General information
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive and most common malignant brain pathology.
This is a very dangerous disease. From the moment the patient first develops symptoms of the disease, if untreated, the person lives for about three months. By providing complex treatment (surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy ), the life of such a patient can be extended by 1-2 years. Currently, scientists are actively working to more accurately determine brain glioma - what it is, and what are the causes of this terrible disease.
So far, experts believe that the tumor develops due to malfunctions in the functioning of brain cells. This pathology is quite rare. According to statistics, per 100 thousand patients with oncological pathologies, glioblastoma is diagnosed in only one case.
Characteristics of headaches
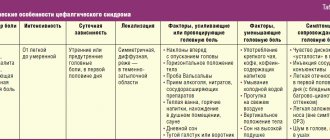
This symptom of glioblastoma belongs to the category of the early and most common signs of the pathology in question. According to statistics, 50% of patients suffer from temporal and frontal pain. Such discomfort is characterized by persistence, increased intensity, and the possibility of intensification after physical exercise. exertion, sneezing and coughing. The pain remains even after taking painkillers.
The pain may be worse in the morning due to fluid accumulation in the brain tissue. Glioblastoma is characterized by a high rate of progression, which is why the harmful effects of toxic components on the brain are very pronounced. Due to the damage, the vessels cease to cope with the function of blood outflow.
Pathogenesis
Gliomas are any malignant brain tumors that form glial cells . When malignant transformation occurs, glial cells, namely astrocytes , become less differentiated, losing the characteristics of functional mature cells. In addition, their connection with neighboring cells is lost, and division becomes uncontrolled.
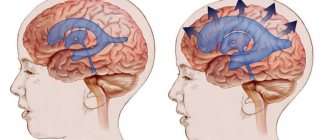
Thus, glioblastoma consists of poorly differentiated astrocytes, it has foci of necrosis and areas of vascular proliferation. A characteristic feature of this formation is a random arrangement of cells, polymorphism of cell nuclei and extensive perifocal edema. The tumor grows rapidly and invades the brain tissue. It is impossible to trace clear boundaries of the affected area. The neoplasm does not metastasize beyond the nervous system.
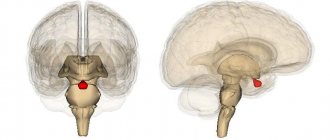
It is most often found in the frontal and temporal lobes. Very rarely, a tumor forms in the brain stem, spinal cord, or cerebellum.
In some cases, glioblastoma develops from anaplastic and low-grade astrocytomas, but most often this lesion is primary.
The tumor spreads to neuroglial cells, whose functions are related to the nutrition and protection of neurons. These cells do not reproduce in adulthood, but there are precursors of glial cells in the brain. If disturbances occur in their development, glioblastoma may develop.
A characteristic feature of glioblastoma, which determines its aggressive course, is its heterogeneity. The nature of the neoplasm differs in different patients. Moreover, even in one patient, the tumor can contain different cells that are not genetically similar, with different mutations. During the treatment process, cells mutate, actively evolve and develop new methods of survival.
Characteristic signs of glioblastoma
During the research, scientists noted that a significantly lower risk of developing glioma – by 40% – is observed in people suffering from various types of allergies . Experts explain this by the fact that in such people the immune system is in an activated state and prevents tumor growth.
Treatment methods
The main method of treating glioblastoma formed in the brain is complete or partial resection of the affected tissue. Depending on the location of the tumor and other clinical features, a classic operation is performed or stereotactic surgery methods (Gamma Knife) are used.
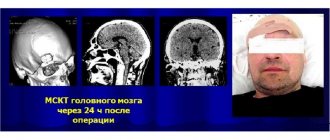
After surgery, a follow-up examination (usually an MRI or CT scan with contrast) is usually carried out within 24 hours to determine the results of surgical treatment. Frequent complications after surgical treatment include hemorrhages in the tumor area, tissue swelling, and an increase in neurological deficit.
The postoperative therapy program is developed taking into account the Karnovsky index. Treatment methods for glioblastoma with a Karnofsky index greater than 60% for patients under 70 years of age include chemotherapy, fractionated radiation therapy, and exposure to an alternating electric field.
Patients over 70 years of age with a Karnofsky index greater than 60% and an active MGMT gene are prescribed hypofractionated radiation therapy, then chemotherapy in combination with fractionated radiation therapy and exposure to an alternating electric field. Treatment of glioblastoma with a Karnofsky index less than 60%:
- Fractionated radiation therapy (indicated for patients under 70 years of age).
- Radiation therapy is hypofractionated.
- Chemotherapy (with confirmed MGMT gene activity).
- Supportive, symptomatic treatment.
Fractionated radiation therapy is performed using a linear accelerator. The number of sessions is usually 10-35. Typically, procedures are performed after complete or partial resection of the tumor. Hypofractionated radiation therapy involves exposing cancer cells to high doses of radiation, thereby reducing the number of sessions (usually 1-5). Hypofractionated therapy is effective against all types of cancer cells.
After treatment, a control MRI examination is carried out once every 2-4 months over the next 2-3 years.
The use of an alternating electric field for zonal suppression of tumor cell division is widely practiced in leading clinics in Germany, Japan and Israel when treating cancer patients. This therapy slows down or stops the process of cancer cell division. The effect after exposure is comparable to the results of chemotherapy.
Unlike chemotherapy, electric field treatment is safe for healthy cells, which are larger in size than cancer cells and therefore are not destroyed. The technique allows you to avoid undesirable consequences that often occur during chemotherapy - resistance to pharmaceutical drugs, accumulation of toxic substances. It is possible to repeat several courses in a row, which means a higher likelihood of recovery.
Targeted therapy using biological products is aimed at increasing the body's own defenses. Special drugs affect tumor cells at the molecular level. Targeted drugs differ from conventional cytostatics in their selective action. They inhibit the development of tumor cells without affecting the renewal of healthy tissue, which significantly reduces the number and severity of side effects after treatment.
Classification
The following types of tumors are identified:
- Multiform . Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common and most dangerous type of tumor. The lesion is well supplied with blood, and vascular necrosis develops very quickly.
- Giant cell . This variety is different in that the cells have not one nucleus, but several.
- Gliosarcoma . This is a tumor with a sarcomatous component.
It is important to conduct an accurate diagnosis and clearly determine the type of formation. This will make it possible to choose the most optimal treatment.
Primary and secondary types of the disease are also distinguished.
- Primary – develops very quickly, over about three months. This type is more common in older men.
- Secondary - is the result of the degeneration of benign formations. This type of disease most often develops in women after 45 years of age.
There are other, less aggressive types of brain tumors.
Four degrees of the disease are determined:
- The first is that there are no signs of malignancy, but the tumor covers new cells. There is a possibility of recovery.
- Secondly, there are already signs of glioma, the tumor is still growing quite slowly. The chances of recovery are reduced.
- Third, brain tissue is involved in the process, the tumor grows quickly and is malignant. Complete recovery occurs in rare cases.
- Fourth, the tumor grows very quickly, the symptoms are very severe. The tumor is inoperable, the prognosis is unfavorable.
The main stages of manifestation of glioblastoma
Oligodendroglioma is a glial neoplasm of the brain that develops from oligodendrocytes. This tumor grows slowly but can grow to a large size. It forms along the walls of the ventricles, grows into their cavity, as well as into the cortex. The disease lasts a long time, sometimes longer than five years. The tumor is removed surgically.
A variety of such neoplasms are:
- oligodendroglioma (has a second degree of malignancy);
- anaplastic oligodendroglioma (has a third degree of malignancy);
- mixed oligoastrocytoma (has a third degree of malignancy), later degenerates into glioblastoma .
Another type of glial tumor is optic nerve glioma .
This neoplasm develops from the glial elements of the optic nerve. It is treated with radiation or surgery.
Principles of glioblastoma treatment
Glioblastoma of the left frontal lobe before surgery
Depending on the type and size of the tumor, the neurosurgeon selects an individual treatment regimen. There is a direct relationship between the timeliness of surgery and the life expectancy of patients with glioblastomas.
Many brain tumors can be removed minimally invasively. The high professionalism of the neurosurgeon makes it possible to perform surgical interventions without opening the skull, which are highly effective and have a low probability of dangerous complications. Neurosurgery for glioblastoma is the first and most important stage of treatment.
Features of the operation
Surgery is performed with the aim of removing the maximum number of malignant cells, significantly reducing signs of intracranial hypertension and neurological deficit. Most often, microsurgical resection using intraoperative fluorescence navigation is used for glioblastomas.
A few hours before surgery, the patient must drink a special solution that causes the accumulation of protoporphyrin specifically in the cells of the malignant tumor. This makes it easier to visualize glioblastoma and makes its contours clearer. As a result, the efficiency of the neurosurgeon, who additionally uses special lighting during the operation, increases.
This innovative method is used relatively recently. Previously, due to the vague contours of glioblastoma, its complete removal was impossible. Due to the high risk of damaging functional areas of the brain, the tumor was only partially removed, which led to frequent relapses.
It is possible to perform a craniotomy - removal of a malignant lesion on the open brain using local anesthesia. Such operations should be performed by experienced and first-class specialists who have some practical experience in modern neurosurgery. With the impressive size of glioblastoma and its destruction of the functional structures of the brain, it is possible to perform partial resection of the malignant focus. This allows you to eliminate significant trauma to healthy tissues that are compressed by the tumor and reduce the severity of existing focal symptoms.
Modern neurosurgery today makes it possible to effectively treat glioblastoma and increase the life expectancy of patients, preserving most of the functions of the brain. After surgery, radiotherapy is performed to prevent relapses of the disease.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is sometimes given to reduce the size of the tumor before surgery. After removal of the glioblastoma, the patient also undergoes radiation treatment. For glioblastoma, it is used mainly after surgery to destroy the remaining tumor tissue. For inoperable tumors, the method replaces surgery.
Radiation therapy involves several sessions. The use of modern techniques can significantly reduce the risk of possible complications such as nausea, vomiting, severe weakness, and swelling of brain tissue.
Chemotherapy
The dosage of chemotherapy drugs is selected individually, taking into account the age and general health of the patient. Chemotherapy is an auxiliary method of treating glioblastoma; it complements and increases the effectiveness of surgery.
But most often they combine chemotherapy and radiation treatment methods, which are used after removal of the pathological focus. Chemotherapy improves the prognosis of the disease and increases life expectancy.
Where to treat glioblastoma
Treatment of glioblastoma requires a highly qualified neurosurgeon, the availability of certain equipment and drugs. It is important to take a responsible approach to choosing a medical center. Most often, patients are sent for treatment of glioblastoma to Moscow, to the Burdenko Institute of Neurosurgery, or Medsi. Here, brain tumor removal and further rehabilitation can be performed.
But the recovery period continues during the first year, and during this time the patient must regularly visit a neurosurgeon. After removal of glioblastoma in Burdenko, certain diagnostic procedures will be prescribed that will assess the patient’s health status, detect even minor deviations from the norm and determine the effectiveness of surgical treatment.
Symptomatic therapy
Symptomatic therapy for glioblastoma can improve the patient’s quality of life, prepare him for surgery, and eliminate unpleasant manifestations of the disease. It is important to follow all the neurosurgeon’s instructions exactly; if your health worsens and additional symptoms appear, be sure to tell the doctor about these changes.
To improve the patient’s overall well-being and reduce the risk of complications, symptomatic treatment is carried out using the following groups of drugs:
- analgesics, narcotic painkillers;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antiemetics;
- anticonvulsants;
- sedatives, antidepressants.
Do not exceed the recommended dosage of prescribed medications. Any changes in the treatment regimen for glioblastoma should be monitored by the attending physician.
Causes
Experts still do not know why glioblastoma develops. The likelihood of developing this disease increases with radiation exposure and congenital mutations. However, scientists have not yet determined a clear dependence on these factors. It is noted that the disease is not inherited, and its development is not associated with smoking, exposure to electromagnetic radiation, or poor nutrition - this has been confirmed in the process of scientific research.
However, risk factors that to varying degrees provoke the development of a tumor are:
- age over 50 years;
- male gender;
- nationality – residents of Asia, Europe, Latin America;
- the presence of genetic pathologies that increase the likelihood of developing gliomas - Turcotte syndrome , tuberous sclerosis , neurofibromatosis , etc.;
- undergoing radiotherapy;
- benign astrocytoma .
There is also an opinion that the development of this disease is increased by certain viruses: human herpes cytomegalovirus , polyomavirus .
Symptoms of glioblastoma
At the initial stage of the disease, there are practically no symptoms, so it is difficult to diagnose it in the early period. Pronounced signs are observed when the tumor has already grown significantly and puts pressure on the brain. The first manifestations of glioblastoma are common dizziness and memory impairment. In some cases, the fingertips become permanently numb.
As the disease progresses, cerebral and neurological manifestations develop.
The development of cerebral symptoms is associated with increased intracranial pressure and progression of intoxication. These are the following manifestations:
- Severe headaches that become more intense when the person lies down.
- Constant feeling of dizziness.
- Nausea that has nothing to do with eating; vomiting, after which there is no relief.
- Constant weakness, drowsiness, severe fatigue.
- Deterioration of mental abilities, lethargy.
- Depression , apathy , irritability.
The manifestation of neurological symptoms depends on the location of the tumor. The following signs may be observed:
- Cramps.
- Impaired vision, hearing, speech, smell.
- Decreased sensitivity or paralysis of the limbs.
- Auditory and tactile hallucinations
- Movement coordination disorder.
- Respiratory depression.
Since neurological symptoms are similar to those of a stroke , this may be the reason for an incorrect diagnosis.
Unfortunately, in the later stages, when these symptoms appear, it is no longer possible to cure the patient. Doctors can only prolong his life.
Symptoms of oligodendroglioma also depend on its location. In all types of oligodendroglioma, intracranial pressure increases. Other symptoms similar to the manifestations of glioblastoma described above also develop.
Tests and diagnostics
Development can be detected in the early stages if a person regularly attends preventive examinations and examinations. In this case, you can take timely measures at the first sign of a threat. It is very important to visit a neurologist and neurologist who can identify the disease.
If there is a suspicion of glioblastoma, a medical history, examination, and laboratory tests are performed.
Next, the doctor prescribes appropriate examinations. The patient may be prescribed the following examinations:
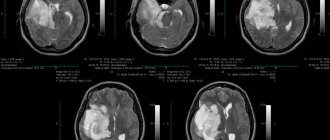
- computed tomography - makes it possible to obtain a high-quality image of the structures of the central nervous system;
- magnetic resonance imaging – using an intense magnetic field, you can obtain a clear image of the structures of the central nervous system;
- functional MRI – allows you to obtain broader information about the tumor, blood flow, tissues;
- biopsy - in the process of selecting material, taking biomaterial;
- MR spectroscopy – allows you to obtain information about metabolism in the brain;
- lumbar puncture - a sample of cerebrospinal fluid is taken;
- PET, SPECT - these studies make it possible to determine the functional activity of brain tissue;
- electroencephalography – carried out to study brain activity.
Diagnostics
The main tasks of diagnosis are to determine the exact localization of the neoplasm, its size, and the degree of proliferation into surrounding structures. Diagnostic examination is carried out mainly using instrumental methods:
- MRI and CT.
- MR perfusion, MR spectroscopy.
- Positron emission tomography.
- A diagnostic operation during which part of the tumor is removed for histological examination of the sample.
- Open (through an incision) or stereotactic (performed using computer navigation) biopsy.
During the instrumental examination, the tumor and the tissues located next to it are visualized in detail, allowing the neurosurgeon to choose the optimal tactics for surgical treatment. In parallel, laboratory analyzes of physiological materials are carried out - histological typing of a tissue sample, immunohistochemical study, analysis of MGMT gene activity (in some types of cancer the gene is switched off), molecular test.
MGMT gene activity is considered a favorable factor in determining life expectancy in patients with glioblastoma detected in the brain. With correct therapy in patients with an active gene, in 10% of cases there are no relapses of the disease within 5 years. For pediatric patients, this figure increases to 25%.
Treatment with folk remedies
In the case of glioblastoma, traditional methods can only be additional treatments aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms. If you replace the traditional treatment regimen with folk remedies, a quick death is inevitable.
- Radish compress – grate the radish and add salt. When the juice begins to stand out, rub the mixture on your head and wrap it with a towel. The course lasts three weeks.
- Soda solution - dissolve 3 g of soda in 100 g of water and drink this solution. Gradually increase the amount of soda to 5 g.
- Chamomile tea - it is prepared from dried chamomile flowers (15 g of raw material per glass of boiling water). Drink instead of tea.
Prevention
The most effective method of prevention is regular attendance at preventive examinations, which make it possible to identify problems at an early stage. It is especially important to undergo annual examinations for people over 45 years of age, because with age the likelihood of this dangerous disease increases.
To reduce the risk of developing this disease, you must follow the recommendations regarding a healthy lifestyle:
- Get a full night's rest - healthy sleep and its sufficient duration are important.
- Spend time outdoors – you need to walk as much as possible every day.
- Avoid stress and emotional turmoil.
- Give up bad habits - do not smoke, do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol.
- Do not abuse spending time with various gadgets.
- Eat right - lots of vegetables, fruits and grains, be sure to have legumes, high-quality proteins, and unsaturated fats. Harmful foods - fast food, smoked meats, soda, confectionery, etc. - must be excluded.
Diet for glioblastoma
Diet for cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery or lifelong
- Groceries cost: 2500 - 4800 per week
With this disease, the patient needs to eat more fat and less carbohydrates. This diet is called a ketogenic diet. Its essence is that the tumor receives less energy for its growth. People are allowed to consume more protein and fatty foods than on a regular diet.
But for now, scientists are studying the mechanism of action of such a diet in malignant brain tumors.
At the same time, it is important to consume foods that will help cleanse the body, strengthen the immune system , improve blood counts and give the body additional strength.
But in general, the following nutritional rules are relevant for oncology:
- Do not make too drastic changes in your usual diet.
- Make adjustments to your diet gradually.
- Monitor how the body reacts to certain foods.
- Do not eat food that you absolutely do not like.
- Do not practice low-calorie diets.
- Try to eat food that does not contain artificial additives and preservatives.
- Be sure to include vegetables, fruits, dairy, legumes, vegetable fats, grains, seafood, green tea, and nuts in your diet.
But in general, it is important that the diet is healthy and does not contain harmful foods and dishes.
Forecast
Survival and life expectancy in this disease directly depend on the type of glioblastoma, its location, and the general condition of the patient.
If proper treatment is not given, only about 10% of people survive more than three months after diagnosis.
With the most aggressive form of the disease - glioblastoma multiforme - even with a competent approach to therapy, a person rarely lives more than one year. However, the likelihood of a favorable prognosis largely depends on the completeness of tumor resection and on some tumor biomarkers.
Complete recovery, provided proper treatment, is possible only with grade 1 or 2 glioblastoma. Treatment will require a very large number of different procedures, and the likelihood of relapse with a fatal outcome will remain.
Glioblastoma grade 4 is most often inoperable. To increase life expectancy, doctors prescribe drug therapy and special procedures. Patients with this pathology are most frightened by the question of how they die from glioblastoma of the brain. Having learned about the diagnosis, a person is frightened by the thought of dying from this malignant disease in severe pain. In such a situation, doctors prescribe painkillers and other medications to alleviate the person’s condition.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The exact causes of glioblastoma and similar tumors in the brain have not been established. The leading role of hereditary factors in the development of pathology has not been confirmed. No more than 5-10% of cases are associated with hereditary predisposition. According to some doctors, the appearance of glioblastoma correlates with alcoholism. Other causes:
- Past viral infections (herpes virus, polyomavirus, cytomegalovirus).
- Past malaria.
- Ionizing radiation (rare).
- Chronic intoxication with harmful chemicals (including salts and vapors of heavy metals).
Malignant tumors of the primary form account for 2% of the total mass of oncological diseases. Scientists identify risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing a malignant neoplasm of neuroepithelial etiology. Among them:
- Male gender.
- Age 40-60 years.
- Diagnosed astrocytoma of I, II degree of malignancy.
- Genetic mutations.
- Diagnosis of neurofibromatosis (about 15% of cases).
Statistics show that people of the white race are more susceptible to pathology. In order to never personally find out how people die from glioblastoma, it is worth paying attention to the first signs of pathology.
List of sources
- A.P. Romodanov, N.M. Mosiychuk. Neurosurgery. - Kyiv: Vyshcha School, 1990. - P. 16. - 105 p.
- Zemskaya A.G. Glioblastoma multiforme of the brain. - L: Medicine, 1976.-S. 192.
- Pishel Y.V. Glioblastomas of the brain. (Pathomorphology, clinical picture, diagnostics, comparative assessment of treatment methods): Abstract of thesis. dis. . Dr. med. Sci. - Kharkov, 1971. P. 32.
- Savchenko A.Yu. Brain gliomas. Omsk: Publishing house. Omsk State Pedagogical University, 1997. - P. 312.
- Fadeev B.P., Zhabina PM Combined treatment of glial and metastatic brain tumors // Bulletin of Surgery named after. I.I. Grenova. - 2005. - No. 1. — P. 80-82.
Diagnosis: types of tumor
If signs of dysfunction of the central nervous system appear, the disease should be diagnosed. There are certain symptoms that are an indicator to see a doctor:
- dizziness, drowsiness. Severe dizziness is associated with intracranial hypertension, compression of the cerebellum, vestibular nerve;
- headache. It is permanent and progressive. The headache is especially severe after sleep and in a horizontal position of the body;
- vomiting and nausea are associated with increased intracranial pressure and irritation of the vomiting center of the brain;
- lack of coordination;
- sensitivity disorder.
- memory and speech impairment. Characteristic for the frontal location of the tumor;
- decreased vision and hearing;
- autonomic disorders - breathing problems, heartbeat and others.
In most cases, a brain tumor does not make itself felt in the early stages of development; symptoms appear when the tumor presses on the brain, the tumor enlarges, resulting in various disorders. Diagnosis of a brain tumor is carried out using the following methods:
- examination by a neurologist;
- magnetic resonance imaging with intravenous contrast. Blood circulation in tumor vessels is studied when planning surgery;
- computed tomography;
- positron emission tomography with methionine;
- biopsy of a brain tumor for histological examination in cases where it is possible.
Contrasting the tumor not only allows it to be clearly seen during diagnosis, but also helps the surgeon when removing it.
According to histological characteristics, glioblastoma of the brain is represented by the following types of tumors:
From the editor: Symptoms, course, treatment and prevention of taiga encephalitis
- glioblastoma multiforme;
- giant cell glioblastoma;
- gliosarcoma of the brain.
Glioblastoma multiforme consists of various types of atypical cells, the tumor is riddled with blood vessels, has many hemorrhages, and is of the highest malignancy. Gliosarcoma contains a mixture of glial and mesenchymal cells and is characterized by bidermality. Glioblastoma of the brain varies according to the location of the tumor: most often it is located in the temples and forehead.