;
- frequent fainting;
- head injuries;
- infectious diseases of the brain;
- stenosis (narrowing of blood vessels);
- aneurysms (dilation of blood vessels);
- epilepsy;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- other neurological diseases.
Although brain tomography is a completely safe procedure, there are still contraindications. First of all, they are due to the presence of metal elements that cannot be removed during the procedure:
- braces;
- pacemakers;
- prostheses;
- staples on vessels;
- foreign objects;
- implants.
If there are fixed metal parts and devices, MRI cannot be performed.
Overweight patients may be limited by the diameter of the tomograph capsule.
It is not recommended to undergo an MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy, however, if there are medical indications, the diagnosis will be carried out. At a later date, the examination will not harm either the mother or the child. Breastfeeding women also do not have to worry: magnetic waves do not affect either lactation or the quality of milk.
When is a diagnosis prescribed?
A brain examination is prescribed for the following ailments:
- developmental anomalies and diseases of cerebral vessels;
- head injuries and bruises, cerebral hemorrhages;
- sharp deterioration of vision and hearing;
- tumor development;
- infectious reactions in the central nervous system - meningitis, HIV infections, abscesses;
- pituitary adenoma, epilepsy;
- pathologies of the base of the skull;
- multiple sclerosis, sinusitis, neurodegenerative diseases;
- aneurysms, thrombosis and other anomalies in the vessels of the head.
Diagnosis is also carried out after surgery. Prescribed for frequent migraines and fainting, tinnitus, sudden deterioration of memory and attention, impaired coordination of movements, and mental disorders.
Indications for MRI of the brain
- Dizziness and headaches, migraine;
- head and neck injuries, concussion;
- congenital abnormalities of brain development;
- visual or hearing impairment, tinnitus;
- disorders of speech, memory, intelligence;
- regular nosebleeds;
- fainting;
- stroke;
- ischemic disease;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- deformations of cerebral vessels;
- degenerative changes (Parkinson's disease, etc.);
- demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis);
- inflammatory processes;
- suspicion of a brain tumor or its presence, as well as suspicion of other brain diseases;
- control after surgery.
Contraindications
Head tomography is not prescribed if the patient has absolute contraindications, but is allowed at the discretion of the doctor in case of relative contraindications. Diagnostics is prohibited if the following conditions exist:
- the patient has prosthetic heart valves, pacemakers or neurostimulators;
- presence of insulin pumps, inner and middle ear prostheses, cochlear implant;
- the patient has an Ilizarov apparatus;
- the presence of metal implants, ferromagnetic particles, fragments in the body.
Relative indications include:
- tremor, the patient’s inability to hold his breath for a long time during examination;
- presence of dental braces, dentures, stents, vena cava filters;
- heart failure, clip instead of gallbladder;
- pregnancy;
- claustrophobia;
- severe pain while standing still;
- coronary artery bypass grafting.
Preparatory stage
The doctor, based on the test results, determines whether to perform a tomography with or without the introduction of a contrast agent. If the first option is chosen, then the patient does not take food or liquid 5 hours before the diagnosis. Before the procedure, you must remove all jewelry and accessories, watches and objects with metal elements.
During a consultation with a doctor, the patient reports the presence of chronic diseases, allergies to medications, claustrophobia, and pregnancy.
When preparing a child for a head tomography, it is not recommended to give him anything to drink or eat 3 hours before the diagnosis. If an MRI is performed with the administration of contrast, the examination is performed on an empty stomach. Before the procedure, the child should be shown to an allergist to check for an allergic reaction to the injected substance.
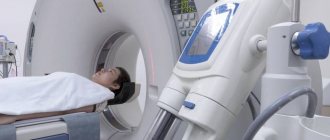
Diagnostic features
If a brain tomography is performed with the introduction of a contrast agent, the examination takes 1-1.5 hours.
Stages:
- the patient removes objects and clothing with metal elements;
- lies on the tomograph table on his back;
- the doctor administers a contrast agent intravenously;
- if there is tremors or inability to lie still, the patient takes sedatives;
- legs and arms are secured with belts, bolsters are placed under the neck;
- the table is pushed into the tomograph capsule - the doctor monitors the procedure from a special room with equipment;
- during the diagnosis, the patient hears slight noises of the tomograph operating - the procedure is safe and painless, a slight sensation is felt in the area of the injection of the substance;
- head diagnostics lasts 15 minutes - the patient is recommended to remain in a stationary position to obtain accurate scan results.
Decoding MRI of the brain
You can receive the test result immediately upon completion of the procedure.
It will take the doctor about 15-30 minutes to decipher the results. Recording images is possible both on a disk (it is provided free of charge), and on film or a flash drive, at the request of the patient.
The patient will be given a disc, as well as a doctor’s report, which will describe in detail the anatomical features of the area under study and possible pathological changes.
The resulting conclusion must be provided to the attending physician to determine a further treatment plan.
Features of examination of children
Brain tomography in children is carried out under the drug n8a8p00ko70z0o-7m9, -6v5 Propofol is administered. Anesthesia helps keep the child still during diagnosis. Children over 5 years old are given a sedative and given psychological adjustment and support before the tomography.
During the examination, the baby is shown cartoons and toys. Some clinics use open tomographs, when only the child's head is placed in the capsule, and the parents stand nearby and hold his hand.
Before diagnosis, it is recommended to take the child to the toilet, remove electronic items and jewelry with metal inserts from clothes and body. Next, the child is dressed in special clothes, “introduced” to the tomograph and allowed to listen to how it works. This helps to calm the baby before the procedure and obtain his consent to the examination.
MRI of the brain for children
The child must remain still during the examination. If necessary, we use sedation or anesthesia.
Indications:
- deterioration of hearing and vision;
- changes in behavior, loss of previously acquired skills;
- frequent headaches, dizziness;
- fainting and convulsions;
- speech delay;
- head injuries with concussion.
Contraindications Preparation
Side effects
After tomography, the patient may experience nausea, dizziness, vomiting, weakness, and disorientation in space. This is a normal reaction. It occurs in people with increased sensitivity, when there are metal objects on the patient’s body, and when the rules for preparing for an MRI are not followed. Unpleasant sensations go away on their own. However, if side effects do not disappear for a long time, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
If the rules are followed, the procedure takes place without pain or side effects. The images help doctors accurately determine the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment.