The Children's Medical Center for Neurology and Pediatrics offers you a service - an electroencephalogram of a child!
Our specialists have many years of experience and excellent reviews!
- EEG procedure;
- How to prepare for an EEG;
- Types of EEG;
- Indications for EEG;
- Contraindications;
- Results (transcript);
- Our advantages.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
– one of the most widely used methods for diagnosing and studying the brain used in modern neurology and pediatrics. EEG allows you to monitor the child’s brain activity, assess functional changes in the cerebral cortex, confirm or refute the presence of lesions and disorders of the central nervous system.
In some cases, an electroencephalogram is indicated for the child to monitor the treatment, its effectiveness and appropriateness.
EEG procedure for a child
Electroencephalography of a child is a harmless procedure, without introducing drugs into the baby’s body, it will not cause painful sensations.
It is quite easily tolerated by children of all ages. Diagnostics are carried out in a room without extraneous sounds or distracting noises. The child usually either sits or lies on a couch, and a special cap with electrodes is placed on his head, which record brain activity in different areas. Because It is difficult for children to sit for a long time without moving, so in order to maintain a calm state, they try to distract them with toys. You can also bring toys with you - this will have a positive effect on the emotional background of the baby.
The specialist accompanies the main study with additional tests: he asks the child to blink, breathe frequently and forcefully (hyperventilation), blinks a flashlight near the child’s eyes (photostimulation) - these tests are necessary for additional stimulation of the brain and provocation of manifestations of a pathological nature.
Outpatient EEG: technique and methodology
Registration conditions
Obtaining reliable and comparable information from an electroencephalographic study is possible with strict adherence to standard conditions for performing an EEG study : the patient (subject) is in a state of quiet wakefulness with his eyes closed under conditions of sensory deprivation. During the examination, the patient sits in a special chair or lies on a couch.
The bioelectrical activity of the brain is extremely sensitive to the influence of external stimuli, responding to any suprathreshold stimulation by changing the amplitude-frequency parameters. In this regard, a mandatory condition for recording spontaneous activity is to perform the study with eyes closed. Also, the EEG room must have sufficient light and sound insulation to ensure sensory deprivation.
A state of calm wakefulness implies emotional peace and muscle relaxation. The patient’s psycho-emotional tension is manifested by changes in the nature of the EEG, therefore a necessary condition for conducting the study is the maximum possible emotional peace and muscle relaxation of the subject. The study should be carried out under thermal comfort conditions.
Before conducting the study, the patient is explained its essence, told about its harmlessness and painlessness, outlines the general procedure for the procedure and be sure to indicate its approximate duration. All this should be done to relieve the patient's inevitable anxiety as a reaction to an unknown influence. Experience shows that for the vast majority of patients, the technique of conducting an EEG examination is not a known and understandable procedure. This gives rise to natural affective tension even in healthy individuals. We should not forget that people with certain doubts about their health status are referred for an EEG examination (except for special psychological or psychophysiological studies of healthy individuals). Thus, in order for the patient to achieve a state of calm wakefulness, the procedure for performing the procedure should be explained to him. Otherwise, it is not the resting EEG that is recorded, but the EEG correlates of the state of anxiety.
To achieve a state of calm wakefulness during the study, either special chairs are used, or the patient is positioned lying on a couch (bed). When using the chair, the patient’s position should be as comfortable as possible, the head should rest on a special headrest to relax the neck muscles, but the occipital and parietal electrodes should not suffer (displace). The need for muscle relaxation, in addition to ensuring maximum emotional peace of the subject, is determined by the fact that tension in the muscles of the head and neck is accompanied by the appearance of electromyogram artifacts.
Standard conditions for performing an EEG technique imply a state of wakefulness, i.e., the presence of consciousness. It should be borne in mind that a person in conditions of sensory deprivation, sitting in a comfortable chair or lying on a couch with his eyes closed in a state of psycho-emotional relaxation, can involuntarily move from a state of wakefulness to the phases of falling asleep and light drowsiness. This will inevitably change the pattern of background activity, which may distort the results of the study. When performing an examination, the doctor must consider the possibility of fluctuations in the patient’s level of consciousness
Procedure for performing the study
➥ Main article: EEG examination (order of execution)
The study consists of two sections: registration of spontaneous (background) activity under conditions of quiet wakefulness and registration of the results of functional tests. Both sections are required for a comprehensive neurodynamic assessment. Registration of background activity allows us to assess the basic state of the mechanisms of bioelectrogenesis. Performing functional tests aims to assess the reserves of regulation of the central nervous system. In epileptic EEG, performing functional tests makes it possible to identify epileptiform EEG disturbances and clarify their localization. In cases where the clinical picture and the nature of the spontaneous EEG do not raise doubts about the presence of severe epileptic disorders in the patient, functional tests on an outpatient basis may not be carried out in order to avoid provoking an epileptic attack.
Registration of background activity is carried out for a sufficiently long time, which makes it possible to register a typical state (pattern) of spontaneous activity for the patient. In the subsequent analysis of amplitude-frequency parameters, stationary fragments of the background EEG are taken.
The most commonly used functional tests in the EEG technique are: 1) eye opening/closing test; 2) rhythmic photostimulation; 3) hyperventilation. The listed tests are performed sequentially at intervals that ensure restoration of the original background EEG state.
The test with opening and closing the eyes (OG/EC) is assessed by the severity of the reaction of desynchronization of background activity. The eye opening/closing test can be replaced by a test with a single flash of light or a single intense sound tone (click).
Test with single flashes of light - photostimulation with 10-15 flashes, the next at varying intervals of 1-2 s. The change (extinction) of the desynchronization reaction is assessed as a correlate of the extinction of the orienting reaction to novelty.
Rhythmic photostimulation (RPS) is performed with flashes of white (less often red) light, which are delivered at different frequencies in the range from 2 to 30-35 Hz. For this purpose, a photostimulator or LED glasses can be used. Flashes of light are sent to closed eyes.
RFS can be performed in an incremental (increasing frequency) and decremental (decreasing frequency) manner. As a rule, these two methods are combined: first, the frequency is increased from 2-3 Hz to 30-35 Hz, then reduced. Frequency increases and decreases are performed in steps of 2-3 Hz. At each “stage” photostimulation is performed for 3-5 s. An increase (decrease) in frequency can be carried out by sequentially changing one “step” to another, or with pauses between “steps” lasting 5-7 s to assess the speed of activity recovery. When obvious signs of paroxysmal activity are recorded on the EEG, photostimulation is stopped.
If special equipment is available, when conducting an EEG, trigger photostimulation can be performed, in which a flash is given when a certain phenomenon is recorded on the EEG, for example, during the descending phase of the wave.
Hyperventilation is a test with forced rapid breathing: the subject performs 20-30 deep breathing movements per minute. The test is carried out for 1-2-3 minutes, depending on the condition of the subject and the symptoms detected. The subject sits with his eyes closed. If obvious signs of epileptic activity are detected, the test is stopped. At the end of hyperventilation, the EEG evaluates the nature and speed of restoration of background activity.
The main method of EEG analysis is visual-logical. It starts already during the registration process. An addition to the visual-logical analysis, which strengthens the evidence base in the neurophysiologist’s conclusions, are the results of a mathematical analysis of the amplitude-frequency and spatial parameters of bioelectrical activity. The results of the study are formalized in a formal conclusion.
How to prepare for a child's EEG
Due to the age of young patients, they may require special preparation for the pediatric EEG procedure in Moscow. If the child is newborn or young, then most likely the examination will be carried out in his sleep. But it’s worth preparing the older kids! It is advisable to tell your child about the upcoming “adventures” in advance at home, in a confidential conversation. Describe in detail how and why EEG is done for children, what are the features of the upcoming procedure. You can playfully talk about the “magic cap” that you have to put on to become stronger and healthier.
Psychological preparation, parental support and positive motivation are extremely important for a child. Because Finding themselves in an unknown environment, young children sometimes get scared, cry and flatly refuse to put on a hat with electrodes; under such conditions, it is very difficult to get a high-quality EEG for a child. The procedure must be carried out calmly, in complete silence and with eyes closed, and if the baby is in a stressful state, this is extremely difficult to achieve. Therefore, in such cases, we cannot do without the help of parents!
On the appointed day, it is better to come to the clinic with clean hair, without hairpins, bows, etc., for girls it is better to let their hair down. It’s good if the child is not tired and not hungry.
How is electroencephalography performed?
The time of diagnostic testing varies depending on the goals set. More often the procedure is carried out in the morning or afternoon. Sometimes electroencephalography of the brain is performed during sleep.
The Yusupov Hospital has a room specially equipped for electroencephalography, protected from light and noise. Only the functional diagnostics doctor and the patient are present in the office. During the study, one of the child’s parents is also in the office.
The patient lies down on a couch or sits comfortably in a chair. A special “cap” with electrodes connected to each other by a network of wires is put on his head, and the study begins. To assess the nature of technical errors from blinking, first the doctor asks the patient to close and open his eyes several times.
Then the subject, at the doctor’s request, closes his eyes and sits or lies quietly, without making any movements. If the patient needs to change body position or go to the toilet, recording of the electroencephalogram is temporarily stopped. If during the examination the patient moves, blinks or swallows, the doctor makes a note on the film or on the computer. These actions of the patient can affect the nature of the curve, and the doctor, in the absence of the necessary information, may misinterpret them, which will affect the nature of the conclusion.
After recording an electroencephalogram, the patient is subjected to stress tests, which allow one to evaluate the brain’s response to stressful situations. When conducting a hyperventilation test, the doctor asks the person being examined to breathe deeply frequently for three minutes. Such actions, if there is a predisposition, can provoke an attack of generalized convulsions or a seizure such as epileptic paroxysms, which occurs with a short-term loss of consciousness without visible convulsions. Photostimulation is performed using a stroboscopic light source that flashes 20 times per second. In this way, the doctor evaluates the brain's reaction to bright light. In susceptible individuals, an epileptic seizure or myoclonic convulsions may occur in response to blinking.
During provocative tests, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are prepared for the development of a pathological reaction of the patient’s body and provide him with qualified emergency care. At the end of the study, the patient is reminded of the need to resume taking medications that were discontinued before electroencephalography.
Standard (routine) EEG of a child – 30 minutes
The most common and accessible form of research is standard (another name is routine) electroencephalography. The obvious advantages of this method are the relative ease of implementation and short duration (no more than 25-30 minutes). Most often, a standard EEG is prescribed during the initial visit, when it is necessary to examine a patient with a variety of neurological and mental diseases. However, to identify pathological changes in the functioning of the brain in epilepsy, a standard EEG study is not enough.
Indications for a child's EEG
Indications for prescribing an EEG for a child may include various symptoms:
- Convulsions;
- Psychological disorders: unmotivated temper, excessive tearfulness of the baby, frequent hysterics, neuroses;
- Cerebrovascular accidents;
- Injuries, bruises, concussions;
- Structural pathologies of the brain, tumors;
- Fainting, loss of consciousness;
- Moderate and frequent headaches, dizziness, loss of orientation;
- Severe fatigue;
- Epilepsy;
- Sleep disorders: problems falling asleep, insomnia, restless sleep, sleepwalking;
- Autism.
Child EEG results (interpretation)
The results obtained in the form of printed sheets with an image of the background curve are sent for processing and decoding. In our clinic, electroencephalogram interpretation is carried out only by doctors of the highest category. They evaluate deviations from the established norm, judge the strength and presence of violations, look at the activity of the brain, how its centers react to stimuli.
After the decoding is completed, a doctor’s opinion is issued, the results of the EEG are highlighted, and the treating neurologist-epileptologist voices certain, more specific recommendations. All results obtained are transferred to a DVD, which is given to the parents of the child being tested, and you will also receive a printed report from the epileptologist with EEG graphs of the child. If you require an urgent decoding of the results, we are ready to provide such a service; its current cost is 2,000 rubles.
It is worth emphasizing that the resulting conclusion is not an accurate diagnosis. Electroencephalography is just one of the methods for diagnosing disorders. And the attending physician can make a final diagnosis only on the basis of a complete, comprehensive examination of the child.
Decoding the electroencephalogram
At the Yusupov Hospital, the electroencephalogram is deciphered by experienced neurologists, leading experts in the field of neurophysiology. Study results that are difficult to interpret are discussed at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of candidates and doctors of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category. Neurologists collectively make decisions regarding the diagnosis and management of the patient.
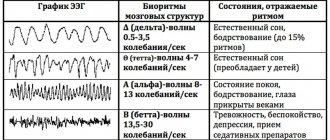
The human EEG contains alpha, beta, delta and theta rhythms. They have different characteristics and reflect certain types of brain activity. An electroencephalogram is a recording in computer memory or on paper. The curves that are recorded during the study are analyzed by a neurophysiologist. It evaluates the rhythm of waves, frequency and amplitude, identifies characteristic elements, recording their distribution in space and time. Then all the data is summarized and reflected in the conclusion and description of the electroencephalogram. The conclusion is based on the analysis of EEG curves taking into account the clinical signs of the disease. It reflects the main characteristics of the electroencephalogram and includes 3 mandatory parts:
- description of the activity and type of EEG waves;
- conclusion according to the description of the electroencephalogram and its interpretation;
- determining the correspondence of clinical signs with EEG results.
In the process of deciphering the electroencephalogram, the doctor must take into account the basal rhythm, the level of symmetry in the electrical activity of the neurons of the brain of the right and left hemispheres, the activity of the commissure, and changes in the electroencephalogram against the background of functional tests. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital make a final diagnosis only taking into account the presence of clinical signs of the disease that worry the patient.
In order to register an electroencephalogram, make an appointment with a neurologist by calling the Yusupov Hospital. After recording the EEG, the doctor will make a conclusion and give recommendations for treating the disease.
Our advantages
- Our specialists always provide the necessary psychological support to children; we will advise and help parents on how best to set up their child in order to easily and painlessly undergo all the prescribed procedures.
- Our analysis and decoding of the electroencephalogram is carried out by epileptologists of the highest category; thanks to their high qualifications, the conclusions based on the results of the EEG are drawn up as professionally, clearly and in detail as possible.
- The comfortable room for EEG monitoring is equipped with everything necessary. All furniture is selected taking into account the age characteristics of small patients. An extra bed is provided for the accompanying parent.
- Tea and coffee are available and free Wi-Fi is available throughout the clinic building.
- Our clinic is located very well, within walking distance from the Kolomenskaya metro station (5-7 minutes).
- If you arrive by car, convenient guarded parking will allow you to park your car freely at almost any time. Parking is free for our patients.