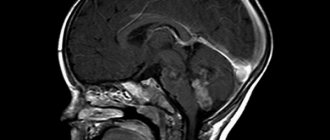
The brain is a complex organ consisting of gray and white matter, blood vessels, nerve fibers, membranes, and venous sinuses. To study anatomical structures, one diagnostic method is not enough. A computed tomography scan can be performed if hard tissue pathology is suspected. Verification of soft tissue changes is best done using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Oncological search is carried out comprehensively using both procedures.
Residents of large megalopolises in Russia (Moscow, St. Petersburg) have access to the services of public and private clinics, the addresses of which can be found on the global network. When choosing an establishment in St. Petersburg, you need to focus on reviews from previous clients of the centers. The addresses are distributed on the global network and in the media. In the city, more than a hundred clinics are equipped with radiation diagnostic methods.
Magnetic resonance imaging scanners are open and closed, low- and high-field. Gradation is carried out based on the structure of the electromagnet location zone.
Equipment for performing computed tomography can be step-by-step, spiral (multispiral). The separation is based on the principles of the scanning procedure.
A radiation diagnostics doctor will be able to determine the type of examination and choose the right type. It is also necessary to take into account the harm to health and the diagnostic benefits of the method of studying the brain. Read the article for details.
CT scan of the brain - what will it show?
X-ray radiation, which underlies the functioning of computed tomography, detects dense formations with a diameter of more than 1 mm. After intravenous administration of an iodine-containing drug, radiology doctors are able to use tomograms to identify vascular anomalies, aneurysms (wall dissection), hemorrhages in the brain parenchyma, and strokes (hemorrhagic, ischemic).
Contrast CT scan of the brachiocephalic arteries shows changes in thin sections. During one scan, from 200 to 500 tomograms are obtained, performed at 1 mm (or other interval). Through consistent study, the specialist determines the pathology. Analysis takes a long time.
Innovative software for CT machines allows for spatial reconstruction of the brain. The spatial model shows the smallest anatomical details. 3D reconstruction is used by neurosurgeons and oncologists before planning surgery.
Computed tomography of the head
Computed tomography of the head is a modern, painless diagnostic examination that involves the use of X-rays and modern computer equipment, which creates images of cross sections of the bones of the skull and brain at different levels.
CT examination data helps the doctor in:
- making the correct diagnosis;
- determining the exact localization of pathological processes;
- determining treatment tactics;
- monitoring the effectiveness of prescribed treatment and determining the dynamics of the disease.
What does a head CT scan show?
CT head
can show:
- the presence of tumors in the structure of the brain;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the head, their exact location and level of organ damage;
- hematomas and cysts;
- bleeding in brain tissue (for example, stroke);
- purulent formations;
- structure and structure of cerebral vessels;
- accumulations of fluid.
CT scan of the brain - why do it?
Clear medical indications have been developed, on the basis of which you can determine when to do a computer examination of the brain:
- Speech disorders;
- Prolonged headaches, dizziness;
- Suspicion of micro- and macro-strokes;
- Identification of the causes of increased intracranial pressure;
- Muscle cramps;
- Tumors;
- Cerebral edema, displacement of structures due to hydrocephalus.
CT angiography (vascular contrast) is performed to study intracerebral blood supply, identify hemorrhagic foci, if MRI is contraindicated. The main purpose is to detect small cancerous tumors.
CT brain perfusion provides information about tissue oxygen saturation and gas diffusion through nerve sheaths.
CT or MRI of the brain - what to do
Magnetic resonance scanning is used to study structures containing water. The brain consists mostly of soft tissue, which makes magnetic resonance examination a popular method for verifying nosological forms. The study determines vascular malformations (pathological joints between arteries and veins), congenital anomalies without contrast. The procedure is harmless and can be performed on children who are able to remain still for 30-40 minutes (duration of the examination). Combined MRI and MSCT of the brain are done when tumors are suspected, metastases are determined, and perifocal structures around the cancer focus are studied.
When is it better to do an MRI of the vessels of the brain and neck:
- Diagnosis of inflammatory processes – abscess, encephalitis, meningitis;
- Mental disorders;
- Stuttering, convulsions;
- Sudden loss of consciousness.
- When is spiral tomography preferable:
- Determination of the state of the ventricles;
- Verification of fluid accumulations;
- Diagnosis of cystic cavities;
- Identification of areas of accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Difficulties arise with prescribing a diagnostic procedure for suspected stroke. In the ischemic variant, it is better to use MRI, which records changes in the physicochemical properties of gray and white matter. If clinical symptoms indicate a hemorrhagic form, it is more rational to prescribe CT.
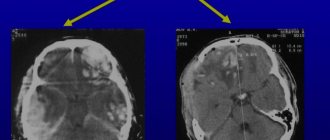
Interpretation of CT images
After completing the procedure, the radiologist receives the images immediately, and it may take him about 30-40 minutes to interpret them. The specialist compares the structures of the brain in different parts of the brain, assesses the size of the brain, identifies pathological areas and their exact location. A CT scan can also help identify fluid accumulation in certain areas of the brain. When a tumor is detected, the radiologist assesses its size. This can be done by direct signs of head tomography, such as darkening in the images, or indirect signs, for example, general cerebral edema. After deciphering the results, the images are given to the patient. He is also given recommendations on which specialist should continue examination or begin treatment: surgeon, oncologist, neurologist, dentist, and so on.
Computed tomography of the vessels of the brain and neck with contrast - how it is performed
Contrast examination is used to visualize the vessels that tightly envelop the brain. Examination of the cerebral arterial network and neck (carotid, vertebral, brachiocephalic artery) allows us to identify the causes of pathological symptoms (dizziness, headaches, short-term loss of consciousness).
Native scanning does not show the soft tissue component. After an intravenous injection of an iodine-based enhancing drug, specialists are able to study the arterial and venous network of the brain. The appearance of pathological circulation indicates neoplasms that have their own capillaries. Atypical vessels appear in the early stages, when the lesion is several millimeters in size. Innovative MSCT of the brain has the ability to verify lesions with a diameter of 0.5 mm. When determining where to do a CT scan, you need to take into account the specifics of the devices.
Using the bolus contrast method, radiology doctors are able to monitor the structure of the vessels of the neck and brain as the contrast spreads.
The CT perfusion method involves studying small capillary networks after the contrast agent has spread through them. The study is used for partial visualization of soft tissue components when it is impossible to use a magnetic resonance procedure. The contrast is excreted by the kidneys after 1.5 days. After CT angiography, women should not breastfeed.
MR angiography of the neck - types, indications
Anomalies, aneurysms, and malformations determine the clinical symptoms of dizziness and unexplained headaches. To verify these nosologies, MRI is performed, and if contraindications are performed, contrast-enhanced MSCT is performed.
The value of both studies is determined individually after analyzing the patient's medical history. A special type is cisternography of the brain, which allows one to estimate the size of the intracerebral ventricles.
For example, with an unsteady gait and double visual objects, vestibulopathy is suspected. Nosology is best determined using MRI of the brain and neck. The presence of metal objects is a contraindication. An alternative is contrast tomography of the brain and neck.
When do you need MRI and MSCT?
During an oncological search, doctors need comprehensive information about the consistency of tissues, the location of anatomical structures, visualization of additional shadows, and the condition of blood vessels (presence of plaques, blood clots, malformations).
The norm in the study of white and gray matter is rare. Specialists often find minor pathological abnormalities that do not require treatment. MRI of the brain and neck is indispensable for verification:
- Aneurysmal dilatations;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases.
The diagnosis of a tumor is more rational than its formation after a person undergoes an MRI-MSCT complex. To prescribe methods for examining the brain and neck, clear indications are required.
If an MRI shows cancer, there is no reason to despair. The final conclusion is formed only after a systemic examination and the use of all necessary diagnostic methods. High-field MRI and CT are the basis of oncological diagnostics. Radiation imaging is informative and highly specific.
When choosing a clinic in St. Petersburg where you can do MSCT, you should pay attention to the availability of important software modes:
- Selective fluid exclusion (Flair);
- Visualization of the total diffusion of molecules;
- 3D modeling;
- Assessment of perfusion parameters;
- Mapping of nerve centers;
- Determination of physicochemical composition (MRI).
The full complex will allow you to obtain maximum information about the structure of brain structures.
Radiation imaging of the neck – when is it performed?
An MSCT of the neck can be done if there are symptoms of intervertebral hernias or compression of the vertebral artery by unstable vertebrae. Neurologists can determine whether a nerve fiber is pinched in the cervical spine. Radiation imaging is used to assess the degree and nature of cerebral circulatory disturbances. The methods identify nosology at an early stage of development, when there are no symptoms.
MRI of the brain and neck is performed to identify or exclude blood clots, atherosclerotic deposits, and blockage of the lumen of the vessel.
Procedures are not used for mass examinations. Scientists have only theoretically substantiated the need for MSCT and MR imaging for early verification of atherosclerotic lesions of the heart arteries. The widespread spread of harmful radiation and the high cost of procedures are limited.
Computer scan of the neck and brachiocephalic trunk
The maximum number of cases of insufficiency of cerebral blood supply occurs in the brachiocephalic complex, which includes the carotid, vertebral, subclavian arteries, and brachiocephalic trunk.
Atherosclerotic deposits in the wall and a blood clot clog the lumen of the vessel. Non-contrast MSCT of the brain reveals abnormalities, helps assess the degree of microcirculation impairment, and visualize enlarged lymph nodes.
Late detection of BC damage is highly likely to lead to disability or death.
The use of multispiral tomography of the brain with contrast detects aneurysms, pathological anastomosis between arteries and veins (malformations). The study helps determine the volume and prevalence of death of brain parenchyma (atrophy), and areas of lack of oxygen supply (ischemia). Information is necessary for specialists when planning surgical interventions to install vascular stents, perform embolization, and remove aneurysmal dilatations.
What MSCT of the brachiocephalic arteries shows:
- Ischemic areas;
- Areas of narrowing of the arteries that do not manifest clinical symptoms;
- Discirculatory encephalopathies;
- Anomalies in the course and structure of blood vessels;
- history of stroke;
- Neoplasms of the neck;
- Thromboembolism.
The information content of spiral scanning is beyond doubt, but there are contraindications:
- Kidney failure (with contrast examination);
- Excessive secretion of thyroid hormones;
- Allergy to iodine;
- Carrying a child;
- Decompensated diabetes.
Vascular stenosis is the leading pathology leading to ischemic strokes. To prevent nosology, surgeons introduced endoscopic revascularization operations. Their use requires early diagnosis using MRI and MSCT of the brain.
Long-term persistence of ischemia due to lack of blood supply contributes to the expansion of the capillary areas located in front of the block. Tissues receive more oxygen, which leads to the development of hyperperfusion syndrome. If such areas are detected on computer angiography, an additional examination is prescribed - CT or MR perfusion, which evaluates the parameters of blood passage through the capillaries. The choice of method is determined by diagnostic tasks.
The option of choice is MSCT perfusion - a method with a quick analysis of the passage of blood through the capillaries without loss of tomogram quality.
MSCT angiography of the aorta – what it shows
The procedure determines the narrowing and expansion of the aorta located below the neck. The vessel is large, so serious blockage is accompanied by hypoxia of the organ complex - heart, brain.
MSCT angiography shows even minor areas of narrowing of the aorta and arteries. The study is characterized by intravenous administration of a contrast agent excreted by the kidneys. Enhancement with iodine-containing products causes restrictions - it cannot be done for people with kidney disease.
Doctors have developed clear criteria that limit the capabilities of multislice tomography:
- Blood creatinine level is more than 130 µmol per liter;
- Excess thyroid hormones;
- Hypersensitivity to iodine;
- Planning for radioiodine scintigraphy.
If any of the described criteria are present, contrast MSCT of the brain is not performed. The procedure can cause disability or death of a person if prescribed unreasonably.
CT scan of the neck and larynx with contrast is not an alternative to MRI and is prescribed for people with contraindications to the procedure.
Preparing for a CT scan
Before carrying out, it is necessary to set the indications for the study.
It should be remembered that this study involves x-ray radiation and its purpose must be strictly justified. In addition, during MSCT, a contrast agent is often administered, which is potentially harmful to the kidneys; the likelihood of adverse reactions when taking certain drugs increases. Therefore, only a doctor can give indications for a CT scan. When planning a study, you need to consider:
- Kidney function status;
- The patient is allergic to contrast media;
- The therapy the patient is receiving (for example, when treating diabetes with metmorphine, the contrast agent can cause complications);
- The patient has increased function or disease of the thyroid gland.
In patients with significant renal impairment or other relative contraindications to MSCT with intravenous contrast, the use of alternative research methods (ultrasound, MRI) should be considered.
MRI of the pituitary gland - what it shows
The pituitary gland is a soft tissue gland located in the area of the sella turcica. A tumor in this zone, an adenoma, leads to damage to the entire endocrine sphere. A computer scan does not show a neoplasm, but with its help it is possible to determine changes in the bone structure (expansion of the bed, calcification).
The pituitary gland is studied using MRI. The procedure shows intrasellar, laterosellar, intrasellar formations. Verification of lesions is achieved with dynamic contrast. The study is based on assessing the accumulation of contrast in the area of the corpus callosum, cerebral ventricles, and sellar zone.
Radiologists identify microadenomas by analyzing the accumulation curve at the initial stage. A pathological focus can be suspected by assessing contrast enhancement of the neck area immediately after injection.
For large formations of the fossa turcica, the features of the contrast accumulation curve during the peak are studied. For example, craniopharyngioma can be traced only 10 minutes after intravenous injection of the drug. MSCT of the brain does not have similar capabilities, but if the patient has metallic inclusions, there is no alternative to computed tomography.
Other ways to examine the head
MRI
MRI of the head
– the main alternative to computed tomography. The magnetic resonance scanning method allows a better assessment of the chemical composition of the tissues of the brain and skull bones. If the task is to study in detail the physical state of the head and brain, it is better to conduct a CT scan. MRI, unlike CT, is a safe procedure, during which there is no negative effect on the patient’s body.
Radiovisiography
This type of study, such as radiovisiography, is used only to identify pathologies or dysfunctions of the patient’s dental system. It will report in detail on the condition and structure of the teeth, but will not show the condition of the brain or skull bones.
X-ray
Radiography today is also used to diagnose the condition of the head and brain. Most often it is prescribed if we are not talking about a complex oncological disease of the brain, hydrocephalus or stroke. X-rays are prescribed, for example, if you need to visualize minor injuries to the skull, the level of its deformation, detect foreign bodies and estimate their size. X-ray can be called the primary diagnostic procedure, after which a CT or MRI is prescribed for a more detailed study.