Numbness in left leg
A feeling of numbness in the left leg in the absence of other symptoms is a dangerous sign, a possible prerequisite for a stroke or ischemic attack.
Numbness of the fingers, one or more, indicates neuropathy of the tibial and peroneal nerves, the presence of an intervertebral hernia. When dislocated in the area of the fifth vertebra, the hernia can, in addition to numbness, cause tingling, cottoniness and mild pain along the outer part of the lower leg. If the symptoms are supplemented by redness, swelling, or limited mobility of the limb, a cardiological or rheumatological examination is necessary. The femoral part of the left leg goes numb due to degenerative-dystrophic processes associated with pinched nerve fibers. Numbness in the lower leg indicates damage to the spine, especially if it worsens with physical activity.
Types of numbness
When parts of the body go numb, the body reacts in this way to harmful environmental conditions. Sometimes the symptom manifests itself in more complex situations, during a stroke or atherosclerosis. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the types of ailment, when it relates to the body’s normal reaction to irritation and requires therapy; the participation of specialists is rarely required.
Let's figure out what kind of numbness you don't need to go to the hospital for:
- Transient, lasting several minutes without repetition.
- After prolonged sitting or lying down.
- Minor tingling, goosebumps.
When you need specialist advice:
- Symptoms recur from time to time.
- Do not stop for a long period.
- In addition to tingling, it is accompanied by a burning sensation, uncontrolled urination, and gagging.
Numbness of the first type often occurs due to prolonged immobility of the limbs. At first, the temperature may change, tingling appears after interaction with cold. If numbness does not disappear after massage procedures, you need to contact a specialist.
Numbness of the leg below the knee
This part of the limb is extremely vulnerable to disorders of the blood vessels and nerve roots. A passive lifestyle and sedentary work can cause pathology. Vascular problems additionally give a burning sensation, loss of sensitivity, cold feet, tingling of the numb area.
Numbness of the right leg is one of the most important signals of sciatic nerve neuropathy, the cause of which is a hernial formation. The symptom intensifies when walking or sitting, and is often accompanied by convulsions.
The same pathologies on the left leg indicate left-sided protrusion of the intervertebral disc. Accompanied by piercing, unexpected pain.
Treatment
The therapeutic technique is determined individually in all situations. Traditional and non-traditional methods of therapy are used. Exercise therapy is carried out for radicular syndromes to improve one’s condition; doctors also recommend massage, reflexology and physiotherapy. Numbness of the body in diabetes is treated by endocrinologists, drugs and diet are prescribed, and lifestyle is adjusted.
Numbness of parts of the body on the right side requires increased physical activity and adjustments to the diet. Nicotine, alcohol, peppery and salty foods have a harmful effect on the condition of the circulatory system and cartilage tissue. You need to dress according to the weather so that hypothermia does not occur; diseases will be treated in time without becoming chronic.
Drug therapy involves the use of:
- Medicines that reduce pain and inflammation.
- Medications that reduce spasms.
- Drugs that aggravate the conduction of nerve impulses.
- Medicines that improve the functioning of the blood supply system.
- Medicines that stabilize blood pressure.
To prevent negative reactions of the body you need:
- Take frequent breaks from work that involves being in the same body position, and do exercises.
- Mattresses and pillows must be of high quality.
- Nutrition needs to be improved to reduce weight and strengthen the diet with vitamins.
- Perform therapeutic exercises that strengthen joints and intervertebral discs, promoting blood circulation.
There is no need to eliminate numbness caused by complex diseases and folk recipes. Such symptoms can be stopped, but the disease will not be cured. As a result, the symptoms will be much brighter and more severe.
Numbness of the leg on the outside
This pathology has a special medical name - paresthesia, and is of a tumor, infectious, neurodegenerative or autoimmune nature. Accompanied by tingling, burning, and pain of varying intensity.
The sensations can be short-lived or long-lasting, of a paroxysmal nature. The most dangerous are long-term sensory disturbances, the cause of which is the course of chronic pathologies: arthritis, osteochondrosis, diabetes and others. Violations of cellular metabolism lead to persistent disruption of nerve impulse conduction.
Treatment of left hemisphere stroke
Impaired blood circulation in the brain leads to serious consequences. To level them out, treatment of a stroke on the left side must be immediate. Prompt assistance will allow you to correctly diagnose and correctly draw up a step-by-step and comprehensive treatment plan.
First aid to a patient
Before doctors arrive, the patient must be given first aid. This will help improve his condition a little. First aid consists of a number of simple actions that the victim’s relatives can perform:
- The patient should be placed on a surface covered with pillows and his head should be raised.
- The patient may have difficulty breathing, so it is necessary to open the windows.
- It is also necessary to rid the person of tight and constricting clothing: unbutton the shirt collar, remove the belt, take off a jacket with a tight neck.
- If there is vomiting, carefully and carefully turn the patient's head to the side. This position will prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
Until the ambulance arrives, you need to stay close to the stroke survivor. He may be in a panic, so you need to try to calm him down.
Drug therapy
In clinical settings, physicians' efforts are aimed at minimizing nerve and muscle damage. The main goal of therapy is to preserve the functionality of the brain and cardiovascular system. The patient is prescribed drugs that restore blood circulation.
Drug treatment is selected according to the form of the disease. Drugs for left hemisphere stroke of ischemic nature include the following groups:
- Thrombolytics. They are used in the first hours after a vascular accident to dissolve blood clots.
- Anticoagulants.
- Medicines that lower blood pressure.
- Neuroprotectors.
- Vasoactive drugs.
In the case of hemorrhagic stroke on the left side, vascular strengthening drugs and drugs that prevent vasospasm are used.
For both types, general medications are also provided, which include diuretics and decongestants, as well as sedatives and hypnotics. During rehabilitation, patients are also prescribed medications to treat bedsores.
Surgery
Surgery is most often necessary for hemorrhagic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain. Surgical treatment is aimed at removing the intracerebral hematoma. The need for surgery is determined taking into account the following factors:
- general condition of the patient;
- volume of the lesion;
- localization of hemorrhage.
Surgery is indicated only in extremely severe cases when the patient's life is in danger. There are also cases when the hematoma is not removed immediately after a stroke, but during rehabilitation.
As a rule, surgical treatment is used for patients whose hematoma size is more than 50 ml. The operation is also indicated for patients with cerebellar damage.
Complications and consequences of numbness in the legs
The consequences of numbness in the legs are very diverse, leading to a wide range of complications. They depend on the cause that led to the malaise. The main thing that the patient needs to understand is that the presence of frequent numbness is not the norm, this is a very dangerous symptom that requires immediate consultation with a doctor. Timely examination will help protect against serious consequences.
Complications preceded by numbness of the legs:
- loss of tissue sensitivity, partial or complete;
- loss of limb mobility;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs;
- leg deformity;
- gangrene;
- necrotization of intervertebral hernia.
Numb fingers
When people suffer from loss of sensation in the fingers or experience severe pain, there is a change in the color of the limbs, in such a situation the issue of vasospasm is considered. A similar condition is typical for Raynaud's syndrome, intervertebral hernia, scleroderma, and osteochondrosis.
Suspicions of osteochondrosis arise if not only the limb goes numb, but also the head begins to hurt; therapy is determined by a specialist. When loss of sensation occurs in the little or ring fingers, neuropathy occurs.
Diagnostics
The initial doctor’s appointment will consist of listening to the patient’s complaints and conducting an examination, on the basis of which the specialist will plan further diagnostic measures. To make a reliable diagnosis and begin treatment, you need:
- laboratory tests that determine a general, biochemical blood test with calculation of glucose levels, lipoproteins, triglycerides and cholesterol. If arthritis is suspected, a urine test is necessary;
- radiography is an accessible study that excludes injuries, inflammation, the formation of tumors, and bone growths;
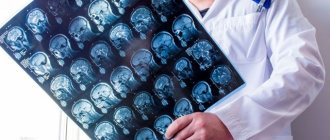
- CT, MRI. Highly informative techniques that provide a complete picture of the size, location and nature of the pathology;
- electrophysiological diagnostic procedures that clarify the characteristics of nerve damage;
- Ultrasound, sonography, duplex scanning. Studies shown in the study of arterial lesions, varicose veins. An assessment of blood flow and its character is given. The sizes of the vessels are measured.
Causes
Numbness of any part of the body indicates a disruption of the nervous system. Paresthesia is a serious cause for concern. The exception is a quickly passing tingling sensation or severe hypothermia.
Causes of numbness on the left side:
- Radicular syndrome. Inflammation due to radiculopathy or radiculitis. Compression of the nerve roots in the spine disrupts blood circulation in the vessels, which is manifested by pain and numbness, which can be observed on both the right and left sides.
- Intervertebral hernia. The limbs and fingertips lose sensation due to compression of the spinal nerves. Accompanied by pain in the back.
- Polyneuropathy. Characteristic of patients suffering from diabetes. High glucose levels contribute to nerve and peripheral vascular damage. Characterized by symmetrical numbness.
- Raynaud's or Tunnel syndrome. With sedentary work, obesity or metabolic disorders, the fingers and hands lose sensitivity.
- Stroke. Speech suddenly becomes slow, facial muscles become numb, and the person is unable to smile. The motor function of the left side of the body is impaired. Depending on the degree of brain damage, paralysis can be complete or partial. The condition requires immediate hospitalization. With timely treatment, the unpleasant symptom goes away in a couple of weeks.
- A benign or malignant tumor in the brain or spine causes pain, numbness, or discomfort on the left side. The tumor compresses nerve endings and blood vessels, reducing the sensitivity of the limbs.
- Taking medications can cause numbness. If a symptom is present, stop therapy or change the medication.
Treatment of pathology
Based on the diagnostics performed, the cause of the numbness is identified. The specialist leading the treatment will draw up a course of therapy using medicinal or non-medicinal methods. The full course may include:
- Taking medications. NSAIDs and steroids effectively eliminate numbness. Complex drug therapy uses painkillers, chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants, vitamin-mineral complexes, drugs that activate blood circulation;
- Ointments, gels, creams. The affected area is rubbed with elements of massage, and then medicinal compositions are applied. The products are used once, less often twice a day;
- Diet. The diet is enriched with foods containing B vitamins.
- Physiotherapy. Methods are used that activate blood circulation, metabolic and regenerative processes in tissues. Currents, magnetic therapy, ultrasound and low-intensity laser radiation are widely used.
- Traditional methods. Used only with the permission of the attending physician. Wraps with honey and camphor alcohol, rubbing, baths based on medicinal decoctions are shown;
- Exercise therapy. A set of exercises is selected individually by a physiotherapy specialist, taking into account concomitant diseases, age and current condition of the patient. Classes must be carried out daily, preferably 2 times for 40-50 minutes;
- Surgical intervention. Manipulations are performed according to the identified diagnosis. Traumatic injuries, neuropathy, damage to the nervous system, and vascular anomalies are promptly corrected.
Numbness of the limbs
15282 21 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Numbness, or paresthesia, is a disorder of the sensitivity of body tissues that occurs due to damage to the peripheral nervous system.
It can be accompanied by various sensations: from tingling, goosebumps to a general decrease in sensitivity of any part of the body, most often the limbs.
The patient feels any tactile influence as if through a layer of cotton wool.
Varieties
Depending on the duration and location, several types of paresthesia are distinguished. Temporary or transient paresthesia may be due to decreased blood flow (ischemic). This type of numbness occurs when there is spasm or compression of the vessels of the limb. Permanent paresthesia is also possible when nerve fibers are crossed or compressed during surgery, trauma, cancer and degenerative changes in the musculoskeletal system.
Reasons for appearance
An example of transient paresthesia is sensory disturbance during a hypertensive crisis.
. This condition is characterized by a sudden increase in blood pressure and is accompanied by symptoms such as severe headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, spots before the eyes, and paresthesia of the extremities.
It should be noted that the clinical symptoms of a crisis can be observed even at low pressure values; the main role is played by the suddenness and difference in the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure.
Raynaud's syndrome
is an episodic disturbance of blood circulation in the extremities due to a sharp spasm of peripheral vessels in response to cold exposure or emotional stress, which quite often causes loss of sensitivity. Most often, the fingers are affected, which from exposure to cold become almost white or bluish-violet and lose sensitivity. After the spasm stops (usually after 15-20 minutes), blood flow in the extremities is restored, as evidenced by the normalization of skin color and sensitivity.
Tunnel or compression syndromes
are among the most common causes of numbness of the extremities. Compression (compression) of the nerve fiber, located in the narrow space between the bone and muscles of the limb, occurs due to swelling that occurs with injuries to the joints and ligaments.
The first symptoms of this condition are pain, sometimes a sensation of current passing (electrical shooting), numbness, weakness and dysfunction, which subsequently lead to muscle atrophy and loss of motor ability of the limb.
Compression of the nerve roots (
radiculopathy
) due to herniated intervertebral discs and tumors is also accompanied by numbness of the limb. Depending on what level of the spine the nerve is pinched, pain and numbness in certain parts of the limb, impaired reflexes, muscle weakness, stiffness in the spine, and pain in the projection of the affected root when coughing or sneezing may occur.
With radiculopathies, pain increases in an upright position of the body and decreases in a lying position.
Polyneuropathies
can cause numbness in the extremities . A sign of polyneuropathy is symmetrical damage to the limbs. Multiple damage to peripheral nerves occurs due to decreased nutrition of nerve fibers (metabolic polyneuropathy). A typical example of peripheral nerve damage is diabetic polyneuropathy. It is characterized by slow progression and gradual development of motor and sensory disorders. Alcoholic polyneuropathy develops much faster.
Its characteristic symptoms include numbness and loss of sensation in the lower extremities, starting with the feet, and soreness of the calf muscles. Later, these symptoms are accompanied by weakness and paresis (decreased muscle strength) of the limbs.
Paresthesia can occur with drug-induced polyneuropathy when taking certain drugs, with uremic polyneuropathy in patients with chronic renal failure, as well as with other diseases.
Paresthesia, a feeling of numbness and pins and needles are the main signs of B vitamin deficiency
. In particular, with a lack of thiamine (B1), polyneuropathy develops, which is manifested by a “pins and needles” sensation.
Cyanocobalamin (B12) deficiency
leads to degenerative changes in the spinal cord, which are accompanied by a feeling of numbness, tingling in the limbs, gait disturbance, memory loss and loss of tendon reflexes.
Similarly, with hypocalcemia
(lack of calcium in the blood), paresthesia and seizures are the leading clinical manifestations of the disease. Calcium deficiency can develop against the background of pancreatitis, sepsis, hormonal disorders (in particular, with hypoparathyroidism), blood loss during major operations and injuries.
Among the demyelinating lesions
diseases that cause numbness in the extremities include multiple sclerosis.
With this disease, demyelination (destruction of the myelin sheath) of nerve fibers occurs in various parts of the central nervous system, which significantly disrupts the conduction of impulses through neurons.
Sensory impairment is one of the earliest and most common symptoms of multiple sclerosis. The patient experiences a transient feeling of numbness, “pins and needles” in various parts of the body, most often in the tips of the toes or hands. This sensitivity disorder is focal in nature.
Loss of sensitivity in the limbs, numbness occurs with polymyalgia rheumatica
. This is an inflammatory disease of the musculoskeletal system that develops after the age of 50. Severe pain in the symmetrical muscles of the shoulders, hips, and neck is combined with an acute inflammatory process. The pain intensifies with movement and does not subside even at night. Muscle stiffness is typical both in the morning and after prolonged immobility. Muscle damage is combined with peripheral arthritis, often on one side, which is accompanied by a slight disturbance of sensitivity and paresthesia.
Occupational hazards, exposure to ultrasound
also lead to sensory and vascular disorders. People who are exposed to vibration for a long time develop increased sensitivity of their hands to cold and periodically experience numbness in their fingers. The skin takes on a cyanotic, marbled color and becomes cold and damp to the touch. Over time, dystrophic changes spread to nerve fibers, muscles, and bones.
Diagnostics and examination
Diagnosis of a disease accompanied by numbness begins with interviewing the patient, which makes it possible to clarify the location and nature of the sensitivity disorder. To exclude the metabolic nature of the disease, blood tests (general clinical and biochemical), determination of the level of glycated hemoglobin, urea in the blood, liver enzymes), calcium levels, vitamin B12 and methylmalonic acid, C-reactive protein and a general urinalysis are necessary.
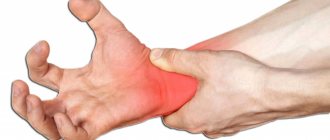
Numbness of hands and fingers
Numbness of the hands due to osteochondrosis is a very common clinical symptom. The root nerves C6, C7 and T1 are formed by their branches at the brachial nerve joint. It is responsible for the performance and sensitivity of the shoulder and shoulder joint, forearm, elbow joint, hand, fingers, wrist joint, etc. If the integrity of the radicular nerve is violated at the level of exit through the foraminal foramen in the vertebra, the numbness effect spreads throughout the entire limb.
Isolated numbness of the fingers with osteochondrosis is relatively rare. Most often, this symptom is a manifestation of a completely different disease. Most often, numbness of the fingers due to osteochondrosis is accompanied by areas of sensory impairment located throughout the upper limb. Along the branch that is ultimately responsible for the innervation of certain fingers of the hand.
If osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops, then numbness of the hands does not appear immediately, but some time after the onset of exacerbation. The frequency with which cervical osteochondrosis and numbness of the hands occur is 2-3 times a year. As the degenerative process progresses, periods of exacerbations become longer and more frequent.
Mild numbness of the fingers with cervical osteochondrosis can be easily diagnosed and classified. For example, if numbness of the fingers due to cervical osteochondrosis affects only the index, middle and part of the ring finger, then there is a high probability of damage to the median nerve, which originates from the C6 root. If numbness is localized in the area of the little finger and affects the lateral surface of the ring finger, then the ulnar nerve, which originates from the C7 root, is most likely damaged.
Thus, based on numbness of the fingers due to cervical osteochondrosis, an experienced neurologist will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis and clarify the location of the degenerative intervertebral disc. This will significantly simplify laboratory diagnostics and allow effective treatment to begin as early as possible.
Numbness of the arms and legs due to osteochondrosis
The process of disruption of the innervation of the upper and lower extremities can occur when:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical and lumbar spine;
- cauda equina syndrome;
- back and neck injury;
- protrusion of intervertebral discs;
- intervertebral disc herniation;
- spondyloarthrosis of uncovertebral, facet and facet vertebral joints;
- poor posture and curvature of the spinal column;
- hematomas, inflammatory edema, etc.
Sudden numbness in the arms and legs due to osteochondrosis is a reason to urgently seek medical help. This condition signals that the innervation process is disrupted. This means that the soft tissues of the upper or lower limb do not receive blood supply, and atrophic processes begin in them. With prolonged compression of the nerve fiber, it will be very difficult to restore its functionality in the future.
A particular danger is numbness of the legs with osteochondrosis, since in this case a rather large nerve, the sciatic, is pinched. It can be affected both at the exit from the spinal column and in the tunnel located in the thickness of the piriformis muscle in the gluteal region.
Numbness of the lower extremities with lumbosacral osteochondrosis may be caused by damage to the L4 and L5 radicular nerves. They can be compressed as a result of protrusion of the intervertebral disc or prolapse of the nucleus pulposus through a crack in the annulus fibrosus. Also, numbness of both lower extremities with osteochondrosis may be a consequence of the development of cauda equina syndrome. This is a life-threatening condition that, without timely medical care, leads to paralysis of the lower extremities, intestines and bladder. The patient may remain disabled for the rest of his life.