Psychotherapy as an effective method for treating endogenous depression
Unlike, for example, reactive depression, which is a response to any traumatic event, it does not depend on external circumstances. The causes of this severe disorder lie within the person. The peculiarity of endogenous depression is that it can develop against the background of favorable life circumstances. Of course, unpleasant events also play a role in the occurrence of the disorder - the death or illness of loved ones, problems at work, and others. But stress is just a trigger for endogenous depression, not its cause.
Experts identify the following symptoms of endogenous depression:
- anxiety,
- mental retardation,
- general depression,
- prolonged deterioration in mood and others.
Endogenous depression: causes and symptoms
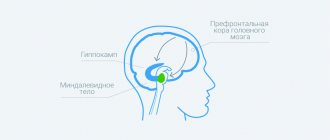
The main reason for this condition is an insufficient amount of hormones such as serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine in the body. That is why the mood of a person suffering from a disorder does not depend on external events.
Some behavioral characteristics of the patient will help to recognize the disease. It is worth considering drastic measures if a person is often in a bad mood, and its quality depends on the time of year (spring and autumn are periods of exacerbation) and the time of day (in the evening the depressive state weakens somewhat). The following symptoms should alert you:
- slow perception of current events,
- inattention,
- inability to concentrate,
- self-deprecation,
- problems with appetite and sleep.
Consultation with a specialist will be necessary if a person complains of pain in muscles, joints, or in the heart area, but there are no organic disorders.
Symptoms
Signs of endogenous depression include:
- causeless or seasonal mood swings;
- experiences associated with mental trauma (they are noticeable at the initial stage of development of endogenous depression);
- narcissism and dependent behavior as very prominent personality traits;
- spontaneous, not caused by external causes, relapses;
- feeling of one's own guilt, self-blame;
- melancholy, apathy, anxiety;
- anhedonia (inability to experience pleasure);
- suicidal behavior (in this case, suicide intentions can be carefully hidden);
- obsessive thoughts of various contents;
- inconsistency of the patient’s reaction to the strength of the stimulus - thus, the disease may begin to worsen due to exposure to the most insignificant factors to which people are normally insensitive.
How to treat endogenous depression
The most effective weapon against endogenous depression is an integrated approach and the use of several techniques. Experts assign an important role in treatment to psychotherapy: as a result of the sessions, the patient will learn to control his condition and gain a sense of stability: in such a situation this is very important.
In some cases, the doctor will include antidepressants in the treatment regimen, the task of which is to restore brain biochemistry and stimulate the production of necessary substances. But, of course, the primary role in endogenous depression is given to psychotherapeutic procedures.
UZ "Mogilev City Emergency Hospital"
“Recognizing a problem is half the success in solving it”
Sigmund Freud
We often hear (observe in ourselves) complaints about depression and loss of strength. The covers of glossy magazines and periodicals are full of titles: “I’m depressed. What should I do?”, “How to overcome depression?” and so on. Meanwhile, depression is by no means a fashion statement, but a very serious emotional illness that affects many aspects of a person’s life.
So what is the difference between periodic mood swings caused by seasonal changes, everyday problems, work or family troubles, and a clinical illness that requires medical intervention?
WORLD STATISTICS
Depressive disorder in the modern world is widespread in all countries, sectors of society and cultures. It can occur in people of different genders, ages and status. At any given time, it affects 5% of the population (approximately 3% of men and 7-8% of women ). Approximately 12% of people will experience at least one episode of depression during their lifetime that reaches a level where medication is necessary.
The lifetime chance of developing this condition is approximately 20% for women and 10% for men . It affects 10% of the population over the age of 40 , of which two thirds are women. Among people over 65 years of age, depression is three times more common . 5% of children and adolescents aged 10 to 16 years are susceptible to depression and depressive conditions . The overall prevalence of depression (of all types) in adolescence ranges from 15 to 40%.
According to the WHO (World Health Organization), depression will take first place among all human diseases by 2021, ahead of cardiovascular disorders and oncology.
So, depression (from the Latin deprimo - “to press”, “to suppress”) is a mental disorder characterized by the “depressive triad”:
- decreased mood and loss of the ability to experience joy (anhedonia);
- thinking disorders (negative judgments, pessimistic view of what is happening, etc.);
- motor retardation.
With depression, self-esteem is reduced, and there is a loss of interest in life and usual activities. In some cases, a person suffering from it may begin to abuse alcohol or other psychotropic substances.
TYPES OF DEPRESSION
- somatic (somatogenic): manifest themselves as a consequence of various (somatic) diseases, such as diabetes mellitus; cancer, etc.)
- endogenous (mental or somatic causes are absent or not obvious);
- seasonal (more often observed in autumn-spring);
- Depression as a side effect of medications:
a) neuroleptic depression (due to taking antipsychotics);
b) depression due to abuse of sedatives, hypnotics, alcohol, cocaine and other psychostimulants;
- reactive depression (due to exposure to traumatic stress; for example, loss of a loved one, divorce, emergency situations, etc.)
MAIN SYMPTOMS OF DEPRESSION
ATTENTION!
These are exactly the symptoms when it is important to prevent further negative changes! They indicate that a depressive disorder has already formed and it is necessary to consult a specialist (psychotherapist) for help!
In addition to the main ones, there are a number of other, additional symptoms:
- Decreased self-esteem, irrational feelings of guilt and loss of self-confidence. A person, regardless of his success in life, constantly feels bad, incapable, worthless.
- A person’s appearance changes - pale face, dilated pupils, dull eyes, dry skin, drooping shoulders, predominance of gray and black clothes, lack of jewelry and cosmetics, sloppiness and indifference to one’s appearance
- Slow, difficult thinking, impaired ability to think and concentrate, decreased intellectual productivity. A person’s attention is scattered, it is difficult for him to concentrate on something, follow the train of thought, or grasp the meaning of the conversation. There are few thoughts in the head, they are usually of unpleasant content and annoyingly revolve around some minor trifles.
- Persistent pessimism and so-called negative thinking - “everything around is bad”, “nothing can be changed”, “I am a complete nonentity”, etc. Pessimism extends both to events of the past and to the future. Such a person sees everything in a dark, gloomy form. Often he sees no prospects for his future at all.
- Basic instincts weaken - sexual feelings and desires, appetite, pleasure from eating and, as a result, loss of body weight. Characterized by sleep disorders in the form of early awakenings and inability to fall asleep. The person stops dreaming.
- A person’s perception of the world around him changes - the world loses its colorfulness and expressiveness, everything becomes as if unreal, everything is seen in dim light. A person seems to himself to be changed, not the same as he was before, cannot share their joys with his family, may complain about the loss of love for loved ones, time drags on slowly or even stops.
- Experiences a number of unpleasant sensations from the internal organs, as if this is a manifestation of some kind of physical illness.
- The most dangerous symptom, both for the person himself and for his family, is thoughts of not wanting to live. With the appearance of these thoughts, there is a very great danger that a person may make a suicide attempt.
ATTENTION!
If at least (3 - 4 or more) of the above symptoms persist in a person for 2 - 3 weeks, there is every reason to think about depression, which needs to be treated!
CONTACTING A SPECIALIST IS MANDATORY!
Where to treat endogenous depression
The Rehab Family mental health clinic is ready to offer support to every patient. She specializes in treating depression, including endogenous depression, without medication. It is possible to undergo treatment both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital setting.
All that is required of those who want to get rid of the disease is to call Rehab Family, and then completely trust the experienced specialists who, after conducting the appropriate examination and diagnosis, will choose the optimal treatment method. For some, cognitive or existential-humanistic psychotherapy may be a priority, for others - Gestalt or art therapy. In any case, the treatment will be successful and will help the patient regain the joy of life.
Endogenomorphic depression, anxiety depression
The term “endogenomorphic” depression was introduced by the German professor Klein in 1974 as a characteristic of a person’s condition with a suppressed, so-called “internal reward” system - when the patient is unable to experience feelings of pleasure and joy.
A separate type of depressive state in a person is the so-called anxious depression. Anxious depression differs primarily in that the leading manifestations of the clinical characteristics of depression (variable affect, mental arousal, as well as somatic tone), with anxiety dominant in the patient, acquire the character of excitement, as opposed to the state of inhibition inherent in typical depression.
Anxiety disorders, as a type of mental disorder, are quite common. According to statistics, this type of disease affects 15-20% of the total number of patients. The occurrence of such a form of depression in a person is completely unrelated to the absence or presence of provoking “pushing” external processes.
Forms of endogenomorphic depression. vital disorders are inherent (melancholy, apathy, changes in circadian rhythm, severe sleep and appetite disorders), the content of self-awareness also changes - fears for one’s own health appear, the patient is characterized by constant self-reproach.
The main pronounced symptoms of anxious depression are persistent mood disorder, asthenia, attacks of nausea, and without any noticeable connection with food intake. However, the main symptom is always the same, this is the presence, in aggravation of the patient’s depressed state, of feelings of persistent anxiety. Often a person’s feeling of constant anxiety is so strong that it is difficult to keep the patient in place, he is haunted by an obsessive thought about the inevitability of some terrible event, the sick person tries to escape, to take cover by any available means.
The large group of endogenomorphic depressions includes bipolar and some unipolar depressions. Professor Klein and many other specialists believed that for depression of an endogenomorphic nature, treatment is necessary, primarily with antidepressants, as well as electrotherapy. And, on the contrary, psychotherapy is not decisive. In the absence of a sufficiently correct diagnosis and effective treatment of depression and anxiety, according to the patterns of the course of endogenomorphic depression, the onset of manic-depressive psychosis and even its death may occur in a neglected patient.
Therefore, in the initial stage of anxious depression, endogenomorphic type, it is so important not to make a mistake in making the correct diagnosis. .
We also recommend reading the article about nymphomania.
Treatment
Pessimism, bad character, laziness, selfishness, promiscuity, etc. have nothing to do with depression. This is a very dangerous serious disease that can be cured if the correct diagnosis is made in time and treatment is started.
People often do not want to turn to psychiatrists about this, considering mental illness a shameful stain, excluding them from society and classifying them as abnormal. The following prejudices also interfere:
- registration at a mental health clinic, ban on traveling abroad and driving;
- fears of taking psychotropic drugs;
- publicity of the disease.
But all this is a relic of the past. Depression is not a socially dangerous disorder and the patient is not threatened by any of the measures described above.
It should be clearly understood that neglect of medical care threatens to worsen the depressive state, worsens health and even leads to suicide, brings discomfort to both the sufferer and those around him,
Often, manifestations of depression are associated with somatic (physical) illnesses and people go to the nearest clinic to see a therapist. They are unlikely to be able to make a correct diagnosis: various laboratory tests will be prescribed, medications will be prescribed for what hurts - the heart, head, stomach. The patient will not receive the desired relief, and time will be lost.
If symptoms of prolonged depression appear, it is advisable to contact the Psychoendocrinological Center. Our specialists can help you get rid of this unpleasant and dangerous disorder.
To treat depression, a combination of psychotherapy and biological therapy and pharmacological agents are used.
Drug therapy
Specific medications are prescribed to patients with different manifestations of the disorder, taking into account its symptoms.
The doctor's instructions should be followed strictly: take medications according to his instructions, come regularly for appointments and report on your condition, without missing out on any details or problems that have arisen.
The medications used are sleeping pills and anti-anxiety drugs, but more often psychotropic drugs - antidepressants, including the usual melipramine and amitripyline, as well as those that appeared not so long ago. The latter have a lot of advantages over the “old” ones: they have less toxicity and side effects, they are better tolerated, and an overdose is not too dangerous. These are Prozac (fluoxetine), Remeron (mirtazipine), fluvoxamine (fevarin), Coaxil (tianeptine), etc.
Naturally, the drug and its dose are prescribed by the doctor strictly individually, then the specialist monitors its effect and, in case of an unfavorable result, cancels it or prolongs it. Such antidepressants do not cause addiction or the development of withdrawal symptoms.
The course of pharmacotherapy lasts from six months to a year and is designed to reduce and completely eliminate the manifestations of depression. The patient should understand that the effect of antidepressants does not occur immediately, but gradually (over several weeks), and it is different for everyone, as is the recovery process. After a couple of months, complete recovery occurs. But there are exceptions: there are cases where the patient felt significantly better within a couple of days after starting to take medications.
Usually the very first sign that depression is amenable to such treatment is the stabilization of sleep, it becomes high-quality, deep, without nightmares. Next, a decrease in anxiety and irritability becomes noticeable, the long-awaited calm comes, and the mood improves.
If the case of the disease was severe, then, after the patient’s condition has stabilized, a maintenance course is also prescribed, which already plays a preventive role. This happens because antidepressants are eliminated from the body quickly and measures are needed to prevent relapse.
The best method is psychotherapy
As already mentioned, pharmacology is ineffective without psychotherapy in the fight against depression. There are the following scientifically based approaches:
- cognitive-behavioural;
- causal;
- psychodynamic.
The patient directly participates in treatment, learns to regulate emotions, cope with different situations, and avoid depression.
First of all, the psychotherapist needs to find out what is the cause of the development of the mood disorder. It is deep in the patient's consciousness, so it is very difficult to understand.
The specialist develops a plan based on eliminating such causes, determines tasks that should be solved during meetings with the patient, and incentive options. A psychotherapy session lasts no more than an hour, since exceeding this time exhausts the patient’s psyche. The patient, under the strict guidance of the doctor, shares his memories, answers intimate questions, that is, talks about what he has kept secret for a long time.
Cognitive behavioral therapy involves the patient systematizing thoughts. He tries to determine and understand what actions led to certain consequences. This method is considered superficial and does not take much time, however, it is also important for recovery.
Psychodynamic therapy was developed on the assumption that depression is based on a person’s unconscious desire to be independent from everyone, but at the same time receive all kinds of support and care from other people. In addition, he harbors resentment and even anger towards these very people around him, but he wants to be good and loved for them. In this case, the therapist must work to ensure that the patient understands the conflict and learns to find a reasonable balance between close relationships and independence, while being able to honestly express his feelings.
Often, psychotherapy uses family and group sessions in which relatives or people with the same problems (respectively) are present. In the second case, patients communicate with each other, recover faster, imbued with a common misfortune, and in the first, loved ones help fight the problem.
The role of a specialist in psychotherapy is reduced to an auxiliary one - he does not give instructions, but, thanks to close cooperation with the patient, he leads the latter to the right decision, destroys painful thinking and builds the right one. That is, the patient goes to recovery on his own, having learned to think positively and not allowing negativity into himself.
A course of psychotherapy contains from 10 to 30 sessions and demonstrates great effectiveness. They are conducted by a professional who knows how to work with difficult situations and experiences, respects patients, can cope with them and help them. The information he receives is kept strictly confidential and confidential.
The influence of insomnia and magnesium deficiency on the development of depression
Chronic insomnia is a fairly common problem: every 10th person suffers from it. Lack of sleep inevitably provokes fatigue, stress, and bad mood. Depression and insomnia are locked in a vicious circle that is difficult to break, but it is possible, and in these ways:
- do not drink tea and coffee;
- do not sleep more than 15 minutes during the day;
- keep the temperature in the bedroom 3-5 degrees lower than usual;
- have dinner early and do not overeat;
- reduce intellectual stress before bedtime;
- be physically active during the day;
- Go to bed strictly on schedule - at the same time.
Sleep hygiene and proper sleep patterns will help restore normal sleep. Sleeping pills should be avoided as they will cause addiction.
Magnesium is an element involved in the transmission of nerve impulses, so it helps the nervous system function normally. Its lack can lead to chronic fatigue, anxiety, irritability, decreased attention, etc. That is, a lack of magnesium can affect the development of depression.
Eating cocoa, peanuts, and buckwheat will help replenish this element (it is available in abundance here). Alcohol and coffee should be removed from the diet.