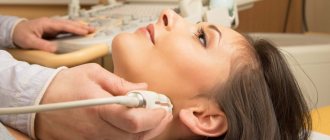
Computed tomography is a method of diagnosing internal organs that allows one to obtain layer-by-layer images to detect serious diseases.
CT is a radiation method, which is based on the different absorption of X-ray radiation by tissues. It is the similarity with radiography that makes many patients doubt whether it is harmful to have a computed tomography scan and how often can this study be done? In addition, they are concerned about the need to use a contrast agent when performing bolus-enhanced CT, which may be accompanied by the development of allergic reactions.
Radiation exposure during computed tomography
Everyone knows the fact that in one year it is permissible to expose the human body to only a certain amount of radiation, which does not exceed normal limits. The permissible annual dose of radiation exposure is 150 m3v. If this standard is observed, radiation does not harm human health.
For example, with regular use for the purpose of preventive fluorography, examination of the mammary glands, and an image of the jaw at the dentist, on average, a person receives at least 15 m3v per year. When performing a computed tomography scan on a standard apparatus for examining the brain, the radiation dose ranges from 1 to 2 m3v, and with a CT scan of the pelvic organs, lungs or abdominal cavity - 6-11 m3v.
According to research, even when undergoing a CT scan several times a year, the dose of radiation received, as a rule, does not exceed the permissible norm.
Is it harmful to have a CT scan with contrast?
Radiation exposure, according to some patients, is not the only danger. To some extent, a radiopaque contrast agent used in some cases for computed tomography can compete with it.
As a rule, it is an inert substance that is not absorbed into surrounding tissues. However, the components included in its composition can cause harm - in some patients they can cause the development of allergic reactions.
This complication may occur in the presence of the following factors:
- hypersensitivity to seafood and iodine;
- renal failure;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diseases of the gallbladder and liver.
The development of minor side effects is observed in only 1-5% of patients. They experience mild nausea, vomiting, skin reactions, and impaired sense of taste and smell. As a rule, these symptoms do not require special treatment and disappear on their own.
There are isolated cases of the development of side effects of moderate severity: Quincke's edema, acute respiratory failure caused by narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi and sudden involuntary contraction of the muscles of the larynx, shortness of breath. To eliminate such conditions, emergency medical care is required.
In extremely rare cases, severe adverse reactions develop: sudden cardiovascular failure, which can result in loss of consciousness and death. Most often, this harm to CT is caused to allergic patients. In such cases, immediate resuscitation measures are required.
If there is a history of a negative reaction to drugs containing iodine, an antihistamine is administered to the patient before starting a contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan. Some patients require special tests to help identify the allergen.
The development of allergic reactions in patients prone to them occurs in fairly rare cases. Rapid intravenous administration of a contrast agent is accompanied by the occurrence of side effects much less often than slow infusion using a dropper.
MRI diagnostics of the spine: indications and contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is used in the diagnosis of almost all spinal pathologies. Researched:
- injuries;
- developmental anomalies;
- inflammatory diseases (spondylitis, osteomyelitis, discitis);
- degenerative processes (osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, protrusion of intervertebral discs);
- malignant neoplasms and metastases.
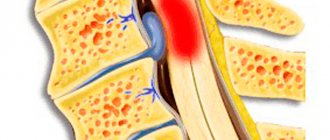
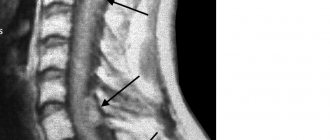
Spinal tumor on MRI (indicated by arrows)
Osteochondrosis
This is a degenerative-dystrophic chronic disease that begins with the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc and spreads further to all elements of the vertebral motor segment.
It makes sense to do an MRI for any persistent back pain, since making an accurate diagnosis during an initial examination by a neurologist based only on clinical signs is not an easy task. Difficulties may be due to the fact that;
- there are individual differences in the structure of the spine, the level of nerve exit from the spinal cord and the innervation of the lower extremities;
- There are a number of diseases that cause similar symptoms: pathologies of the hip joints, ischemic neuritis of the lower extremities, vascular diseases, abdominal and pelvic organs.
Therefore, a neurological examination can only suggest the localization of the process. To make a final diagnosis, it is necessary to visualize the process on MRI, which will allow you to immediately choose the right treatment tactics.
Spondylitis
An inflammatory disease in which early diagnosis and adequate treatment tactics make it possible to avoid severe disabling consequences.
Most often it is the result of the introduction of microorganisms with the bloodstream into the adjacent space of the spinal disc (there are no vessels in the disc itself). This disease is quite rare and is often mistaken for degenerative, leading to inappropriate treatment. X-rays and CT scans do not detect spondylitis at an early stage. Therefore, in case of persistent back pain that is not amenable to conservative treatment, increased inflammatory markers in the blood or fever, it is necessary to do an MRI of the spine. If the diagnosis of spondylitis is delayed, spinal cord damage and sepsis may develop.
The key signs of spondylitis on MRI are:
- inability to visualize the boundaries of the intervertebral disc and the adjacent vertebral body;
- increased signal intensity from the disc itself and the vertebral body.
MRI with intravenous contrast, in this case, reveals the spread of the inflammatory process and the formation of an epidural abscess. Standard MRI without contrast makes it possible to distinguish spondylitis from degenerative and tumor processes.
Dynamic studies (repeated) are prescribed for patients with a confirmed diagnosis of spondylitis and who have little improvement after conservative treatment. This is due to the fact that changes in inflammatory markers in the blood are not always indicative of assessing the effectiveness of treatment. Repeated MRIs may reveal abscess formation that requires surgical drainage.
Spinal injuries
According to the state of neurovascular formations, they can be:
- uncomplicated (without damage to the spinal cord and spinal nerves);
- complicated (with their damage).
Spinal cord injury occurs:
- acute - directly at the time of injury by foreign bodies or bone fragments;
- early - in the next 10 days, as a result of compression by hematoma, edema, secondary displacement of the vertebrae;
- later - after several weeks, and sometimes even years, due to the scar-adhesive process or the formation of cysts.
MRI makes it possible to establish a diagnosis in 98% of cases, as it visualizes:
- ligaments;
- intervertebral discs;
- membranes of the spinal cord;
- spinal cord and its pathologies (hemorrhages, swelling, ischemia);
- violation of the structure of the vertebral bodies.
MRI of the lumbosacral spine shows a herniated disc at the level of the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral vertebrae, which puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots.
MRI is the main method for diagnosing post-traumatic disc herniations.
In a certain group of patients with spinal trauma in the acute period, there are no signs of vertebral damage on the radiograph. But after 3-8 months. sudden sharp pain occurs at the site of the previous injury. Repeated examination reveals a compression fracture of the spine.
This is explained by the fact that in the acute period hemorrhage occurred in the vertebral body. After its resorption, aseptic inflammation and destruction of bone structures developed. The action of axial load on the weakened vertebral body led to its compression fracture.
MRI allows you to visualize these hemorrhages in the acute period and take timely measures, which significantly affects the patient’s future health.
Metastatic lesions of the spine
The appearance of pain in the spine, an increase in existing pain in the spine and lower extremities in patients with cancer should be the reason for urgent MRI of the entire spinal column with intravenous contrast.
However, the scope of primary diagnostic measures depends on the severity of the patient’s problems at the time of examination. Asymptomatic lesions in the spine of a metastatic nature, identified on CT or scintigraphy, should be confirmed by MRI with contrast.
The appearance of threatening symptoms in the form of weakness in the limbs, dysfunction of the pelvic organs or sensitivity is the reason for performing an emergency MRI of the entire spine with contrast, even if the patient has a history of degenerative disease of the spine.
Magnetic resonance imaging is contraindicated in patients:
- having implants or foreign bodies made of ferromagnets in the body;
- wearing non-removable electronic devices (pacemakers, cochlear implants, insulin pumps and others);
- with vascular clips installed on the arteries of the brain;
- pregnant women in the first trimester;
- if it is impossible to remain still due to claustrophobia, pain or other reasons.
Our clinic does not examine children under 5 years of age or adults with a body weight of more than 130 kg or a waist circumference of more than 150 cm.
Indications and contraindications for CT
Computed tomography allows you to identify the pathological process and clarify the diagnosis in patients with various conditions:
- diagnosed with cancer, metastases, suspected cancer;
- frequent, prolonged headaches without obvious causes;
- cerebrovascular accident and the accompanying consequences of this disorder;
- attacks of seizures, convulsions, loss of consciousness;
- conditions after injuries;
- inflammatory processes localized in various parts of the body.
Computed tomography has undeniable advantages - with the help of this study you can assess the condition of almost any organ. In addition, computed tomography is also used to clarify pathology previously identified during other examinations. This study can only harm patients with the following contraindications:
- syndrome of impairment of all renal functions;
- applied plaster or metal structure in the examined area;
- claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces);
- violent behavior caused by mental disorders.
In addition, the use of CT is contraindicated in patients with excessive body weight exceeding 150 kg, pregnant women (especially in the first three months) and children under 14 years of age (except in cases of extreme necessity).
How to properly prepare for an MRI
The examination does not require special preparation, but there are some points you need to be aware of. First of all, these are metal objects on clothes. This applies to hooks on buttons, details on a belt, and pins on a jacket lapel.
Doctors pay special attention to women’s wardrobes, because they wear jewelry more often than men. In addition, bras often have metal wires and clasps. Before entering the examination room, the patient will be advised to remove all jewelry and other clothing items that have even small metal parts.
Due to the fact that metal can be not only outside the body, but also inside it, each patient is asked to fill out a questionnaire in which it will be necessary to answer several questions of the following nature:
- are there metal bridges on the jaw;
- whether there were operations to insert metal plates;
- whether smile restoration was carried out using metal pins.
A positive answer to at least one question indicates that examination with an MRI machine is contraindicated. Another factor prohibiting magnetic resonance imaging is the presence of a pacemaker.
Which is less harmful: CT or MRI?
One of the modern informative diagnostic methods, in addition to CT, is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). CT and MRI are not considered alternative methods. MRI is used to study organs that have a high fluid content, but are reliably protected by the bone skeleton: the brain and spinal cord, intervertebral discs, joints and pelvic organs. And with the help of CT it is preferable to examine the musculoskeletal system and lung tissue.
Both CT and MRI have almost equivalent information content when studying the genitourinary and digestive systems. However, computed tomography, compared to magnetic resonance imaging, requires much less time to perform, so it is preferred in emergency cases.
How harmful is it?
So, is MRI harmful to your health? As we have already mentioned, during magnetic resonance imaging, the patient’s body is exposed only to a powerful electromagnetic field, and this frightens many. However, scientists have not established the fact that they cause harm to the human body during MRI.
The fact that scientists have not found something does not mean that it does not exist.
Sometimes patients become ill during the procedure, but the reason for this is not the radiation, but the confined space. The MRI camera is very small; some patients find it very scary to stay in such a confined enclosed space for half an hour, and without moving.
If a person is too afraid, he should tell the doctor about this even before the diagnosis begins. For patients who are too afraid to undergo an unfamiliar procedure or are intimidated by limited space, the following options are available:
- Conduct scanning not in a closed, but in an open device. There are such methods, and recently they are being used more and more often.
- During the procedure, you can lie not on your back, but on your stomach. Many people like this position better.
- It is allowed not to place a special pillow under your head. To ensure that the patient receives more air, a special fan can be turned on.
- It must be remembered that the subject has a special panic button at his disposal. If problems arise, the procedure can be interrupted immediately.
- If the patient suffers from claustrophobia, he may be advised to take a sedative before the MRI.
Principles of protection
Patients who doubt the safety of radiation diagnostic methods should familiarize themselves with some principles of reducing radiation exposure:
- reduced time period: the duration of screening can be reduced by refusing to perform screening simultaneously in the sagittal and transverse projections, reducing the current strength of the X-ray tube, as well as the number of tomography phases;
- conducting computed tomography through bismuth screens: in this way, it is possible to reduce radiation exposure without compromising the quality of the images;
- increasing the distance: reducing the radiation dose can be achieved by increasing the distance between the X-ray tube and the body of the subject. You can protect other parts of your body that may be exposed to radiation by using lead shielding.
In cases where CT is used in pediatric patients, the use of sedatives is recommended, since immobility of the subject is important to obtain good quality images. For this purpose, you can also use special belts and pillows to ensure the child’s immobility during the examination.
Computed tomography is often the only possible method for diagnosing certain pathologies, for which there is no high-quality alternative, so the question of whether CT scanning is harmful is often inappropriate. This examination is used to confirm complex diagnoses and immediately begin treatment, especially when it comes to preserving the patient’s quality of life. If all recommendations are followed, the patient should not worry that a CT scan will cause irreparable harm to their health.
CT scans of any organs can be done at affordable prices at the Yusupov Hospital in Moscow. The clinic is equipped with a modern tomograph of the latest generation, thanks to which the experienced, highly qualified doctors of the Yusupov Hospital receive high-quality images. Based on the results of computed tomography, doctors create the most effective treatment tactics, individually for each patient.
Children
MRI scans may often be ordered for children. Parents are often concerned about the need to expose their baby to a powerful electromagnetic field. Those who do not understand the operating principle of the device are especially worried.
To perform an MRI, there must be strict clinical indications. This is a unique procedure that will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis. It may also be prescribed to clarify how effectively the treatment is being carried out.
MRI is safe for babies, but sometimes they may need anesthesia. We are talking about young children who simply physically cannot lie still throughout the entire procedure.
Anesthesia may be required if:
- the baby is too active;
- he does not want to lie in one position;
- the child is scared or does not want to be examined.
For older children, MRI is performed without anesthesia. The main thing is to explain the essence of the procedure and how important it is to carry it out. To prevent your child from being frightened by sound, you can use earplugs. They will not allow noise to affect their psychological state. The impact of the device on the senses will be minimal.