Why does pathology occur?
Doctors consider primary and secondary neuropathy. The primary cause is injuries, infectious diseases and hypothermia. The list of reasons that can cause a secondary type of illness is much more extensive. These include:
- disc displacement;
- neoplasms of any nature;
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusion;
- osteophytes;
- spasmodic muscles;
- curvature of the ridge;
- tunnel syndrome;
- intervertebral hernia;
- post-injection suppuration.
Symptoms of inflammation of the sciatic nerve
Pain, which can even occur due to lifting a heavy bag or hypothermia, night attacks are the main indicator of sciatica. In addition to the sharp shooting pain syndrome, doctors advise paying attention to:
- “pins and needles” and numbness from the buttocks and below;
- constipation, urinary incontinence;
- weakness and gradual muscle atrophy, limping.
When a person moves or stands for a long time, pain is more disturbing. During attacks, redness of the skin, swelling, chills, and sweating are quite possible. At first, the pain syndrome is not very expressive, but gradually becomes so strong that there is a danger of loss of consciousness. It almost hurts for a person to breathe. If the disease is not treated, the entire leg will suffer: it will become cold, bending and unbending it will be problematic, and then the ability to move the foot and toes will be lost.
Pinching symptoms
Doctors consider several syndromes that indicate that the patient has a pinched nerve.
- Lesera – straight leg does not rise;
- Sikara – pain intensifies if a person bends the foot;
- landing - it is impossible to take a sitting position yourself.
It hurts to walk and squat, but if you lie down or sit with your legs spread wide apart, it goes away. Signs of inflammation and pinching of the sciatic nerve are quite expressive, but they can still be confused with other diseases:
- spondylitis;
- myeloma;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- phlebothrombosis;
- arterial insufficiency.
Sciatic nerve neuropathy (piriformis syndrome)
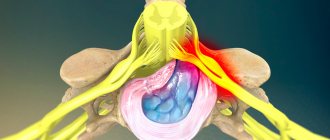
The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the human body. There are a total of 2 sciatic nerves in the human body, each of which is formed by combining fibers of the last two lumbar (L4 and L5) and the first three sacral (S1, S2 and S3) nerve roots of the spinal cord. Simply put, the sciatic nerve originates at five different levels of the spinal cord in the lumbosacral spine, which bears the main axial load during human life.
Radiculopathy is a lesion of the roots of the lumbosacral spine, which is manifested by pain and impaired sensitivity, as well as a decrease in muscle strength.
Radiculitis and sciatica are outdated terms that were previously used in relation to the concept of radiculopathy. Sciatica also has another name, completely similar in meaning - sciatic nerve neuropathy .
Causes of sciatic nerve neuropathy
The cause of damage to the sciatic nerve may be entrapment (compression, irritation) by an intervertebral hernia, spasm of the piriformis muscle, or gluteus maximus muscle.
The main causes of inflammation of the sciatic nerve can be hypothermia, spinal diseases, spinal injuries, joint inflammation, diabetes, heavy physical activity, and various infections.
Piriformis syndrome
In some cases, the underlying cause of sciatic nerve neuropathy may be piriformis syndrome . This muscle is located under the gluteus maximus muscle, and the sciatic nerve passes under or through it. This syndrome is characterized by stretching or irritation of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. The pain is most often associated with a reflex spasm of the piriformis muscle, which can result in stretching or irritation of the sciatic nerve. There are many causes of spasm of the piriformis muscle, one of which may be lumbar osteochondrosis (lumbosacral osteochondrosis).
Symptoms of radiculopathy:
- Lesion of L4 – pain in the anterior thigh, along the inner surface of the knee joint and lower leg, hyperesthesia along the anterior surface of the thigh and lower leg, weakness of the lower leg flexors and hip adduction, the knee reflex is reduced, the Achilles is preserved.
- Lesion of L5 – pain along the sciatic nerve with irradiation to the first toe, hypoesthesia on the back of the big toe, along the anterior outer surface of the leg, weakness of the dorsiflexion of the main phalanx of the 1st toe – it is impossible to stand on the heel.
- S1 – pain along the sciatic nerve, radiating to the heel and 3 – 5 fingers, hypoesthesia along the posterior outer surface of the leg, weakness of the fingers and the entire foot, the Achilles reflex fades.
Diagnosis of sciatic nerve neuropathy
The diagnosis is made based on the characteristic signs of the disease, radiological studies - radiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment of sciatic nerve neuropathy
, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - injection (intravenously, intramuscularly), blockades, analgesic mixtures drips, gabapentins, antioxidants, vascular therapy, B vitamins, muscle relaxants, anticholinesterase drugs, ointments, gels, dry heat, corsetry are used externally. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also used - diadynamic currents, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, darsonval, myoton, amplipulse, reflexology, laser therapy, hydrotherapy, gymnastics, massage, manual therapy. If conservative treatment is ineffective and there is a disc herniation with root compression, neurosurgical treatment . The scope of surgical treatment is individual. Physical therapy, massage, aqua aerobics, underwater traction, and swimming are very important. These measures are important in order to prevent complications (especially with long-term illness) in the form of muscle and tendon contractures, as well as the development of stiffness in the joints.
Prevention
Prevention of radiculopathy involves strengthening the back muscles. To prevent sciatica, you need to:
- keep your back straight: walk with a straight back, do not sit leaning forward too much;
- when working sedentarily, often get up and walk around the room;
- Do regular exercise to strengthen your back muscles;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- do not overcool;
- Women, especially those who already have periodic back pain, should not wear high-heeled shoes.
How to make a diagnosis
The disease is determined by a neurologist based on the results of motor tests that reveal the presence of the syndromes described above. But laboratory and instrumental studies are still necessary. As a rule, they are limited to x-rays in two planes. It may be necessary to obtain a more clear picture of the condition of the spine. In this case, a tomography will be prescribed. A radioisotope scan is done if a tumor is suspected.
When a person has inflammation of the sciatic nerve, treatment at home is not always acceptable, because the disease can manifest itself in such a serious form that the patient is prescribed bed rest in a hospital setting. Nerve-related illnesses must be taken seriously or you may lose your ability to move.
An immediate visit to a doctor is necessary in the following cases:
- severe numbness that prevents you from moving;
- increased body temperature;
- transfer of pain to other locations;
- incontinence of metabolic products;
- swelling in the lower part of the ridge.
Diseases of the femoral nerve include neuritis and neuropathy.
Neuritis is a disease characterized by inflammation. This is how it differs from neuropathy (in other words, neuropathy). The disease represents any dystrophic, degenerative changes in the large nerves included in the lumbar plexus. With neuritis, various nerve fibers of the peripheral nervous system, including the femoral one, can suffer.
The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the human nervous system, and also one of the thickest (can reach 1 cm in men). It is located in the lower part of the human body and originates in the lower part of the spine, then passes to the buttocks, where it exits through the pyriform opening in the pelvis and passes in the gluteal region between the gluteal muscles. Further, it passes along the lower limbs, where in the popliteal cup it branches into several small branches.
Pinching of the sciatic nerve (compression) is a syndrome of its compression by surrounding tissues, characterized by a specific symptom complex with motor, pain and trophic disorders in the innervation zone. Since the sciatic nerve is a large peripheral nerve, including in length, its pinching can occur at various levels.
How to treat inflammation of the sciatic nerve
Treatment measures are aimed at:
- relieving the patient of pain;
- improved sensitivity of the limbs;
- restoration of leg functionality.
To achieve this, they resort to methods of traditional and alternative medicine. Treatment begins with pain relief. Then physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, and manual therapy come into play. In parallel, the rich experience of traditional medicine can be used.
Medicines prescribed for the treatment of sciatica include the following groups of drugs:
- non-steroidal;
- corticosteroids;
- vitamin complexes;
- biogenic stimulants;
- muscle relaxants;
- decongestants;
- angioprotectors.
External means are widely used - warming creams and ointments, which contain snake or bee venom, hot pepper, camphor, turpentine. Massage for inflammation of the sciatic nerve helps improve blood circulation and restore muscle tone.
A huge role in restoring leg functions belongs to physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, magnetic and laser therapy, electrophoresis, and dynamic current treatment. Various types of physical exercises, selected for a specific patient, reduce muscle spasms and strengthen the body.
To heal at home, you will have to be patient, since sciatica responds better to the efforts of professionals. There are cases when the disease started precisely because of insufficiently active therapeutic measures. The more complex the case, the more effective drugs have to be prescribed. So, if non-steroidal drugs do not help, although a person takes them for a long time, steroid drugs are prescribed, which have significant side effects.
In many clinics, in addition to the main treatment, patients undergo courses:
- acupuncture;
- ozone therapy;
- herbal medicine;
- cupping and vacuum massage;
- stone therapy;
- treatment with leeches;
- cauterizations.
Many recipes for compresses, lotions, and tinctures have been developed. But it is better not to try them on yourself without consulting your doctor. The doctor knows where and how they can help or harm. Therefore, it is necessary to consult.
Spa and hydrotherapy is an excellent way to improve overall health and regulate various pathologies, including inflammation of the sciatic nerve, the symptoms and treatment of which, due to their diversity and complexity, require long-term and careful attention.
If therapeutic methods do not produce results, the nerve has to be decompressed. This is done surgically.
It is not enough to know how to treat sciatica, that is, inflammation of the sciatic nerve. It is necessary to be aware of how to protect yourself from such a serious, life-spoiling and health-robbing illness.
Among the preventive measures, doctors recommend the following:
- do not freeze;
- strengthen immunity;
- lift weights correctly;
- develop posture;
- sleep on hard mattresses;
- beware of sudden movements.
A healthy body significantly increases the likelihood that the spine will work correctly, and the nerve roots will avoid inflammation and will not be pinched.
We specialize in the treatment of the musculoskeletal system, even in severe stages of disease. We have been helping thousands of patients avoid surgery for 10 years!
Our doctors
This is the strongest team of experts who teach at the RUDN Department. We are the clinical base of leading universities, where the best doctors in Moscow, unique specialists from Russia and abroad are trained.
Symptoms of a pinched sciatic nerve
All symptoms of pinched sciatic nerve can be divided into local manifestations and immediate signs of compression of the sciatic nerve. Local symptoms of a pinched nerve in the hip joint are manifested by aching/pulling pain in the buttock, sacroiliac in the hip joints, the intensity of which increases with hip adduction, in a standing position, squatting, walking, but in a sitting/lying position with legs apart, the pain decreases . Piriformis syndrome is often accompanied by minor sphincter disorders, manifested by a pause before urination.
Immediate symptoms of compression of the sciatic nerve in the infrapiriformis space and adjacent vessels are:
- Dull pain in the thigh with a characteristic vegetative coloring (feelings of chilliness, burning, stiffness).
- Pain irradiates more often along the innervation zone of the tibial/peroneal nerves or throughout the entire leg.
- Decreased superficial sensitivity, less often the Achilles reflex.
- When the fibers that form the tibial nerve are predominantly involved in the pathological process, the pain syndrome is localized in the calf muscles of the leg and intensifies when walking.
The main causes of pinching:
- Spinal diseases (osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, etc.).
- The presence of benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Trauma (an adult can simply sit down poorly, resulting in a pinched nerve).
- Inflammatory process in the body (prostate, gall bladder, intestines).
In addition, the sciatic nerve can become inflamed as a result of spasm of the piriformis muscle, which thus pinches the nerve.
In addition, hypothermia of the body is a favorable condition for the development of sciatica. It is enough to chill the sciatic nerve a little for sciatica to develop (the same as inflammation).
There are three main stages (mild, moderate, severe), which differ from each other in the severity of the disease.
The main signs indicating sciatica are:
- numbness of the limbs;
- goosebumps;
- the occurrence of sharp pain, lumbago (this phenomenon is often called lumboischialgia) in the lumbar region (pain sensations can move from the lower back to the buttocks and transform into a different type of pain);
- pressing, aching or burning pain in the leg(s);
- impairment of motor activity (it may be painful for a person to walk or he will completely lose the ability to move).
In addition, both legs can hurt when the sciatic nerve is pinched. However, this condition is rare. Typically, the patient may feel tingling or goosebumps. In the event that the pain affects both limbs, the patient has a hard time tolerating this variant of the disease.
Sciatica is a complex disease, the characteristic symptoms of which are pain, periodic tingling, weakness and numbness that occurs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back and buttocks to the legs and thighs.
Sciatica: what is this disease?
The sciatic nerve has the longest extension in our body. Each spinal root begins at a five-level segment of the lumbosacral region. Each descends down the legs and branches along the way, supplying small nerve processes with such parts of the body as:
- Shins;
- Hips;
- Knees;
- Fingers;
- Feet.