What is the essence of the EEG procedure?
An electroencephalogram records electrical signals from brain cells and allows us to identify epilepsy, trauma, neoplasms, inflammatory processes, and changes in blood vessels. Pathology is indicated by disturbances in the electrical activity of neurons, which are recorded using special sensors placed on the patient’s head.
Using an electroencephalogram, the doctor can:
- analyze the performance of the brain;
- identify foci of pathologies;
- assess the nature and extent of damage;
- confirm or clarify the diagnosis;
- monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
Diagnostic methods for headaches
There is a special questionnaire that allows the patient to verbally describe his or her feelings. Migraine and cranialgia present similar symptoms; lesions in the skull, neck or spine may be accompanied by characteristic symptoms in other parts of the body.
Brain pathologies are often diagnosed only through hardware studies. Therefore, not only complex, but also differential diagnostics are carried out using laboratory and instrumental research methods. They are prescribed after an examination and anamnesis based on the data reported by the patient and available in his medical history.
When the study is considered sufficiently complete, the data obtained is analyzed. If a clinical picture emerges that indicates the possibility of developing several diseases, without any special arguments that outweigh the opinion in one direction or another, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Encephalogram
A study based on the study of brain function. Electrical potentials are emitted from the scalp, which are recorded on the encephalogram. By recording bioelectrical activity, the electroencephalograph, using special sensors attached to the skin according to the international scheme, produces an indirect result in the form of a recording on a paper tape or a converted file on a computer. Sometimes several types of studies are done - regular (routine), long-term or overnight EEG.
An electroencephalogram may be required to confirm information about negative processes in the brain, tumors and injuries, determine the exact location of the damage, and determine the state of the central nervous system.
CT scan
Headache is only one of the symptoms for which a CT scan is recommended. Computed tomography is a non-invasive way to obtain information if the disease is accompanied by weakness and lethargy, hearing and vision impairment, and lack of coordination of movements that accompany frequent headaches.
The main purpose of a CT scan is to detect damage to brain cells and structures and transfer the obtained data to a storage medium accessible for study.
Magnetic resonance imaging is used as a research method for chronic headaches, if there are accompanying symptoms - dizziness, loss of consciousness, abnormal blood pressure and tests confirming the presence of tumors. Until recently, it was considered an auxiliary diagnostic method, helping to confirm an existing assumption.
Now this method of layer-by-layer scanning is capable of identifying diseases of the central nervous system, lesions of the pituitary gland, tumors of the brain, hemorrhages, and showing some diseases of the organs of vision and hearing.
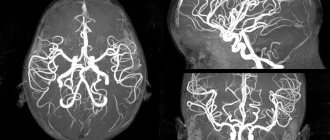
Angiography
Allows you to examine the condition of blood vessels in the head area. This is done in three ways:
- using an X-ray machine and an injected contrast agent;
- using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner and drugs with gadolinium;
- using a CT scanner and a substance containing iodine to produce a contrast image.
The procedure is carried out by an angiography technician, who also gives a preliminary assessment of the resulting picture, and then a neurosurgeon or vascular specialist studies the results.
Spinal tap
A procedure that rarely brings pleasant sensations, but is safe if the sample is taken by an experienced doctor. It is carried out in case of suspected presence of an abscess or tumor; it helps to determine the composition of the CSF. After taking the puncture, the contents are subjected to detailed examination.
In what cases is EEG prescribed?
After a conversation with the patient and studying the medical history, the specialist decides to prescribe encephalography. Typically, indications for an EEG are frequent headaches, sleep problems, fainting, fatigue and chronic fatigue.
Deterioration in well-being may be a sign of disorders in the functioning of the brain. The above ailments often arise due to:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head;
- inflammatory processes in meningitis and encephalitis;
- endocrine disorders;
- malignant or benign neoplasms.
For patients suffering from epilepsy who have undergone neurosurgical interventions and head injuries, EEG monitoring is mandatory.
How to prepare for an electroencephalograph examination?
Monitoring the electrical activity of the brain does not require complex training. During the examination, it is important to simply follow the doctor's instructions and remain calm. Flashes of light and noise are part of the procedure.
Three days before the examination, it is recommended to stop taking tranquilizers, anticonvulsants and sedatives. 24 hours before the examination, do not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, or eat chocolate. The day before monitoring, wash your hair. Have a snack an hour before the examination. Before starting, loosen your hair and remove metal jewelry.
Preparing for magnetic resonance imaging
Examination of the pelvic organs (organs of the female reproductive system, prostate gland, bladder) requires the following measures:
- the procedure is carried out with a full bladder: you should not urinate for several hours, and an hour before the scan you should drink half a liter of clean water;
- It is recommended to cleanse the intestines with an enema or laxatives;
- half an hour before the study, it is advisable for the patient to take an antispasmodic drug (“No-spa”);
- women of childbearing age indicate the day of the menstrual cycle.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal organs is performed on an empty stomach or after a light snack if the procedure is scheduled for daytime or evening hours. A few days before diagnosis, you should exclude from your usual diet foods and dishes that contribute to increased gas formation. These include legumes, whole milk, and sweets. Also avoid foods that cause constipation (flour, rice, chocolate). It is advisable to take enzymes and sorbents (activated carbon) during this period. On the eve of the study, the patient is recommended to take an antispasmodic.
Examination of other parts of the body does not require special preparation. Immediately before scanning, you must remove keys and other metal items from your pockets and remove jewelry.
How is an EEG performed?
The examination takes place in several stages.
Preparatory stage
- the patient enters the office, protected from light and sound;
- an encephalograph “cap” consisting of special sensors is put on it;
- The sensor wires are connected to a device that records the bioelectric impulses of the brain.
Diagnostic stage
- the encephalograph transmits data to the monitor in the form of a graph;
- the power of electric fields and its distribution in different parts of the brain are recorded;
- Functional tests are carried out: the patient is asked to blink, look at flashes of light, breathe less often or deeper, listen to a sharp sound.
Final stage
- the electrodes are removed from the patient;
- print out the results.
How long does the electroencephalogram procedure take?
A regular encephalogram (routine EEG or diagnosis of a paroxysmal state) takes from 20 to 30 minutes.
During the examination, a number of tests are carried out:
- rhythmic photostimulation;
- hyperventilation;
- load in the form of slow blinking.
If it is necessary to evaluate certain brain functions, the specialist adds additional tests, which he informs the patient about in advance. Such tests include:
- clenching your fingers into a fist;
- being in the dark;
- sleep deprivation for a certain period;
- night sleep monitoring.
Interpretation of survey results
Even a qualified specialist is not always able to accurately name the cause of the patient’s poor health and immediately make a diagnosis. The doctor may be alerted to focal changes on the EEG. In this case, magnetic resonance imaging will be required to exclude a tumor or cyst.
When you contact a medical doctor, you will be able to undergo all examinations as quickly as possible, without delaying your visit to specialists.
If you need to do an EEG of the brain and you want to do it using modern expert-class equipment and in the shortest possible time, call the phone number listed on the website or leave a request in the feedback form.
Medical staff will answer your questions and conduct all necessary examinations within one business day. Let's take care of your health together!
How to do a Check-up for complaints of headaches
The Check-up examination program includes the following procedures:
- daily observation;
- MRI of the brain and one part of the spine;
- duplex/triplex scanning of extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries;
- radiography of one part of the spine with functional tests;
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring;
- electroencephalography;
- ECG;
- blood test for 10 indicators and urine test.
Consultations are carried out by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist. During the final conversation, the patient is introduced to the detailed results of the examination and is given a medical report with recommendations for prevention or treatment. If necessary, additional examinations are prescribed.
| CheckUp Headache program | ||||
| The program includes: | ||||
| B01.023.001 | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a neurologist | 2000 | 1 | 2000 |
| В01.023.002 | Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a neurologist | 1500 | 1 | 1500 |
| B01.029.001 | Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an ophthalmologist | 2000 | 1 | 2000 |
| A05.23.009 | Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain | 5760 | 1 | 5760 |
| A05.03.002 | Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine (one section) | 5760 | 1 | 5760 |
| A04.12.005.005 | Duplex/triplex scanning of extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries | 3000 | 1 | 3000 |
| A06.03.019 | X-ray of the spine with functional tests (one section) | 2000 | 1 | 2000 |
| А02.12.002.001 | 24-hour blood pressure monitoring | 3500 | 1 | 3500 |
| A05.23.001 | Electroencephalography | 2000 | 1 | 2000 |
| А11.12.009 | Taking blood from a peripheral vein | 250 | 1 | 250 |
| B03.016.002 | General (clinical) blood test (hemoglobin, leukocytes, platelets, erythrocytes) | 320 | 1 | 320 |
| A09.05.010 | Study of the level of total protein in the blood | 190 | 1 | 190 |
| A09.05.042 | Study of the level of alanine transaminase (ALT) in the blood | 190 | 1 | 190 |
| A09.05.041 | Study of the level of aspartate transaminase (AST) in the blood | 190 | 1 | 190 |
| A09.05.022.003 | Study of the level of total, free and bound bilirubin in the blood | 380 | 1 | 380 |
| A09.05.020 | Blood creatinine level test | 190 | 1 | 190 |
| A09.05.017 | Blood urea level test | 190 | 1 | 190 |
| A09.05.023 | Blood glucose test | 220 | 1 | 220 |
| A05.10.006.1 | Registration, interpretation, description and interpretation of electrocardiographic data (ECG) | 1000 | 1 | 1000 |
| B03.016.006 | General (clinical) urine analysis | 285 | 1 | 285 |
| TOTAL: | 38175 | |||