Take the first step
and make an appointment with your doctor!
Ovarian cyst is a common disease of the female reproductive system, occurring in 30-50% of women of reproductive age (15-39 years). This pathology, depending on the severity, can cause consequences ranging from minor discomfort and pain to infertility and potentially even death. Removing an ovarian cyst is one of the most effective ways to treat it. However, it has both undoubted advantages and obvious disadvantages. They need to be known so that surgical treatment is adequate and does not bring even more problems than the disease itself.
What is an ovarian cyst?
This pathology consists of the appearance in the ovary of a benign neoplasm, consisting of a clearly defined membrane filled with liquid or porridge-like contents. Depending on the reasons for their appearance, the following types of cysts are distinguished:
- Functional. Such a cyst is formed in women of childbearing age (less commonly, menopause) from ovarian follicles when the ovulation process is disrupted (for example, due to hormonal imbalance). In this case, the egg sac does not dissolve, giving rise to a mature egg, but is preserved and increases in volume. A functional cyst in most cases only causes discomfort and does not threaten a woman’s health. Over the course of about 2-3 menstrual cycles, it independently decreases in size, resolves and disappears.
- Organic. A cyst of this type no longer goes away on its own and is a full-fledged pathology. It differs from the functional one by a denser wall and different types of contents. The only way to treat it is a careful operation to remove the ovarian cyst while preserving intact organ tissue (as far as possible).
The mechanism of appearance of an organic cyst can be different, which also determines the difference in the structure of its subtypes - for example:
- dermoid variety (teratoma) is formed due to a disruption in the process of embryogenesis in the ovary and is a capsule containing tissues atypical for this organ - hair, skin, teeth, bones, sometimes even the rudiments of full-fledged organs;
- an endometrioid cyst is formed due to the introduction of uterine endometrial cells into the ovaries; its cavity contains a characteristic dark brown thick liquid consisting of old menstrual blood;
- a parovarian cyst is formed from the tissues of the ligamentous apparatus of the ovaries; it can be located near the ovaries themselves or closer to the fallopian tubes.
The causes of ovarian cysts can be:
- accidental or violent injuries, careless surgery, etc.;
- hormonal imbalances caused by taking medical hormones, contraceptives, eating disorders, various diseases, stress;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs caused by infectious pathogens, exposure to negative environmental factors (for example, cold);
- various metabolic disorders - in particular diabetes mellitus.
In the vast majority of cases, the cyst is a benign formation that does not threaten the woman’s life. However, if left untreated, it can cause the following complications:
- Cyst rupture. This is a violation of the integrity of the membrane, due to which its contents enter the abdominal cavity. Depending on the type of tumor, its size and other factors, rupture can be accompanied by either minor pain or severe shock.
- Twisting of the cyst. In this case, the tumor does not burst, but the ligament that connects the affected ovary to the uterus is twisted. Because of this, the blood supply to the organ is disrupted, which leads to its atrophy and, as a consequence, impaired reproductive function.
- Malignization. This is the transformation of a cyst from benign to malignant. Malignization occurs quite rarely and depends on the type of tumor, its size and other factors. Most often, a mucinous cyst, characterized by a high growth rate, degenerates into a malignant tumor.
- Impact on surrounding organs. Increasing in size, the ovarian cyst affects the fallopian tubes and uterus, bladder, and intestines. This often leads to discomfort, pain, disturbances in urination, defecation, and reproductive function.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Obviously, pathology that can potentially lead to such complications must be treated. Curing a functional cyst is quite simple: it either goes away on its own or with the help of medications. With an organic cyst, the situation is more complicated - as a rule, drug therapy in this case is ineffective. The only way to remove it is surgical treatment.
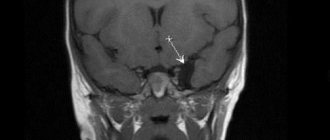
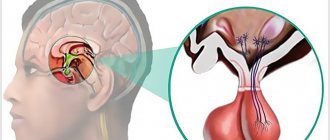
Brain cyst - causes and symptoms
The causes of brain cysts in children and adults can be previous infectious diseases, head injuries, inflammatory processes, abnormalities of intrauterine development, cerebrovascular accident with the formation of necrosis and ischemia. For the same reasons, cysts of the septum of the brain and pituitary gland may occur.
Most often, neoplasms do not interfere with the normal course of a person’s life and are discovered during examinations. Exceptions are newborns, in whom the cerebral cyst is detected in the prenatal period and does not pose a danger to the further development of the fetus. In most cases, vascular cysts of the brain cause neurological disorders and can manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- visual impairment caused by compression of the optic nerves;
- throbbing headache;
- with a pituitary cyst, hormonal status may be disrupted, which leads to a decrease in potency in men and disruption of the ovulation process in women;
- numbness of the limbs and disruption of the vestibular apparatus.
If such symptoms occur, you should seek help from a specialist, and the sooner this is done, the more favorable the prognosis for a full recovery.
Methods for removing ovarian cysts
To remove an ovarian cyst, it is necessary to carefully separate the tumor from healthy tissue and remove it from the abdominal cavity. The methods used can be divided into 2 categories:
- Classic cystectomy. This operation is performed through an incision in the wall of the abdominal cavity under the direct visual control of the doctor over the tumor and surrounding tissues. Classic cystectomy does not require the use of special instruments and is generally easier to perform. However, the open incision can become infected and cause irritation, and the operation leaves a fairly large and noticeable scar on the body.
- Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cyst . This minimally invasive method involves excision of the tumor using an endoscopic device (laparoscope) inserted through a small puncture in the abdominal wall. This somewhat complicates the operation itself and increases the requirements for the qualifications of the specialist performing it. But after it there is no open incision, which reduces the risk of infection, and there are practically no unaesthetic scars left.
Today, laparoscopic cystectomy is the preferred method for removing ovarian cysts. Classic surgery through an incision is performed only in extreme cases or in the absence of appropriate specialists and instruments. Therefore, laparoscopic cystectomy will be discussed in detail below.
Indications and contraindications for removal of an ovarian cyst
Resection of an ovarian cyst using a laparoscope is prescribed if it does not disappear on its own or as a result of drug (hormonal) therapy within 3 menstrual cycles. Indications for this operation are also:
- The appearance of a cyst after menopause - in this case it is not a violation of the natural process of ovulation and, therefore, will not go away on its own;
- Cysts and neoplasms are relatively small in size (up to 10 cm).
There is a list of situations in which laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst is not recommended or is strictly excluded - these include:
- Obesity of 3-4 degrees due to an increased fat layer of the abdominal wall, which interferes with the use of a laparoscope;
- High risk of stroke or myocardial infarction, decompensation of chronic pathologies;
- Infectious process, massive bleeding, peritonitis (inflammation) in the abdominal cavity;
- Malignancy of a cyst is its transformation from a benign tumor to a malignant one, in this case laparoscopy can only be used to biopsy its sample;
- Excessive (over 10 cm) size of the cyst, due to which it cannot be removed without an incision on the abdominal wall;
- A bleeding disorder that, if treated surgically, can cause extensive blood loss and death;
- Extensive adhesive process, making it difficult for the laparoscope camera to view the problem area.
At the request of the patient, the operation can be performed without any clear indications. For example, if she does not have the opportunity or desire to wait 3 months until the cyst goes away on its own (which may not happen). However, doctors still recommend using drug therapy first as the most gentle way to get rid of the problem.
What is a knee cyst? Symptoms and treatments
While there is nothing eternal in the world - everything is subject to wear, aging and damage. The human body is no exception. In particular, the knee joint. This part of the body is an anatomical structure that allows various types of leg movements. Unfortunately, diseases can develop in such an important node for humans. One of them is a cyst.
general information
What it is? If you look from the outside, it's a tumor. There is an accumulation of fluid inside the knee, which leads to the appearance of tumors. They are all benign, round or oval. There are also one-sided and two-sided, single-chamber and multi-chamber. The size of tumors is no more than 20 - 100 mm. There are several varieties of this disease. A description follows.
A Baker's cyst is a compacted object. It can have a diameter from twenty to one hundred millimeters. Single chamber.
Ankylosing spondylitis cyst is one of the variants of the previous type. Rarely observed.
A meniscal cyst is a chamber filled with a liquid substance. There are two menisci inside the knee. In fact, these are just cartilages that act as gaskets, similar to a sickle. Their task is to cushion the joint. This is where this foreign reservoir appears.
Subchondral cyst - occurs mainly in older people. It does not reach a large value. Tumor 5 - 15 mm. Develops along with knee arthrosis.
Parameniscal cyst is almost the same as the previous one. The difference is that several cystic formations will appear after a meniscus tear has occurred. If it reaches large sizes, it will most likely aggravate the situation.
Ganglion cyst - originates from the innermost areas of the knee joint. Filled with liquid consistency. On palpation, a compacted elastic formation is felt. Rarely seen.
Synovial cyst - can develop if there is increased generation of synovial fluid. Appears in the synovial area and grows towards the popliteal fossa.
Prerequisites for the appearance
Before talking about the reasons, it should be noted that this disease develops in both children and adults. More often in boys than in girls.
The cause of a cyst in children may be immaturity of the body, insufficient development of the ligamentous apparatus, or problems with tissue stiffness. All these reasons are based on inflammation of the cavities of the knee joints.
Men and women also have enough prerequisites:
- fractures, dislocations of knees;
- large and prolonged forces to which the joints are exposed;
- meniscus injuries;
- arthritis resulting from inflammation;
- knee arthrosis
; - synovitis, bursitis in chronic form.
Symptoms
The difficulty of detection lies in the fact that at first the disease may not bother you. Often, signs (an unclear formation) are noticed by chance. There is usually no pain during movement or palpation.
The symptoms look somewhat different if it is parameniscus disease. Pain appears almost immediately when walking and bending or straightening the knee, but no external signs are observed for some time. And even a tumor is found only through examination.
The most vulnerable to the disease is the external meniscus - it is the most mobile. This is where the disease most often penetrates.
If the medial meniscus is affected, then if you bend the knee, swelling will appear in the front part of it. It disappears when unbent.
Survey
The traumatologist will accurately make a preliminary diagnosis after examination. But for successful treatment it is necessary to know exactly how the disease progresses inside the knee. For this purpose, a special examination is prescribed. Ultrasound, radiography. A minor incision is made in the muscle of the joint, an MRI and a puncture of the fluid are made. A set of these examinations will allow the doctor to correctly diagnose: the size of the formation, location, and other data.
Treatment options
Cystic diseases progress in different ways. In some cases it is acute, in most cases it is chronic. Therapy can also be performed in different ways. There are surgical and conservative options. They are listed below:
- Use of soft tissue or plaster casts;
- treatment using natural and physical factors;
- dissect the cyst and remove fluid from it (the use of hydrocortisone is not excluded);
- You can use folk remedies.
In fairness, it should be noted that surgical methods are preferable to conservative ones, since after using the latter, the possibility of relapses of this disease cannot be excluded. If the cyst is a by-product, it disappears on its own after treatment of the underlying disease.
The best treatment for meniscal cysts is arthroscopy.
Treatment among the people
It should be noted immediately and categorically that the best option to get help is to visit a doctor. If the disease is not advanced, you can, of course, use proven folk methods. But this is at the discretion of the patient himself. Here are some of such methods.
If it is determined that the cyst is caused by arthritis and arthrosis, you can use burdock leaves. Prepare until the last month of summer. Wash and grind using a meat grinder or blender. Squeeze out the juice and keep in a cool place. You need to drink it for thirty days. Dose - a teaspoon per day. It happens that one course is not enough. In this case, the course described above is repeated after a month.
You can use regular or blue clay. It needs to be prepared with a tincture of ordinary anti-inflammatory herbs: chamomile, calendula, sage. To prepare the decoction, use a tablespoon of herb per two hundred grams of clay. The resulting solution is applied to the knee.
Healthy joints to you!
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Preparing to remove an ovarian cyst
It begins with diagnostics, which is necessary to accurately determine the presence of a neoplasm, its size, location, indications and contraindications for surgery. A comprehensive medical examination before removal of an ovarian cyst includes:
- Initial consultation and medical history , thanks to which the doctor learns about other problems with the reproductive system and the body in general, possible injuries, hypothermia, metabolic disorders and other factors contributing to the development of cystic pathology;
- Manual examination , which consists of palpating the suspected cyst through the abdominal wall and allowing one to determine the size, shape, position, density and other characteristics of the neoplasm;
- Pelvic ultrasound is a non-invasive study that provides a clear visual representation of the cyst using ultrasound “candling” of the abdominal organs;
- Colposcopy is a visual examination of the vagina and cervix using an optical colposcope, which allows one to assess possible changes in the genital tract due to cyst growth;
- Fluorography - with its help, the doctor can identify neoplasms in a woman’s lungs and mammary glands, thereby confirming the possible oncological nature of the ovarian cyst;
- Blood tests - general, biochemical, clinical, histological, coagulability, blood group and Rh factor, infectious diseases.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Also, in order to clarify the diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvic organs, taking a smear from the vagina or cervical canal and other tests may be prescribed.
Laparoscopy has certain restrictions on the thickness of the abdominal fat layer under which it can be performed. If the patient is overweight, the doctor may prescribe a special diet and exercise to reduce body weight. It is recommended to start taking activated charcoal approximately 1 week before surgery.
Immediately the day before laparoscopy, the patient must:
- take a bath and epilate the abdomen and intimate area so that hair does not interfere with the operation;
- eat no later than 19:00 and drink before 22:00 the evening before;
- immediately before the procedure, cleanse the intestines with an enema.
Such preparation for surgery to remove an ovarian cyst is necessary for the most convenient access of the laparoscope to the abdominal cavity and the maximum possible view. This significantly reduces the risk of damage to healthy tissues and organs, internal bleeding and other complications.
Ovarian cysts during pregnancy
Often, an ovarian cyst is first diagnosed during pregnancy (according to literature data, in 2% of women). But in most cases they are functional cysts less than 6 cm in diameter, which resolve on their own in the second trimester.
Pregnancy is a special condition, and the management tactics for pregnant women with ovarian cysts take into account, on the one hand, the impact of treatment on the mother’s health, and on the other, the risks of adverse effects on the fetus.
Scientists have developed standards that determine when surgical treatment is necessary and when only dynamic observation is possible.
If ovarian cysts are diagnosed in a pregnant woman, the indications for surgical treatment are:
- persistent (long-term) ovarian cysts after 16 weeks of pregnancy and larger than 6 cm in diameter;
- cysts that have a high risk of malignancy according to ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and the CA-125 tumor marker;
- cysts manifested by clinical symptoms (pain);
- emergency situations associated with the presence of an ovarian cyst (torsion, suppuration, rupture)
It is preferable to perform the operation using a laparoscopic approach, since it has been proven that laparoscopy is a safer and more gentle method of surgical intervention in any trimester of pregnancy.
Of course, even this high-tech method of diagnosis and treatment during pregnancy has its own characteristics:
- the operation should be performed with the woman positioned on her left side, especially in late pregnancy, so that there is no compression of the inferior vena cava and, as a result, a decrease in the return of blood to the mother’s heart, hypotension and circulatory disorders of the placenta;
- initial entry into the abdominal cavity is possible using a Veress needle or in an open manner, if the anterior abdominal wall is mobile and moves well. But we must remember that in the later stages of pregnancy, all abdominal organs are displaced by the enlarged uterus, so it is preferable to carry out the first entry under ultrasound guidance;
- it has been proven that the introduction of tocolytics - drugs that relax the uterus, for prophylactic purposes during and after surgery is unjustified;
- the use of these drugs should be strictly individual and in the presence of a high risk of premature birth;
- During and after the operation, it is necessary to monitor the condition and heartbeat of the fetus in order to detect the slightest disturbances and change the tactics of the operation in time.
Thus, surgery in pregnant women with ovarian cysts is complex and requires certain training not only of the surgeon, but also of all personnel, and should be carried out in highly qualified specialized institutions.
How is surgical removal of an ovarian cyst performed?
Although laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure, it is performed only by a suitably qualified specialist in a hospital setting. The operation is performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia) with tracheal intubation or the use of a mask. This method of pain relief allows for better control over the quality of anesthesia.
The patient is positioned on the operating table, the head of which is tilted down at an angle of 30 degrees. Thanks to this, the intestines move towards the diaphragm and free access to the ovaries. To further improve visibility and provide the instruments with the necessary freedom of action, carbon dioxide is released into the abdominal cavity through a puncture in the navel through a tube, which inflates the abdomen and increases its internal volume. The operation then proceeds as follows:
- A laparoscope, a tubular instrument with a miniature camera and a light source, is inserted into a puncture made in the navel. With its help, the doctor establishes visual control over the operated organ and the surrounding area, assesses the size and shape of the cyst, and its condition. Based on this examination, a conclusion is made about the need for further use of laparoscopy or classical cystectomy.
- Through lateral punctures in the abdomen, the doctor inserts additional instruments into the abdominal cavity. With their help, under visual observation through a laparoscope, he peels out the inner surface of the cavity and sucks out its contents. In some cases, the doctor performs partial or complete removal of the ovary with a cyst in women with a strong spread of the pathological process in its tissue.
- At the final stage, the doctor examines the operated organ and surrounding tissues for bleeding or other injuries. If there are none, the instruments are removed from the patient’s body, the gas is sucked out from the abdominal cavity, the punctures are sutured and covered with bandages. The anesthesia tube is removed from the patient's trachea, she is brought to consciousness and transferred to a regular ward.
The postoperative period after laparoscopy lasts an average of 14 days. The patient is discharged from the ward after 3-5 days, the stitches from the punctures are removed after 7-10 days. If complications arise during the operation, the rehabilitation period can be increased depending on their severity.
Efficiency and safety of ovarian cyst removal
The invasive and minimally invasive methods of surgical removal of ovarian cysts used today show fairly high efficiency and a low level of risk associated with complications. However, they do happen sometimes and you need to be aware of them:
- Pain syndrome. It occurs most often due to the accumulation of carbon dioxide residues in the abdominal cavity. They act on large clusters of nerves, causing them to become irritated. This does not pose a threat to life, but it causes discomfort that passes over time.
- Adhesive process. Occurs due to scarring of tissue in places where surgical instruments impact them. Adhesions after removal of an ovarian cyst occur quite rarely, but can lead to disruption of the anatomical structure of the reproductive organs and, as a result, to infertility.
- Subcutaneous emphysema. Also a non-life-threatening complication caused by the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the upper layer of subcutaneous fat. It occurs when the surgical technique is violated, but goes away on its own.
- Bleeding. This complication already poses a real threat to the patient’s life. It occurs due to a violation of the surgical technique, poor diagnostics, or for other reasons. Internal bleeding leads to the accumulation of blood in the abdominal cavity, causing acute peritonitis to develop in it.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
The cost of surgery to remove an ovarian cyst using a classical or laparoscopic technique is today affordable for the vast majority of patients of reproductive age. The price may vary depending on the chosen method of surgical intervention, size, type, position of the cyst, and other complicating factors. In most cases, this procedure provides a high chance of complete recovery from this pathology.
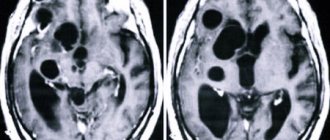
Types of cysts. Diagnosis and treatment
Depending on the location, cystic neoplasms are divided into two types: retrocerebellar - located directly in the brain tissue and arachnoid - localized in the meninges.
offers effective treatment of vascular neoplasms of the brain, including cerebral cysts in newborns, only in leading clinics in Russia, Europe and Israel. To make a correct diagnosis, advanced diagnostic methods are used:
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and head;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- examinations for autoimmune diseases;
- heart tests and blood pressure monitoring;
- neurophysiological research.
Based on the results of the examination, a method of treating the cyst is prescribed: conservative with drug therapy, or radical by removing the brain cyst. The results of treatment depend on the timing and size of the vascular formation, and in general, with the right treatment method, the prognosis is favorable.