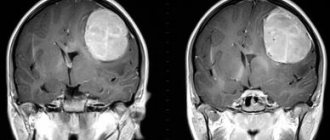
The study of intracranial (intracranial) structures presents certain difficulties, which is associated with the structural features of the human body. Using magnetic resonance imaging, doctors can assess the condition of the brain without invasive manipulation.
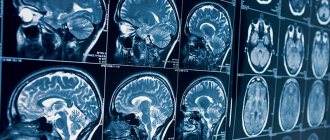
A series of slice-by-slice images of a child's brain
Many parents are interested in the age at which an MRI can be done. This type of instrumental diagnostics does not carry ionizing radiation load. and is safe for the patient's health.
The basis of the research is the phenomenon of magnetic resonance, when hydrogen atoms in water molecules undergo vibrational movements under the influence of a force field. The change in the position of charged particles is recorded using sensitive instruments, the information is processed and converted into layer-by-layer images. For a detailed study of the state of brain structures, specialists adjust the minimum thickness of the scanned section (from 1 mm).
In the diagnosis of oncological and vascular diseases of the brain, contrast-enhanced MRI is often used. The child is given an intravenous injection of a “coloring” solution. The drug is eliminated from the body within 24-72 hours.
At what age are MRIs performed on children?
Magnetic resonance of charged particles does not affect the child’s health, therefore MRI diagnostics of brain diseases is one of the most popular ways to determine cerebral pathologies.
At what age can children have an MRI? The study is prescribed from the second month of the child’s life, but there are certain features of the procedure.
The patient needs to maintain a motionless body position for a sufficiently long time. Movements contribute to the appearance of artifacts in the photo and reduce the information content of the scan.
Since babies cannot lie for a long time without moving, general anesthesia is used. For children under 5 years of age and with increased excitability of the nervous system, the study is carried out under anesthesia, in a hospital setting. The baby is being observed by an anesthesiologist.
At an early age, MRI under general anesthesia is performed when alternative diagnostic methods (ultrasound, EEG, etc.) are insufficiently informative.
Hydrocephalus on MRI images
After 5 years of age, children can have an MRI scan at any diagnostic center. If desired, one of the parents can be present at the procedure. No special conditions are required for native research. Contrast tomography for children under 12 years of age is performed in a hospital. Intravenous administration of the drug and the nuances associated with this manipulation make it necessary for the child to remain under supervision. Adolescents are examined with an intensifier in all diagnostic clinics that have the appropriate license.
MRI of the brain in children under anesthesia: pros and cons
If anesthesia is unavoidable, the specialist on duty – an anesthesiologist – will take into account all the characteristics of the child’s health and illness, and his possible reaction to sedatives. Based on this data, the appropriate drug will be selected.
Advantages of anesthesia during tomography
- ensuring a static body position;
- the ability to conduct diagnostics for children of any age with various diagnoses, even in the presence of abnormal mental states in which it is impossible to control movements;
- absence of stress and fear of unfamiliar surroundings and extraneous noises.
Cons of anesthesia
The main disadvantage of sedatives for both adults and children is the likelihood of allergies. This is only possible if the drug is not selected correctly. Experienced specialists rarely make such mistakes.
What does an MRI show in children?
Magnetic resonance diagnostics reflects the structural features of the CNS (central nervous system). Photos visualize:
- white and gray matter;
- bark;
- membranes of the brain.
Tomograms allow you to see the area of the sella turcica, study the pituitary gland, and assess the condition of the surrounding tissues.
Contrast MRI reflects the nature of the blood supply to cerebral structures and shows pathological changes in intracranial vessels.
In the diagnosis of oncological processes, the ability of neoplasms to accumulate soluble gadolinium salts (chelates) is used. The contrast procedure visualizes intracranial tumors with a diameter of 3 mm.
When performing an MRI of the brain in children, one can see disorders associated with inflammatory, degenerative-dystrophic, and neoplastic changes in cerebral structures. Based on the scan results, the following are diagnosed:
- disorders of cerebral blood supply;
- ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes;
- encephalopathy;
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- parasitic lesions;
- delayed consequences of head injuries;
- multiple sclerosis;
- congenital anomalies;
- brain abscesses;
- inflammation of the cranial nerves;
- possible consequences of poisoning;
- pituitary diseases;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
Among the cerebrovascular pathologies diagnosed using MRI are:
- thrombosis of intracranial vessels;
- stenosis of veins and arteries;
- violation of the integrity of the vascular wall;
- aneurysms of the brachiocephalic arteries;
- vasculitis;
- embolism;
- pathological bends of veins and arteries;
- cavernomas;
- arteriovenous malformations, etc.
Magnetic resonance imaging is more informative regarding ischemic changes in the brain. Hemorrhages appear on MRI images after a few hours.
Abscesses, hematomas, cysts with serous and purulent exudate are determined on layer-by-layer images in the form of clearly defined rounded lesions. The liquid contents of the formations provide an intense signal during resonance research.
Brain cyst (indicated by arrows) with different MRI scanning modes
Malignant tumors have a convoluted network of blood vessels and accumulate contrast solution more slowly. MRI signs of malignancy of the formation are:
- lack of a clear contour of the pathological focus;
- the weakly intense signal of the affected area at the beginning of the scan intensifies as contrast accumulates;
- signs of perifocal edema.
MRI of the brain is done in children to clarify the size and location of the pathological area. Tomograms show changes in the structure of cerebral structures, features of the interaction between affected and healthy tissue. The method is informative regarding the visualization of demyelinating processes.
Contraindications for performing an MRI of the child’s brain
Prohibitions on research can be absolute or relative. The first include medical electronic devices implanted into the human body. These are heart pacemakers and cochlear devices. The presence of a foreign body made of metal in the orbit and metal clamps on the vessels (the magnetic field can move them, which will lead to intracranial bleeding, which is life-threatening). Contrast tomography is not used for patients with hematopoietic anemia and those who suffer from renal failure and severe liver pathologies. In them, removing the contrast agent from the body with urine is difficult and can lead to intoxication.
Relative limitations will be a panic reaction to closed spaces (claustrophobia), metal braces and prostheses, intense pain syndrome that makes it difficult to maintain a calm body position, diseases that require regular monitoring of vital parameters.
Because young patients have low body weight, they are not subject to weight restrictions. Choose specialized centers for research.
MRI of the brain for children - indications
Magnetic resonance imaging helps diagnose central nervous system pathologies in the early stages.
Indications for MRI in children are:
- delayed mental and physical development;
- recurring headaches (cephalgia);
- nausea, vomiting for no apparent reason;
- dizziness, fainting;
- signs of stroke;
- transient ischemic attacks;
- progressive increase in skull size;
- speech disorders;
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity in the absence of eye pathologies;
- hearing impairment;
- congenital and acquired anomalies of the development of the skull and cerebral structures;
- decreased coordination, vestibular disorders;
- convulsions;
- motility disorders.
The method is used if the development of a cerebral tumor is suspected. For skull injuries, scanning is prescribed in a delayed period if there are signs of impairment of the functionality of the central nervous system.
MRI of the brain is done in children before surgery. With the help of the study, the size and location of the pathologically changed area is clarified, and the volume and nature of the upcoming operation are predicted.
Signs of encephalopathy on MRI images
During the rehabilitation period, scanning is prescribed to monitor recovery processes and diagnose complications.
How to prepare for a child's brain MRI?
Preparing a small patient for screening involves a preliminary conversation about the upcoming procedure. The baby must know everything that will happen to him. This will reduce his fear and anxiety and allow him to remain still and calm. It is important to convey that there will be no pain, that the parents will be there.
If stain enhancement is planned, food and fluid intake should be limited before brain MRI. The baby does not need to be fed for 2-6 hours. Before the session, be sure to visit the toilet. Before starting an MRI, make sure that there are no metal objects on the baby’s body and check the pockets.
How is an MRI of a child's brain performed?
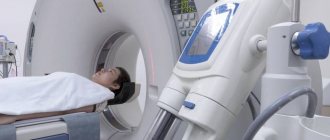
The study is done using a tomograph consisting of a mobile table and a wide tunnel. To improve scanning quality, additional gradient magnetic coils are used that create an alternating force field. The data is converted into a series of layered images by a complex computer program.
The child lies face up on the tomograph table. If contrast enhancement is necessary, an intravenous catheter connected to an automatic injector is installed. The head and body are fixed with special fasteners and bolsters, and headphones are worn to protect against noise.
The doctor and x-ray technicians are in the next room; one of the parents can stay with the child. Communication with the subject is maintained through an intercom.
MRI of a child's brain
The table with the patient is rolled into the tomograph tube. Scanning occurs in the axial, sagittal and frontal planes. The doctor studies the photo and, if necessary, reconstructs a 3D model of the brain.
Contrast MRI involves a break in scanning. After a series of native images, the child is injected with a gadolinium solution. As the “staining” preparation fills the vascular bed in the area of interest, the study continues.
MRI of the child’s brain is performed both on tunnel tomographs and on open devices. The latter are characterized by weak power, so photographs do not always allow a detailed study of the state of cerebral structures.
When is an MRI of a child’s brain required and what does it show?
There are a large number of cases when a child cannot do without an MRI of the brain. Any pathological condition is a signal for a detailed examination. Thus, the most common complaints with which people turn to scanning are:
- systematically occurring pain in the head;
- dizziness, “unreasonable” fainting;
- unjustified decrease in visual or auditory function;
- muscle tension, cramps;
- mental retardation of the child;
- post-traumatic condition, when there were bruises, hematomas, fractures, penetrating head wounds;
- patient complaints of persistent or recurring tinnitus;
- changes in gait, loss of coordination and sense of the surrounding space;
- progressive deficits in attentiveness and decline in memory levels;
- intellectual delay or degradation of previously acquired knowledge and skills;
- complaints of tingling in the limbs, numbness, loss of sensitivity.
MRI of the brain effectively shows changes in the organ such as:
- development of epileptic syndrome;
- violation of the integrity of the vascular network, internal hemorrhages;
- changing the configuration of vascular channels;
- sclerotic manifestations;
- pituitary disorders;
- hypoxia (insufficient oxygen “nutrition”);
- cysts and tumor formations of various nature.
If the treating doctor suspects cancer, an MRI is performed with contrast enhancement. This allows you not only to see the boundaries and size of the anomaly, but also the degree of its growth into adjacent structures, the presence of cancerous processes (metastases) and their migration to neighboring areas.
How to prepare a child for an MRI?
It is necessary to tell the child how the procedure goes and how long it takes. Being in a confined space and noise during the examination can frighten the child, so it is better to warn in advance about the peculiarities of the scan.
Before an MRI of the brain, doctors recommend maintaining a sleep schedule and avoiding stressful situations. An excited state, nervousness, and fear can negatively affect the reliability of the research results. It is advisable to avoid the use of tonic drinks; compotes, water, and juices are suitable to quench thirst.
An hour before an MRI with contrast, the child needs to have a snack. This will help avoid nausea and dizziness.
If you experience severe pain, claustrophobia, or increased nervousness, you can discuss taking analgesic and sedative medications with your doctor. Self-administration of medications is prohibited. If you have concomitant diseases, you must notify the specialist about available appointments.
Before scanning, jewelry and metal accessories are removed; it is advisable to dress the child in a comfortable home suit or pajamas that do not restrict movement.
MRI is not performed if:
- metal non-removable medical structures in the area of interest;
- implanted electromagnetic devices;
- tattoos made with metal-containing inks (in teenagers).
Contrast scanning is prohibited for severe liver and kidney diseases. Possible contraindications should be reported to your doctor.
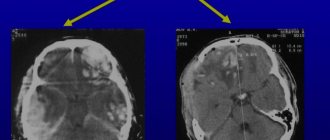
Brain tumor on MRI in a child
Most clinics in St. Petersburg provide free telephone consultations, where specialists will tell you how to properly prepare a child for an MRI. Following the recommendations will help increase the efficiency of the diagnostic procedure.
Does a child need anesthesia for an MRI of the brain?
Due to age characteristics, during an MRI session, a general immersion of the child into sedative sleep is used. Before reaching the age of five, children find it difficult to control their movements and remain motionless for a long time. In order not to reduce the results of the study to zero, short-acting mild anesthetics are used, which are indicated even for infants.
The patient receives a limited amount of anesthetic through an intravenous injection or through a breathing mask. The entire time the baby is under anesthesia, his condition is monitored by an experienced pediatric anesthesiologist. If, during the history taking, an allergy to sedatives is revealed, the doctor decides to resort to another method of examination. From 5-7 years of age, the use of anesthesia is usually no longer required. But a lot depends on the mental characteristics of the child; the decision on medical immersion is always made on an individual basis.
Who prescribes a brain MRI for a child?
Signs of central nervous system diseases in childhood are a reason to consult a doctor. If necessary, the specialist will prescribe an MRI of the child’s brain.
A referral for testing can be obtained upon initial visit to the hospital and in case of low information content of other diagnostic methods. MRI of the brain in pediatrics is prescribed:
- neurologists;
- neurosurgeons;
- endocrinologists;
- oncologists;
- ophthalmologists;
- otolaryngologists.
More often than not, the child is recommended to see several specialists before the scan, which helps clarify the expected diagnosis.
Are there any contraindications to MRI of the brain in a child?
A separate procedure is absolutely safe, but there are external factors that can interfere with screening:
The presence of built-in ferromagnetic elements in the form of implants and electronic stimulators. Any metallic element inside the body should be reported to the radiologist (including braces in the oral cavity).- MRI of the brain with staining is not performed in cases of allergies or renal failure.
- The patient has a strong fear of closed spaces.
- Intolerable pain syndrome that makes it difficult to remain motionless for a long time.
- Mental disorders in a child with contraindications to the administration of anesthesia.
If factors have been identified that do not allow you to resort to tomography, the doctor will select an alternative method, or will refer you for a scan using open-configuration equipment.
How often can an MRI of the brain be done?
MRI examination allows diagnosing all kinds of neurological diseases that are difficult to diagnose using alternative methods.
Magnetic resonance examination of the brain is prescribed in the following situations:
- Neoplasms and their metastases.
- Epilepsy.
- Suspicion of cystic cavities.
- The presence of parasites that have entered the head through the bloodstream.
- Meningitis, encephalitis.
- Rehabilitation after stroke, traumatic brain injury.
- Development of multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, etc.
This diagnostic method does not carry any radiation exposure, so an MRI of the head can be done as many times as necessary to make an accurate diagnosis.
The mechanism of performing MRI of the brain in children
Children's scanning is carried out in the same way as for adults. When the baby is ready, he and his parents or close relative enter the room with the scanner. He is placed on a mobile table, and the diagnostician shows the correct position of the body. To make a high-quality MRI of a child’s brain, his torso is fixed and pushed into the ring of the device. The accompanying people leave, the doctor starts the tomograph. The procedure will last about half an hour. Its duration is determined by the readings and condition of the scanned person.
If enhancement is necessary, the drug will be painlessly administered before the examination. Thanks to it, the visualization of the desired areas will become better. The operating scanner is very noisy, so the patient will be given headphones.
Diagnostic results will be ready within an hour. This is a disk with photographs and a description for them prepared by a radiologist. You don’t have to wait for them and ask them to be sent to you by email. For a child, an examination is stressful; it is better not to subject him to unnecessary expectations.
Remember: no matter what the data from the tomograph is, maintain composure.
Take the pictures to your doctor. He will plan further actions: prescribe therapy or send for further examination. Sometimes he can recommend another professional if his competence in the treatment issue is not enough.
When the case is difficult, you have the right to show the results to other specialists whose opinion is important to you.