Pathologies in the formation and development of the neural tube begin at 2-4 weeks, when a woman does not even know that she is pregnant. Among the reasons leading to disruption of the formation of the neural tube are external factors: alcohol poisoning, smoking, maternal illness, taking medications, and unhealthy diet.
The defects of this organ are so severe that they are often incompatible with life. And it is impossible to detect an anomaly with the naked eye. The pathology of neural tube formation can only be detected by screening ultrasound of the fetus, so this study cannot be ignored.
| Price for screening ultrasound in our clinic | |
| Recording the study on DVD + PHOTO - AS A GIFT! | |
| 1st trimester: Ultrasound during pregnancy with early diagnosis of congenital malformation and calculation of the risk of Down syndrome (11 weeks 6 days – 13 weeks and 6 days), one fetus, using 3D/4D reconstruction | 2000 |
| 1st trimester: combined test with calculation of the risk of Down syndrome + blood sampling for biochemical screening (PAPP-A and free beta-CG) and fetal ultrasound (11 weeks 6 days – 13 weeks and 6 days), one fetus using 3D/4D reconstruction | 3300 |
| 2nd trimester: Ultrasound during pregnancy (18 weeks 0 days – 21 weeks and 6 days), one fetus, using 3D/4D reconstruction | 3100 |
| 3rd trimester: Ultrasound during pregnancy (30 weeks 0 days – 34 weeks and 6 days), one fetus, using 3D/4D reconstruction + Dopplerometry | 3600 |
Anencephaly
The content of the article
Anencephaly is the complete or partial absence of the cerebral hemispheres, and in some cases, the skull bones and soft tissues. Occurs in 1 case out of 10,000, the anomaly is accompanied by other disorders - cleft lip or hard palate, absence of the pituitary gland, spina bifida.
This happens if for some reason the anterior neuropore does not close at 3-4 weeks of pregnancy. Because of this, the frontal extensions of the neural tube, from which the cerebral hemispheres would later begin to develop, do not develop.
Instead of the “gray matter” rich in neurons, fibrous tissue is formed, in which single nerve cells, cystic formations and blood vessels are present. In 71% of cases, the fetus lacks the fronto-occipital zone and the spinal column, in 24% - the occipital lobe with the spinal column, and in 5% - the temporo-parietal zone. The baby's body does not have any abnormalities.
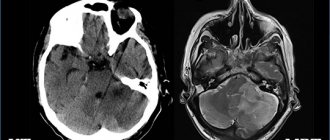
On ultrasound, anencephaly is diagnosed at 11-12 weeks of pregnancy, the accuracy is 96%.
The pathology is characterized by the following echo signs:
- the skull bones are not visualized;
- soft tissues of the brain are anechoic;
- in the vascular system of the brain there is a malformation - an incorrect connection of blood vessels, veins and arteries;
- maternal polyhydramnios (excess amniotic fluid).
The diagnosis of anencephaly is not limited to ultrasound examination alone. When there is a neural tube defect, the hormone alpha-fetoprotein increases in a woman’s blood. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, she is advised to stop the pregnancy, because if the newborn does not have a brain, the lungs, heart, and kidneys will fail after a while.
Ultrasound diagnosis is the primary, but not the main method of diagnosis. If neural tube pathology is detected during an ultrasound examination, the woman is prescribed amniocentesis - taking amniotic fluid from the amniotic sac under the control of a transabdominal sensor for the purpose of laboratory testing.
If a high concentration of alpha-fetoprotein and the enzyme acetylcholinesterase is detected, the pregnant woman is sent for MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Unlike ultrasound, this method allows you to see the fetal brain in a 4D projection, magnifying the image several times.
The sooner a diagnosis is made, the sooner a woman can terminate her pregnancy. It makes no sense to preserve it with such a diagnosis, because the baby will live for a maximum of a week.
Causes and consequences of abnormal development of the neural tube in the fetus
The formation of a fetal tube is a complex and multifaceted process; failure in at least one element leads to severe defects in the development of the organ. They affect the child’s brain and his spine, because the connection between the neural tube and notochord is very tight.
Defects are formed in situations where the formation of the neural tube does not occur completely or does not close. This may cause:
- Spina bifida. It is formed at the base of the column, where a hole is formed through which the spinal cord will exit.
- Anencephaly is formed in the upper part of the neural tube and leads to the immaturity of some elements of the brain and the development of the fetal skull.
- Chiari malformation is characterized by “leakage” of brain tissue into the spinal canal.
- Encephalocele manifests itself as partial protrusion of the brain and membranes through the cranial bones.
The reasons for the formation of such defects have not yet been precisely established. At some point, ontogenesis fails, which subsequently leads to disruption of the entire system. Since the tube is laid in the late gastrula and this stage is completed on the 25th day, its mechanism has not been well studied.
It is known that the likelihood of defects is influenced by hereditary factors and diseases affecting the nervous system.
It influences the formation of the problem and environmental conditions, as well as the condition of the mother. Negative aspects that increase the risk of neural tube defects include:
- radiation exposure;
- arsenic or lead poisoning;
- prolonged fever in a woman in the initial stages of pregnancy;
- lack of nutrition;
- viral infections;
- vitamin A hypervitaminosis;
- excess weight or diabetes in the mother;
- lack of folic acid in a pregnant woman;
- a woman taking certain medications.
The condition of the mother is the first factor that affects the formation of a tube in the fetus. If a woman is in an environmentally unfavorable area, where harmful substances (pesticides, exhaust gases, petroleum products, etc.) can enter the air and water, she inhales them, and together with the blood, these products enter the baby’s body.
For an adult, the risk is lower, since his body is already formed and is able to process most hazardous substances. In the body of the embryo, the defense mechanisms do not yet work and any harmful effect can disrupt the course of processes and lead to the development of pathology, including changes in the condition of the tube.
Poor nutrition also has a negative effect. A lack of nutrients leads to disruption of the processes of organ formation, as well as an excess of biologically active components such as vitamins.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a fetal developmental abnormality in which the number of ventricles in the brain increases. Normally, there should be four of them, and through them the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid occurs. When the production or absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the circulatory system is disrupted, fluid accumulates in the ventricles, expanding them.
The cause of the pathology is the improper development of the neural tube of the embryo. This happens in the early stages of up to 4 weeks, and in 20% of cases the cause is intrauterine infections.
With hydrocephalus, the accumulated cerebrospinal fluid stretches the ventricles, putting pressure on the brain. As a result, the skull expands and the head takes on an irregular shape.
In the early stages, the defect is difficult to notice; it is detected starting from the 10th week of pregnancy. On ultrasound, the expansion of the frontal lobes is noticeable, the fontanelle becomes more convex, and the head is disproportionately large.
The gynecologist, conducting a screening ultrasound, takes measurements between the temples along the superciliary line (BPR) and, starting from the 16th week, measures the distance between the forehead and the back of the head (LZR). Comparing the results with normal indicators characteristic of a given stage of pregnancy, the doctor makes other measurements.
An increase in the indicators of BPR and LZR does not always indicate pathology. It is quite possible that the baby himself is large if the other measurements of his body also exceed the norm. Only if the head parameters are significantly increased with normal body parameters, the doctor diagnoses “hydrocephalus”.
It is head measurements that make it possible to distinguish hydrocephalus from a congenital increase in the size of the cerebral ventricles. With this disease, there is no intracranial pressure, so the size of the skull is normal.
Hydrocephalus is often accompanied by other developmental defects. Ultrasound shows smoothing of the convolutions of the brain, abnormal formation of blood vessels, anomalies in various parts of the spinal cord, and an increase in the hemispheric fissure.
Another sign of hydrocephalus in the fetus is uterine hypertonicity throughout pregnancy. If the cause of the development of the pathology is an infection, then the woman will be worried about feeling unwell.
The specialist assesses the degree of development of hydrocephalus and gives recommendations and forecasts regarding the baby’s future. In some cases, the abnormality of the neural tube in the fetus is so pronounced that treatment of the child will be ineffective. In this case, the woman is offered an abortion. However, the opposite situation happens, and after treatment the baby will lead a full life.
Microcephaly
Microcephaly is a complex pathology of the brain, expressed in a decrease in the size of the organ in the fetus. The cause of underdevelopment of the brain is a violation of the division of nerve cells at the stage of formation of the neural tube of the embryo.
The pathology is provoked by several factors: in 40% it develops against the background of cytomegalovirus in the mother; there is also a hereditary form of Giacomini-Penrose-Beck disease.
Microcephaly is rare: 1 case in 5,000, and is often accompanied by other disorders of the central nervous system such as lisencephaly (impaired formation of the cerebral cortex), microgyria (small size of the cerebral convolutions), cerebellar anomaly, and underdevelopment of the spinal cord.
In terms of diagnosis, microcephaly is the most difficult defect. The ultrasound examination is based on the criterion of the ratio of the length of the femur and the circumference of the fetal head, which should not be less than 2.5. However, interpretation is complicated by the fact that the exact gestational age is not always known. False-positive and false-negative results may be due to the small size of the fetus or impaired bone growth in other pathologies.
The accuracy of ultrasound diagnostics for microcephaly is 67.4%, and in 85% of cases the diagnosis is made after 22 weeks of pregnancy. Starting from 2 weeks, the structure of the skull can be easily seen on ultrasound. With microcephaly, it has an irregular shape, the forehead is sloping, the ears are low, and the jaws are underdeveloped. There is also dilatation of the cerebral ventricles.
In addition, in 60% of cases, the fetus is diagnosed with other disorders of the central nervous system, diseases of the kidneys, heart and other internal organs.
Diagnosis of microcephaly is always complex. If a pathology is suspected, a woman's amniotic fluid is analyzed and the fetus is karyotyped. Only after a thorough examination is the woman told about the diagnosis, and she herself decides what to do next.
Types of pathology
Spina bifida
The most common type of defect. At the base of the spine, in this area there is a partial protrusion of the spinal cord. With extensive non-union, over time, problems arise with trophism and sensitivity of the skin, improper formation of the feet, pathology of posture, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Spinal cysts and hernias
- Meningocele is a lesion of the membranes, a protrusion of the dura mater.
- Meningoradiculocele - the opening enters the meninges and spinal nerves. Paresis or paralysis develops.
- Meningomyelocele – the spinal cord along with roots and membranes emerges into the hernia. The child's condition is serious, there are no motor functions, and the functioning of the pelvic organs is disrupted.
Anencephaly
Develops in the upper part of the tube; parts of the brain are not fully formed. The anomaly is more common in girls. The pathology is incompatible with life.
Encephalocele
There is partial protrusion of the brain and membranes through the bones of the skull. Rarely seen.
Chiari malformation
The rarest disorder in which brain tissue leaks into the spinal canal.
The main symptoms of the disorders are physiological deformation, paralysis, convulsions, developmental delay.
Encephalocele
Encephalocele is a type of brain hernia in which the meninges extend beyond the skull through cranial defects. The pathology occurs due to non-separation of the end of the neural tube in the 4th week of pregnancy. As a result, a polypoid mass forms in the fetus: in 75% of cases it is localized on the back of the head or the vault of the skull, and in 25% it protrudes through the facial area.
On ultrasound, encephalocele is diagnosed at the 11-12th week of pregnancy, when ossification of the skull bones occurs. The monitor screen shows a low-echoic formation outside the cranial vault. It consists of medulla, and with meningocele, cerebrospinal fluid is also visible.
In some cases (with encephalocystomeningocele), part of the cerebral ventricle is visualized inside the hernia. In addition, the fetus has microcephaly, hydrocephalus and other intrauterine defects. Typically, with encephalocele, a woman experiences oligohydramnios, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Other signs of fetal encephalocele include:
- wide bridge of nose;
- asymmetrically located eye sockets;
- deformation of the skull.
In early pregnancy, an increase in alpha-fetoprotein is observed.
Ultrasound diagnostics up to 24 weeks of pregnancy is 87% effective, however, with the basal form of the pathology, making a diagnosis will be difficult. In most cases, a woman is recommended to terminate her pregnancy due to severe defects in the child and the impossibility of his rehabilitation in the future.
Among the causes of cerebral hernia are:
- toxic effects on the fetus (smoking, alcohol, drugs);
- taking potent medications;
- infections, mostly hidden;
- viruses (flu, rubella, hepatitis) in the mother;
- work in heavy production;
- genetic factor.
In some cases, if the hernia is small, the baby undergoes surgery during the first 3 years of life. But even with a favorable outcome, he will lag somewhat behind his peers in psycho-emotional development. If the polyp-like growth is not removed, it will attract infections and cause discomfort. In this case, the baby dies within 1 year of life.
Causes
Neural tube defects are structural anomalies caused by delayed or incomplete closure. Formed in the embryonic period.
Why does pathology develop:
- hereditary factor;
- Patau, Turner, Edwards syndrome;
- radioactive radiation, poisoning with arsenic, lead, pesticides;
- taking anti-epileptic drugs shortly before or immediately after conception;
- unbalanced diet, vitamin A hypervitaminosis;
- increased spinal pressure in the fetus;
- viral diseases in pregnant women, rubella is especially dangerous;
- significant and prolonged increase in temperature in the early stages;
- obesity caused by diabetes.
But the main cause is considered to be folic acid deficiency during pregnancy.