When a person feels numbness in their legs
, this means that the sensitive part of the peripheral nerve is affected. Not only sensitivity is lost, but also burning and tingling, tightness, “cottoniness”, goosebumps, coldness, sometimes the accuracy of movements is impaired and a feeling of uncertainty when walking and dizziness occurs. The nerves of the lower limb are numerous, begin in the spinal cord, and branch along their course into many branches. The legs receive nerve impulses through both large (femoral, sciatic, tibial) and small nerves. The central analyzer of sensitivity is the structures of the brain.
The nerves of the lower limb can directly receive mechanical damage (for example, bony outgrowths of the vertebrae, so-called osteophytes, “ossified” ligaments, herniated intervertebral disc), and also be damaged as a result of the inflammatory process or metabolic (metabolic) disorders. CELT doctors, who have modern diagnostic equipment at their disposal, will help you find the cause.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
Do you always need to see a doctor?
There is no need to worry only if there is numbness
left or
right leg
occurs once after an uncomfortable position (what is popularly called “served time”). Soon after the physiologically normal posture is restored, the numbness should also disappear. Other harmless reasons include:
- Hypothermia - the human body reacts to cold starting from the lower extremities, so it is best to keep them warm;
- Wearing ill-fitting shoes that are too tight or narrow can lead to numbness in your toes
; - Bearing a fetus - a symptom occurs due to an increase in the volume of fluid in a woman’s body;
- A sedentary lifestyle and frequent sitting leads to numbness in the feet
and legs below the knee.
In all other cases, especially when numbness recurs regularly, it is imperative to look for the cause. Most likely, some pathological process is occurring in the body, and given the extreme “fragility” of nerve fibers and the complexity of their regeneration, delaying diagnosis can lead to irreversible consequences. The following points should be of particular concern:
- there is no obvious reason for the numbness, but it often recurs;
- problems with coordination arise, the leg “clings” or “stammers”;
- walking becomes difficult;
- difficult or impossible to distinguish between warm and cold;
- worries about weakness or dizziness;
- urination is impaired.
These symptoms may indicate a circulatory disorder in the nervous system, that is, they may be signs of a stroke. Or they may indicate acute damage to the nervous system of some other etiology. With such disorders, the timing of medical care is important. For example, if it is possible to restore blood flow in the brain during the first three hours, then there may be no consequences in the form of paresis or paralysis or speech impairment. Modern medical technologies used in CELT make it possible to help those who had no chance yesterday.
Loss of sensation in fingers and toes
In some cases, impaired sensitivity of the fingers may be associated with the development of Raynaud's syndrome. This is angiotrophoneurosis, in which remote areas of arterioles are affected and the distal sections of the upper and lower extremities cease to receive a sufficient amount of blood. This is accompanied by a feeling of numbness.
But in most cases, impaired sensitivity of the fingers is associated with the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. Or carpal valve syndrome may develop. Numbness is accompanied by a decrease in muscle tone and severe pain that occurs in the evening. Pathology often occurs in people who work at a computer.
Loss of sensitivity in the toes can occur due to a number of pathologies:
- flat feet and club feet with compression of the nerve fiber;
- hallux valgus or varus deformity of the foot;
- deforming osteoarthritis of small joints of the foot;
- compression of the plantar, tibial or peroneal nerves;
- diabetic angiopathy and neuropathy;
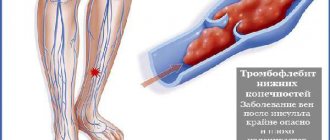
- vascular pathologies, such as obliterating endarteritis (mainly occurs in men aged 30–35 years), varicose veins of the lower extremities (mainly develops in women of childbearing age during pregnancy), atherosclerosis.
Impaired sensitivity of the foot may be a sign of radicular syndrome against the background of lumbosacral osteochondrosis. It is possible that the sciatic nerve is damaged in piriformis syndrome and the development of a number of other pathologies.
Etiology
Most common causes of numbness in the legs
consist in the presence of pathological processes in the spine - however, this is not all. The etiology of this symptom may be as follows:
- arthritis;
- pathological conditions of a systemic nature;
- multiple sclerosis;
- blood flow disturbances.
The area in which the feeling of numbness is localized will help to more accurately determine the cause.
| Numb area | Diseases characterized by this symptom |
| Hips/thigh |
|
| Above the knees |
|
| Calves of the legs |
|
| Below the knees |
|
| Foot/feet |
|
| Numbness in left leg |
|
| Numbness in right leg |
|
Legs go numb: reason
Numbness in the legs is a loss of sensation in a limb, which is often accompanied by a feeling of “cottonness,” burning, or tingling in the same area. The most striking example of numbness in the lower extremities is the feeling that occurs if you “sit out” your leg.
Loss of sensation in the legs can occur in the upper or lower part of the legs, in the feet, and even in the big toe area. Depending on the location, frequency and intensity of numbness, doctors determine possible causes, prescribe instrumental studies and subsequently select a course of treatment. Doctors distinguish between harmless causes that cause discomfort and do not require special help:
- uncomfortable posture;
- hypothermia;
- uncomfortable shoes (often causes numbness in the toes
)
; - sedentary lifestyle (causes loss of sensation in the feet and legs below the knees due to blood stagnation);
- pregnancy and others.
If you experience numbness suddenly and quite often, and normal sensitivity does not return for a long time, it is better to seek help from a specialist. Symptoms are considered especially alarming if, in addition to numbness, the following is noted:
- urinary disturbance;
- loss of limb coordination;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- migraine, etc.
If your legs go numb below the knees
, a burning sensation and goosebumps appear, our specialists pay attention to the condition of the spine and the functioning of the peripheral nervous system.
The feet become numb
due to spondylosis, poor circulation, intervertebral hernias and diabetes.
Quite often, legs can go numb due to post-traumatic stress disorder. If the thumb goes numb
, doctors, in the absence of problems with the spine, suspect polyneuropathy or a disorder of the peripheral nervous system due to intoxication, metabolic failure, etc.
Legs go numb: reason
Numbness of the lower extremities is a fairly serious signal that a malfunction is occurring in the body’s functioning, the integrity and process of regeneration of nerve fibers is being disrupted. However, many patients of our clinic, after several attacks, put up with unpleasant sensations and, taking vitamin complexes, buying tights, using ointments for varicose veins, continue to self-medicate.
In our practice, there was a case when a patient aged 63 years first felt that his leg was going numb
, then I noticed discomfort in the hip area when walking, but against the backdrop of a one-time loss of consciousness and high blood pressure, I still went on a pre-planned trip. Just a couple of days after visiting his son, he was hospitalized with a stroke. Therefore, it is important to be attentive to your health and not let things take their course.
In addition, you should not self-medicate. One of our patients, having independently diagnosed herself with “varicose veins,” treated this disease for a long time with various medications and ointments. However, the cause of numbness and heaviness in the lower legs was an intervertebral hernia, which was discovered in a more advanced state due to severe pain in the lumbar region.
Often, loss of sensitivity leads not only to injury to a part of the body, but also to disability due to damage to the spine. In addition, this is one of the symptoms of an incurable disease - multiple sclerosis. Experienced neurologists at our clinic, using all their accumulated knowledge and the modern material and technical base of the medical institution, are ready to help and solve the problem that has arisen. It is important not to delay your visit to the doctor and get diagnosed in a timely manner.
Clinical manifestations
In pathological conditions, numbness of the legs is a symptom that is always accompanied by a number of others. Depending on the etiology, they may be different, but the general picture is approximately as follows:
- Feeling of heaviness in the lower extremities;
- Gait disturbances;
- Inability to distinguish cold from hot;
- Fatigue, constant weakness and weakness;
- Tingling and goosebumps;
- Cramps and increased pain at night;
- Sudden and sharp appearance of pain in the chest and spine;
- Itching and burning of the skin, sometimes blueness;
- Severe headaches and dizziness.
Types, types and levels of sensory impairment
There are different types of sensory impairment, which differ in the level of damage to the nerve fiber and the localization of the pathological process. When exclusively distant nerve endings are affected, the peripheral type develops. There are also cortical or cerebral types of sensitivity disorders, the cause of which is a disruption in the functioning of analyzers in the structures of the brain.
Levels of sensitivity impairment are differentiation of the depth of the lesion depending on the patient’s sensations. Thus, at the first or remote level, only the nerve endings in the fingers or toes are affected. At the second level, numbness extends into the hand or foot like socks or gloves. The third level of sensory loss may affect the limbs up to the elbow or knee. At the fourth level, the sensitivity of the entire affected limb is impaired. At this stage, muscle strength usually decreases, tremors and other signs of total neuropathy may appear.
Next, we will consider individual types of sensory impairment of the upper and lower extremities.
Sensitivity disorder of conduction type
Violation of conductive sensitivity is an interruption of the chain of transmission of nerve impulses at the level of the spinal cord. There may be a conduction-type sensitivity disorder in osteochondrosis with compression of the radicular nerve. Also, conduction sensitivity disorders occur with stenosis of the spinal canal, displacement of vertebral bodies, inflammation of the dural membranes, etc.
It is important to understand that disorders of deep sensitivity occur on the affected side. For example, if the radicular nerve in the cervical spine on the right side is subjected to compression, then a deep sensitivity disorder will be detected on the right limb. And the left hand will suffer from numbness and superficial paresthesia.
Impaired tactile (skin) sensitivity
Any violation of tactile sensitivity requires a thorough diagnosis of the condition of the brain and spinal cord. If skin sensitivity is impaired, the patient complains that he does not feel cold and heat, cannot determine the structure and consistency of a substance by touch, etc.
Impaired skin sensitivity often occurs when certain branches extending from the nerve plexus are compressed. For example, if the tactile sensitivity of the fingers decreases, compression of the median and radial nerves should be excluded. If the skin sensitivity of the forearm decreases, it is important to carefully diagnose the condition of the ulnar nerve, etc.
Socks and gloves type impairment of peripheral sensitivity
Impairment of peripheral sensitivity can develop according to the neural, polyneuritic or distal type. If a certain nerve is affected, a neural sensitivity disorder of the lower extremities or arms develops. With multiple lesions of nerve fibers, a total decrease in sensitivity develops.
Thus, with polyneuropathy, sensory disturbances like socks and gloves often develop. If such signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. This condition may indicate a violation of cerebral circulation, the development of diabetic or toxic neuropathy, etc.
Segmental type of sensitivity disorder
Segmental sensory loss can occur with degenerative damage to the spinal cord structures. The dorsal roots and horns, nodes of the spinal nerve plexuses, and fibers of the white commissure are often affected. The segmental type of sensory impairment is always accompanied by pain and loss of a number of reflexes, which is easily diagnosed by an experienced neurologist during the initial examination.
There is also a cortical type of sensitivity disorder. It occurs when the cerebral cortex is damaged. With it, there are cramps in the arms and legs, and epileptic seizures often appear. May develop in persons who abuse alcoholic beverages.
Diagnostics
The use of modern instrumental diagnostic methods makes it possible to establish the cause quickly enough. Doctors have the following methods in their arsenal:
- radiography - reveals bone deformations, calcifications and other dense formations;
- - allows you to examine the bones and substance of the brain and spinal cord, and other soft tissues;
- MRI - detects defects in almost all structures, the vascular mode gives an objective picture of blood flow;
- electroneuromyography (ENMG of the lower extremities) - reveals defects in neuromuscular transmission;
- Ultrasound or sonography detects cysts, tumors and other formations, allows you to evaluate the structure of blood vessels;
- general clinical and biochemical blood tests.
CELT doctors have accumulated vast clinical experience, daily comparing data on various diseases. Specialists will be able to find out the exact cause of suffering and suggest the most effective method of treatment so that everything ends in recovery.
Causes of impaired sensitivity in hands and feet
A sudden loss of sensation in the legs or arms is an alarming sign in which the development of a cerebral stroke or spinal canal stenosis cannot be ruled out. But more often in practice, less dangerous causes of impaired sensitivity in the hands are identified, which can consist of both a physiological temporary limitation of blood flow and developing diseases of the musculoskeletal system and the autonomic nervous system.
The main causes of sensitivity disorders are:
- damage to the peripheral and central nervous system (for example, due to poisoning with salts of heavy metals);
- traumatic effects on the structures of the brain and spinal cord (concussions, bruises, dislocation, fractures of vertebral bodies with displacement and entrapment of the dural membrane, etc.);
- malignant and benign neoplasms in the brain, spinal canal;
- disruption of the blood supply to the brain and spinal cord (may be ischemic or hemorrhagic);
- iron deficiency anemia, in which the number of red blood cells decreases and secondary oxygen starvation of brain structures is observed;
- diabetic angiopathy and neuropathy - due to the fact that with constant changes in blood sugar levels, the body cannot adequately regulate insulin production and the functioning of the vascular wall and neural network is disrupted;
- atherosclerotic damage to the inner wall of large and medium-sized blood vessels, leading to a decrease in the intensity of blood flow;
- infectious damage to the autonomic nervous system;
- osteochondrosis, complicated by protrusion and intervertebral hernia with radicular syndrome, leading to pinched nerve fiber;
- instability of position and displacement of the vertebral bodies in the form of retrolisthesis and antelesthesis;
- poor posture and curvature of the spinal column;
- spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis and vertebral subluxations;
- tunnel syndromes (carpal, carpal, cubital, pyriform, etc.);
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals and certain medications;
- alcohol and drug intoxication and withdrawal syndrome;
- deficiency of certain vitamins (mainly group B) and minerals in the peripheral blood;
- violation of the integrity of the conductive nerve network (for example, with deep cuts, gunshot and knife wounds);
- complications of the early postoperative period.
This is not a complete list of reasons for which there is a violation of the sensitivity of the hands and feet. Only an experienced neurologist can exclude all risk factors during the initial history collection.
Our doctors
Novikova Larisa Vaganovna
Neuropathologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Pankov Alexander Rostislavovich
Neurologist
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Why you shouldn't ignore leg numbness
Ignoring the symptom and neglecting to visit a doctor can lead to adverse consequences and progression of the pathology underlying the numbness.
Failure to seek medical help in a timely manner can lead to the following consequences:
- complete and permanent loss of sensation;
- loss of motor function (paresis, paralysis);
- intervertebral hernia, sequestration of hernia;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs;
- amyotrophy;
- atrophic ulcers;
- leg deformity;
- gangrene.
The outcome can be very depressing, so you should not delay visiting your doctor.
Treatment
Any numbness that occurs several times over a short period of time—a week or a month—requires consultation with a doctor. The sooner the cause is identified, the greater the chances of a positive outcome. You need to understand that a nerve is a dynamic formation that has its own extremely complex physiology. For severe damage to nerve tissue, intense exposure to any pathogenic factor for just a few minutes may be enough, and nerve regeneration takes months. The nerve can be kept healthy or fully restored only if measures are taken in time.
Treatment of numbness in the legs
, first of all, is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused this symptom. Its selection is carried out individually, based on diagnostic data, situation and indications of the patient. The treatment itself is carried out in a complex and may include the following:
| Techniques | Features of application |
| Drug therapy |
|
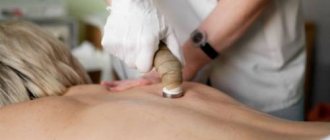
| Manual therapy | Therapeutic techniques aimed at eliminating blocks in joints and muscles that lead to compression of nerve roots and blood vessels, as well as stimulating blood flow in the affected area. |
| Physiotherapeutic procedures | Using techniques aimed at stimulating blood flow in the affected area:
|
| Exercise therapy | Performing a set of individually selected exercises under the supervision of an instructor will help strengthen the muscle corset around the spine, stimulate tissue trophism and blood flow. |
Tingling sensations in the legs due to a hernia: how to restore blood circulation
When a spinal hernia occurs, the intervertebral disc is displaced and subsequently extends beyond the vertebra. With this condition, not only back pain occurs in the area
lumbar region, but also numbness of the leg, because blood circulation is impaired. For this reason, motor ability decreases and the patient’s quality of life deteriorates.
The leg becomes weak due to compression of nearby tissues by the ruptured fibrous ring. The pathological process reduces sensitivity completely or partially and leads to pain in the lower extremities. When you feel your calves, you feel pain. And this is already a sign of advanced disease, which is fraught with dangerous complications - in the advanced stage, the patient will not be able to move independently. When blood vessels are compressed and tissue circulation is impaired, pain occurs, sensitivity dulls, a feeling of goosebumps appears, and tingling occurs.
How to eliminate numbness
In a spasmodic state, it is difficult for the patient to move, and he will need first aid to relieve discomfort in the numb area:
- Massage the calf muscles and apply warming gels to the affected area.
- Orthopedic patches are used
. They can be bought at a pharmacy without a prescription. Therapeutic stickers remove tension from muscles prone to cramps and improve blood flow in the tissues in the affected area.
If you cannot cope with the numbness on your own, and the spasms do not go away, it is better to call an ambulance.
How to treat pathology
If you have an illness, contact a neurologist. After examining and interviewing the patient, the doctor will find out that the leg is cold and the lower back is red and swollen. The doctor will prescribe a general blood test, then treat with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain:
- Selective drugs are administered by injection, which have an analgesic effect. Injections are given intravenously or intramuscularly with muscle relaxants that have a relaxing effect. The dosage of medications is determined by the doctor and depends on the course of the disease and the severity of damage to the calf muscles.
- To speed up the healing process, physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis and magnetotherapy) are used, influencing the body with direct electric current while simultaneously administering medications through the skin. Beneficial substances are instantly delivered to the diseased area.
- An X-ray of the spinal column will reveal a hernia and even the slightest shift of the intervertebral disc.
- The patient will benefit from a back and leg massage performed by a specialist. Manual therapy removes tension and spasms of the lumbar muscles, normalizes blood circulation, and releases the pinched nerve.
Painless physical procedures such as laser heating and cryotherapy are aimed at eliminating inflammation, pain, swelling and numbness of the foot.
Preventive actions
To prevent the condition from worsening, a person should engage in physical therapy. Under its influence, the lumbar region relaxes, and the vertebrae of the back are stretched, releasing pinched nerve roots. Gymnastics relieves compression of nerve fibers by a hernia:
- Hanging on the bar for a few seconds every day helps a lot. This exercise will allow you to stretch your back.
- LKF eliminates pinching, warms up the muscle frame, and restores blood flow in a numb leg. Physical activity strengthens the muscles of the back, preventing the vertebrae from moving further and affecting the hernia.
- You can stretch your spine with water aerobics or swimming.
- Numbness in the legs can be relieved by walking on tiptoes.
- In case of pathological conditions, the Kuznetsov applicator helps. Place your feet on a linen mat with needle modules and slowly move from your heels to your toes. Yoga mat acts on the skin, increasing metabolic processes, reducing pain by relaxing muscles.
- Cycling, in addition to improving blood flow, engages all muscle groups, which prevents numbness.
- Feet should always be warm and not freeze.
- Eating foods rich in B vitamins will prevent discomfort.
- Contrasting foot baths also have a beneficial effect on your well-being.
To prevent serious consequences, comprehensive treatment is carried out under the supervision of a specialist who knows the individual characteristics of the patient and takes into account the degree of mobility of his legs. To restore normal functioning of the spine, treatment sessions should be carried out daily, using the exercises that were shown during medical sessions in a medical institution.
Traditional methods of treatment
Alternative medicine methods help relieve the feeling of wobbly legs. But self-medication is dangerous; before using traditional recipes, you must obtain the approval of a therapist.
- Cucumber tincture is effective. To prepare it, chop pickled cucumbers (2-3 pieces) and add them to cubes of finely chopped red pepper. The mixture is poured with water. The infusion is stored in a place where sunlight does not penetrate. Before rubbing, the mass is filtered and then applied to the numb leg.
- In case of a pathological condition, wrapping the limb with pumpkin porridge is useful. The compress is additionally wrapped in cellophane and wrapped in a warm thing. Keep it for half an hour.
Back healing can be done using a safe technique called chiropractic, which is based on the relationship between the spine and the nervous system.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Prevention
In order to eliminate such a manifestation as numbness of the legs, you must adhere to simple rules, which are as follows:
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Reducing salt intake;
- Active lifestyle;
- Proper, balanced nutrition;
- Providing the body with all the microelements and vitamins it needs;
- Avoiding high-heeled shoes or keeping them to a minimum;
- Sports activities;
- Attention to your health;
- Timely seeking professional help if certain symptoms occur.
MC CELT specialists give a positive prognosis for timely treatment of numbness in the legs. Trust your health to professionals!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Treatment of diseases accompanied by numbness in the leg
Based on the examination, the specialist makes a diagnosis and prescribes therapy. If the cause of the disease is a circulatory disorder, treatment can be conservative or surgical. In this case, therapy is carried out by a phlebologist or vascular surgeon.
Neurological diseases that do not require surgical intervention (polyneuropathy, neuritis, multiple sclerosis, osteochondrosis) are dealt with by a neurologist.
When numbness develops in the leg due to severe compression of the nerves, nerve roots and spinal cord (trauma, herniated intervertebral discs, spinal cord tumors), surgical treatment is often required, which is carried out by neurosurgeons. Neurosurgery may also be required for cerebral stroke.
You can sign up for a paid consultation with a neurosurgeon at the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. A.K. Eramishantsev by phone: 8.