Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a research method in the field of neurology that makes it possible to induce depolarization or hyperpolarization in brain neurons. This technique is widely used in the Yusupov Hospital and makes it possible to study the excitability of cortical neurons, the interaction of different parts of the brain with each other, and the localization of functions in the cerebral cortex.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain: reviews
Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain in Moscow is a relatively new and very promising direction in medicine. Using this method, it is possible to map different cortical representations, which in itself is extremely important for understanding the functional organization of the human brain, as well as the mechanisms of its control.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain makes it possible to accurately determine the boundaries of the location of various brain functions, for example, the cortical representation of visual analyzers, speech centers, and memory.
Reviews of transcranial magnetic stimulation among doctors in Moscow and other Russian cities are positive, since the procedure allows the development of new approaches to the rehabilitation of patients with neurological diseases.
The procedure is very accurate, informative, effective and painless. The technique allows many people to get rid of serious diseases.
Mechanism of treatment with transcranial electrical stimulation
The therapeutic therapeutic effect of TES therapy is based on the ability to stimulate endorphin production processes in the human brain. During the procedure, the most sensitive and anti-pain structures in the brain are activated due to the ability of currents to penetrate soft tissue and bone.
Under the influence of transcranial currents, the production of endorphins is activated, they begin to concentrate in the blood, brain and cerebrospinal fluid. The hormone endorphin is capable of normalizing various disorders in the human body, while maintaining the natural course of normal processes without interfering with them. In addition, due to the increased production of endorphins, the patient has no pain during the procedure, which is explained by the ability of the hormone to relieve pain.
Content:
- Mechanism of treatment with transcranial electrical stimulation
- Main indications and contraindications of the technique
- Technique of TES therapy
- Equipment for transcranial electrical stimulation
The antidepressant effect of transcranial electrical stimulation is achieved by stabilizing the patient’s psychoneurological state, which also leads to a positive anti-stress effect, normalizes the patient’s sleep, improves his mood and increases his performance. This physiotherapeutic technique accelerates the healing of the skin and mucous membranes in the body, helps the regeneration processes of peripheral nerve fibers and liver parenchyma cells. TES therapy stimulates the immune system, slows down the growth processes of various (including malignant) tumors, and normalizes the physiological status in the human body.
The effect of the transcranial electrical stimulation procedure can be maintained in the body for several days, which gradually allows you to train the defense system. Thus, this technique trains the brain to actively produce endorphins on its own, and no addiction occurs during the procedure.
Transcranial electrical stimulation can be combined with therapeutic techniques such as:
- physiotherapy;
- balneological treatment;
- manual therapy;
- treatment with medications.
You cannot combine TES therapy with reflexology and morphine-like analgesics. The use of this technique systematically helps to reduce the consumption of pharmaceuticals, including hormonal agents, analgesics, and antidepressants with immunomodulators. According to the latest research, transcranial electrical stimulation is highly effective in treating all kinds of neurological pathologies, reducing their symptoms by 90%.
Cyclic transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain
The technique is indicated for children with pathologies such as autism, encephalopathy with delayed speech development, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The complex of transcranial magnetic stimulation and drug therapy helps improve speech, it becomes clearer, vocabulary increases, and children’s cognitive interest increases. Patients leave positive reviews about the effectiveness of the procedure.
At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists use transcranial magnetic stimulation to treat complex diseases in adult patients aged 18+.
TMS has proven effective in treating depression, schizophrenia, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Effects
Transcranial brain stimulation has a wide range of therapeutic effects. This:
restoration of a full psycho-emotional status: improvement of mood, normalization of sleep, fight against depression and depression (data have now been obtained on the positive effect of TES therapy for clinical depression);- relief of pathological craving for alcohol and drugs;
- improvement of microcirculation, blood flow in the vessels of the brain, supply of tissues with oxygen and nutrients;
- normalization of blood pressure;
- stimulation of the immune system;
- improvement of tissue regeneration;
- restoration of liver detoxification function, regulation of metabolism;
- inhibition of inflammatory processes.
Rhythmic transcranial magnetic stimulation
Rhythmic transcranial magnetic stimulation is a proven effective method for treating a number of diseases of the nervous system, successfully used in the Yusupov Hospital.
The technique is used in the treatment of the following pathologies:
- post-stroke pain syndrome;
- Parkinson's disease stage 3;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- migraine;
- neuropathic pain;
- multiple sclerosis;
- spinal injury;
- tinnitus and others.
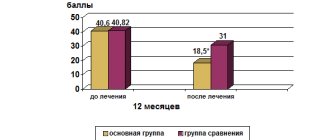
The clinical effect is observed after 10 therapy sessions, for depression - after 20. Experienced neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital, in combination with transcranial magnetic stimulation, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, can also prescribe medication and physical therapy.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
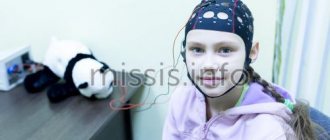
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive, painless and absolutely safe technique that is currently actively used for the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of neurological diseases. For diagnostic purposes, it is used to record evoked potentials of the brain (visual, auditory, or somatosensory), and allows one to reliably determine the presence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and functional disorders in muscle function. Using appropriate recording electrodes, you can assess not only the condition of the muscle as a whole, but also its individual components.
The TMS method allows you to analyze not only the work of muscles, but also the state of peripheral nerves, spinal cord roots, and even the direct motor cells of the spinal cord itself. For example: you can estimate the speed of impulse passage along the nerve from the brain to the very motor point of the muscle, and the method allows you to differentiate the motor and sensory fibers of the nerve.
In addition to diagnostic use, TMS is used for painless stimulation of almost any muscle in our body (including the pelvic organs) and the treatment of a wide range of neurological and mental diseases. Due to its effectiveness and safety, the TCS method is used not only in Russia, but also in the USA, France, Germany, Austria, Israel and a number of other developed countries.
Modern TCS devices, such as Neuro MS\D, are capable of performing stimulation both at the level of the brain (this is where its name “transcranial” comes from) and at the level of the peripheral nervous system. Treatment is aimed primarily at changing the functional state of nerve structures.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation: technical principles
Unlike electrical stimulation, magnetic nerve stimulation is carried out not by an electrical discharge, but by using an inductor coil that creates an alternating magnetic field. The coil is placed directly over the desired area of the brain (brain or spinal cord) or over the area of the peripheral nervous system that needs to be stimulated.
Stimulation is performed with both single and rhythmic magnetic pulses.
Using an electromagnetic coil instead of electrical electrodes not only makes the procedure completely painless, but also allows you to stimulate almost any nerve in the brain, spinal cord or peripheral system.
The magnetic field induced by the coil can have either an inhibitory or excitatory effect on the muscle. Depending on the goal, the stimulation frequency can vary from 1 Hz to 100 Hz.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation: performing the procedure
HEALTH TESTS On Line
- Before performing magnetic stimulation, it is necessary to determine the motor response threshold (the minimum magnetic field strength for the appearance of a motor response). This threshold can vary significantly from person to person.
- A stimulation point or zone is then selected.
- After selecting the stimulation zone, the doctor selects the appropriate program for the patient and the procedure begins. During the procedure, the doctor controls the time and pattern of movement of the corresponding muscles.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation: areas of application
DIAGNOSTICS
- study of motor response to magnetic stimulation of peripheral nerves;
- determination of the speed of impulse transmission (diagnosis of nerve sheath disorders);
- assessment of the excitability of motor cells in the brain;
- determination of radicular delay time (radiculopathy) - F-wave study;
- diagnosis of the causes of hearing or vision impairment;
- stimulation of the phrenic nerve to determine the response of the diaphragm.
TREATMENT - INDICATIONS
- lesions of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- vascular and vertebrogenic pathologies, urinary incontinence;
- neuropathy, demyelinating disorders of the peripheral nervous system,
- spinocerebellar degenerations, pain syndrome, radiculopathy, migraine;
- atrophy of the optic and auditory nerves of various etiologies;
- depression, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Benefits of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
- Painlessness and comfort during the procedure. Stimulation procedures are usually carried out in courses of 4-5 procedures per week. Unlike electrical stimulation, when performing magnetic stimulation there is no pain from electrical discharges, this is especially noticeable when the patient’s motor response threshold is high.
- Reliable confirmation of the presence of radicular syndrome.
- Safety. The strength of the magnet of the stimulation device does not exceed the induction of most MRI devices, and with proper control of the motor response of the muscles, the procedures are absolutely safe for the patient.
- The ability to innervate almost any muscle deep in the body, including the pelvic muscles and directly the motor cells of the spinal cord.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation: contraindications to its implementation
The method is not possible if the patient is suspected of having a cerebral aneurysm, has a pacemaker, or is pregnant. When diagnosing epilepsy, the method should be used with extreme caution, since transcranial brain stimulation can trigger the development of an attack.
Medicine does not stand still; scientific research is carried out every day, thanks to which new effective methods for treating many diseases emerge.
The Yusupov Hospital is equipped with modern medical equipment that allows the latest proven diagnostic and treatment methods to be applied in practice.
The hospital staff includes leading Russian doctors who are ready 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to provide patients with high-quality medical care that meets European standards. You can make an appointment at the hospital by phone.
Content:
- Transcranial therapy: what is the principle of the technique based on. 1.1. Transcranial neurostimulation: main advantages.
- Indications for transcranial electrical stimulation.
- Effects provided.
- Transcranial brain stimulation: contraindications.
- How does a TES therapy session work?
Transcranial brain stimulation has long been widely used in neurology for the treatment, rehabilitation and maintenance of quality of life in Parkinson's disease, mental disorders, after a stroke, and neuroinfections. Due to its high efficiency, safety and complex action, TES therapy is also successfully practiced in narcology to combat alcohol and drug addiction. At the same time, this physiotherapy procedure not only eliminates the craving for alcohol or psychoactive substances - the body is completely healed, cleansed and restored.
Transcranial brain stimulation: contraindications
Before starting a course of TES therapy, the narcologist at the Ugodie clinic carefully collects anamnesis and, if necessary, prescribes additional laboratory tests to exclude possible contraindications. These include:
oncological neoplasms;- epilepsy, complications of neuroinfections and other diseases accompanied by convulsive syndrome;
- severe form of hypertension;
- rehabilitation period after ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- violations of the secretory function of the thyroid gland.
A relative contraindication is damage to the skin in the area where the electrodes are attached. The physiotherapy procedure should be postponed until the wounds have completely healed.