Brain meningioma is a common type of tumor of benign origin, less often of malignant origin. It is characterized by slow growth, but with timely treatment it has a good prognosis. Treatment tactics depend on the location and structure of the tumor, and how strongly neighboring structures are involved. Basically, surgical removal of meningioma allows for complete cure and minimizes the risk of relapse. If the tumor degenerates into malignant, metastases may appear, which significantly worsens the prognosis for treatment and life. What is brain meningioma, what are its causes and symptoms, and what treatment can a doctor prescribe?
Briefly about the disease
Despite the fact that meningioma is classified as brain cancer, this tumor does not affect the nerve tissue itself, but forms on the surface of the hard shell. It has some features that distinguish it from other neoplasms - a protrusion on the head in the form of a bump and a change in the shape of the skull. The tumor most often affects the cranial cavity, but can also be on the surface or affect deep structures of the brain. Depending on the location of the neoplasia, the clinical picture, prognosis and choice of therapy are determined.
In almost 95% of patients, meningiomas have a benign course and only in 5% of cases degenerate into malignant cancer. They belong to primary tumors that form from the meninges. The disease is more often diagnosed in women, less often in men. In general, the formation grows slowly, does not have pronounced symptoms and can be diagnosed accidentally during a scheduled or unscheduled examination. The size of the formation can range from a few millimeters to nodes 15 cm in diameter.
In 2% of cases, multiple meningiomas are diagnosed, which complicates treatment and worsens treatment prognosis. The cause of this condition is most often late diagnosis, when cancer cells have metastasized to neighboring brain tissue.
According to its structure, meningioma is divided into:
- typical - a benign tumor that does not pose a particular danger to human life, has a slow growth, and can be treated with surgery.
- atypical - the formation is prone to rapid growth and relapse, but with timely diagnosis and treatment it has a good prognosis for recovery.
- atypical - a malignant tumor, rare, characterized by rapid growth, capable of destroying and spreading to healthy cells, has an unfavorable prognosis.
Brain meningioma in the international classification of diseases is classified under ICD 10 code – D32.0. Morphologically, it has clear limitations and looks like a spherical node fused with the dura mater of the brain. The formation may have several foci of growth. Most often it is diagnosed in the cerebral hemispheres, occipital lobe, temporal areas, and wings of the sphenoid bone.
Treatment of brain meningioma is successfully carried out in Moscow at the Burdenko Oncology Center. At the clinic you can undergo a comprehensive examination and receive consultation from neurosurgeons. Only advanced technologies and effective techniques are used to treat cancer tumors.
Types of tumors
Neoplasms that form in the brain can be:
- Benign – tumor tissue does not contain cancer cells. Neoplasia of this type is characterized by clear edges and slow growth. They are much easier to treat surgically, but can become malignant, that is, turn into cancer;
- Malignant tumors contain abnormal cells that can divide uncontrollably and metastasize to other organs. In this case, the disease is difficult to control; in the later stages, surgery is impossible. Treatment in this case is difficult, has a high cost and, as a rule, poor prognosis.
Brain glioma
Glioma
This type of tumor is diagnosed more often, accounting for approximately 60% of all types of cancer that form in the brain. The tumor is formed from glial cells. In most cases, this is a primary neoplasm, most often formed in the area of the chiasmata or ventricles, but it can also affect the brain stem; pathogenesis rarely extends to the bones of the skull, however, in rare cases this is possible. The size of gliomas is usually up to 14 cm. Metastases are rare, growth is usually slow, but due to penetration into adjacent tissues, the boundaries of the lesion are difficult to distinguish.
Three varieties are known
- astrocytoma – diagnosed more often than others (it accounts for about 50% of gliomas);
- oligodendroglioma – up to 10% of cases;
- ependymoma – less than 7%.
According to the World Health Organization classification, there are 4 stages of glioma:
- The first stage is benign. It is characterized by slow growth. Example: giant cell astrocytoma.
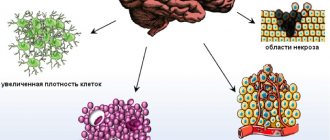
- Second stage. Features: borderline malignancy with slow tissue growth, easily progresses to stages 3 and 4. In this case, only one symptom of cancer is identified - cellular atypia.
- Third and fourth stage. In this case, the tumor has all the signs of cancer, for example, necrotic changes in glioblastoma multiforme.
Brain astrocytoma
Removal of a large GRADE II WHO astrocytoma of the right temporal lobe (before surgery)
This malignant neoplasm of varying degrees of aggressiveness is diagnosed quite often. The beginning is given by degenerated glial cells - astrocytes (hence the name - astrocytoma). There are:
- Common astrocytomas: protoplasmic, fibrillary and hemisrocytic.
- Special astrocytomas: cerebellar, piloid, microcystic and subependymal.
Astrocytomas are distinguished by the stage of malignancy:
- The first stage (benign tumor) includes piloid or pilocytic astrocytoma of the brain.
- Second stage of malignancy: fibrillary tumor is also an ordinary neoplasia, second degree of malignancy.
- The third stage is already cancer. It includes anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain.
- The most life-threatening are glioblastomas (giant cell glioblastoma and gliosarcoma), which are classified as stage 4 and are characterized by rapid growth and the ability to metastasize.
In addition to the ones mentioned, there are other types of astrocytomas, for example, ependymoma (develops from ventricular cells), oligodendroglioma (forebrain) - grow quite slowly without the formation of metastases, and glioma of the brain stem.
Meningioma of the brain
Removal of a large middle cranial fossa meningioma before surgery
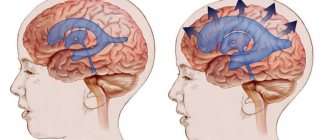
Pathogenesis begins with pathogenic cells in the superficial membrane that surround the brain tissue. The neoplasm is oval in shape, grows slowly, and is therefore considered benign. Meningiomas are diagnosed in 15% of cases (of all brain tumors). The risk of degeneration into cancer is about 3-4%. The clinical signs that appear are caused by increased intracranial pressure and tissue compression. With malignancy (degeneration of somatic cells into carcinogenic ones), meningiomas become aggressive. Usually more than one lesion forms and may spread to the spinal cord. After surgical treatment, there is a high probability of relapses. As a rule, pathology is diagnosed by chance, because symptoms appear only when the lesion reaches a large size. There are no early signs of the disease.
Note. Meningiomas often form in females.
Other types of brain tumors
There are quite a lot of types of neoplasms. Here are some of those that are diagnosed relatively often (besides those mentioned above):
- medulloblastoma is a brain cancer that originates from the structures of the cerebellum;
- germinoma - formed from germ cells, most often it is detected in the first half of a person’s life;
- Craniopharyngeoma - develops in the pituitary gland at the base of the brain;
- Shawnoma – formed from degenerated Schwann cells;
- tumors in the pineal gland area.
Causes of brain meningioma
The exact causes of meningioma are not known, but the following factors may be a trigger for the development of the tumor:
- age after 40 years;
- hormonal imbalance;
- long-term use of contraceptives;
- irradiation;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- heredity;
- neuroinfections.
People working in hazardous enterprises are at risk. Secondary causes of the disease include other oncological processes occurring in the body. Multiple clinical studies have shown that genetic factors, or more precisely a defect in chromosome 22, which is located near the gene for neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF 2), will play an important role in the formation of the disease.
Symptoms
The danger of all cancers, including brain meningioma, is hidden in the absence of symptoms in the early stages. Some initial signs of the disease do not cause concern in a person, since they can manifest themselves in the form of a minor headache and increased fatigue. Severe symptoms are observed in the presence of a large formation or compression of nearby brain structures by the tumor. They are divided into two categories:
- General cerebral signs - develop due to circulatory disorders in the brain or tumor pressure on soft tissues. The patient has dizziness, nausea, vomiting, memory deteriorates, and frequent mood swings.
- Local signs are expressed in impaired mobility of the limbs, decreased visual and auditory function.
A characteristic and perhaps the first sign of the disease is a headache, which can be bursting, dull or aching. It appears in the area of the back of the head, forehead or temples. A headache can bother a person periodically or bother a person constantly.
Brain meningioma is accompanied by a number of symptoms that significantly worsen the patient’s general condition:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- paresis of limbs;
- decreased visual acuity, double vision;
- loss of charm;
- hallucinations;
- epileptic seizures;
- impaired coordination and gait;
- nausea, vomiting.
Similar symptoms may be present in other types of brain tumors, so if any sign appears, do not hesitate to visit a doctor. The sooner a person consults a doctor, the greater the chance of a successful recovery.
The clinic of meningioma at the location of the tumor can give its own characteristic symptoms:
- wings of the sphenoid bone – epileptic seizures;
- cranial fossa – decreased vision, charisma, mental instability;
- frontal lobe – impaired memory and concentration, mental disorders, increased irritability;
- cerebellum – unsteady gait, paresis of limbs, convulsions;
- temporal lobe – tremor of the upper and lower extremities, speech impairment.
All symptoms intensify as the tumor grows and surrounding tissues are damaged. Pathology can only be recognized based on the results of a comprehensive examination.
All of the above signs may be present in other types of brain cancer, so to make a diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and undergo hardware diagnostics. The results of the examination will help confirm or exclude the diagnosis.
Diagnostics
If brain cancer is suspected, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes:
- Electroencephalogram - assesses the functioning of the brain.
- Angiography - reveals the intensity of the blood supply to the cancer tumor. Prescribed before surgery to remove a tumor.
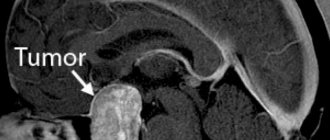
- MRI is an informative examination method that allows you to accurately determine the location and size of a tumor.
- CT scan – visualizes the brain, determines the location and size of the tumor.
- Biopsy - determines the nature of the formation.
To obtain a complete clinical picture, laboratory tests of urine and blood are prescribed. The results often reveal the cause of the disease. After undergoing a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor, based on the results obtained, has the opportunity to obtain a complete picture of the disease, make a final diagnosis, and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Diagnosis of a brain tumor
The first is a neurological examination to assess the general condition of the nervous system (checking reflexes, nerve sensitivity, muscle tone, etc.). Visual acuity, visual fields, and ophthalmoscopy must be assessed - tumors of the pituitary gland or occipital region can lead to vision problems, and increased intracranial pressure affects the fundus.
An electroencephalogram is used to assess the electrical activity of the brain - on the electroencephalogram, displacement of the midline of the brain by the tumor can be observed if it is large. Echo-EG can detect increased intracranial pressure and ventricular deformation.
The main method is MRI. For accurate diagnosis, MRI with contrast can be used to visualize blood vessels - there is an increased number of vessels in the area of the tumor. MR spectroscopy (to detect metabolic disorders in the brain) may also be used.
The best non-invasive method for making a diagnosis is positron emission tomography (PET). It makes it possible to identify the degree of the malignant process, the exact location and level of blood supply to the tumor. Single-photon emission computed tomography is an effective hardware diagnostic method that allows you to determine the type of tumor and its location by visualizing a 3D image.
In some situations, with difficult-to-reach localization or multiple lesions, stereotactic tumor biopsy is used to determine treatment tactics. During surgery, tumor tissue is collected for histological examination. Histology allows us to determine the type of tumor and the degree of malignancy.
Surgical removal of brain meningioma
The choice of therapy for brain meningioma depends on the location of the tumor, its size, as well as the age of the patient and the characteristics of his body. If the tumor grows slowly, there are no severe symptoms and no signs of compression of surrounding tissues, the doctor may limit itself to observation, since sometimes removing a meningioma can cause more harm than good. Indications for surgery are:
- rapid growth in education;
- suspicion of malignancy;
- symptoms in the form of visual impairment, headache, paralysis.
Contraindications to surgery may include advanced age, tumors in hard-to-reach places, severe chronic diseases of internal organs and systems.
In the neurosurgical practice of doctors, when benign meningioma is diagnosed, surgical treatment predominates. During the operation, it is important to remove not only the tumor itself, but also its tissues that are located nearby. In practice, microsurgical or endoscopic techniques are most often used, which allow the tumor to be removed with maximum precision.
The choice of surgery to remove the tumor depends on its location. The technique of surgical treatment may differ; it can be performed by opening the skull or using a transsphenoidal approach (through the nose). If the formation is on the surface, then complete excision is performed. However, most often the tumor is located near important areas of the brain, then only part of the tumor is removed. The prognosis in this case is less favorable; there is a possibility that in the near future the formation will begin to grow again. Removal of meningioma is always carried out with an opening of the skull, which significantly increases the risk of complications and the recovery period, which can last from several weeks to several months.
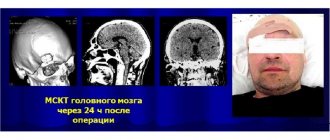
After the operation, 3 months later, the person must undergo a follow-up examination - MRI. The results will help assess the general state of brain function and exclude the emergence of new foci of the disease. It is recommended to undergo a repeated examination after a year. When a tumor is partially removed, control is carried out much more often, since there is always a possibility of growth of the tumor or its degeneration into malignant cancer.
Radiosurgery, which consists of exposing tumor cells to ionizing radiation, is considered effective in the fight against cancerous tumors. It is performed if it is impossible to perform surgery or if the tumor is located in hard-to-reach areas of the brain.
If the meningioma has a malignant course or the operation failed to completely remove the tumor, the doctor will prescribe radiation therapy. The procedure allows you to influence cancer cells and promote their death. Radiation therapy is quite popular in the treatment of brain cancer, but has many contraindications and side effects.
Recently, meningiomas have increasingly been removed using stereotactic radiosurgery. It involves irradiating cancerous tissue from different angles without affecting healthy brain structures. This technique is effective if the tumor size does not exceed 3.5 cm in diameter, and self-formation is located near vital brain structures.
For benign tumors, chemotherapy is not prescribed. However, to relieve general symptoms, the doctor may prescribe pharmaceutical drugs from different pharmacological groups: analgesics, immunostimulants, antispasmodics, vitamin therapy and others. Rehabilitation of patients is also considered an important stage, which can take up to 6 months. The recovery period consists of following a diet and a healthy lifestyle. In the postoperative period, it is important to exclude fatty and smoked foods, fast food, and also give up smoking and any alcohol. For complete recovery, the doctor may prescribe acupuncture, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and other procedures that will help speed up recovery and reduce the risk of tumor regrowth.
Medis Clinic organizes as soon as possible:
- Diagnostics according to the protocol accepted in the world;
- Hospitalization in a modern hospital equipped with everything necessary;
- Help from the best doctors in treating brain tumors;
- Surgery for brain cancer at the highest level;
- Comfortable living conditions and quality care;
- Competent rehabilitation programs;
- Post-operative observation and further treatment program;
- Support at all stages and resolution of all emerging issues.
Surgery for brain cancer begins with diagnosis; first you will have a consultation with a neurosurgeon and a comprehensive examination. The price of treatment for a brain tumor will depend on the characteristics of the disease and the class of the selected surgeon.
Treatment of brain meningioma
The Burdenko Neurosurgery Center offers a range of services for the diagnosis and treatment of brain meningioma of any location and complexity. Removal of meningioma in the center is carried out using microsurgical instruments and an operating microscope under general anesthesia. If necessary, the clinic’s doctors perform cranioplasty, which allows you to hide skull defects after surgery. Neurosurgeons at the Burdenko Clinic use the latest technologies and programs for the treatment of brain cancer that meet international standards. Prices for treatment are developed individually; they are established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation. At the clinic you can apply for a quota for free treatment, but to do this you need to collect a whole package of documents and get a decision from the medical board.
Types of tumor removal surgery
If there is a tumor in the brain, its radical removal is required. Because of this, surgical intervention becomes traumatic and often impossible. Especially if vital parts are located near the tumor.
But even with maximum excision of the tumor body, the surgeon must carry out the procedure without touching healthy tissue.
Methods for removing brain tumors:
- craniotomy;
- endoscopy;
- stereotactic trepanation;
- excision of individual skull bones.
Craniotomy
Craniotomy or craniotomy is an operation in which surgical access to the working area is formed directly on the skull, creating an opening.
When creating direct access for instruments, the specialist removes part of the bone tissue along with the periosteum.
Trepanation is a classic technique. The total duration of the procedure is from 2 to 4 hours.
Upon completion of the operation, the hole in the skull is closed with the previously removed bone fragment and fixed with titanium plates and screws.
ATTENTION! Particularly dangerous are craniotomy operations involving access to the base of the skull, the part of the skull that supports the lower parts of the brain.
You may be interested in learning more - Craniotomy - a surgical intervention necessary to access brain tissue
Endoscopy
Endoscopic trephination is performed using an endoscope inserted into the skull through a small hole.
It is equipped with micro-optical equipment that sends images to a monitor and allows you to monitor the progress of the operation.
Upon completion of the basic manipulations on the brain, the removed tissues are removed from the skull using a micropump or electric tweezers.
Stereotactic trepanation
Excision of the tumor by stereotactic surgery does not require open intervention.
Instead of the usual surgical scalpel, a beam of gamma radiation, photons or protons is used. This light beam of radiation destroys the tumor.
The method is widely used for brain cancer.
ATTENTION! Stereotactic surgery is painless and does not require anesthesia.
Excision of individual skull bones
The operation is a type of craniotomy.
During surgery, some bones of the skull are removed to provide access to the tumor.
But upon completion of the manipulations, the bone flap is not returned to its place, but is removed forever.
Complications
Surgery to remove meningioma is a complex procedure, so complications cannot be ruled out even with careful planning and proper execution. Common complications include bleeding from tumor vessels and surrounding tissues, which can lead to necrosis and cerebral ischemia. In the postoperative period, neurological disorders sometimes appear:
- paresis and paralysis.
- decreased sensitivity in the limbs;
- decreased visual acuity and hearing;
- mental disorders.
- meningitis.
After the operation, the patient remains in the clinic for several weeks under medical supervision. At risk for developing complications are the elderly, as well as those who have a history of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, suffer from diabetes or are obese.
Prognosis and prevention of brain tumors
Small benign tumors that are accessible for surgical treatment have a favorable prognosis. However, many of them tend to relapse. This requires repeat surgery or radiation therapy.
Tumors of a malignant nature, hard-to-reach localization, large size and metastatic nature have an unfavorable prognosis, since they cannot be completely removed. Old age and the presence of concomitant pathologies (heart failure, chronic renal failure, diabetes mellitus, etc.) complicate surgical treatment.
Forecast for life
If meningioma is of benign origin, and the tumor is diagnosed in time and appropriate treatment is carried out, then the prognosis for recovery is favorable. A person has the opportunity to return to their usual way of life. With a malignant neoplasm, there is a high risk of metastases, which increases mortality in the first 2 years of life. In 3% of cases, a benign tumor develops anew after treatment. The secondary appearance of the tumor is most often present in the cavernous sinus and wings of the sphenoid bone. It is important to understand that even a small formation can negatively affect a person’s well-being, especially if it is located in important parts of the brain, compresses blood vessels or disrupts blood flow. The prognosis for life without surgery in 60% of patients is unfavorable, but in such cases the doctor selects alternative treatment methods that will help improve the patient’s quality of life.
In order to detect meningiomas in time, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor if you have frequent headaches. Timely diagnosis and correct treatment will help preserve life and health. With brain meningioma, it is difficult to predict the prognosis, but if the tumor is benign, in almost 100% of cases there is a complete recovery.
There are no special preventive measures to prevent meningioma, but a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and quitting smoking and alcohol will help reduce the risk of pathology. Perhaps the main preventative measure is to periodically visit a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination at least once a year.
If a person has undergone treatment for meningioma, he must be observed by a neurologist for a long time, undergo prescribed examinations and strictly follow all medical instructions.