Hemangioma
– a common benign tumor of vascular tissue. Outwardly it resembles a bright crimson or red formation that rises above the skin. Its surface is lumpy and uneven, sometimes it heats up on its own for a short period of time.
Hemangioma in adults cannot provoke any serious disturbances in the functioning of the body, but everything depends on the location of the growth and its size. Hemangioma located on internal organs, such as the kidneys or liver, can cause mechanical compression, which leads to impaired functional activity.
Where does hemangioma appear?
In 80% of cases, hemangioma in adults, a photo of which you can easily find on the Internet, occurs in the form of a single structure; in the remaining cases, several such elements are observed in one place at once. Very rarely, the lesion occurs in the area around the ear.
There are cases when hemangioma occurs on the lip of adults, which causes a lot of inconvenience and discomfort. Also, such lesions can be located in the genital area. This course of the disease is considered the most dangerous, as it is often accompanied by bleeding, infection, and ulceration. Most often, this lesion occurs in the neck or head:
- On the eyelids and around the eyes.
- On the cheeks: both on the outer and inner sides.
- In the region of the nose.
- Near the hairline.
Often vascular hemangioma in adults spreads throughout the body. It can also affect internal organs, which can be detected by ultrasound and computed tomography. If you begin to notice that a hemangioma has begun to grow on your skin, consult a doctor immediately. The sooner you start treatment, the easier and faster it is to get rid of the problem.
Hemangioma cavernous
Cavernous hemangioma is a congenital benign formation, externally representing a sharply limited vascular tumor that tends to grow rapidly. Cavernous hemangioma consists of mature vessels and various cavities (cavities) filled with blood. Types of cavernous hemangioma:
- Branched hemangioma. It is characterized by the appearance of soft nodular formations located mainly in the inner layer of the skin. The nodes are interconnected by dilated branched vessels, can be of both venous and arterial origin, and are prone to grow into deep-lying tissues. Hemangiomas are found in the soft tissues of the face, head and lower extremities, sometimes reaching quite large sizes.
- Pineal hemangioma. It is characterized by the formation on the skin (in the forehead, nose, lips, eyelids or ears) of individual dark red tumor-like elements of various sizes.
Groups and risk factors for hemangioma In girls, this type of hemangiomas occurs twice as often as in boys. Risk factors are:
- presence of cases of tumor development in the family;
- hormonal disorders in the mother during pregnancy.
Causes of cavernous hemangioma Impaired vascular development in the prenatal period.
Symptoms of cavernous hemangioma
- A soft tumor of bright color, the surface is smooth or lumpy, the color ranges from cherry to bluish, located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue (usually in the head, face and neck);
- when the tumor is compressed due to the outflow of blood, its color turns pale and its size decreases;
- when screaming or coughing, hemangiomas can increase in size;
- if the formation is located deep enough, the skin over the formation may be unchanged;
- aggressive rapid growth in the first weeks of life, ending by the first year.
Diagnosis of cavernous hemangioma
- Angiography;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT) – for damage to the jaw bones;
- tissue puncture followed by morphological examination.
Treatment of cavernous hemangioma
- Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where it is possible to remove the entire tumor within healthy tissue without cosmetic damage.
- Conservative therapy. Sclerosing (shrinking) therapy is carried out using the method of cauterizing the hemangioma with 70% alcohol. It is advisable to use it in children only for small cavernous hemangiomas.
- Hormone therapy is a method of treating complex hemangiomas.
- Soft x-ray irradiation – treatment of extensive facial hemangiomas.
Prognosis The course of hemangiomas is benign in most cases. Cavernous hemangiomas do not regress. Cosmetic defects after treatment are usually absent or insignificant. Complications: massive bleeding, development of inflammation of the vessels from which the tumor is formed.
Prevention of cavernous hemangioma
- If there are cases of hemangioma in the family, consult a doctor during pregnancy;
- monitoring the level of hormones in the blood.
Created using materials:
- Gropyanov A. M. On the issue of cavernous liver surgery // Clinical medicine. – 1959. – No. 11. – P. 127–129.
- Melamud M. Ya., Fishbein A. V. Liver hemangiomas // Clinical medicine. – 1983. – No. 8. – P. 16–19.
- Slynko E. I. Surgical treatment of vascular tumors of the spine and spinal cord // Ukrainian Neurosurgical Journal. – 2000. – No. 1 (9). – pp. 55–64.
Causes
To date, doctors have not been able to determine the exact cause of why hemangioma occurs in adults on the arm or any other part of the body.
The nature of the congenital form of the lesion is as follows: during the period of growth, the body produces an excessive amount of connective tissue, which is why it has to become denser. The luminaries of modern medicine do not have the necessary equipment that would allow them to identify hemangioma on the body in adults in the early stages, a photo of which you can easily find on the Internet.
A hemangioma on the leg of an adult, which manifests itself as a bright red tumor, will not grow over time or torment you with unpleasant sensations. It is not known for certain what causes an adult body to manifest such an ailment on the skin. Common causes of hemangioma in the adult population include:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Environmental influence.
- Diseases of internal organs, in particular the endocrine system.
- Disorders in the cardiovascular system.
- Exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet radiation.
Reasons for development
The direct causes of the development of meningiomas have not been reliably studied to date. However, there are a number of factors that can provoke their occurrence:
- Most often, brain meningioma is diagnosed in mature patients, after 40 years;
- It is known that women are more susceptible to developing brain meningioma than men. This is due to the fact that tumor growth is greatly influenced by female sex hormones;
- the occurrence of various tumors in the brain is often associated with high doses of ionizing radiation;
- the influence of such negative factors as chemicals and toxic substances, trauma, exposure to a mobile phone and others;
- A significant role in the development of meningioma belongs to genetic diseases, one of which is neurofibromatosis type 2, which causes multiple malignant meningiomas.
Symptoms of hemangioma in adults
Hemangioma of the skin is quite difficult to recognize in the initial stages. At first, you will be able to notice how your skin begins to gradually turn red, small spots of irregular shape appear on it, which can be easily picked out. Over time, they unite into one large formation with a large tumor point in the center, from which all the small blood capillaries diverge.
It should be noted that hemangioma on the head of an adult develops quite quickly; it grows to its peak state in 2-3 weeks.
There are several types of hemangiomas, which are differentiated by location and manifestation of symptoms. Most often, simple, cavernous, combined and mixed types are distinguished. Only a qualified specialist can determine what has affected your skin. Sometimes a hemangioma can occupy significant areas on the human body, causing serious discomfort.
Classification of hemangioblastomas
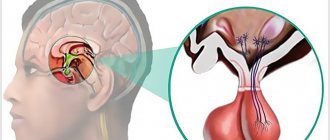
Macroscopically, brain hemangioblastomas are divided into 4 types:
- solid formation - a soft-tissue purple node enclosed in a membrane, on a cut it appears as a spongy mass (occurs in 30% of cases);
- large smooth-walled cyst - a cystic formation with a cavity containing a yellowish transparent liquid, on the wall of which a small nodule (mural nodulus) of the tumor is identified (incidence rate - 60%);
- mixed type - a neoplasm characterized by the presence of a solid node, within which numerous small cysts are found (diagnosed in 4%);
- simple cyst - an ordinary smooth-walled cyst that does not contain a mural node (observed in 6%).
The predominant localization of hemangioblastomas is the posterior cranial fossa (PCF). Typical lesion sites:
- left and right cerebellar hemispheres (85%);
- IV ventricle (6%);
- cerebellar vermis (5%);
- brainstem (3%);
- cerebellopontine angle (1%).
According to the latest data, there is not a single report of the transformation of hemangioblastomas into a malignant form.
Treatment
Hemangioma on the skin does not pose any danger to the body other than aesthetic discomfort. However, if such a formation begins to grow, it can lead to some negative consequences, such as infection, blood loss, impaired blood clotting, and an effect on some internal organs. In rare cases, tumors disappear on their own; in others, measures need to be taken.
At the Healthy Skin Center, experienced specialists using modern diagnostic methods will easily select for you an effective and safe treatment that will save you from hemangioma on the skin forever.
At the Healthy Skin Center, you will be offered a radio wave surgery method to get rid of hemangioma. This effect allows you to achieve both clinical and cosmetic effects. After exposure to a demato-oncological magnifying glass, no scars or cicatrices remain on the skin. Under the influence of high-frequency radiation, the affected cells completely evaporate, which protects the treated area of skin from the subsequent development of hemangioma.
Contact the Healthy Skin Center, they will always help you.
Neurosurgical treatment of GBM
Intracranial hemangioblastomas undergo standard surgical removal. If the tumor is inoperable (mainly with lesions of the brain stem), radiation therapy or non-invasive radiosurgical removal (preferred) is prescribed. Radiosurgery produces significantly better results compared to conventional radiation therapy. In addition, modern stereotactic radiosurgery techniques rarely cause side effects and do not require a long course of radiation (often just 1-2 sessions are sufficient).
Gamma Knife
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor. Depending on the damage to the vessels, capillary, arterial, arteriovenous and cavernous forms are distinguished.
- Capillary hemangioma
- Arterial hemangioma
- Arteriovenous hemangioma
- Cavernous hemangioma
Capillary
– presented in the form of spots, slightly protruding above the skin level, of varying diameters, from bright pink to bluish-purple. A variant is telangiectasias (“spider veins”), in which rays – stripes, like cobwebs – diverge from the spot.
Arterial
– is a spot from pale to deep pink, clearly demarcated, with superficial localization a pulsation is detected.
Arteriovenous
The form is distinguished by a large affected area (up to 10 cm in diameter), superficial location, bluish-purple color, tortuous bundles of blood vessels, thinning and easy bleeding.
Cavernous
– develops in newborns and increases as the child grows. It is presented in the form of a single formation, which has a lobular structure and protrudes above the skin level like a “mulberry”, bluish-purple in color. There is no favorite localization; it can spontaneously regress.
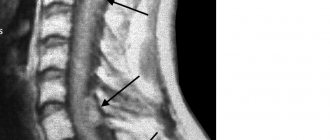
Spinal hemangioma
Hemangiomas are the most common benign vertebral tumors. They occur in every tenth adult. In most cases, the thoracic and lumbar spine are affected, very rarely the cervical spine. As with localization in the liver, most often such neoplasms do not pose a threat and do not cause any symptoms. If they are discovered, it is by chance, during an examination for other reasons. Many people spend their whole lives not even realizing that they have such a pathology.
If a vertebral hemangioma still makes itself felt, then the typical manifestation of the disease is back or lower back pain, depending on the level of the lesion. If the tumor protrudes beyond the vertebra or leads to a decrease in its height, and because of this the spinal cord and nerve roots are compressed, then more serious symptoms occur: severe pain in the spine, which can spread to the arm or leg, weakness, numbness in certain parts body, impaired control of the rectum and bladder.
Sometimes serious complications arise, such as compression fractures of the vertebrae, compression of the spinal cord as a result of hemorrhage from the hemangioma.
Spinal hemangioma, which causes pain and other symptoms, requires treatment. Different methods are used:
- Embolization. An embolic drug consisting of microscopic particles is injected into the blood vessel feeding the hemangioma. It blocks the lumen of small vessels, disrupts the blood flow to the tumor and causes its death.
- Percutaneous puncture vertebroplasty. During this minimally invasive procedure, special cement is injected into the cavity inside the vertebra through a needle. For a compression fracture, a miniature balloon can be inserted into the cavity and inflated with fluid to restore the normal configuration of the vertebral body.
- Surgical removal of tumor and damaged vertebral tissue. This method is the most traumatic, and is currently rarely used.
- When a significant part of a vertebra is destroyed, bone grafts, screws, and metal rods are used to stabilize the spinal column.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Diagnosis and treatment of hemangioma
Diagnostics: Skin ultrasound, deep dermatoscopy, cytology.
Treatment: removal using radiosurgery.
In our center, tumor removal is performed by a dermato-oncologist using radio wave surgery under local anesthesia.
In order to remove the formation more efficiently, the doctor uses a dermato-oncological magnifying glass, which allows for more detailed and complete removal of skin tumors without leaving pathological cells in the wound. Therefore, after removal, we can say with complete confidence that the formation has been completely removed and you will no longer have it. Read more about tumor removal in our center...
The cost of removing a single hemangioma starts from 900 rubles.
How to recognize cavernous hemangioma
Parents can guess that a child has a vascular tumor by the appearance of the formation. It almost always has a round shape. The color of the formation depends on the depth of its location. If the hemangioma is localized in the upper layers of the skin, it has a red or purple color. With deeper subcutaneous formations, typical cyanosis of the skin occurs.
If you feel the vascular tumor, it may shrink. This metamorphosis is due to the fact that when pressed, blood flows out from the vessels of the formation. If the child has a cough, the formation, on the contrary, increases in size and becomes brighter.
Removal of a hemangioma is necessary, if only because such a tumor tends to grow. In some babies it reaches simply gigantic proportions. We recommend that you do not delay your visit to the doctor, because the smaller the formation, the easier it will be to remove it with minimal discomfort for the child.
Removal of hemangiomas
Hemangioma is a benign disease that forms from the internal tissue of capillaries, arteries and veins.
The favorite place for localization of hemangioma is the skin of the face, neck, scalp, and less often - on the body and limbs. This pathology most often develops in newborns and progresses quite quickly, reaching significant sizes. In adults, the disease rarely develops, and more often it is a hemangioma that was not removed in childhood.
Rice. Typical types of hemangiomas and their localization
Body hemangioma
Single hemangiomas of the body
Neck hemangioma
Hemangioma of the scalp
Hemangioma of the lip
Types of hemangiomas
- Arachnids - represent an expansion of small vessels. In the center of the mesh there is a small red nodule, from which convoluted capillaries radiate along the radius - telangiectasia.
- Capillary tumors are vascular tumors that appear almost immediately after birth; they look like a nodule or raised red spot on the skin.
- Venous - soft dark blue papules , which are most often found in the face and ears in patients aged 50 years.
Removal of hemangiomas in children
Skin hemangioma in children , as a rule, does not require therapy. The reason is the possible self-removal of the stain after a few years. Often the defect disappears by the age of 5-10 years. If the lump grows rapidly and brings discomfort to the child, then it is recommended to remove it at any age.
Hemangiomas in adults
very rarely disappear without therapy. The need for removal is due to:
- traumatization of hemangioma (can cause significant blood loss)
- with possible infection of the hemangioma due to traumatization of the tumor or scratching
- impairment of blood clotting as a result of vascular damage
Benefits of laser hemangioma removal
The laser beam has unique characteristics. It is able to penetrate to any depth, target unnecessary cells and destroy them without affecting neighboring healthy structures. The use of laser is indicated for almost all types of vascular tumors, since this method:
- It is quick, non-invasive and painless (local anesthesia is sometimes used).
- Does not lead to scarring or tissue pigmentation.
- Does not require a long rehabilitation period.
Cost of hemangiomas removal at the Medservice clinic
| NAME | PRICE |
| Consultation and dermatoscopy | For free |
| Removal of hemangioma on the face: | |
| up to 3 mm per 1 piece. | 450 rub. |
| more than 3 mm per 1 mm diameter | 480 rub. |
| Removal of hemangioma on the body: | |
| up to 3 mm per 1 piece. | 350 rub. |
| more than 3 mm per 1 mm | 380 rub. |
Call online Make an appointment
Diagnostics
Siemens Magnetom Sola at the Spizhenko Clinic
Cavernous malformations can be asymptomatic for a long time. However, until the tumor reaches a significant size and begins to put pressure on the brain tissue, causing headaches and other neurological complications.
But often the discovery of a cavernoma can be accidental when a patient consults a specialist with complaints of another neurological disease. The main method for diagnosing cavernoma is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), in the images of which vascular neoplasms of the brain are clearly visible.