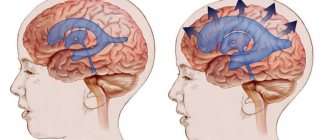
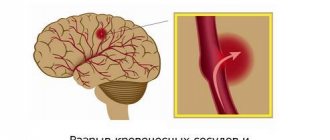
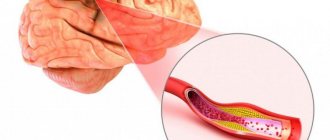
An aneurysm is a pathological condition in which the walls of arterial vessels are stretched. With a cerebral aneurysm, intracranial vessels are damaged.
The disease occurs in 2 types:
- course of the disease according to the type of tumor;
- course of the disease with rupture of the vessel.
The course of the disease according to the type of tumor is characterized by a symptom of compression. The aneurysm increases in size and damages the cranial nerves (oculomotor, trigeminal, facial). The course of the disease with rupture of the vessel is characterized by hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space or into the substance of the brain.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of complaints, anamnesis, clinical symptoms, computed tomography, MRI, and x-ray data. If there are indications for removal surgery, surgical treatment is performed: clipping and endovascular removal. Since 1999, the 10th revision of the classification of international diseases has been introduced in Russia. Aneurysm of cerebral vessels has a personal code according to ICD-10 I67.1.
Prevalence
The exact prevalence of the disease cannot be determined. Aneurysm often occurs without any specific or nonspecific symptoms. It is possible to detect such damage only after the death of a person at an autopsy; 50% of cases are found in this way.
The prevalence of aneurysm in the world is 10-15 people per 100,000 population.
After rupture of an artery into the subarachnoid space, the immediate mortality of patients is 15%. 25% of patients with ruptures will die within the first 2 days after the incident, and 50% within the next 3 months. An aneurysm can appear in a person or be present from birth. The rupture occurs at the advanced age of 60 years.
Disability and aneurysm
To assign a disability group, the patient will need to pass a commission. Typically, an aneurysm often causes patients to experience serious health problems. When assessing a person’s ability to work, doctors take into account many factors, including: the effectiveness of surgical treatment, the patient’s working conditions, the type of aneurysm, its location, etc. Depending on the condition of a particular patient, he may be assigned first (the person needs constant outside help ), second (poor performance remains) or third group of disability (a person is able to care for himself independently, he does not need outside care).
Author of the article:
Sokov Andrey Vladimirovich |
Neurologist Education: In 2005, she completed an internship at the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov and received a diploma in the specialty “Neurology”. In 2009, she completed her postgraduate studies in the specialty “Nervous Diseases”. Our authors
Causes
The main link in the pathogenesis of the disease is the thinning of the layers of the vascular wall. The wall cannot resist and adapt to blood pressure and begins to stretch. The stretching accelerates due to the filling of the cavity with blood, and a vortex blood flow is formed.
The reasons that trigger the process can be various diseases:
- inflammatory diseases of the membranes of the brain, meningitis lead to the destruction of the layers of the artery wall, it becomes less plastic;
- damage to the skull and brain;
- the presence of a focus of infection, which may not be located in the brain, for example, syphilis, infective endocarditis (the pathogen enters the skull with the general bloodstream);
- high blood pressure leads to thinning of arterial vessels;
- diseases with impaired immune response - systemic lupus erythematosus;
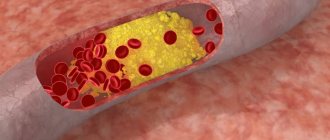
- dyslipidemia, which leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the body;
- neoplasms that can grow into the head arteries, but may not be located near the brain and damage the vascular wall with their decay products.
Preventive actions
- It is necessary to constantly monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- You should give up all bad habits.
- Nutrition must be correct.
- If possible, it is necessary to avoid stressful situations.
- If the patient has already been diagnosed with an aneurysm, then physical activity is contraindicated for him, and he also needs to take medications prescribed by the doctor. This measure is temporary and must be observed until the operation to remove the aneurysm is performed.
Clinical manifestations of aneurysm
The main symptoms are associated with the large size of the aneurysm. It begins to compress the brain tissue. Therefore, if the sizes are small, then there will be no signs of the disease. Diagnosis of an aneurysm in this case is random.
With rapid growth of the formation, symptoms appear:
- pressing severe headache;
- dysfunction of the brain, speech, vision, hearing;
- the appearance of spots before the eyes;
- dizziness that occurs at rest or with minor physical exertion;
- loss of memory, attention, concentration;
- vomiting, nausea, dysphagia;
- constant fatigue, fatigue;
- seizures.
The aneurysm may rupture. This is influenced by several reasons: a rapid increase in blood pressure, a stressful situation, injury, fever, nicotine or alcohol abuse.
When a rupture occurs, the person most often loses consciousness and becomes comatose. The severity of the disease depends on the size and location of the formation. If the aneurysm was in the subarachnoid space, then there will be a subarachnoid hematoma. Clinically, this will manifest itself as compression symptoms. If the location of the vascular protrusion was in the substance of the brain, a hemorrhagic stroke will occur. This is a more serious condition.
Symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm:
- severe headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- impairment of consciousness, speech, vision, hearing, coordination;
- convulsions.
At the first symptoms of a rupture, it is necessary to take the person to the hospital or call an ambulance. First aid consists of laying the patient down with an elevated head, ensuring a flow of fresh air, unbuttoning and removing all clothing that prevents the person from breathing, and checking the patency of the upper respiratory tract.
Diagnostics
The disease is often asymptomatic, so detecting a cerebral aneurysm is difficult. The doctor should think about the presence of this formation in the patient if he has severe headaches, dysfunction of brain structures, or seizures.
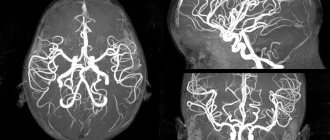
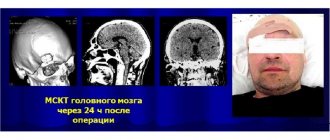
If suspected, the patient is referred to special instrumental research methods: CT, MRI, X-ray, electroencephalography.
The most important and informative methods are computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. In the pictures you can see the parameters of a cerebral aneurysm:
- dimensions;
- location;
- thrombus formation;
- hemodynamics inside the formation.
X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessels of the brain has a high diagnostic value. On an x-ray, you can see the thickness of the vascular wall, the presence of a thrombus in the lumen of the vessel, stretching of the intima and adventitia of the arteries.
X-ray allows for a differential diagnosis in the early stages of the disease and to distinguish a malignant neoplasm from a cerebral aneurysm. X-ray radiation, even in small doses, affects the body with the appearance of negative effects. For pregnant women, pediatric patients, and patients with other diseases, it is preferable to undergo CT and MRI.
Electroencephalography records the biological potentials of the brain and shows the activity of white and gray matter. If brain function abnormalities are detected by EEG results, the patient may be suspected of having a cerebral aneurysm and sent for additional studies, for example, MRI, where the diagnosis of I67.1 will be confirmed. Electroencephalography does not have negative effects on the human body.
Medicines
Photo: grud.guru
If a strange and sharp headache occurs, a person must immediately contact the nearest medical institution for qualified help. The disease is not treated with medication, but there is prevention and rehabilitation after surgery.
Surgical intervention is currently the only and most promising method of treating aneurysm. Treatment with special drugs is used only to stabilize the patient or in a situation where surgery is contraindicated or not possible at all.
Chemical drugs cannot eliminate an aneurysm; they only reduce the likelihood of vessel rupture by eliminating critical factors. Some medications are included in a complex of general therapy, which is aimed primarily at alleviating the symptoms of the initial pathology in patients. What vitamins and medications are taken for cerebral aneurysm?
Calcium channel blockers
The main representative of the nimodipine group. The chemical drug reliably blocks calcium channels in the muscle cells of the vascular walls. The vessels dilate. Blood circulation in the cerebral arteries is significantly improved. These drugs are simply irreplaceable in the prevention of dangerous arterial spasms.
Antacids
The principle of action is based on blocking H2 histamine receptors in the stomach. As a result, its acidity decreases and the secretion of gastric juice is significantly reduced. This group includes Ranitidine.
Anticonvulsants
Today, Fosphenytoin is the main representative of this group. The drugs cause reliable stabilization of membranes in nerve cells. Pathological nerve impulses noticeably slow down and do not spread.
Antiemetic drugs
Prochlorperazine is mainly used. The gag reflex is reduced by blocking postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic region of the brain.
Painkillers
Morphine is very effective for pain relief. The level of pain is reduced as a result of the effect on specific opioid receptors.
Antihypertensive drugs
Recently, three main drugs have been used: labetalol, captopril, hydralazine. Due to the effect on enzymes and receptors, the overall tone of the arteries is reduced and rupture is prevented.
Treatment of cerebral aneurysm
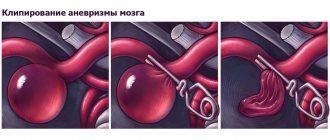
Treatment for such a vascular defect involves surgery and removal of the aneurysm. The operation is considered a mandatory procedure if the size of the protrusion reaches 7 mm. During the operation, the defect is removed and the integrity of the brain vessels is restored. There are several methods of surgical operations for this disease: clipping and endovascular removal.
Clipping
Clipping, a microsurgical operation, is the most commonly used method for treating unruptured aneurysms.
The essence of the operation is that the surgeon opens the skull, finds the location of the aneurysm and removes it. The operation carries great risks for the patient's life. The surgical intervention consists of several stages:
- Opening the integrity of the skull. The location of trepanation depends on where the vascular defect is located. Most often, trepanation is performed in the parieto-occipital region.
- Then the membranes of the brain are separated with a scalpel: hard, arachnoid, soft.
- The third step is to find the aneurysm and remove it. This stage is the most critical; the protrusion must not be allowed to rupture. Hemorrhage into the brain matter can lead to the death of the patient. To prevent rupture, a staple or clip is placed at the base of the defect, and the aneurysm is cut off and removed from the skull.
- The final stage is exit from the wound. It is necessary to apply stitches in the correct sequence.
Endovascular removal
Endovascular operations are performed only in high-tech centers. This manipulation requires special specialized equipment, as well as qualified specialists. The MEDSI clinic meets all the requirements for performing endovascular aneurysm removal surgery.
Craniotomy is not performed for this type of operation. The surgeon reaches the aneurysm through the great vessels. The catheter is inserted into the carotid or femoral artery and advanced to the brain. The operation is performed under the control of Doppler ultrasound or CT. The needle with the catheter is brought to the aneurysm, with the help of balloons it is switched off from the general blood flow, and the surgeon removes the aneurysm.
There is another way to separate the aneurysm from the general blood flow. A special chemical is released into the artery, which reaches the protrusion in the brain, forming emboli in the artery.
The highly specialized technology has a number of advantages:
- there is no need to make penetrating wounds of the skull, this contributes to less trauma to the patient;
- the postoperative period is halved;
- The patient does not require general anesthesia;
- if the aneurysm is located near the brain stem or in its depth, it can only be removed using endovascular surgery.
The operation may contain modifications and proprietary techniques.
Every operation carries a risk of complications. With endovascular removal of a cerebral aneurysm, complications are also possible:
- spasm of the arteries, ischemia of areas of the brain;
- rupture of protrusion of an iatrogenic nature;
- blood clot formation in an artery;
- death of a patient for an unknown reason during a removal operation.
Postoperative period
After surgery, the patient may experience consequences from removal of a cerebral aneurysm:
- noise in ears;
- loss of vision or loss of visual fields;
- incoordination;
- dizziness and frequent headaches;
- anxiety, malaise, increased irritability;
- fast fatiguability.
The most common problem in the postoperative period is thrombus formation. After applying a clip or suture to a vessel, atherosclerotic plaques may settle, which will close the lumen of the vessel and lead to cerebral ischemia.
Also, in the early period after surgery, the sutures may come apart, which threatens hemorrhage into the medulla or subarachnoid space.
Possible consequences of surgical treatment
After craniotomy, the patient may suffer from tinnitus, severe headaches, loss of hearing and vision, loss of coordination, etc. Moreover, these consequences can be either temporary or permanent.
The main danger of the endovascular technique for treating aneurysms is the formation of blood clots, as well as damage to the integrity of the vascular walls. However, most often such complications arise due to medical error, or due to emergency situations during surgery.
To minimize the development of serious complications in the long-term postoperative period, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- You cannot wash your hair after trepanation for a period of 14 days or more.
- Any sports that involve the possibility of a head injury should be prohibited.
- You should adhere to a dietary diet, completely avoid drinking alcohol and eating spicy foods.
- Smoking tobacco is prohibited.
- For six months or more after the operation, it is prohibited to visit steam rooms and saunas.
Rehabilitation process of patients
A patient who has suffered a rupture of a cerebral vascular protrusion requires rehabilitation. Methods used in the rehabilitation course:
- if the patient has muscle paralysis and is in a supine position, splints are used;
- carrying out massage procedures;
- rehabilitation using applications containing clay and ozokerite.
If there are indications for the use of physiotherapeutic procedures, they are included in the general rehabilitation course.