Signs
Symptoms directly depend on which part of the brain the tumor is located in and how large it is. Pain begins to bother you if the tumor is growing or has already grown to an impressive size. The functioning of certain organs may also be disrupted.
Can appear:
- headache;
- problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- epileptic seizures;
- paralysis;
- lack of coordination;
- swallowing disorder;
- paralysis;
- breathing disorder.
Such a cyst is removed only as a last resort, when there are clear indications and the symptoms are life-threatening and disrupt the most important functions of the body. If the cavity grows rapidly, emotional and mental disorders, convulsions, and seizures appear; these are also clear indications for surgical intervention.
Types of brain cysts
K»Ã°ÃÂÃÂøÃÂøúðÃÂøàðÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýààúøÃÂà÷ðòøÃÂøÃÂ:
- Ã] ²²Pa · ãâtely · ãâte ¸.
- ÃÂàÃÂÃÂúÃÂÃÂÂÃÂ: ÿÃÂþÃÂÃÂþù (ø÷ úûõÃÂà¾Ãº ðÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýþù þñþûþÃÂÃºà ¸) øûø ÃÂûþöýþù (ÃÂüõÃÂø ð ÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýÃÂàúûõþú ø ôÃÂÃÂà ³Ã¸Ã ÃÂúðýõù).
- ÃÂàÃÂÃÂõÿõýø ÃÂð÷òøÃÂøÃÂ: ÿþûþÃÂÃÂà ¸, ÃÂòõûøÃÂøòðÃÂÃÂøõÃÂàò ÃÂð÷üõÃÂð àøûø ÿÃÂõúÃÂà°ÃÂøòÃÂøõ ÃÂþÃÂÃÂ.
Editorial: What is lacunar ischemic stroke
ÃÂÃÂòðõàø ÿþ üõÃÂÃÂàþñÃÂð÷þòðý øÃÂ: ðÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýðà(ýð ÿþòõàÃÂýþÃÂÃÂø üþ÷óð), ÃÂõÃÂÃÂþÃÂõà»ÃµÃ±ÃµÃ»Ã»ÃÂÃÂýðà(ò óûÃÂñøýõ ÃÂõÃÂþà³Ã¾ üþ÷óþòþóþ òõÃÂõÃÂÃÂòð).
ÃÂõÃÂÃÂþÿþûþöõýøõ úøÃÂàò óþû þòýþü üþ÷óõ:
- ÷ðôýÃÂàÃÂõÃÂõÿýðàÃÂüúð;
- ÿÃÂðòðàòøÃÂþÃÂýðàôþûÃÂ;
- ûõòðàòøÃÂþÃÂýðàôþûÃÂ;
- ÃÂõûàüõöôàÿþûÃÂÃÂðÃÂøÃÂüø;
- ûþñýðàÃÂðÃÂÃÂÃÂ;
- ÃÂõüõýýðàÃÂðÃÂÃÂÃÂ;
- üþ÷öõÃÂþú;
- ÃÂøÃÂúþòøôýðàöõûõ÷ð.
ÃÂÃÂðÃÂýþøôðûÃÂýðàúøÃÂÃÂð üþöõà A ÷óþòþü úðýðûõ, ýð úþýÃÂõ ýõà VALUE The úÃÂõÃÂÃÂÃÂð.
Kinds
Cystic cavities are differentiated according to the following characteristics:
- Localization. The arachnoid cyst of the brain is located between the soft tissue and the membrane. Cerebral - directly in the brain tissue. An arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst rarely causes symptoms. This is explained by the fact that the subarachnoid cyst does not directly affect the brain itself, but is located between it and the outer membrane.
- Location. A lacunar cyst develops in the frontal lobes. In the pineal body - pineal. There may also be a cyst of the posterior cranial fossa, left temporal lobe, right, etc. A retrocerebellar cyst is located in the cerebellum. In severe cases, neoplasms can affect the entire hemisphere (hemisphere). This can cause critical conditions. Damage to the occipital, frontal region, and pyrineural septum is dangerous. Sometimes the spinal cord may be affected.
- Etiology. Takes into account the reasons for the appearance of cysts. Primary is formed due to genetic disorders. This is a congenital anomaly that affects the tissues of the head. At some stage of fetal development, brain tissue is formed with disturbances. The baby may be born with a cyst or it will grow later. If the baby develops normally, parents may not even be aware of the congenital anomaly for many years. Often newborns with it are no different from healthy peers. Secondary - the result of birth injuries, operations, stroke, coronary artery disease, infections, etc. Most often, one lobe of the brain may be affected.
Any cyst can capture healthy tissue or displace it. In severe pathogenesis, brain tissue can be compressed and pinched. On one side they are pressed by the cyst, on the other by the bones of the skull. The consequence is that the functions of the department that is affected are disrupted. This is dangerous as it threatens health and life. This option requires immediate medical attention.
Sometimes neoplasms can spread to the spine. This can provoke dangerous consequences.
When a brain cyst appears, size and growth rate are of no small importance. Most often these are tiny tumors. They do not compress brain tissue and practically do not interfere with normal life. But large tumors require urgent treatment and constant monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Due to a post-ischemic cyst, the blood supply can be seriously impaired. The tissues do not receive proper nutrition and atrophy, and zones of necrosis form.
It is necessary not only to detect the neoplasm itself, but also to find out for what reasons it appeared. Only by knowing the reasons can you effectively build a treatment regimen.
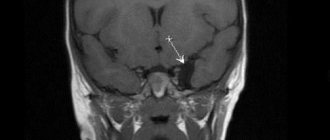
Cavity formation in the brain
Fig2. General view of an intracerebral brain tumor with volumetric effects
1. In the photographs, the tumor is characterized by a volumetric component in the process of growth with an increase in its own mass, the so-called “plus tissue” sign.
Fig3. General view of a brain tumor in the frontal lobe on CT
2. Brain tumors have a mass effect, due to the volumetric influence of their own stroma, displacing and expanding the normal anatomical structures of the brain.
Fig4. An example of the volumetric effect of a tumor on the corpus callosum, shown on an MRI image
3. For benign brain tumors, it is typical to have clear boundaries on MRI and CT, since they have a capsule that separates them from brain tissue, a so-called expansive growth pattern (as a result of an increase in size, adjacent parts of the brain are displaced, pushed aside), relatively slow growth rates and absence of metastasis.
Fig5. example of a benign tumor (indicated by an asterisk), with a capsule, expansive growth and volumetric effect on MRI
4. For malignant brain tumors, the absence of clear contours and boundaries is typical; on the contrary, their edges are not visible, they are characterized by an infiltrative type of growth (that is, they spread their cells between the cells of healthy tissue - infiltration), necrotic decay (in the center the tumor begins to devour itself due to lack of nutrition, which leads to self-digestion of the central areas of the tumor), high rates of growth and development (short-term dramatic outcome) and metastasis (spread of the tumor to neighboring areas of the brain along the membrane and through the cerebrospinal fluid).
Fig6. Malignant tumor of the left frontal lobe with edema, necrotic decay and without distinct boundaries
5. In MRI and CT images, brain tumors in most cases accumulate contrast agent after intravenous contrast enhancement, which is a sign characteristic of tumors, although some tumors do not accumulate contrast, but this is more typical for the initial stages of formations.
6. The tumor changes the MR signal, becoming brighter or darker in the brain substance, since it consists of a separate type of tissue, although there are tumors that are “not visible” on imaging or not visible without contrast. Almost all brain tumors are visible on MRI, but can be missed on CT.
Fig7. An example of a change in brightness (MR signal) on a tomography in a region of the brain affected by a tumor
7. Perifocal edema is a feature not only of a brain tumor, but is very characteristic of tumor formations affecting the substance of the brain. Edema increases the mass effect of the tumor, leads to increased intracranial pressure and can cause displacement of brain structures or their pinching in anatomically narrow places (herniation).
Fig8. Severe perifocal edema of the brain substance surrounding the tumor on an MRI image
Due to the fact that brain tumors are not always represented by ovoid, round formations, as patients are accustomed to perceive them, and other pathological processes in the body tissues can lead to exactly this kind of shape, diagnosis becomes quite difficult and sometimes requires extraordinary knowledge and experience.
Cysts in the brain are benign neoplasms, which are a bubble with liquid contents inside. Young children and adults face a similar problem. Not everyone knows what a cyst is.
From the editor: Proper first aid for a stroke
They are localized both in the left hemisphere and in the right. The clinical picture of the disease largely depends on this. Congenital cysts most often appear between the ages of 30 and 50 years. The growth of these tumors can be fast or slow.
In the latter case, wait-and-see tactics are often used. A cyst in the brain can be arachnoid (located in the area of the arachnoid membrane) and intracerebral. Depending on the location, the following types of neoplasm are distinguished:
- pineal gland;
- dermoid;
- choroid plexus;
- colloidal.
What is the danger
It is believed that four out of five cavity cerebrospinal fluid formations pose no threat to humans. They do not appear in any way and practically do not grow. In most cases, cysts are found by chance during an MRI. Surgeon intervention is not required for such development of the tumor.
Sometimes such intracranial anomalies can behave aggressively. Most often these are the disorders that develop according to the second type. Cysts grow quickly after a concussion or an inflammatory process. They can reach impressive dimensions.
If the cyst grows, it begins to put pressure on the brain tissue. This provokes pain and functional disorders. It is very dangerous that blood circulation and the respiratory reflex are disrupted. This leads to irreversible consequences and tissue necrosis. Over time, if the tumor behaves aggressively and does not slow down its growth, neurological disorders appear. Convulsions and partial or complete paralysis may occur. As a result, this condition can lead to disability. You cannot live with such cysts; they need to be treated.
It is important that a person listens to his feelings. It is necessary to notice signs of an anomaly at the earliest stages of its development. If we are talking about a child, then parents should monitor as carefully as possible any change in his behavior or physical condition.
The most dangerous thing is rupture of the cyst tissue. Exudate gets inside the skull. The result is severe intoxication and death of the patient. If the compaction has reached a large size, the cavity is removed or drainage is installed.
If the cyst is located on the transparent septum of the brain, even small-sized neoplasms can cause pain and neuralgia. To reduce tension and pain, the doctor may prescribe diuretics in combination with analgesics.
Other types of brain cysts
The following types of cysts are also common:
- Cyst of the epiphysis of the brain, the symptoms of which are severe headaches, drowsiness, disorientation, double vision. It also makes walking difficult. At the initial stage of the disease, drug treatment is used. A neglected cyst that increases in size is removed surgically.
- Vascular plexus cyst is a benign neoplasm that manifests itself at certain stages of fetal development in the womb. Such a brain cyst in a child most often resolves on its own. In some cases, a brain cyst in a newborn occurs as a result of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Infectious infection of the fetus can also lead to it. In rare cases, this formation leads to pathological changes in other body systems. A congenital brain cyst is determined using a procedure called neurography. It is absolutely harmless to the child's health. Diagnosis of such a cyst in adults is made using ultrasound examination.
- Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns occurs in 1% of premature infants. It is detected by ultrasound in the first 24 hours of a child’s life. This fetal brain cyst occurs as a result of hemorrhage of the germinal matrix. It can be unilateral or bilateral. Pseudocysts are the safest health consequence of childbirth. They do not require special treatment. As a rule, by the first year of a child’s life they completely resolve.
- A cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a neoplasm that arises between the meninges. Its formation is promoted by inflammatory processes (meningitis, stroke), trauma and surgery. It is diagnosed in adulthood, since in the early stages its symptoms are practically not expressed. Symptoms of a liquor cyst: nausea, vomiting, mental disorders, loss of coordination, convulsions, paralysis of the limbs.
- A subependymal cyst occurs in newborns after a cerebral circulatory disorder or during hypoxia (insufficient oxygen supply to the brain). This disease requires medical supervision.
- Porencephalic cyst of the brain is a formation that occurs in its tissues due to melting of the affected area. It leads to very serious consequences such as hydrocephalus and schizencephaly.
- A lacunar cyst forms in the area of the pons, in the cerebellum, subcortical ganglia, and optic thalamus. Most often it occurs as a result of age-related changes and atherosclerosis.
- Colloidal cyst is of congenital origin. It appears as a result of embiogenesis. A person can have it all his life, but it does not cause him any problems. It is believed that it is hereditary. This cyst blocks the flow of fluid. It is often accompanied by headache, epileptic seizures, weakness in the legs and high intracranial pressure. The symptoms of this disease manifest themselves most clearly in adulthood. Sometimes this disease causes hydrocephalus and cerebral hernia. In rare cases, it is fatal.
Colloidal cyst
Cysts of different parts of the brain
In some cases, doctors diagnose the following diseases:
- A pituitary cyst of the brain is a benign formation. It appears mainly in people aged 30-40 years. There are practically no pituitary cysts in children and adolescents. This disease is dangerous because the tumor affects the central nervous system. Most often, such a cyst is removed surgically.
- A cerebellar cyst can occur for a number of reasons. Most often, its treatment is aimed at resolving adhesions. If the cyst is formed as a result of autoimmune processes or infection, anti-inflammatory therapy will be needed. Surgical intervention is performed if there are signs of hemorrhage, convulsions, or loss of coordination of movement. In most cases, this disease is completely curable.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear if the cyst is medium to large in size. It can be:
- visual impairment;
- hearing loss, tinnitus;
- headache that is not relieved by medication;
- pulsation in the head area;
- nausea that does not go away after vomiting;
- problems with coordination;
- changes in skin sensitivity;
- involuntary movements of arms and legs;
- violation of muscle tone;
- lameness;
- paralysis;
- convulsions;
- hallucinations, mental disorders.
Basic signs
Acquired and congenital vertebral cysts are classified according to the place of their formation. Symptoms of the pathology are largely related to the location of the pseudotumor, its type, size, and stage of growth. Sometimes the neoplasm develops for a long time, without giving obvious signs, and sometimes it causes pain to the patient in the early stages. The severity of pain is determined by the pressure of the cyst on the spinal roots and its proximity to the nerve ganglia.
There are main signs that develop in all types of benign vertebral tumors:
- Sharp and dull pain, concentrated in the area of the cystic capsule, which disturbs the patient even at rest, intensifying with movement. Usually there is a return of pain (irradiation) to the thoracic and pelvic region, buttocks and limbs.
- Radicular syndrome, which develops with the growth of spinal cysts localized near the spinal nerve root and ganglia (nerve plexuses), which are compressed as the tumor grows and moves. It manifests itself:
- pain and shooting in completely different parts of the body - neck, arms, legs, lower back, sacrum, behind the sternum, in the esophagus, stomach, which is determined by which nerve node is irritated;
- muscle weakness and atrophy (shrinkage);
- impaired sensitivity in the legs and arms, as well as in the area of the affected root.
- If a spinal cord cyst has formed, then as it enlarges, neurological manifestations of varying severity occur:
- increasing weakness in the lower extremities, gradual atrophy of muscles controlled by the affected spinal nerves;
- impaired skin sensitivity to pain, cold and heat due to damage to cells that perceive pain and temperature fluctuations;
- burning sensation, cold goosebumps, tingling, numbness in the arms, legs, fingers;
- headaches, sound hearing impairment (noise, ringing), dizziness, feeling of pulsation in the head, increased blood pressure;
- double vision, blurred vision, spots and threads before the eyes;
- sudden loss of consciousness, seizures;
- disruption of the intestines and genitourinary system;
- the appearance of lameness, loss of coordination of movements, balance, changes in gait.
How to live
If there are no symptoms of the anomaly, it does not grow, you can calmly live with it. Such patients only need to undergo regular MRI scans to monitor whether it has begun to enlarge. Such benign anomalies rarely develop. To help the patient, the doctor may prescribe restorative conservative treatment. There are medications that improve blood circulation and oxygen supply to tissues.
It is important for patients with cysts to be monitored and undergo regular examinations.
Treatment
Two treatment methods are used:
- Conservative. Medicines are used to maintain the patient's condition. They improve blood circulation and metabolism. Drug therapy is especially advisable if there are many cysts. It is important to decide on treatment tactics. It depends on the cause of the appearance of neoplasms, their size, location, and growth rate.
- Operational. It is not always necessary to have surgery. And a cyst may be inoperable if it is located in the deep structures of the brain. If surgery is indicated, there are different types: bypass surgery, drainage, surgery with an endoscope. In fact, it is very rare to resort to the help of a neurosurgeon in the presence of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst. This is a last resort. Sometimes complete removal of the cyst tissue is required to maintain quality of life. The prognosis depends on the location of the anomaly, its size, the condition of the patient’s body, age, etc. The percentage of successful operations is quite high.
If a congenital cyst is discovered in a newborn, it can be promptly removed using a bypass or endoscope. Microsurgery is possible. An arachnoid cyst in a child does not resolve on its own. Such cases require close attention from doctors. It is important to immediately decide how to deal with it, for what reasons it appeared. The baby should be carefully monitored by a neurologist. If the tumor progresses, surgery is required.
To avoid complications, rehabilitation treatment is required after surgery. Otherwise, a postoperative cyst may form.
Drug treatment
There is no need for therapy if the tumor is small in size and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
It is enough to simply undergo periodic preventive examinations. But if the cyst begins to grow, then at first it is necessary to carry out drug treatment. According to ICD-10, the disease is coded G93. The patient is prescribed drugs that promote the resorption of adhesions. Tablets or injections are used to lower cholesterol levels.
Natalya Schneider, neurologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences, talks about the use of nootropic drugs:
In order for the functionality of brain cells to be maintained at the required level, they need to be supplied with glucose and oxygen. To do this, the patient uses nootropic substances: Nistenon, Picamilon. Naturally, it is also desirable to protect cells from the negative effects of changes in intracranial pressure. In this case, the patient is prescribed antioxidants.
During treatment, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial agents will be needed. Typically, patients are treated with tablets for 10-12 weeks. The treatment course is repeated after about six months. Therapy is prescribed only by a doctor. He also decides on the advisability of its extension. You can also use folk remedies, but it is also necessary to coordinate their use.
What will resolve it?
If the cyst is not subject to surgery, drug treatment is indicated. There are drugs that can resolve scars and sutures after surgery. They can shrink cerebrospinal fluid cysts.
One of these drugs is Actovegin. It is considered quite effective. Before prescribing the drug, the doctor sends the patient for a full examination. He must know in which area the tumor is located, what size it is, and most importantly, why it appeared.
Do not underestimate the capabilities of modern medications. They can improve metabolism and blood circulation. This is a good stimulus for the body. It is important to complete the full course. It is possible that for prevention it will be necessary to repeat it regularly. It is difficult to completely remove such tumors with the help of medications.
Causes
If the appearance of cysts was preceded by a difficult pregnancy in the expectant mother, experts call such tissue defects primary. Provoking factors are:
- uncontrolled use of medications by a woman;
- alcohol abuse;
- past infectious diseases;
- abdominal injuries.
If the formation of a tumor occurred in the postneonatal period of life, then the reasons may be:
- neuroinfections - for example, meningitis, or encephalitis, tuberculosis or syphilis;
- surgical interventions on brain structures;
- agenesis of the corpus callosum – absence of an anatomical unit or its replacement with a cyst;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- helminthic infestations;
- intracerebral bleeding.
From the editor: Structure and diseases of the central nervous system
Sometimes an arachnoid vesicle is identified as a result of examinations that were performed for other indications. The reasons for such formations are not reliably known - the person himself does not remember what could have been the impetus for the formation of the intracerebral cavity.
How can traditional medicine help?
The task of folk remedies is the same as traditional ones - to improve blood circulation, metabolism, and eliminate symptoms. Properly selected recipes will help cope with annoying headaches and can even slow down the growth of the cavity.
In folk medicine it is common to use:
- Hemlock. The crushed seeds of the plant can be infused in half a liter of olive oil. You need to mix and leave the product for three weeks in a cool place. It is recommended to instill this oil solution 2 drops into the nose 2-3 times a day.
- Dioscoreim Caucasian (root). 4 parts of the root need to be crushed and poured with vodka (1400 ml). The infusion is poured in stages. First, take half the roots and pour 700 ml of vodka in a glass container. You need to leave it for 5 days. Then you need to drain all the liquid and pour a fresh portion of vodka (700 ml) over the roots. Leave again for 5 days. The infusion should be taken one teaspoon three times a day.
- Decoctions of raspberries, licorice, wormwood, elecampane, chamomile, and calendula will help reduce intracranial pressure.
For some reason, many people believe that folk remedies are safe. This is wrong. To avoid unpleasant consequences, you should definitely ask your doctor whether you can use them specifically. It is the doctor who must select the folk remedy. Otherwise, it may not only not help, but also seriously harm. In addition, some medications are incompatible with herbs or alcohol.