According to statistics, such a problem as cerebral aneurysm occurs in 5% of the population. Often such an anomaly occurs covertly and is discovered only through the efforts of a pathologist. In half of the cases, aneurysms, which are small in size, do not rupture. Moreover, such a condition is extremely dangerous, since if a gap in education nevertheless occurs, the person runs the risk of becoming disabled, or even the matter may even end in death.
What is a ruptured brain aneurysm and who can it threaten?
The essence of the problem
An aneurysm is an enlargement of a section of the lumen of an artery. A rupture is called a serious complication when, due to damage to the formation, blood begins to flow into the brain, leading to irreversible changes in it. Experts say that in a third of cases, a breakup ends in the death of the person.
From a physiological point of view, the process is as follows: in the area where the aneurysm has formed, the vessels become inelastic, weaken and do not resist blood flow. It is because of this that a protrusion is formed, i.e. a small sac literally filled with blood. If the education is small, a person may not know about it. But the problem is that it can increase in size over time, and this leads to a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels. The weak point of an aneurysm is called the apex - this is where it ruptures most often.
Bleeding in the damaged area lasts literally seconds, but this is enough for serious disorders to begin in the brain. At first, the body tries to cope on its own, reflexively spasming the artery so that a blood clot forms, which will stop the release of blood and save life. But it also happens that this process is delayed. And in such a situation the prognosis is unfavorable.
What kind of unique artificial vessels were created in Russia? More details
Causes
The main provocateurs of pathology are surges in blood pressure. People with hypertension are most susceptible to stroke. Often, increased blood pressure is not a separate disease, but is a sign of a more severe disorder in the body.
The causes of a burst vessel are also:
- Atherosclerosis . High cholesterol content promotes the accumulation of fat cells on the vascular walls, from which atherosclerotic plaques are formed, narrowing the lumen. This area quickly loses strength and elasticity. Under blood pressure, small cracks and blood clots form in the vessels. Trying to work as usual, the vascular wall breaks.
- Congenital defects of cerebral vessels . With this pathology, blood penetrates directly into the veins, bypassing the capillaries. Because of this, the pressure in the venous vessels rises, which leads to rupture of their walls.
- An aneurysm is a pathological disorder that is either congenital or acquired. Arterial (sometimes venous) vascular walls become very thin. Swelling, protrusion, and stretching of the damaged vessel occurs. Because of this, its elasticity disappears. If a vessel in the brain bursts, hemorrhage occurs, which threatens serious swelling and loss of a large amount of blood.
- Inflammatory processes that cause vascular dystrophy develop in diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, acute vitamin deficiency, severe intoxication, encephalitis and other diseases.
- Thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia . An increased or decreased platelet count changes the cellular composition of the blood, which provokes an increase in pressure and rupture of the vascular wall.
- Neoplasms in which blood vessels that supply nutrients to the tumor are torn. The numerous arteries leading to the tumor inside the skull are prone to rupture, but this occurs when blood pressure rises.
- Taking certain medications (contraceptives, anticoagulants, narcotics) provoke vascular disorders and can become the root cause of a burst vessel in the head.
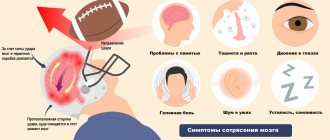
Symptoms of a rupture
As doctors note, a ruptured aneurysm has a clear clinical picture. All signs appear suddenly. A sharp headache occurs, which many characterize as unbearable. The situation may also be accompanied by vomiting, and in particularly severe cases, loss of consciousness and coma follow.
A breakup can occur against the backdrop of some emotional events and upheavals, or it can happen spontaneously. There is a risk of re-bleeding. So, after the first rupture, a blockage of the wall may occur, but after 2-3 weeks the situation can repeat. Doctors note that after repeated hemorrhage, the prognosis becomes unfavorable. After the person returns to consciousness, he or she experiences weakness, dizziness, and poor orientation in space. Rapid breathing and increased heart rate may also occur. In addition, stiff neck muscles, problems with oculomotor functions, loss of speech, and paralysis may occur.
The general condition of a person in such a situation is regarded as serious - he needs emergency medical care.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The clinical picture of blockage of the blood vessels supplying the brain can vary over a very wide range.
Symptoms depend, first of all, on the location and extent of the ischemic area. Early warning signs may include frequent dizziness and headaches, decreased memory and intellectual productivity, presyncope and sudden short-term fainting (syncope), false tactile sensations (paresthesia).
With more pronounced pathology, numbness, partial paralysis, certain speech disorders (articulation disorders, inability to quickly update the necessary words, impoverishment of vocabulary), various dysfunctions in the field of recognition, coordination of movements and spatial orientation, fine motor skills (in particular, writing) are added. , emotional response, behavior, physiological processes and many others.
With stroke, the same focal symptoms develop, by definition, acutely, catastrophically; Unlike disorders of brain activity during transient attacks or crises, such symptoms are persistent.
Diagnosis of suspected thromboembolism includes a mandatory consultation with a neurologist, as well as, if indicated, a number of related specialists (cardiologist, neurosurgeon, etc.). The most informative instrumental research methods are X-ray contrast multislice computed tomography (MSCT in angiographic mode), Dopplerography (ultrasound assessment of the patency of the great vessels), and MRI angiography.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Risk factors
The question of why some aneurysms are asymptomatic and do not lead to serious consequences, while others rupture, worries many doctors and scientists. Based on a number of studies, risk factors have been identified that increase the likelihood of rupture. Among them:
- age point - risks increase for people over 50 years of age;
- location of the formation - if the aneurysm is located in the middle or anterior cerebral artery;
- size of the formation - aneurysms larger than 5 mm become dangerous.
If a person has such risks, it is important to begin treatment as quickly as possible in order to prevent a potential disaster.
Dried apricots will cleanse blood vessels, and raisins will calm the nerves. 6 dried fruits instead of tablets Read more
Why does the gap occur?
There are several reasons why a cerebral aneurysm begins to rupture. One of them is genetics. Here we are talking about the fact that weakness of the artery wall is inherited. Also on the list of causes that provoke the problem are kidney pathologies, injuries, cancer, and atherosclerosis.
The following factors can damage the integrity of the vessel wall::
- increased physical activity;
- a history of arterial hypertension;
- emotional tension;
- drinking alcohol;
- development of infections accompanied by high fever.
How are they treated?
First you need to provide first aid to the person. Naturally, urgent hospitalization will be required, but it is impossible to leave the situation unattended until the ambulance arrives. The patient should be laid so that the head is elevated - this will ensure the necessary outflow of blood and prevent the development of brain swelling. You should also worry about the flow of oxygen; accordingly, you need to relieve the neck - unbutton your shirt, loosen your tie, etc. If you lose consciousness, you should protect the person by clearing the airways - remove dentures, turn your head to the side. It is also worth applying cold objects to the head to reduce the risks of swelling and hemorrhage.
Aneurysm treatment is predominantly treated surgically. The method is selected depending on a number of parameters - the location of the formation, the person’s condition, the severity of the violations and the time that has passed since the moment of rupture.
Cleaning of blood vessels. How to get rid of cholesterol plaques Read more
The following treatment options are used for therapy::
- Clipping is a microsurgical method that involves placing a clip on the base or body of the aneurysm: this will shut it off from the bloodstream.
- Endovascular method - here an intervention is performed by inserting a catheter through the femoral artery.
- Combined method - first a blood clot is injected into the aneurysm, and then it is clipped.
There is such a nuance that it is important to perform the operation in the first 72 hours after the start of bleeding, since the risk of recurrent hemorrhage is high. If you are late, spasm begins to increase, ischemia develops, and the operation will not make sense.
1.General information
Obviously, there is no need to describe in detail the key role and countless functions of the brain in the human body. Let us only note that the central nervous system, i.e. The brain and spinal cord are an incredibly complex organ that controls absolutely all processes, including the activity of the endocrine glands (which, in turn, regulate the functioning of internal organs through hormones). For the most part, this control by the central nervous system is carried out automatically, without the participation of consciousness. However, the neural tissue of the brain, like any other living tissue, can perform its functions productively only if there is a constant supply of nutrients and energy, i.e. oxygen necessary for redox biochemical reactions. The brain receives all this through the bloodstream. And if for some reason the flow of arterial blood enriched in the lungs is sharply reduced or completely blocked, a catastrophe will very soon occur in this area, in the literal sense of the word.
Ischemia (lack of blood supply) triggers dystrophic and degenerative changes (structural and functional degradation of tissue, which, against the background of constant starvation, copes with its tasks increasingly poorly); then atrophy occurs - gradual death and reduction in volume. In the event of a sudden interruption (ischemic attack), if the blood supply is not restored quickly enough, necrosis begins - mass death of specialized cells. In general, this terrible phenomenon is called “infarction” (of the myocardium, kidney, spleen, etc., including the brain), however, in relation to the central nervous system, the term “stroke” (literally “stroke”, more accurate modern) is more often used term – stroke, i.e. acute cerebrovascular accident). Strokes are divided into two unequal groups: rarer hemorrhagic strokes (hemorrhages), caused, for example, by the rupture of a congenital arterial aneurysm, and ischemic strokes (over 80% of all strokes), associated with restriction or blocking of blood flow through the vessels supplying the brain.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Consequences of a breakup
Of the most common consequences if a person remains alive, the following points:
- paralysis and paresis;
- problems with speech if the hemorrhage is in the left hemisphere;
- problems urinating or constipation if damage occurs in the corresponding brain structures;
- mental problems - aggression, rage, apathy, depression may appear;
- cognitive disorders - memory problems, inability to remember new information;
- epilepsy.
So you should worry about your health in advance in order to prevent the appearance and, especially, rupture of a defect.
Consequences of a stroke
When a patient has a blood vessel burst in his head, the consequences can be very disappointing. It all depends on the degree of vascular damage, the location of the hemorrhage and the timeliness of medical care. Often, a stroke ends in death within the first weeks due to the death of neurons and the resulting chemical processes.
If displacement of brain tissue and hemorrhage into the ventricles has not occurred, then the prognosis is more favorable. But even then the person is threatened with:
- Constant attacks of pain in the head.
- Paralysis of the limbs of one half of the body.
- Mental disorders, nervousness.
- Impaired speech, hearing, vision.
- Facial asymmetry.
- Inability to move without support.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Deterioration of memory and thought process.
- Lack of consciousness with the functioning functions of breathing and heartbeat.