If you suspect a concussion or the diagnosis has already been established, you will need to be examined by a neurologist. If any studies have been previously performed, be sure to take their results for consultation, incl. the pictures themselves. If studies have not been performed, they will be recommended and performed based on the results of the examination.
- Symptoms of a concussion
- What to do if you have a head injury
- Concussion Screening
- Trauma to the cervical vertebrae due to concussion
- Nose injury due to head injury
- What happens if a concussion is left untreated?
- Treatment of concussion at the Echinacea Clinic
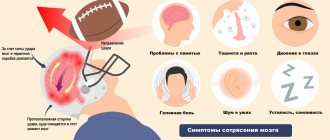
Symptoms of a concussion
Symptoms of a concussion (one or more of the following):
- Headache;
- agitation or drowsiness;
- Poor tolerance to bright light and loud sounds;
- Confusion;
- Dizziness and coordination problems;
- Loss of consciousness - from a few seconds to hours;
- Memory impairment (events immediately before the injury and/or immediately after the injury are usually lost from memory);
- Slurred speech;
- Noise in the ears, double vision;
- Convulsions;
- Different pupil sizes
- Disorientation in time, space, self, etc.
A poorly treated concussion is dangerous, first of all, because of its long-term consequences , which occur 6-18 months after the traumatic brain injury. If you doubt the presence/absence of a concussion, it is better to play it safe and clarify the situation with the help of a neurologist. In doubtful cases, we will clarify the patient’s condition using magnetic resonance imaging , brain evoked potential studies and other highly sensitive diagnostic methods.
Symptoms of concussion in children and adults
Below is a list of concussion symptoms in children.
- Brief loss of consciousness.
- Headache in older children or restless behavior in infants.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- A sleep disorder can manifest itself as either insomnia or hypersomnia.
- Temporary loss of vision is rare.
- Inability to focus vision.
- Children compensate for the injury for a long time, feel satisfactory, but then develop a rapid deterioration in their condition.
- Sometimes the temperature rises.
Watch a video about the symptoms of concussion in children:
In adults, clinical manifestations are generally similar . Below is a list of the main symptoms of a concussion in an adult.
- In the acute period, loss of consciousness lasts from several minutes to half an hour.
- Amnesia for events preceding the trauma or for those occurring immediately after.
- Headache.
- Nausea and single vomiting.
- Possible increase in temperature.
- Visual impairment in the form of temporary blindness.
- Lethargy, sweating, decreased performance, absent-mindedness.
- Nystagmus in the direction of damage.
Attention! If symptoms from the above lists appear, you must contact a traumatologist to diagnose the pathology and provide assistance.
Watch a video about the symptoms of a concussion in an adult:
What to do if you have a head injury
Immediately after an injury? If one or more of the listed symptoms appear after an injury, you must call an ambulance. If there are no strict indications for hospitalization or if you refuse hospitalization, you can get the necessary help in our clinic.
What help can you provide yourself?
- Lay the victim on his side; this will prevent inhalation of vomit even during loss of consciousness;
- Apply cold to the head to reduce the increase in brain swelling;
- Unfasten clothing that is blocking breathing, belt, trouser waistband;
- Stay close to the victim, because Possible vomiting, psychomotor agitation, and falling when trying to stand up.
After being discharged from the hospital.
If the patient remains unwell after discharge from the hospital, there is usually a persistent increase in intracranial pressure and/or damage to the joints and ligaments connecting the skull to the cervical spine. This is easy to establish using magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and x-ray examination of the cervical vertebrae. This will require a slight correction of the course of treatment (special exercises and medications), which usually leads to improvement within 1-2 weeks. The total planned course of medication after a concussion is at least two months.
Signs of a concussion in children
The main signs of a concussion are loss of consciousness for a short period of time, poor spatial orientation, headache, dizziness and weakness. In some cases, vision may deteriorate. Symptoms of a concussion in a child also depend on age.
Clinical manifestations of this condition in infants are as follows:
- frequent regurgitation (possible single vomiting);
- pale face;
- decreased appetite and refusal to eat;
- swelling of the fontanelle;
- poor sleep, moodiness, crying for no reason.
Signs of a concussion in children from three to six years of age: possible short-term loss of consciousness, nausea and vomiting (one-time), dizziness, bradycardia, pale skin, sweating. The child can show where it hurts and what exactly happened.
How does a concussion manifest in schoolchildren?
- obvious loss of consciousness (10 to 15 minutes);
- Strong headache;
- severe lack of coordination;
- constant nausea and vomiting;
- presence of neurological symptoms;
- The temperature during a concussion in children remains normal.
Please note that a characteristic feature of concussion in childhood is an increase in symptoms. If immediately after the injury the child’s condition can be described as quite satisfactory, then over time it noticeably worsens.
If you have a head injury, consult a specialist! Timely diagnosis and treatment will help avoid many complications and serious consequences. On our website you will find a list of doctors and diagnostic measures that a child may need after a concussion.
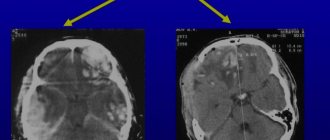
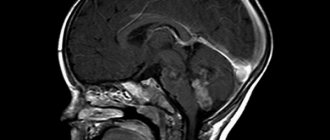
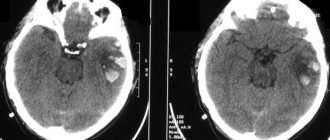
Concussion Screening
Why do you need a concussion evaluation? To promptly notice and treat possible dangerous conditions that often accompany a concussion:
- The release of blood into the membranes and substance of the brain;
- Fractures of the bones of the skull, orbits, face, cervical vertebrae;
- Hemorrhage in the orbital tissue and eyeball;
- Inner ear injury;
- Foci of death of brain matter.
MRI and X-ray computed tomography of the brain will show brain swelling, hemorrhage, traumatic changes in the brain, damage to the bones of the brain and facial skull.
To assess the mobility of the vertebrae after injury, an x-ray of the cervical spine with the head tilted forward and backward (fractures, dislocations and subluxations of the vertebrae are clearly visible).
Evoked potentials of the brain are the most accurate research method today, providing information about disturbances in the conduction of impulses in various parts of the brain (visual, auditory, sensory, motor pathways of the nervous system).
Can there be a fever with a concussion?
Let's consider whether the temperature can rise during a concussion. As can be seen from the symptoms, a rise in temperature can accompany a concussion .
To understand the mechanism of hyperthermia, you need to understand that in the human body there are clusters of nerve cells called nerve centers. They are part of the structure of the central nervous system. During a concussion, brain detritus does not form, but its structures can be displaced and damaged without cell death. The hypothalamus is the center of thermoregulation. When it is damaged, the function of body temperature control is impaired. The hypothalamus can be damaged as a result of edema.
There is another variant of the etiology of fever. Autonomic disorders caused by concussion. In this condition, the blood vessels dilate, which contributes to an increase in body temperature.
Hyperthermia is also . In this case, hypothermia occurs with subsequent expansion of the capillaries or the addition of an infectious pathology.
Another reason is the mental state of the patient. Doctors distinguish the concept of thermoneurosis, in which non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have no effect, but they manage to cope with the infectious version of hyperthermia.
Important! When hyperthermia occurs, there is always damage to the hypothalamus, which contains other important nerve centers. In the event of an increase in temperature, it is necessary to inform the doctor about this in order to diagnose the phenomenon, correct treatment or hospitalize it in specialized hospitals.
The temperature rises to a subfebrile level; neurologists note that it usually takes about a week to restore connections between neurons and normalize the temperature. At this time, the patient needs peace, absence of emotional excitement and sleep for at least 8 hours.
Trauma to the cervical vertebrae due to concussion
Injuries to the cervical vertebrae often go unrecognized because their symptoms are similar to those of a concussion.
The skull is firmly fixed to the first cervical vertebra by joints and ligaments. Therefore, the impact force acting on the skull is necessarily transmitted to the cervical vertebrae . Most often, with a concussion, the ligaments and joints connecting the cervical vertebrae are affected (traumatic subluxations). Fractures and dislocations of the cervical vertebrae are less common.
If, after hitting your head, you continue to experience dizziness, unsteadiness, pain in the back of your head or underneath it, pain in the eyes, visual disturbances, or pain when moving your neck for a long time, we will definitely perform an X-ray or MRI scan of the cervical vertebrae. Traumatic subluxations of the cervical vertebrae are usually easily removable ; their symptoms resolve within a few hours after reduction.
Why does the temperature rise during a concussion?
A common cause of fever during traumatic brain injury is the presence of an inflammatory process in the body that began even before the injury. If a person had a cold the day before, then after an injury the temperature during a concussion can rise to 38.5 or higher. But this is just a coincidence: the concussion itself does not cause the fever. In this case, the injury became only a catalyst for another inflammatory process.
But the concussion itself also causes fever. Although the human brain appears to be well protected, it is vulnerable to various mechanical damage. Gray matter is located in cerebral fluid, which protects it from impacts on the skull. With a strong impact, the brain approaches the bone tissue and hits it. As a result, brain structures are displaced, which leads to the appearance of microcracks in blood vessels, ruptures in capillaries and disruption of neural connections.
The human neural network is a collection of nerve cells (neurons) of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system. A neural network consists of neurons that are chemically or functionally connected to each other. One neuron is connected to many others using neural connections.
With a traumatic brain injury or concussion, the patient's temperature may rise. Neurologists say that its fluctuations in the range of 37-37.5 degrees are absolutely normal. During injury, the brain's thermoregulation center, the hypothalamus, can shift. And for neural connections to return to normal and the functioning of the thermoregulation center to improve, it takes at least a week. After this period of time, the indicator becomes normal - 36.6 degrees.
As for a significant increase in temperature - above 38 degrees, it can occur when the patient’s condition is serious. Fever is a sign of the development of infection in an open wound or hematoma, which has become an environment for the development of pathogenic bacteria. If you do not provide timely assistance to the victim and do not hospitalize him, then there is a risk of developing meningitis and a rapid rise in temperature to fatal levels of 41-42 degrees.
So, we found out whether there can be a high temperature with a concussion and bruise of the brain. It is worth understanding that its increase in such an injury does not always occur. It all depends on the general health of the victim, the individual characteristics of the body and the nature of the injury.
Read also
Neuralgia
Neuralgia is a disease that is a lesion of the peripheral nerve.
It manifests itself as a strong, burning, acute pain that is felt in the area of innervation of the affected (along) nerve. Types… Read more
Pelvic pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the muscles that form the pelvic floor and organs located in the small pelvis, caused by microtrauma, chronic deformation of the sacrococcygeal region due to anatomical…
More details
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is a brain lesion that occurs against the background of liver pathology and is caused by liver failure. There is acute hepatic encephalopathy, which occurs on…
More details
Myelitis
Myelitis is a neurological pathology characterized by inflammation of the gray and white matter of the spinal cord, which leads to damage to myelin (the substance that forms the sheath of nerve fibers) and the axon (the process...
More details
Myasthenia gravis
MYASTHENIAS – a disease associated with a disruption of the immune system, as a result of which antibodies are produced against the body’s own tissues involved in the transmission of nerve impulses, which...
More details