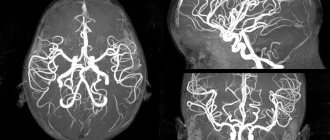
Computed tomography of the vessels of the brain and neck is part of a comprehensive examination of the head. CT angiography provides detailed images of blood vessels and assesses blood flow patterns. After a study with intravenous contrast enhancement, the obtained data is analyzed using special image reconstruction algorithms. At the Yusupov Hospital, radiologists perform CT angiography of vessels at an affordable price using modern devices from leading global manufacturers.
The study is carried out by doctors who have undergone special training in leading domestic and Russian radiology centers. If a complex pathology is detected using CT of the brain vessels, patients have the opportunity to receive advice from professors and associate professors. Doctors treat patients using the latest medications registered in the Russian Federation. Surgeons are fluent in the techniques of traditional and innovative surgical interventions. The medical staff is attentive to the wishes of patients.
Indications and contraindications for vascular computed tomography
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe CT scans of cerebral vessels if there are the following indications:
- Cerebrovascular accident;
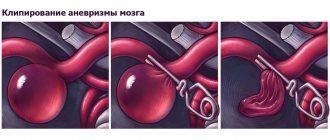
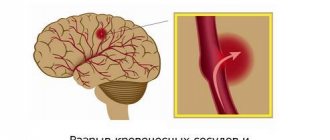
- Vascular aneurysm;
- Arterial thrombosis;
- Anomalies in the anatomical structure of the vessels of the brain and neck;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Suspicion of the presence of benign neoplasms.
CT angiography is performed for cerebral atherosclerosis, headaches, impaired memory and attention, insomnia and other symptoms that suggest vascular pathology of the brain. The study is indicated for patients suffering from vasculitis. CT scans of brain vessels are prescribed to patients suffering from epilepsy and migraine attacks. The study is performed in case of severe visual impairment or loss of consciousness.
CT angiography of the brain is a necessary method for examining patients suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, and cerebral vascular aneurysm. In the case of ischemic stroke, computed angiography is used to determine the paths of collateral blood flow and assess the level of closure of the artery lumen by a thrombus or embolus. CT angiography of cerebral vessels is of great importance in preparing the patient for surgical interventions.
This study is also performed if the patient has contraindications to magnetic resonance angiography, in cases where previously conducted alternative examinations gave questionable results. CT scans of cerebral vessels are performed with contrast in most cases. It penetrates into the smallest vessels and capillaries. Thanks to this, the doctor is able to detect minimal deviations from the norm.
CT angiography of cerebral vessels is not performed on women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, patients with heart and kidney failure, and children. Contrast computed tomography of brain vessels is not prescribed if the patient has an allergy to iodine and seafood, hyperkinesis (involuntary movements), or excess body weight. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital individually decide on the possibility of performing CT angiography of the brain for patients with endocrine diseases.
The essence of the technique
Typically, computed tomography of the part of the body being examined, which doctors themselves abbreviate as CT, is only one of the components of the study of the head, brain and cervical region. The technique for obtaining a highly informative picture of deep and shallow vessels is based on the principle of layer-by-layer scanning of tissue using X-ray radiation.
Content:
- The essence of the technique
- Who is the examination contraindicated for?
- Preparation and technology
- Angiography results
All obtained data are summarized using a computer program. It provides the radiologist with detailed visualization, which is a three-dimensional model of internal organs, large vessels and capillaries. To make the picture even clearer and with good contrast, a contrast stage is additionally used. It involves the introduction of a contrast agent into the blood, which makes the vessels more prominent against the general background.
The basis for computer diagnostics is the same radioactive radiation that is used to obtain images through a standard X-ray machine. The only difference is that for angiography, scientists have designed detectors that generate a reduced background radiation rays.
This means that the modernized approach, aimed at studying vascular structure, is practically harmless for ordinary consumers. The only significant exception is pregnant women. And although for adults the radiation dosage received is within normal limits, the intrauterine fetus is too sensitive to the slightest fluctuations in the radioactive background.
Contraindication applies to women at any stage of pregnancy. If you ignore this medical recommendation, then the risk of developing physical abnormalities in the unborn baby increases several times. For others, obtaining a layer-by-layer image of the bloodstream is considered safe.
Due to the fact that blood flow to the head is closely connected with the cervical region, doctors suggest immediately examining the two parts of the body presented. Such an integrated approach gives refined results, which qualitatively influences the development of subsequent treatment. It often happens that the cause of cerebral circulation insufficiency is not the vessels of the head, which cope with the tasks assigned to them “excellently”. The problem lies in pinched arteries or veins located in the neck. This situation occurs quite often, especially among people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
The most important advantage of this non-invasive method for diagnosing the condition of blood vessels is the ability to conduct the study several times if it was not possible to obtain the required clarity the first time. Failures of this kind usually occur due to involuntary movement of the patient, who is located directly in the device.
The manipulation technique correctly reveals to the doctor the following aspects of the victim’s health:
- anatomical location of blood vessels in the head and neck;
- structure of the vascular network;
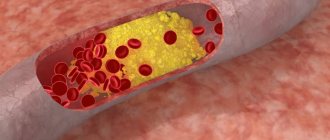
- the presence of atherosclerotic plaques;
- the dimensions of the veins, arteries themselves and their lumens;
- the presence of vascular constrictions and the original source of the problem;
- presence of collaterals.
Since the three-dimensional projection covers a fairly large area of the body under study, an experienced doctor will be able to examine not only the site of the disease, but also possible associated changes and complications.
Typically, a cardiologist or vascular surgeon refers the patient to the diagnostic room. But it happens that doctors of related specialties prescribe angiography to eliminate the risks of extensive damage. Among such doctors are phlebologist and vertebrologist.
The following diseases or suspicions of them are called the fundamental reasons for conducting such a comprehensive check:
- vasculitis;
- changes in the carotid artery;
- kinking syndrome;
- swelling of the neck;
- painful syndrome in the cervical vertebrae;
- embolism;
- thromosis;
- angiopathy, as an independent diagnosis, or as a consequence of the development of diabetes;
- tumors of benign or malignant type;
- control image after local surgery;
- compression of blood vessels by tumors of various etiologies or scar tissue.
All of the above can be determined by additional examinations and tests such as classic ultrasound and blood biochemistry. Also, before sending for a layer-by-layer scan, the attending physician must listen to the existing complaints of his patient and study the history from the medical record.
Having collected all the information together, the doctor will make a verdict about insufficient nutrition of the brain and problems with its blood supply, which is caused by inadequate vascular activity. CT angiography will help find the original source of the problem.
Preparation for CT angiography of cerebral vessels
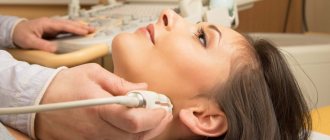
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe computed tomography of cerebral vessels only if there are absolute indications, when other methods cannot establish a diagnosis. The study is carried out after a comprehensive examination of the patient. Radiologists take into account the presence of contraindications for performing the study. Before the procedure, the patient should inform the radiologist about taking medications, as they may cause undesirable consequences. Take medications in consultation with your doctor 12 hours before diagnostic tests.
On the eve of the examination, the patient is recommended to drink plenty of clean, still water. This will allow you to quickly remove the contrast from the body. 3-4 hours before the test, the patient should completely abstain from eating and drinking so as not to provoke a gag reflex. You must come to the procedure having removed your metal jewelry. To prevent an allergy to the contrast agent, the procedure nurse administers an antihistamine.
For whom is MRI of cerebral vessels recommended?
MRI angiography of cerebral vessels is usually required by such conditions and diseases as:
- previous head injuries (TBI, SHM);
- strokes, micro-strokes;
- frequent headaches of unknown origin;
- frequent dizziness;
- episodes of loss of consciousness;
- coordination problems;
- visual or auditory dysfunction;
- epilepsy;
- rapidly developing diabetes mellitus;
- suspicion of a tumor process;
- tracking the results of conservative or surgical treatment, etc.
Contraindications to MRI of cerebral vessels
This diagnostic procedure has a fairly narrow list of contraindications. Among them:
- patient weight over 120 kg;
- severe form of claustrophobia;
- inability to lie in one position for a long time and motionless;
- early stages of pregnancy;
- the presence in the body of metal implants, prostheses, insulin pumps, vascular clips and devices (pacemakers, defibrillators, etc.).
1 MRI of the brain
2 MRI of the brain
3 MRI of the brain
CT angiography technique of the vessels of the head and brain
The patient is placed on the tomograph table and a contrast agent is injected into his vein. After this, the CT scanner is activated. The table moves, moving the head under the X-ray beams. The duration of the procedure depends on the equipment parameters. The use of special software allows radiology doctors to obtain an ideal 3D (volume, three-dimensional) model of the vascular bed. This is especially important in diagnosing vascular development anomalies and planning vascular operations.
Modern tomographs that the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with make thin sections with a size of no more than 1 mm. The duration of the scan is no longer than 15-20 minutes. During this time, the patient cannot move. The operation of a CT scanner is accompanied by crackling and noise, which causes some discomfort.
For patients who have a fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia), computed angiography of the vessels of the head is performed using open-type devices. Due to the high speed of examination and the open body, even patients with claustrophobia feel as comfortable as possible
The use of iodine-based contrast during CT angiography of cerebral vessels makes it possible to accurately and reliably visualize the structure and location of blood vessels, identify a neoplasm, and determine its size and nature. The technique is especially effective for determining pre-stroke conditions. In some patients, the administration of contrast causes nausea, a feeling of heat, and increased sweating. These sensations quickly pass on their own.
Using CT angiography of arterial vessels, doctors identify signs of organic brain diseases. They are grouped into the following 5 main groups:
- Changes in the position of blood vessels;
- Changes in the number of vessels;
- Changes in the shape and width of the lumen of blood vessels;
- Changes in the circulation of the contrast agent along the vascular bed of the brain;
- Extension of the contrast agent beyond the walls of the cerebral vessels.
For various diseases of the brain, the main one is one angiographic symptom identified during CT angiography. More often, several angiographic signs are determined simultaneously, which are combined with each other in various combinations. Each group of angiographic symptoms of organic brain diseases does not have the same diagnostic value.
Some morphological and functional changes that doctors detect using computed tomography of cerebral vessels are observed only in pathological processes (thrombosis, brain tumors, aneurysms). Their identification directly indicates anatomical changes and their localization in the brain.
Indications for diagnostics
A CT angiography procedure may be prescribed by a doctor if the patient has the following symptoms or diagnoses:
- dizziness;
- ischemic disease;
- sudden hearing loss;
- numbness or pain in the limbs;
- pain of unknown etiology, indicating vascular disease;
- abnormalities in the structure of the circulatory system;
- vascular aneurysm (pathological expansion);
- heart disease;
- vascular dissection (dissection).
CT angiography is actively used in the diagnosis of atherosclerosis, vasculitis, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, and embolism. It is also used during postoperative monitoring to determine the effectiveness of treatment.
Benefits and possible risks of CT angiography of the brain
CT scan of the head and cerebral vessels is a modern, highly informative research method. It has the following advantages:
- Takes no more than 20 minutes;
- Painless;
- Safe and minimally invasive.
During computed angiography of the vessels of the head, the patient receives less radiation compared to conventional angiography, and the diagnostic accuracy is significantly higher. The price of CT angiography of cerebral vessels is quite affordable.
Risks when performing computed angiography are associated with the effects of radiation on organ tissue and the use of contrast. Regular use of CT angiography can provoke the formation and growth of malignant tumors. The risk from a single procedure is minimized.
To reduce the likelihood of developing allergic reactions to contrast, the doctor clarifies whether the patient has previously had an allergy to iodine. The computer tomography rooms at the Yusupov Hospital are equipped with modern medications and a set of tools to provide emergency care in the event of an emergency. There is a resuscitator nearby.
Who is the examination contraindicated for?
If we put aside the most important prohibition for testing - pregnancy, then all other contraindications can be classified as relative. In practice, this means that the decision to ignore them is made by the doctor individually, based on the preponderance of benefit over possible harm.
Such relative contraindications include:
- renal failure;
- heart failure;
- diabetes;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- an allergic reaction to iodine in its pure form or seafood in particular.
All of the above applies only to situations where, in addition to the traditional part of the examination, the patient was prescribed a contrast stage. But since a thorough study of the condition of the vascular bed is almost never possible without it, contraindications are relevant for almost all patients.
The main danger when examining with contrast is the iodine-containing components of the solution for the procedure. If the patient is allergic to them, then they try to replace the drug with rarer analogues.
If the patient is not aware of whether he has an allergic reaction to iodine, then at the stage of preparation for the study he should undergo an allergy test.
Separately, situations are considered when the patient is breastfeeding at the time of diagnosis. To avoid negative consequences for the child, doctors insist on refusing to feed at least 36 hours after the diagnosis. During this time, most of the harmful components of the contrast solution will be excreted by the kidneys naturally - with urine. To speed up this process, you need to drink more fluids. In this case, it is necessary to express the milk and pour it out.
Also questionable will be the use of CT scans for young children, elderly people, and patients with uncontrolled movements. The latter include a group of people with mental disorders and nervous disorders. The most important condition for obtaining clear visualization is to remain completely still throughout the entire procedure. Otherwise, the photo will have to be redone again.
Another relative contraindication is the short time interval between CT and x-ray examination. Doctors recommend maintaining an interval of about four weeks between repeated tests.