Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
A concussion is a form of traumatic brain injury. In which short-term memory loss may occur, brain dysfunction is reversible. Usually the cause is various traumatic situations. In case of injury, the protective fluid is not able to prevent the impact of brain tissue on the bone tissue of the skull. The injury requires hospitalization and consultation with a specialist.
Classification
Concussion is classified into three degrees:
1.
Mild degree.
The victim is conscious, and within half an hour after the injury there are typical complaints of headache, dizziness, nausea, and disorientation in space. After half an hour the condition returns to normal. 2.
Average.
Consciousness is preserved, short-term memory loss occurs, the symptoms are similar to mild, dizziness persists, there may be a headache, nausea, the victim is disoriented in space. 3.
Severe degree. For her, loss of consciousness lasting a couple of minutes, maybe several hours, is accompanied by retrograde amnesia. Symptoms of headache, dizziness, nausea, disorientation in space can remain for two or three weeks, problems with sleep, and loss of appetite occur. Organic brain lesions lead to the appearance of vascular dementia. This is a secondary disease, that is, occurring against the background of some pathological process. The main reason is a previous ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
Concussion
Encyclopedia of Health / Encyclopedia of Children's Health
The child suffered a concussion. How is this injury treated? What consequences should we expect now?
Worldwide, the leading month for injuries is July. In Russia, January and February are also the most dangerous months for injuries. Slippery. And our winter fun is wild.
EMERGENCY ON HILL
If a child, after hitting his head, feels very bad or his condition worsens before our eyes, call an ambulance. You can take him to the doctor - go to the emergency room yourself. The position: let the baby lie down, come to her senses, and then, lo and behold, everything will work out - it’s fundamentally wrong. Yes, the main treatment for a concussion is sleep and rest, but how do you know that it is a concussion and not a brain injury - a more serious injury that requires urgent hospitalization and mandatory drug treatment.
Distinguishing a concussion from a bruise is a matter for specialists.
In the emergency room, if a concussion is suspected, the child will be given an X-ray, they will look for skull cracks and hemorrhages, and the regional neurologist will be informed about your injury. If necessary, they will be sent to the hospital.
WHAT IS POSSIBLE, WHAT IS NOT POSSIBLE
For a minor concussion, the doctor will prescribe bed rest and long sleep for the child. This treatment can be successfully carried out at home, the main thing is not to violate the regime. Parents often ask what can and cannot be done during a concussion.
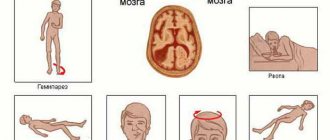
| WARNING SYMPTOMS *The child is pale, sweating, weak *has trouble concentrating his eyes *complains of a headache and nausea *does not want to eat, vomits when trying to feed him *watching TV can also provoke vomiting *is inhibited, answers at random, repeats the same things several times phrases *poor orientation in the space of his own apartment and in time *in rare cases, vascular disorders that occur during a concussion are manifested by a slight increase in temperature. A short-term loss of consciousness is also a symptom of a concussion, but the child does not always understand whether it happened. If he does not remember what happened immediately before the injury and immediately after it, then there was a loss of consciousness. And three or four signs are enough to suspect a brain injury. |
If the head is no longer dizzy and does not hurt, the child can read a little, but it is better if his parents read aloud to him. You can listen to music, but not through headphones!
Now more than ever, children benefit from fruits and vegetables, fortified drinks and fresh air. But you can’t go for a walk, which means you need to ventilate the room often.
But what is not useful is watching TV, videos, playing on the computer, Gameboy or Tetris. Flashing frames irritate the brain.
Even after a mild concussion injury, the patient will stay at home for 7-10 days. Doctors, playing it safe, are in no hurry to prescribe such children to school or kindergarten too quickly. Now they can’t possibly hit their heads again while running around during school breaks. For a month or two, the child will also be exempt from physical education lessons and any other sports activities.
A more severe injury - brain contusion - will require longer adherence to a gentle regimen.
WITHOUT CONSEQUENCES?
Parents usually ask: “Will there be any consequences of the injury?” In most cases, everything ends well. But it happens that after a concussion, a child’s intracranial pressure increases; when everyone has forgotten about the injury, headaches appear out of nowhere; Sometimes visual acuity deteriorates, the child suffers from increased fatigue, irritability, and it becomes difficult for him to withstand a heavy school load...
Do not allow children to ride a bicycle without a helmet. Not to mention snowboarding, skateboarding or snow scootering!
When the acute period of the disease passes, doctors recommend doing an electroencephalogram. But, even after making sure that the child no longer has any problems, do not erase the memory of the injury - a concussion - from consciousness forever, just as do not throw away the doctors’ opinions. Who knows how this event will come back to haunt us in the future. And convince your child to take care of his head in the future.
Symptoms of a concussion
General symptoms:
The victim complains of memory loss, dizziness, tinnitus, double vision, intense headache, nausea leading to vomiting, and fatigue. There is sleep disturbance, daytime sleepiness, irritability, and emotional lability. After the injury, confused speech appears, short-term memory loss (retrograde, anterograde amnesia), increased sensitivity to light, noise, balance is disturbed, uncoordinated movements, smell and taste are lost.
Symptoms that may bother you for a longer period:
- intense headache, may be migraine;
- difficulties with reading, remembering, writing;
- absent-mindedness, difficulty concentrating;
- nausea, vomiting;
- drowsiness, weakness;
- dizziness.
Brain concussion
Vomit
2657 05 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Concussion: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
A concussion is a functionally reversible form of closed craniocerebral injury without organic damage to the brain, resulting from a bruise, blow, and in rare cases as a result of a sudden movement of the head.
Causes of concussion
A concussion can result from a traffic accident, a fall, domestic, sports and work-related injuries, as well as injuries received as a result of street fights and collisions during public events, or exposure to a blast wave. Even a seemingly minor head injury can lead to a concussion. Thus, the fact of an injury may already indicate a possible concussion.
The mechanism of concussion is not precisely known. Most likely, the injury causes some problems with the functioning of the brain's nerve cells (neurons). It is assumed that there is a functional disconnection between the brain stem and hemispheres of the brain. It is believed that due to concussion, a temporary disruption of interneuronal connections occurs. A slight displacement of the layers of brain tissue may appear, their nutrition may deteriorate and the connection between some brain centers may be disrupted, which contributes to the development of functional disorders. In this case, macroscopic and histological changes in brain tissue are not detected.
Among all brain injuries, concussion ranks first in frequency. In most patients, recovery occurs within 1-2 weeks.
If the patient's condition continues to deteriorate over time, and more severe forms of traumatic brain injury have been ruled out, then it is necessary to look for other causes of the existing symptoms - psychological problems, mental illness, side effects of medications or other concomitant diseases.
Classification of the disease
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), concussion is coded S06.0. This nosology is one of the clinical forms of traumatic brain injury.
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and clinical symptoms, three degrees of concussion are distinguished.
Mild concussion. The victim does not have any impairment of consciousness, but disorientation, headache, dizziness, and nausea may occur during the first 20 minutes after the injury. Then general health returns to normal. A short-term increase in body temperature (37.1-38°C) is possible.
Moderate concussion. Although the victim does not lose consciousness, pathological symptoms such as headache, nausea, dizziness, and disorientation may be observed. All of them last more than twenty minutes. Short-term memory loss (amnesia) may occur, most often retrograde amnesia with the loss of several minutes of memories preceding the injury.
Severe concussion. It is necessarily accompanied by loss of consciousness for a short period of time, usually from several minutes to several hours. The victim does not remember what happened - retrograde amnesia develops. Pathological symptoms bother a person for 1-2 weeks after the injury (headache, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, disorientation, loss of appetite and sleep).
Symptoms of a concussion
Physical (somatic) symptoms:
- dizziness at rest, which intensifies when changing body position, turning or tilting the head - this is explained by impaired blood circulation in the vestibular apparatus;
- throbbing headache;
- nausea;
- one-time vomiting;
- rapid breathing, tachycardia;
- blurred vision or double vision;
- flashing of flies or stars before the eyes;
- imbalance;
- increased sensitivity to light or noise;
- ringing, noise in the ears.
Behavioral, emotional symptoms:
- drowsiness;
- increased fatigue or general weakness;
- irritability;
- depression;
- anxiety;
- excessive hours of sleep;
- difficulty falling asleep.
Cognitive symptoms:
- lethargy and impaired coordination of movements;
- short-term confusion;
- slow, incoherent speech;
- difficulty concentrating;
- difficulties remembering.
Diagnosis of a concussion
The diagnosis of a concussion is established on the basis of anamnesis, examination and the exclusion of more severe traumatic brain injury.
The doctor examines the patient's entire body for abrasions, bruises, joint deformities, changes in the shape of the chest and abdomen, and bleeding.
In the first hours after a concussion, the victim’s pupils are dilated or constricted - a traumatic brain injury of any severity leads to disruption of the nerve pathways responsible for the functioning of the eyes. The reaction of the pupils to light is normal. The victim complains of pain when moving the eyes to the sides; fine horizontal nystagmus (involuntary trembling movements of the eyeballs) is observed if the eyes are moved to the most extreme positions. Slight asymmetry of tendon reflexes and unsteadiness in the Romberg position (legs together, straight arms extended forward to a horizontal level, eyes closed) may be detected. The level of consciousness is assessed using the Glasgow Coma Scale and is 14-15 points.
The list of laboratory tests includes:
- general blood analysis;
Concussion grades
| Important! | |
| Even after a minor concussion, complications can occur (headaches, irritability, sleep disturbances, inability to concentrate). You need to see a doctor urgently. | |
✔ 1st degree concussion - slight fainting, feeling normal 20 minutes after the injury. ✔ 2nd degree concussion - disorientation lasts more than 20 minutes. ✔ 3rd degree concussion - loss of consciousness for a short period of time. The victim does not remember what happened.
First aid for concussion
Proper first aid for traumatic brain injury helps relieve unpleasant symptoms, prevent the development of complications, and shorten the period of treatment and recovery.
Basic rules for providing first aid for a concussion:
- The victim should not be lifted if he has fallen. If an injury has occurred and the patient is conscious, he is placed on a horizontal surface.
- The head is turned to the side so that vomit does not enter the respiratory tract.
- Loosen the tie, unbutton the collar buttons.
- Monitor breathing and pulse.
- Cold is applied to the site of the impact, which promotes vasoconstriction and prevents the development of swelling of brain tissue.
- If there are wound injuries, clean with hydrogen peroxide and cover with an aseptic bandage.
- An ambulance is called to transport the patient to the hospital. If the victim is conscious, you can take him to the hospital by taxi.
Symptoms of a concussion
You can suspect something is wrong immediately after an injury.
Symptoms:
• Paleness, sweating, weakness. • The victim has difficulty concentrating his gaze. • Headache, nausea and vomiting. • Slow reactions, inappropriate answers. • The victim has poor orientation in space and time. • No appetite. • Temperature increase. • Brief loss of consciousness. • Feeling of “brain fog” or unsteady legs. • Sleep disturbances (appear later) • Fatigue, feeling tired • Noticeable damage, nosebleeds.