What are the dangers of colds and flu in pregnant women?
Respiratory infections pose two threats. Firstly, they may be accompanied by fever, which can lead to defects in fetal development. And secondly, influenza and ARVI during pregnancy can lead to the development of complications. During pregnancy, a number of changes occur in the immune response, as well as in the functioning of the heart and lungs, making the mother's body especially vulnerable. Therefore, colds and flu in expectant mothers are much more severe than in non-pregnant women and are often complicated by bacterial infections, including bronchitis and pneumonia.
The World Health Organization has included pregnant women at risk of developing severe and/or complicated influenza. It has been proven that pregnant women with the flu require hospitalization 4 times more often than non-pregnant women. Among patients in the third trimester, 8% require hospitalization in intensive care units [3].
Timely vaccination can prevent infection with the influenza virus during pregnancy. If infection has already occurred, the woman needs to begin treatment for ARVI or influenza during pregnancy as early as possible.
Prevention of intercostal neuralgia
To prevent neuralgia from occurring in the intercostal space, you must adhere to some simple rules. Particular attention to preventive measures should be paid to those who have already suffered from this disease and those who are at risk (for example, there are provoking pathologies).
- It is necessary to include in the diet more foods containing B vitamins (cereals, liver, fatty fish, vegetables, meat, legumes, nuts, etc.). Nutrition should be balanced and complete.
- It is important to avoid hypothermia and drafts, especially during physical activity.
- It is necessary to observe a work regime, preventing overstrain of the intercostal and back muscles. If you need to stay in the same position for a long time, you must take breaks while doing physical exercises (bending, turning).
- It is necessary to undergo preventive examinations by specialists for the timely detection of spinal diseases.
Are you tired of living with pain? Make an appointment with a neurologist at the medical office. We will help you cope with the disease and return to a healthy life!
Is it necessary to bring down a high temperature during pregnancy and what medications can be used?
It is important to manage fever in pregnant women in a timely manner, since high temperature can negatively affect pregnancy. It is especially dangerous in the first 12 weeks, when the formation of all organs and systems occurs. Hyperthermia in pregnant women during the first trimester doubles the risk of developing neural tube defects (future brain and spinal cord defects) and may also be associated with other birth defects and adverse outcomes in the baby [1].
It is not known for certain which temperature exceeding the greatest danger. Thus, data from a cohort study involving more than 77 thousand women showed that the incidence of malformations was approximately the same among those who reported a fever below 39 and above 39 degrees in the first trimester [1].
The drug of choice for reducing fever is paracetamol, which is approved for use throughout pregnancy [2]. In addition, ibuprofen is used as an antipyretic and analgesic in the first and second trimesters. Multivitamins containing folic acid can reduce the risk of developmental defects due to hyperthermia [1].
How to determine that it is neuralgia?
It may take some time from the moment a pregnant woman feels severe pain in the sternum until she consults a neurologist. It is, of course, in the patient’s interests to reduce this period as much as possible, but this is not always possible. The first thing to do is to rule out pain of cardiac origin. It is necessary to remember that heart pain most often occurs suddenly and passes quickly. In addition, it can be easily relieved (removed) with a validol tablet dissolved in the mouth.
An attack of intercostal neuralgia lasts much longer. Sometimes the pain does not leave a woman during the day and increases significantly with physical activity. Often with neuralgia, you can find a body position in which the pain will go away, however, it is not always possible to stay in it for a long time.
How to reduce a sore throat? What antiseptics can I take?
During pregnancy, it is allowed to use a number of antiseptics for sore throats, so it is not necessary to endure sore throat and other unpleasant symptoms during this period. Medications that expectant mothers can take include:
- ambazon, which has an antimicrobial effect against streptococci, daily dose 4–5 tablets 0.04–0.05 g;
- the combination of lysozyme + pyridoxine exhibits an antiseptic effect against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, fungi and viruses. Vitamin B6 in its composition has a protective effect on the oral mucosa. Prescribe 2 tablets 3-4 times a day.
In addition, warm drinks, which are indicated in unlimited but reasonable quantities, help reduce sore throat.
Can pregnant women take any expectorant medications?
Therapists and obstetricians-gynecologists recommend that pregnant women refrain from taking expectorant medications if possible. The vast majority of drugs in this group are prohibited for use during pregnancy, including herbal remedies, which are often considered “safe” by consumers. In fact, plantain syrup, preparations based on thyme and thyme extract, and other popular herbal remedies are contraindicated for pregnant women.
At the same time, the drug ambroxol is still approved for use by pregnant women in the second and third trimesters with the label “with caution.” The same applies to bromhexine - it is prescribed, but only after a careful assessment of the benefit/risk ratio, and only the attending physician can carry it out. Therefore, primary care providers who advise pregnant women with requests for expectorant medications should limit themselves to insistent advice to consult a doctor. And the only recommendation that should be given in such situations is to drink warm drinks and sufficiently humidify the air in the room.
How to treat neuralgia?
During pregnancy, spinal shock wave therapy, therapeutic massage and most medications are prohibited. To alleviate the condition somewhat, a pregnant woman can take the following measures:
- Take a paracetamol tablet. It would be good to coordinate this step with your doctor, however, as a necessary measure, you can take the medicine yourself.
- Take a position in which the pain will be felt minimally. Lying on a hard sofa or rug with a small tight cushion placed under the lower back usually helps to relieve tension and spasm from the intercostal muscles. It is recommended to place a similar smaller cushion under your neck.
- You can ask your spouse to give you a light back massage. The key word here is easy. The movements should be rubbing and stroking. Under no circumstances should you massage anything, much less “straighten” anything.
- Neurologists allow the use of light warming rubs based on natural balms with essential oils in pregnant women. Do not rub the skin “red” or use oils that are contraindicated for pregnant women, for example, wormwood.
- During remission, it is worth paying attention to special gymnastics or yoga for pregnant women. These exercises strengthen the muscle corset and increase the elasticity of the ligaments, thus preventing the next attack of intercostal neuralgia.
It is worth noting that in the vast majority of cases, all pain associated with the musculoskeletal system goes away within a few weeks after childbirth.
What can a pregnant woman take for a debilitating dry cough?
Antitussive drugs, like mucolytics, are prohibited from taking during pregnancy at all or are allowed under the supervision of a doctor after assessing the risks and benefits. Thus, the popular centrally acting antitussive drug butamirate can be taken only in the second and third trimesters and only after consultation with a doctor. The peripheral drug prenoxdiazine is also used with caution during pregnancy. Thus, when counseling a pregnant woman with a dry cough, she should be advised to immediately visit a doctor.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia during pregnancy
The clinical picture usually develops very quickly. When making any movement of the body, a woman feels a lumbago in the intercostal space. Further mobility becomes difficult.
Gradually, the clinical symptoms of intercostal neuralgia during pregnancy subside, but they reappear when making any movement. Characteristic signs of the disease are:
- pain in the intercostal space (increases when turning the body or palpating the muscle);
- difficulty taking a deep breath;
- stiffness of movement, inability to tilt to the side or turn to the side;
- lag of the chest on the affected side during breathing.
If symptoms of intercostal neuralgia appear during pregnancy, then you need to make an appointment with a neurologist or vertebrologist as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an examination and make a preliminary diagnosis. While carrying a baby, exposure to X-rays, MRI examinations, etc. should be avoided whenever possible. Therefore, you should carefully choose a doctor. The specialist must have extensive practical experience in order to make the correct diagnosis without additional examination methods.
Is it possible to be treated during pregnancy with infusions, decoctions of medicinal herbs or herbal teas?
Despite their natural origin, not all preparations based on medicinal plants, including herbal teas, are safe during pregnancy. Herbs may contain active substances that negatively affect the development of the fetus or increase the tone of the uterus. Herbs can cause miscarriage or stimulate premature labor. Medicinal plants that are unsafe during pregnancy include [4, 5]:
- chamomile - can promote uterine contractions;
- licorice root - may increase the risk of premature birth;
- laxative herbal teas based on senna and other plants - active intestinal peristalsis can stimulate the contractile activity of the uterus;
- common twig - stimulates the production of estrogen, may increase the risk of miscarriage;
- echinacea - activates the synthesis of oxytocin; aloe vera - stimulates the contractile activity of the uterus;
- calendula - has an abortifacient effect and many others.
However, there are also medicinal plants that have been proven safe during pregnancy. Among them [6]:
- raspberry leaves;
- peppermint leaves;
- plantain oval seed shell;
- garlic.
Since the list of medicinal plants that are unsafe during pregnancy is quite large, it is still better to take herbal medicines during this period after consulting with your doctor.
Are any antiviral drugs allowed during pregnancy?
The treatment regimen for influenza in pregnant women includes antiviral drugs from the group of neuraminidase inhibitors. They are active against influenza A and B viruses, and their effectiveness has been demonstrated in numerous clinical studies [7, 8]. Antiviral drugs of this group disrupt the ability of viral particles to penetrate into cells, which leads to localization of infection in the body, alleviation of the condition and reduction of the likelihood of complications during pregnancy [7]. According to international and Russian recommendations, neuraminidase inhibitors are the drugs of choice for influenza, including during pregnancy [8]. Their effectiveness is highest when taken within the first 48 hours after the onset of the disease, so when the first flu symptoms appear, it is very important to consult a doctor and begin treatment. Let us remember that neuraminidase inhibitors are prescription drugs ( also in this case it is necessary to make sure that the patient has the flu and not ARVI in pregnant women - editor's note.
).
Causes of intercostal neuralgia during pregnancy
Intercostal neuralgia during pregnancy develops for a number of reasons. In the first place is a gradual but permanent deformation of the spine. Normally, by the end of the first year of life, a person has fully formed 4 main physiological curves of the spinal column. They are necessary to ensure uniform distribution of shock-absorbing and mechanical loads. Also, lordosis and kyphosis provide balance to the body when walking upright.
During the development of pregnancy, due to the growth of the uterus, a gradual straightening of the lumbar lordosis occurs. The physiological curvature is smoothed out and, to compensate, the thoracic kyphosis is strengthened and the cervical lordosis is smoothed. Thus, by approximately 25–28 weeks of pregnancy, a woman’s spinal column takes on the appearance of an almost even structure. Physical activity is largely compensated by the increased tone of the muscular frame of the body. But gradually this becomes insufficient and pathological changes begin.
The main reason for the development of intercostal neuralgia during pregnancy is a woman’s refusal to use a prenatal bandage. In second place is the physical unpreparedness of the body to bear an unborn child. This is expressed in the weakness of the muscular frame, the presence of problems with degeneration of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs, and insufficient performance of the circulatory and cardiovascular systems.
The human spinal column is not only a supporting structure that provides mobility of the body and attachment of the upper and lower extremities. Inside the spinal column is the spinal canal. There is the most important part of the autonomic nervous system - the spinal cord. It ensures the performance of the whole body, all internal organs, sensitivity, muscle contractility, etc. With pathologies of the spinal cord and the radicular nerves extending from it, not only paresis and paralysis develop, but also difficulties arise in the functioning of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and chest. Arrhythmia, breathing problems, spasms in the intestines and biliary tract, etc. may occur.
The spinal canal is formed by the vertebral bodies and their arcuate processes. The stability of the position of the vertebral bodies is ensured by the intervertebral cartilaginous discs separating the vertebral bodies. The natural curves of the spinal column are necessary to ensure that the intervertebral discs are not subject to excessive shock-absorbing load and that they do not lose their elasticity and normal height.
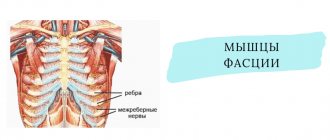
The radicular nerves extend from the structures of the spinal cord. They are paired and are responsible for a specific segment of the body. In the thoracic region of the spinal column, radicular nerves arise, the branches of which are responsible for the innervation of the intercostal muscles.
This is part of the respiratory muscles, due to the contraction and relaxation of which inhalation and exhalation occur. Impulses pass through the structures of the spinal cord from the respiratory center in the brain. They give commands to the intercostal muscles depending on the concentration of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the circulating blood.
Intercostal neuralgia is a pathology in which the process of transmission of nerve impulses through the respiratory intercostal muscles is disrupted. The main reasons for its development during pregnancy can be:
- poor posture and displacement of the vertebral bodies, resulting in compression of the dural membranes of the spinal cord and radicular nerves;
- the height of the intervertebral discs decreases and their shock-absorbing ability is lost due to the high level of female sex hormones in the blood;
- gradual deformation of the chest occurs, including due to an increase in the vital volume of the lungs;
- the load on the costovertebral joints increases due to an increase in the total weight of the pregnant woman;
- There is a deficiency of microelements and vitamins responsible for the functioning of the nerve fiber.
Potential risk factors may include:
- excess body weight of a pregnant woman, including that associated with fluid retention and the development of edema syndrome;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- hard physical labor;
- refusal to use a prenatal bandage;
- back injuries;
- viral infections (including herpetic form);
- improper organization of sleeping and working spaces;
- wearing high-heeled shoes;
- multiple and polyhydramnios pregnancy.
An experienced physician should rule out all potential causes and risk factors at the time of making an accurate diagnosis. The success of future treatment depends on this.
How to boost immunity during pregnancy?
The following help increase the body's defense against respiratory infections during pregnancy:
- a balanced diet that compensates for a woman’s needs for nutrients, vitamins, and microelements;
- healthy sleep;
- laughter – helps to activate the immune response [9];
- taking probiotics, which normalize the composition of the intestinal flora, which helps reduce the risk of respiratory infections and reduce the severity of cold symptoms [10];
- taking multivitamin complexes containing vitamin D, which helps relieve cold symptoms and reduce the incidence of infection [11].
In addition, to increase the immune response, the doctor can prescribe interferon alpha-2b drugs - intranasal or rectal (there may be restrictions on the duration of pregnancy, for example, some of them are prescribed only after 14 weeks - editor's note).
Is it possible for a pregnant woman to apply mustard plasters and pepper plaster?
Despite the fact that both mustard plasters and pepper plaster act externally and do not affect the development of the fetus, they are potentially dangerous for pregnancy. Heat treatments can increase uterine contractility, which is associated with an increased risk of miscarriage or premature birth. In addition, increased microcirculation, which occurs under the influence of mustard plasters or pepper patches, can change uteroplacental blood flow, which is also undesirable. The greatest danger is posed by thermal procedures in the first and last trimester of pregnancy - in the first they increase the risk of miscarriage, in the last - premature birth.
Consequences of trigeminal neuralgia for a pregnant woman
The disease itself does not have a particular impact on the course of pregnancy and the fetus itself. The presence of neuralgic pain is rather a severe psychological factor that overshadows the wonderful period of waiting for the baby and aggravates other health problems.
You should be aware that signs of neuralgia may be similar to manifestations of dental diseases or damage to the maxillary sinuses. Therefore, if complaints similar to damage to the trigeminal nerve appear, it would be correct to consult a dentist and otolaryngologist. In difficult cases, tomography may be recommended to identify causes of pain such as a brain tumor or multiple sclerosis.