What is the danger of a retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst?
A long asymptomatic course of the disease in combination with the slow growth of the cyst is in itself dangerous.
Parents may not realize that their child has a tumor in the brain. Although the tumor is benign, if left untreated it can have life-threatening complications. For example, one of these complications is the rupture of a cyst, in which the cerebrospinal fluid filling it spills into the brain tissue, which leads to death. In addition, no one can give an absolute guarantee that the tumor will not degenerate into malignant. And this is already a serious danger to life.
Causes
Obviously, a brain cyst in a newborn does not just appear. The reasons for its occurrence are quite serious and often cause different consequences:
- congenital pathologies of the central nervous system
- injuries
- cerebral hemorrhages
- past infections, especially meningitis and encephalitis
- herpes virus infection
- impaired blood circulation in the brain tissue and, accordingly, hypoxia
All this leads to the death of brain tissue, and cavities filled with fluid form in such areas. In most cases, the formation remains in place, it does not grow, and does not pose any particular risk. But in some cases, their growth is still possible, and then there is a danger of developing brain pathologies.
Cyst growth occurs for reasons such as:
- Increased pressure in the cavity itself.
- Infection with infectious diseases.
- A concussion already in the presence of a cavity formation.
- Bruises, injuries to the toddler.
Brain cyst in a child: treatment, consequences
Parents should be extremely attentive to the health and well-being of their children.
If your child periodically complains of blurred vision, or dizziness and headaches, then you cannot put off going to the doctor.
A brain cyst formed in a child causes a lot of anxiety and worry. But if proper measures are taken in a timely manner, serious neurological problems can be avoided.
Symptoms of cystosis
Pathology can affect any part of the brain. Depending on which area is damaged, certain symptoms occur. If the cystic cavity is localized:
- In the occipital zone, the child’s vision suffers.
- In the cerebellum there is a violation of stability and coordination of movements. The baby begins to walk later, has difficulty moving, and suffers from attacks of severe dizziness.
- Near the pituitary gland - as the child grows older, hormonal imbalances will begin, which will greatly affect his physical development.
Important! The rapid growth of a cystic tumor is always accompanied by high intracranial pressure. At the same time, the patient begins to complain of bursting pain in the head, morning sickness, weakness
Intensive growth of the formation can cause separation of the bone sutures on the skull, so treatment should not be delayed.
Children with a cyst in the brain constantly experience headaches that cannot be relieved by painkillers. Due to the pronounced signs of the disease, they cannot develop according to age. In severe cases, patients suffer from epileptic seizures. Some groups of cystic formations are prone to rupture, which can be fatal.
Diagnostic features
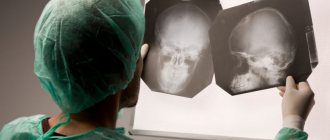
The disease can be diagnosed after the birth of a child using neurosonography. This ultrasound examination is carried out through the fontanel and provides reliable information without ionizing load on the body. Such a diagnosis can only be carried out on newborns and children up to the twelfth month of life, until the sutures of the skull finally fuse together.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=TzJjeC342ew
Neurosonography is indicated for the following pathological conditions:
- Infant suffocation.
- Fetal hypoxia.
- C-section.
- Infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
- Genetic abnormalities.
- Recession or bulging of the fontanel.
- Birth injuries.
- Lack of weight.
- Detection of pathology during intrauterine development.
- Profound prematurity.
- Prolonged labor.
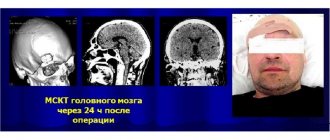
Subsequently, MRI or CT is used for examination, which makes it possible to accurately determine the location of the cystic cavity, its size and shape. During these diagnostic measures, children under 6 years of age are in medicated sleep. Based on the results obtained, the doctor draws conclusions and determines further treatment tactics.
Prevention
Many unfavorable factors lead to the occurrence of cystic formations. Since the abnormal process often begins during the development of the fetal nervous system, preventive measures mainly concern pregnant women. They need:
- Categorically give up bad habits.
- Do not abuse medications.
- Treat chronic diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid contact with sick people.
- Regularly consult a gynecologist and follow his recommendations.
Sometimes injuries, including birth injuries, lead to the growth of cysts, so you need to take the choice of a clinic and a doctor who will deliver the baby very seriously in order to reduce all possible risks to nothing.
Parents who do not ignore the first symptoms of the disease in their children and seek medical help in a timely manner can count on a successful treatment outcome.
After all, the sooner the disease is detected, the better for the patient.
What you need to know about a cyst in a child's head
The deviation occurs while in the womb, or when the baby is born. It can be diagnosed through an ultrasound scan of the head. The procedure is carried out through the fontanel.
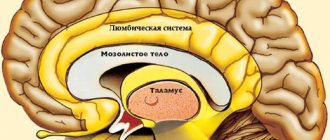
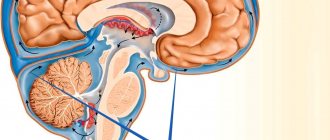
The cyst is located on those areas of nervous tissue that have already died. It is located in different places, so there are several types of neoplasms:
1. retrocerebral; 2. cerebral; 3. arachnoid.
Retrocerebral pathologies cause the tissue in the brain to die, therefore, it cannot function normally. The prerequisites for such a deviation are strokes, head injuries, cerebrovascular accidents, and the consequences of operations.
Subependymal cysts are located directly in the brain. They appear due to hypoxia and intracerebral hemorrhages. In this case, the child requires regular examinations and monitoring using MRI. If an increase in pathology is noticed, the tissues around it are subject to compression, which can lead to serious complications. The disease can be cured both conservatively and surgically.
Arachnoid formations are located in the arachnoid membrane. They are typical for males and are the result of hemorrhages, head injuries and inflammation.
Why does a baby develop a cyst?
The reasons for the formation of pathology are different:
1. The deviation appears due to the fact that the woman suffered an infectious disease during pregnancy. At the same time, dangerous microorganisms entered the embryo through the placenta, causing all kinds of disorders and inflammation in the brain. 2. Features of intrauterine development. At the beginning of pregnancy, the fetus may develop a cyst that disappears on its own over time. 3. Often, pathology is formed due to injuries received during childbirth - incorrect position of the baby, difficult passage through the birth canal, and so on. 4. Circulatory disorders in the child’s brain. Lack of blood supply provokes the death of the tissue on which the cyst appears.
Whatever the prerequisite for the appearance of pathology, it must be constantly monitored so that serious complications do not occur.
A cyst in a child’s head is dangerous due to the following consequences:
1. intracerebral hemorrhages; 2. problems with coordination; 3. loss of vision and hearing.
It is important to promptly notice the deviation, diagnose it and carry out the necessary treatment measures. Unfortunately, sometimes the symptoms are not clearly expressed or there are none at all. In this case, only special studies can help make a diagnosis.
How does a cyst form?
The source of intracerebral cyst creation is ependyma. It is neuroepithelium. Ependymal cells are a thin membrane lining a narrow canal that is central to the spinal cord and the walls of the cerebral ventricles.
During a pathological process that leads to the appearance of a new formation, the activation of cellular hyperplasia begins. Cell division also slows down. The cyst can develop on top of the ependyma (that is, in the gastric cavity) or grow under its layer.
Various negative effects can disrupt the normal blood flow of some brain areas. Lack of nutrients and oxygen leads to the formation of a necrosis zone. As a result, after the tissue dies, a cavity appears that fills with liquid. This is how a cyst is formed.
Features of treatment
You don’t need to despair at all if your baby has a vascular cyst. Its spontaneous disappearance is usually observed after a short amount of time. However, you should not leave the child’s condition uncontrolled. It is imperative to identify the infection that caused the deviation, and do not forget to do an ultrasound scan every two months.
If a subendymal cyst is detected, then special therapy is also not required. Over time, the problem will go away, but you will still have to do an MRI twice a year and periodically visit a specialist.
The greatest danger, especially for a premature baby, is an arachnoid cyst. It is characterized by rapid growth and progression, causing various disorders in the functioning of the brain. The doctor decides how to treat the tumor on a case-by-case basis. The tumor does not go away on its own, and conservative or radical therapy can be used to remove it. Drug treatment involves the use of drugs to eliminate the cyst and severe symptoms. The doctor may prescribe:
- antibacterial agents;
- antiviral drugs;
- drugs to improve immunity and blood circulation.
But in some cases, treatment is carried out using surgery, endoscopy, and craniotomy. If a newborn has a cyst in the head, then the use of traditional methods is strictly prohibited, since this can only aggravate an already difficult condition, even leading to death.
Treatment methods
Ultrasound is the safest method for diagnosing cysts in children
Neurosonography, an ultrasound examination of the brain, is considered the most reliable diagnostic method for newborns and infants. This procedure is also performed for children with prematurity, as well as for infants after a difficult pregnancy and delivery (in cases where hypoxia was observed).
To determine the location, shape and size of formations, the following diagnostic methods are often prescribed:
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Before surgical intervention and conservative treatment, it is necessary to undergo a set of tests: general urine and blood tests and other diagnostic methods.
If a child is diagnosed with a small cyst, and it does not cause changes in his behavior, then only observation and control by a specialist is required. At the initial stages of development, the neoplasm is treated conservatively with several groups of drugs:
- antiviral and antibacterial;
- immunomodulatory;
- nootropics (Picamilon, Pantogam) to supply the body with glucose and sufficient oxygen;
- medications Longidaza and Karipain to improve blood supply.
If the cyst enlarges, surgical treatment is required. In practice, two types of intervention are used: palliative or radical. The first method involves removing the contents of the tumor while preserving the walls of the bladder, which poses a risk of relapse. There are two types of such an operation:
- Shunting. A channel is created in the brain to drain cystic fluid. A significant drawback of the method is the possibility of infection.
- Endoscopic surgery. The contents of the tumor are removed through a puncture in the head. The method is not applicable to all cysts due to the inaccessibility of some areas of the brain to the endoscope.
Radical removal of a cystic bladder is an operation accompanied by craniotomy, as a result of which the formation is removed along with the walls. The procedure is traumatic and is accompanied by a long rehabilitation period.
Surgery is not necessary for all types of cysts:
- subependymal requires regular monitoring and examination, removal is necessary only when neurological symptoms progress;
- new formation of the intermediate sail is the least dangerous anomaly, requiring only monitoring of the baby;
- a choroid plexus cyst, as a rule, disappears on its own in the first year of a child’s life;
- the need to remove a retrocerebellar cyst depends on its size;
- arachnoid and dermoid are necessarily removed.
The essence of pathology
The fact that, according to statistics, the disease has become much more common than before is not due to the fact that the pathology has become more frequent, but to the improvement of diagnostic methods. They have become more accurate and accessible.
A cyst is a pineal-shaped cavity that contains fluid inside. It can be found in almost any part of the body. Do not be afraid that this tumor has appeared on the brain of a newborn. Often it disappears on its own, simply dissolving.
Very often, small bubbles with liquid resolve on their own. Not only newborns, but also adolescents, adults, and the elderly can suffer from this phenomenon. In general, this is a multifaceted pathology.
A vascular cyst in a child’s brain can be detected in the womb. It is normal and often resolves on its own. Despite this, the disease is considered dangerous, since if it is poorly located or large in size, it can interfere with the brain’s ability to properly perform its functions.
Today, diagnostic methods have reached amazing heights. They have become very accurate and accessible. Even during pregnancy, you can determine the presence of a cyst. Most often it is a choroid plexus cyst (CPC).
Diagnosis can also be carried out in a newborn. It is recommended to carry out a study of the newborn’s brain if a birth injury has occurred, the pregnancy has been problematic, or suspicious signs have appeared. These tiny bubbles can be unmistakably detected immediately after the baby is born.
If there are no direct indications, then newborns do not undergo brain ultrasound. Certain symptoms may indicate that there is a cyst.
Impaired blood circulation, abnormalities in metabolic processes, or lack of oxygen during intrauterine development are currently known causes of cysts in the brain in infants. Depending on the provoking factor, a number of tumors are distinguished:
- arachnoid (forms as a congenital pathology or due to an inflammatory process; the help of a surgeon may be required to eliminate it);
- formation of choroid plexuses (occurs in response to infection with the herpes virus and rarely requires surgical intervention);
- choroidal (its appearance is provoked by infections or compression of the skull during childbirth; therapy is carried out with medication or surgery);
- subependymal (formed due to lack of oxygen and removed surgically);
- periventricular (occurs due to infection, developmental problems, or complications during pregnancy; surgery or conservative treatment may be performed to eliminate it).
Treatment
First of all, with such a diagnosis, parents need to cope with their feelings and proceed to therapy as calmly as possible. Proper treatment most often leads to complete recovery. If the cyst is small and does not grow, and the baby does not change his behavior, it may not require treatment at all. It is enough just to show it to the doctor regularly.
The safest is considered to be a choroid plexus cyst. They do not treat it, but only observe the dynamics. The brain does not suffer in any way. But this does not mean that everything should be left to chance. It should be understood that the cyst appeared for some reason: an inflammatory process, an infectious lesion. This means that the doctor must identify what specific infection led to the death of brain cells and urgently eliminate it. After a few months, even if the child’s condition does not cause any concern, you still need to repeat the ultrasound.
For subependymal cysts, it is necessary to conduct an examination several times a year using MRI (done under general anesthesia in a closed circuit) or MR. Treatment is not required if the cyst does not grow. Most likely, the brain tissue will recover on its own. Such cysts most often resolve without outside intervention, but they can cause serious complications if the cystic cavity enlarges. This leads to a lot of fluid accumulating inside it, and pressure increases. Over time, the cavity begins to put pressure on adjacent brain tissue.
Sometimes the tumor can grow quickly. At the same time, it has a negative effect on tissues and blood vessels. A large cyst in a newborn compresses the tissues and changes their position. Because of this, the baby may experience seizures, which, if left untreated, quickly progress. Neurological symptoms in such cases increase, the child’s condition worsens, and a hemorrhagic stroke may even occur.
It is especially important to treat arachnoid cysts. It does not go away on its own, so surgery will be required.
If such a neoplasm occurs, the child must be constantly monitored by a neurologist.
If the tumor is detected at an early stage, conservative treatment will be sufficient. Three main groups of drugs are used:
- antiviral;
- to strengthen the general condition of the immune system;
- to improve blood circulation in the brain.
Medicines must be taken strictly according to the schedule until the doctor stops them
It is important to choose the dose accurately, since it is very easy to overdose on drugs for a newborn. To improve blood circulation and better lymphatic drainage, massage is recommended
If it is definitely established that the cyst in a newborn continues to grow, the help of a surgeon may be required. He will have to remove the tumor. There can be two types of operation:
- Palliative. The surgeon will remove the contents of the cyst without removing its walls. The disadvantage of this method is the high probability of relapse. For surgery, bypass or endoscopic intervention may be used. When a shunt is performed, the surgeon creates a channel in the child's head through which fluid is drained. Due to the shunt, brain tissue can become infected, which is a big disadvantage of such operations. With the endoscopic method, a tiny puncture is made in the head, through which the contents of the cyst are removed. This method cannot always be used, since some areas of the brain simply cannot be reached with an endoscope.
- Radical. This is an open brain surgery in which the bones of the skull are opened (the bone is drilled). Through the resulting hole, the cyst and adjacent tissue are removed. This is a traumatic method, after which a long recovery is required.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
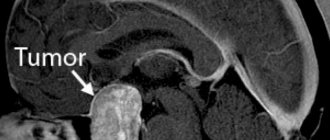
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using methods that help to detect the location of the tumor, examine the structure, condition, and estimate the size. MRI can handle the tasks.
Separately about treatment methods
The treatment process for asymptomatic cysts is not carried out separately. The main thing is to be observed by doctors, regularly monitor whether the formation is growing, and notice unpleasant symptoms. This can be done once a year or once every six months if the sensations are alarming.
Conservative treatment is carried out with drugs. After tomography and determination of the size of the anomaly, medications are prescribed.
You will have to visit specialists regularly throughout your life; no one can guarantee how the tumor will behave in a year or twenty years.
Medium-sized cysts do not require surgical removal. If the growth is not intense, doctors eliminate the factors contributing to the growth.
Infectious diseases, head injuries, bruises and concussions can lead to the disease.
If the cyst of the intermediate velum is type III, that is, it is of a severe degree, doctors recommend surgery. Urgent tumor removal is prescribed for the following factors:
- The pressure often rises, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid increases, and it puts pressure on the brain.
- The cerebrospinal fluid becomes excessive, and pronounced neurological symptoms appear.
- The patient often loses consciousness and has attacks of paralysis.
- The tumor grows too quickly and puts pressure on the brain structures.
Operations vary by type. Using a spinal drainage, the skull is punctured and the cyst fluid drains from the skull.
The second method of operation is better tolerated by the patient. The person undergoes radical resection. The affected area of the brain is opened, and the cyst is carefully pulled out, without damaging the membranes and preventing fluid from spilling onto the meninges and cranial membranes.
An additional method is endoscopy. It is easily tolerated by patients, but is not considered progressive. The affected area is punctured to perform the bypass procedure.
If there are no complications, recovery lasts no more than 7-10 days. After this, history is unlikely to repeat itself. But throughout his life, the patient must be registered with a neurologist.
Symptoms
A newborn cyst has certain signs. Symptoms are affected by tumor size, type of pathology, location and complications. Small cysts may not show themselves at all. But if there are certain abnormalities in the baby’s body, a disease can be suspected.
Large cysts under the influence of increased pressure on surrounding tissues have certain symptoms:
- very frequent regurgitation;
- sleep disorders;
- mental retardation;
- the child is excessively whiny and restless;
- convulsions;
- does not feel pain;
- presence of limb tremor;
- swollen or pulsating fontanel;
- muscle hypertonicity or hypotonicity;
- disturbances in coordination of movements;
- numbness of the limbs.
Read more about the signs of a cyst in the head here.
A large cyst in a newborn can cause pathological disorders in the newborn’s organs. A cyst in the head of a newborn may increase due to the following factors:
- with increasing fluid pressure on the walls of the cyst;
- with inflammatory processes in the children's body;
- head injuries of any nature - concussion, bruise, etc.
Even if a child has a cystic tumor, it may not manifest itself until adolescence. But even in this case, the child needs regular medical supervision.
The most dangerous period for the development of a cyst is adolescence, since it is during this period that even the most inconspicuous and harmless cyst can begin to rapidly develop to enormous sizes.
If a child has a large cyst, it can put pressure on the brain tissue, causing the following negative consequences:
- constant headaches accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- decreased hearing, impaired vision, sense of smell;
- lack of healthy sleep;
- poor coordination in space;
- high intracranial and blood pressure;
- seizures, loss of consciousness;
- epilepsy attacks;
- numbness of arms and legs.
Symptoms largely depend on where the cyst is located. If the tumor is located closer to the back of the head, it is fraught with poor vision, double vision, and the appearance of a “blurred” look.
A cyst-like formation in the cerebellum area negatively affects the child’s coordination in space. If the tumor is located in the area of the pituitary gland, the functioning of the endocrine system is disrupted. With the most severe types of cysts, the child may lag behind in development, both mental and physical.
As the cyst grows in a newborn, it compresses the brain tissue and causes mental disorders in the baby. Cysts continue to grow for the following reasons:
- An increase in pressure inside the cavity formation.
- Development of inflammatory and infectious diseases in the body of a newborn.
- Concussion in a child against the background of existing cystic formations and injuries.
Physiological cysts do not increase and do not manifest themselves in any way. But, despite the apparent safety, they must be monitored.
Main symptoms of the pathology:
- The newborn burps constantly and profusely.
- The baby refuses breastfeeding.
- Motor coordination is impaired.
- Mental reactions slow down against the background of a sharp decrease in motor activity.
- Developmental disorder, the child is lagging behind in height and weight.
- Muscle spasms.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the cystic cavity. A cyst in the occipital part of the brain in newborns provokes visual disturbances. When the cerebellum is damaged, coordination and speech development are impaired. If the formation is localized at the base, then mental disorders occur.
As a result of the enlargement of the cavity, the ventricles of the brain are displaced, resulting in attacks of severe vomiting and lethargy. If the disease continues to progress, the cranial sutures separate and the fontanel does not heal. This condition provokes the following symptoms:
- Increased muscle tone.
- Trembling of limbs.
- Headache.
- The baby becomes restless and cries often.
- The fontanel bulges and pulsates.
- Pain sensitivity decreases.
If the symptoms described above occur, it is recommended to contact a neurosurgeon who will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and identify the location of the cyst. After the examination, treatment is necessary.
Manifestations and causes
Often the following reasons contribute to the appearance of cystic formations in the head of a newborn baby:
- infectious diseases of the mother suffered during pregnancy, during which their pathogens can penetrate the placenta into the baby’s brain tissue and provoke the development of various inflammatory processes;
- injuries received during or after childbirth, as a result of which such anomalies form at the site of hematomas and intracranial hemorrhages;
- disturbances in blood circulation, as a result of which brain cells die and cysts form in their place;
- infectious diseases of the brain in newborns (meningitis, encephalitis, etc.);
- congenital abnormalities in the functioning of the central nervous system.
If the cavity with fluid in the child’s head is small, then it often does not manifest itself at all, and it can only be identified during neurosonography, which, as a rule, is indicated for all infants to identify possible pathologies.
Those formations that are large in size may manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- the baby burps frequently and profusely, sometimes he vomits like a fountain, which is associated with increased intracranial pressure;
- gains or even loses weight poorly;
- has poor appetite, refuses breastfeeding or formula bottles;
- cries often and for a long time, sleeps poorly;
- he has tremors in his limbs;
- the fontanel may swell and constantly pulsate;
- the movements of the baby’s limbs are not coordinated;
- The child has visual and hearing impairments (does not focus on objects, does not turn towards sounds).
Symptoms and diagnosis
As already mentioned, a head cyst in newborns is determined in the first year of life using ultrasound. This diagnosis is effective as long as there is an “exit to the brain” through the soft tissue of an unovergrown fontanel.
Neurosonography
For older children, examinations are carried out using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner and computed tomography. The advantage of these methods is that, thanks to them, it is possible to determine whether we are dealing with a cyst or a tumor.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=wXlOR0xt5J4
Diagnosis of brain cysts in newborns does not always occur on time. The reason for this is the fact that to diagnose it it is necessary to carry out neurosonography, and the latter is not performed on all newborns.
Also, the reason for conducting neurosonography is the presence of the following symptoms in a newborn:
- convulsions;
- insufficient development of the baby’s psyche and motor skills;
- increased drowsiness;
- increased lethargy;
- constant tremor of the limbs;
- frequent cases of vomiting;
- causeless loss of consciousness;
- causeless hearing and vision impairment;
- detected paresis of the limbs;
- cases of epileptic seizures;
- sleep disorders.
All of the above symptoms should alert parents and force them to contact a pediatrician for an examination for the formation of abnormal cavities.
A cerebral vascular cyst refers to accumulations of cerebrospinal fluid circulating within their plexus. It is produced to nourish the brain cells and tissues of the future baby, and the plexuses are early signs of the development of the central nervous system of the fetus.
If the brain develops too quickly, free space appears between the vessels and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. And then a cyst appears. Why this accumulation of fluid occurs in some places, none of the experts can say for sure.
And there is no urgent need to understand this, because it does not affect the baby’s health. These accumulations look like a cyst during ultrasound examination, which is why they are designated as such in the reports.
Changes are detected by ultrasound or sonography. According to the recommendation of the World Health Society, these studies are performed on all children under one year of age. Neurological disorders are determined using ultrasound.
Sonography is prescribed if there is a history of:
- birth trauma in a baby;
- infectious disease of the mother during pregnancy;
- difficult pregnancy;
- fetal prematurity;
- deviations in size at birth;
- pronounced disturbances in the shape of the head;
- a defect in the structure of the baby’s organs.
According to research, such cysts are found not only in children who are developmentally delayed. These formations are equally found in normally developed children.
How does an intermediate velum cyst form?
During the period of intrauterine development, the embryo has folds of the meninges on the upper wall of the third ventricle, which may not connect, after which a cavity is formed. The result of non-fusion of the sheets of the folds of the meninges after the birth of the child is the cause of the appearance of the intermediate velum cyst.
In a child, a cyst of the intermediate velum occurs for the following reasons:
- Violation of the formation of the central nervous system at the time of pregnancy.
- If the process of labor is accompanied by damage to the head (large fetus, number of babies more than one).
- When the expectant mother suffered an infectious disease (meningitis) during pregnancy. Microorganisms and viruses enter the brain through the blood.
- Medicines used by the pregnant woman.
- Consumption of alcohol, tobacco products during pregnancy, the influence of radioactive substances, poisons from various chemical industries.
Symptoms of a brain cyst: how does it manifest itself?
Large cystic cavities can cause:
- aching or acute headache;
- disturbances in the functioning of the organs of hearing and vision;
- double vision or blurred vision;
- sleep pattern disorder;
- noise in the head;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- high cranial pressure;
- weakening of muscle tone;
- fainting, seizures, or tremors;
- frequent belching;
- increased pulsation in the fontanel area;
- epilepsy attacks;
- sometimes numbness of the limbs, up to their temporary paralysis.
The growing cyst puts pressure on the tiny child's brain, causing strange behavior and disruption of the overall course of development.
In newborns and infants in the first months after birth
the cyst manifests itself as follows
- Excessive regurgitation after each feeding
- Impaired coordination of movements
- Slow psychomotor development
- Lagging behind normal height and weight
- Recurrent seizures
The final diagnosis is made after an ultrasound of the child’s brain. The use of modern equipment eliminates the negative impact on the baby’s brain and his body as a whole.
If the progressive nature of the pathology is detected, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed, which is repeated several times a year.
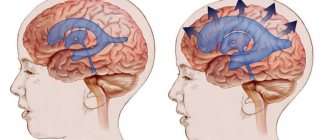
The rapid growth of a cyst in the brain poses a huge danger to the child due to tissue compression, increased pressure inside the skull and the subsequent manifestation of even more severe symptoms.
An increase in the intensity of seizures and even the development of a hemorrhagic stroke is likely.
Mothers do not always suspect that something is wrong with their baby. Often, the brushes in the baby’s head do not manifest themselves in any way and do not bother the newborn. However, there are some signs that suggest that the baby has cysts:
- swelling of the fontanel or its pulsation;
- frequent causeless vomiting, regurgitation;
- developmental delay, motor skills;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- blurred vision.
Although cysts most often do not change in size, they can sometimes become larger. This is evidenced by the following symptoms:
- disturbances in the functioning of the sense organs;
- headache;
- change in intracranial pressure;
- epileptic seizures or fainting;
- lack of coordination.
Large cysts under the influence of increased pressure on surrounding tissues have certain symptoms:
- very frequent regurgitation;
- sleep disorders;
- mental retardation;
- the child is excessively whiny and restless;
- convulsions;
- does not feel pain;
- presence of limb tremor;
- swollen or pulsating fontanel;
- muscle hypertonicity or hypotonicity;
- disturbances in coordination of movements;
- numbness of the limbs.
Read more about the signs of a cyst in the head here.
How to treat a cyst in the head
Cyst symptoms:
1. profuse and frequent regurgitation; 2. muscle spasms; 3. developmental delay; 4. slowing down of mental reactions; 5. lack of coordination; 6. refusal of breastfeeding; 7. visual disturbances; 8. delayed speech development; 9. hearing impairment; 10. lethargy; 11. vomiting; 12. decreased pain sensitivity; 13. pulsation of the fontanelle; 14. anxiety, frequent crying for no apparent reason; 15. trembling of limbs; 16. increased muscle tone.
If a pathology is detected in a child, the doctor chooses individually one of the possible ways:
1. Observe the tumor and wait for it to resolve on its own. Intervene only if the deviation progresses. 2. Use conservative methods of therapy if the cyst in the baby’s head is mild and develops extremely slowly. Take medications that restore blood circulation and have antibacterial and antiviral effects. 3. Perform surgery if the pathology progresses rapidly. This is done by craniotomy, bypass or endoscopic surgery.
Today, neoplasms in the head of children are diagnosed more and more often. This does not mean that the modern generation is sick more; it’s just that the capabilities of modern medicine have expanded significantly, which makes it possible to make correct diagnoses even for the youngest patients.
Thus, if a child has symptoms of a cyst in the brain, then you should definitely contact a specialist and undergo the necessary examination. Although in most cases the pathology does not cause trouble for the baby, it is important to constantly monitor it so as not to miss the moment of its development.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
Like any other volumetric formation of the brain, a cyst may not manifest itself for a long time, or even a lifetime. But if there is an intensive growth of such a formation, then the symptoms will not keep you waiting.
At first, the symptoms of a brain cyst cannot be distinguished from those of an aneurysm or tumor. Characteristic is the appearance of general cerebral symptoms, which develop as a result of increased intracranial pressure and slight swelling of the brain substance; focal (local, local, nest) symptoms, which arise due to compression of adjacent brain structures by the cyst; and the so-called “neighborhood” symptoms that occur when swelling of the brain substance increases and spreads beyond the boundaries of the cyst.
General cerebral symptoms
General cerebral symptoms include:
- bursting, paroxysmal, sometimes pulsating headache, which is practically not relieved by analgesics;
- persistent nausea, the appearance and increase of which does not depend on food intake;
- vomiting: appears most often at the height of the headache, in most cases in the morning and does not bring relief;
- sometimes photophobia,
- lacrimation;
- decreased visual acuity;
- sleep disturbance: insomnia, drowsiness;
- decreased intelligence, memory, concentration;
- mood lability;
- Periodic syncope (fainting) is possible.
Focal symptoms
Focal and neighborhood symptoms are:
- partial Jacksonian seizures (in other words, focal seizures). They arise as a result of irritation of the cerebral cortex cyst. They can appear in an arm, leg or half of the body, and sometimes manifest as auditory or visual hallucinations - it all depends on the location of the cyst in the brain. A distinctive feature is that the patient is conscious during an attack;
- hemiparesis and paralysis. Unilateral decrease in strength in the limbs, often accompanied by loss of sensation;
- dysfunction of the cranial nerves. Hearing loss in one ear, loss of visual fields, severe facial asymmetry, etc.;
- loss or impairment of speech perception;
- dizziness, unsteadiness while walking;
- sometimes generalized epileptic seizures accompanied by loss of consciousness. They occur in patients with increased convulsive readiness of the brain.
These are the main and most common focal symptoms. In fact, there are many more of them, since the appearance of one or another symptom depends on the location of the cyst in the brain. Sometimes a large brain cyst can lead to deformation of the skull bones or suture dehiscence. This symptom occurs mainly in children, since their bones are quite soft and not fully formed. If such symptoms appear, do not delay your contact with a specialist (in this case, a neurologist). Only a doctor using specific research methods is able to establish the correct diagnosis.
Symptoms of the disease
Pathology at the embryonic stage is not considered a serious disease. In its normal state, the size of the cyst does not change; it remains that way for life.
At the initial stage there are practically no symptoms and pain. The person feels as usual, without noticing any deviations in well-being.
When tumor growth is detected, this is accompanied by the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. The symptoms that appear are the same for both older patients and children. Among the symptoms:
- Aching, sharp, cramping headaches.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- Asymptomatic, sharply manifested nausea, with retching and vomiting.
- Fainting conditions.
- Cramps at night.
- Noise in the ears.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Visual hallucinations, often auditory. It seems to a person that his name is being called, and extraneous sounds are heard.
- Bad mood, depression, irritability.
A patient with an intensively growing cyst gets worse every day. He is vulnerable, irritable, and gets tired quickly. Insomnia is often present in addition to the listed symptoms.