The causes of Parkinson's disease are those factors that influence the occurrence and development of this disease throughout human life. Typically, this disease is chronic; as the pathology develops, permanent degenerative changes occur in the body as a result of the death of brain cells.
The reasons why these processes occur have not been fully studied to this day. Medicine at this stage can only talk about those factors that directly or indirectly influence the development of Parkinson's disease. They are considered to be the causes of this disease. In order to more accurately begin to talk about what provokes parkinsonism in a particular case, it is necessary to understand the basis of the pathology and how it affects the processes in the human brain.
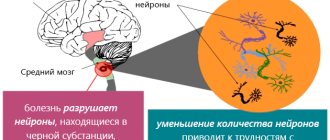
Death and damage to dopaminergic cells
Content:
- Death and damage to dopaminergic cells
- Heredity in parkinsonism
- Genetic predisposition
- Brain injury
- Brain diseases
- The presence of harmful and lack of beneficial substances
- Spiritual reasons
Typically, the pathology manifests itself in the fact that in the midbrain the composition of the black substance begins to actively change. This substance in its normal state contains cells capable of producing the substance dopamine. Dopamine is necessary for the connection of nerve processes or neurons of the substantia nigra with the striatum of the brain. With a lack of dopamine, a disturbance in the coordination of movements occurs, motor ability decreases, all this progresses until the person completely loses his ability to work and independence. The synthesis of dopamine decreases, and as a result, the neurotransmitter function with which a person coordinates his own movements decreases.
When dopaminergic cells in the brain are damaged or killed, dopamine production drops sharply, which leads to a lack of interaction between the substantia nigra and the striatum in the human brain. When 80% of dopaminergic cells are lost, symptoms of Parkinson's disease begin to appear. As their synthesis in the body decreases, the disease progresses to more complex stages.
Experts still cannot accurately answer the question about the causes of damage and death of nerve cells that provoke parkinsonism. According to experts at the University of Cambridge, genetic mutations that undermine the natural process of rejecting defective mitochondria may be to blame for this process. As you know, mitochondria act as a kind of battery for the cell, destroying and creating energy for them. If defective mitochondria are detected, they need to be eliminated. However, there are defects in the genetic code of Parkinson's disease that interfere with the process of repairing mitochondrial defects. This study suggests that if patients are given medications to remove unnecessary mitochondria during therapy, the development of parkinsonism can be prevented.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment strategies for Parkinson's disease depend on the stage at which the patient begins receiving the necessary therapy. For this reason, neurologists prefer to separate therapeutic approaches aimed at relieving early and late symptoms.
Treatment in the early stages involves the use of medications that stimulate the synthesis of dopamine in the brain. The therapeutic effect is achieved by stimulating dopamine releases and blocking reuptake. Thanks to this, it is possible to reduce the rate of neuronal death. Basic drugs can be used as part of complex treatment or as monotherapy. The combination of necessary substances is selected by a neurologist based on the clinical picture of parkinsonism and the individual characteristics of the patients.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in the later stages remains an inevitable stage, since drug therapy can only slow down destructive processes. Progressive pathology is complemented by new symptoms that are difficult to relieve. At a certain point, the usual effectiveness of medications decreases. The patient experiences hypersensitivity of dopamine receptors and a kind of withdrawal syndrome due to the body's resistance to substances taken for a long time.
Against this background, doctors are forced to prescribe constantly increasing doses of medications to patients by reducing the intervals between doses. An alternative solution is to switch to a combination treatment regimen, which uses drugs from several groups. In some cases, surgery may be possible to implant an electrode into the patient that provides deep brain stimulation. This method allows you to stop resting tremor and restore motor activity in people suffering from Parkinson's disease.
Heredity in parkinsonism
According to many studies, it has been found that Parkinson's disease also has a hereditary cause. If you carefully study your family history, you can identify signs of a gene mutation, although scientists have not yet been able to identify the gene itself. The inheritance pattern of this disease has also not been identified to date, so heredity is still only an assumption in the theory of the development of Parkinson's disease.
It is believed that the most likely type of inheritance of parkinsonism is autosomal dominant. This type suggests that in each generation the manifestation of Parkinson's disease will be noticeable. However, the likelihood of an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance is also high. He says that the disease is inherited through several generations. Men are more often affected by this disease. In order to determine a more accurate mode of inheritance, many tests were carried out, as a result of which experts began to doubt the hereditary factor in the occurrence of the disease in principle. Based on the results of the research, it turned out that only in 5% of cases of Parkinson’s disease there is a related predisposition to the disease.
Causes of Parkinson's disease
To date, a complete list of the causes of Parkinson's disease has not been fully identified. However, we can mention some factors that could trigger the development of this disease. Among them: aging, ecology (external environmental factors), heredity. There are cases when parkinsonism occurs as a result of a person having certain diseases.
Causes of Parkinson's disease:
- physiological old age of the body, in which case there is a natural decrease in the number of neurons that are responsible for the production of the neurotransmitter domafin;
- heredity;
- long-term residence near highways, operating enterprises or near railways;
- vitamin D deficiency, obtained from exposure to ultraviolet rays on our body, and also protects the structural cells of our brain from destruction;
- poisoning of the body with chemicals (for example, ethanol, carbon monoxide, technical alcohol, etc.);
- previous neuroinfections (for example, encephalitis);
- tumors and frequent brain injuries.
Our clinic has opened a treatment room for Parkinson's disease and extrapyramidal disorders.
Extrapyramidal disorders are diseases characterized by movement disorders. They can be either primary (occurring independently) or a consequence of other diseases.
Extrapyramidal diseases include diseases such as:
- Trembling of hands, head;
- Violent movements in the limbs and torso;
- Gait disturbances;
- Memory disorders.
The office is attended by highly qualified doctors - doctors and candidates of medical sciences, specializing in this section of neurology. We carry out a comprehensive clinical differential diagnosis of conditions associated with impaired motor functions, establish the cause of extrapyramidal disorders and prescribe adequate specialized treatment. The health status of patients is monitored.
With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment (drug therapy, use of botulinum toxin), patients experience long-term and stable remission, lost functions are restored and the quality of life is significantly improved.
Registration is carried out by phone
Genetic predisposition
From assumptions about the hereditary factor of parkinsonism, there follows an assumption about a person’s genetic predisposition to this disease. Parkinson himself suffered from this pathology, along with several other members of his family. Various studies over different periods of time have confirmed the likelihood of a genetic factor as the cause of the disease in the range from 2.5 to 94.5% of all cases of the disease. Such a scatter could not but cause disagreements among neurologists around the world regarding their view of the issue being studied.
The basis of such disagreements is the fact that parkinsonism syndrome may be part of the clinical picture of other neurological pathologies with a hereditary nature of transmission.
Parkinsonism is most often detected in elderly people, to which not all relatives live.
In addition, in the absence of exogenous factors, some metabolic disorders caused by parkinsonism may not appear at all. Therefore, the use of clinical data to establish a genetic predisposition to Parkinson's disease does not allow us to draw reliable conclusions about the causes of the disease.
Less often in medical circles you hear about a recessive type of genetic predisposition to Parkinson's disease, linked to sex characteristics. However, any study reveals a genetic predisposition to the disease in no more than 3-8% of cases. At the same time, this pattern turns out to be different in populations of different countries. It is important to mention here that in Sweden a pattern of predominance of the so-called 0 blood group in patients with parkinsonism has been identified. The same trend is emerging in Norway, but in Finland it is completely absent. Therefore, experts conclude that a possible cause of parkinsonism is the hereditary transmission of a defect in the tyrosine hydroxylase fragment.
Brain injury
Even the mildest single brain injury can increase the likelihood of developing neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, as American doctors have repeatedly stated. Neurologists trace the relationship between any concussion and the occurrence of senile dementia, based on a study of 300 thousand older Americans over 12 years. Data showed that when patients suffer brain injuries, they develop parkinsonism in 71% of all cases of the disease. Moreover, out of 300 thousand case histories, half contained records of tuberculosis incidence.
Doctors noted that when suffering a moderate concussion, the risk of developing pathology is about 56%, and when suffering a concussion along with tuberculosis - 83%. Experts suggest that a concussion reduces the resistance of this organ to the factors of aging. Along with mechanical concussion, depressive states also have a negative impact on the stability of the human brain, which has been proven by Canadian scientists.
Brain diseases
Another factor that can provoke the occurrence and development of Parkinson’s disease is a number of diseases and their complications in the human brain. Often, after suffering viral or infectious processes in the brain, complications can occur, for example, meningitis, encephalitis and others. These infectious processes weaken the immune system, can destroy brain cells and, as a result, lead to secondary parkinsonism.
Pathology can be caused by various vascular diseases, for example, atherosclerosis of blood vessels, circulatory disorders in the body. Tumors in the brain area can also play an important role in the development of Parkinson's disease.
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
There are true Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism syndrome - a complex of symptoms that develop after head injuries and severe intoxication.
Characteristic signs of the disease:
- Tremors in the arms and legs - in Parkinson's disease, they occur at rest. Frequency of up to 6 involuntary movements per second. Occurs at an early stage of the disease. Starts with one arm, then spreads to the other side of the body. A “yes-no” symptom may be observed. During sleep and at rest, the tremor stops, but intensifies during emotional shocks.
- Hypokinesia – decrease in motor activity. This symptom manifests itself as a change in handwriting, speech, and the disappearance of characteristic facial expressions.
- Muscle rigidity – increased muscle tone. The limb freezes in a bent or straightened state. A typical symptom is the “supplicant pose.”
- Postural instability - this symptom occurs in the later stages of the pathological process. Patients have difficulty starting and finishing movement. The body may begin to move faster than the legs. In this case, the center of gravity shifts and the patient falls.
In addition to the main diagnostic signs, Parkinson's disease is accompanied by autonomic and mental symptoms. They are individual. Both obesity and exhaustion, sweating, drooling, psychosis, and hallucinations are observed.
The presence of harmful and lack of beneficial substances
With severe intoxication in the body, brain tissue is poisoned by toxins, which also sometimes causes a pathological process. The occurrence and development of Parkinson's disease can be influenced by poisoning with manganese, heavy metals, drugs, carbon monoxide and other substances. A striking example of the occurrence of Parkinson's disease in young people is the discovery of a massive incidence of this disease in 1977 among a group of young people who used synthetic heroin.
There is no direct relationship between the incidence of Parkinsonism and alcohol consumption, but in medical circles it is believed that alcohol abuse, as well as drugs, provokes weakening of brain cells and creates a favorable environment for the development of Parkinson's disease.
Sometimes the disease can be caused not only by the presence of harmful substances in the human body, but also by insufficient levels of beneficial ones, for example, vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D in the human body is responsible for the formation of a protective barrier aimed at combating free radicals and toxins. Therefore, with its deficiency in old age, all of the above substances freely enter the brain and have a detrimental effect on its cellular structure, which is a prerequisite for the occurrence of Parkinson’s disease.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is an incurable destructive disease. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms, reducing the rate of patient degradation, improving quality and increasing the active period of life.
In the conservative treatment of Parkinson's disease, the following drugs are used:
- Drugs that increase the amount of dopamine in the brain - Levodopa. To stabilize the active substance in tissues, Tasmar (Tolcapone) is prescribed.
Tasmar is prescribed as part of combination therapy for Alzheimer's disease - in parallel with the main therapeutic agents. The drug reduces the activity of the enzyme that converts levodopa into one of the phenylalanine derivatives. Levodopa is an effective drug used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
- Dopamine receptor agonists - to stimulate this area, mimic the action of the neurotransmitter.
- MAO inhibitors – inhibit enzymes that break down dopamine. For example, such as Segan (Yumex, Selegiline, analog Deprenil, Eldepril).
One of the effective anti-Parkinsonian medications is the drug Segan (Yumex). Its main active substance, Seleginine, reduces the destruction of dopamine in the brain, and also enhances the effect of another substance - levodopa, which, when it enters neurons, is converted into dopamine. The use of selegiline improves brain function and also has a positive effect on mood and overall well-being.
- Dopamine reuptake inhibitors - increase the sensitivity of receptors to the neurotransmitter.
- Anticholinergics - to relieve symptoms of the disease such as hypersalivation, hyperhidrosis and excessive activity of the sebaceous glands.
If conservative treatment of Parkinson's disease is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated. Destructive operations and stimulation of brain areas are used.
Methods of surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease:
- Thalamotomy - indicated when the main symptom is tremor and only one side of the body is affected.
- Pallidotomy - such an intervention for Parkinson's disease is performed when the main symptom is movement disorders.
- Neurostimulation – if conservative treatment of Parkinson’s disease is ineffective or if there is intolerance to medications. This procedure involves implanting electrodes into brain structures. The patient can independently regulate the intensity of stimulation.
The intervention is permitted for Parkinson's disease with bilateral involvement. This operation is reversible and easily tolerated. The downside is its high cost.