Hospitalization and treatment under the compulsory medical insurance quota. More details after viewing the pictures.
- Aneurysm clipping
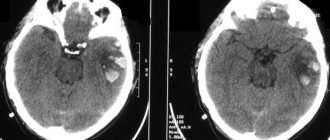
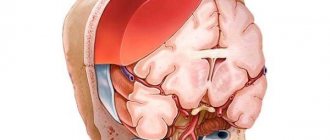
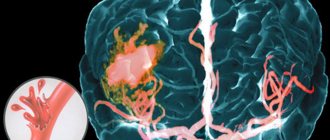
A cerebral aneurysm is a local protrusion of the arterial walls. The disease often occurs without symptoms. As the brain aneurysm grows, a significant thinning of the walls of the formation occurs, which can lead to its rupture and the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
Depending on the shape, a cerebral aneurysm can be spindle-shaped or saccular. The exact type of disease can only be determined during a comprehensive diagnosis. Saccular aneurysm is much more common.
Causes of the disease
An aneurysm is a dangerous condition that primarily requires surgical treatment. Otherwise, complications will not be avoided. Experts believe that the disease is a consequence of developmental abnormalities that disrupt the structure of the vascular wall. Often, a cerebral aneurysm is combined with connective tissue dysplasia, polycystic kidney disease, and vascular disorders. The acquired form of the disease can be a consequence of traumatic brain injury. Also, a cerebral aneurysm occurs against the background of atherosclerosis and hypertension.
The vascular wall defect itself occurs gradually. Against the background of degenerative processes, tissue damage or underdevelopment, the area loses its former elasticity. Under the pressure of blood flow, the vascular wall begins to bulge. This is how a brain aneurysm forms. Most often, the formation occurs in the place where the arteries branch and there is the strongest pressure on the vessel wall.
Symptoms of an aneurysm
Two variants of the course of the disease can be distinguished: apoplexy and tumor-like. The characteristics of the clinical picture depend on the types of aneurysm. The tumor-like form of the disease is accompanied by an active course. In a short period of time, the aneurysm increases in size and compresses important anatomical structures of the brain.
A tumor-like aneurysm is most often localized in the area of the cavernous sinus or chiasm. When the chiasmal region is damaged, visual acuity decreases. Over a long period of time, optic nerve atrophy occurs. If a cerebral aneurysm is located in the cavernous sinus, paresis occurs and damage to the branches of the trigeminal nerve occurs. As the pathology develops, oculomotor disturbances occur and strabismus may appear.
Signs of a ruptured aneurysm
A sharp headache is the first symptom of a ruptured aneurysm. The pain syndrome is initially local in nature. But very quickly the headache spreads and becomes diffuse. In this case, patients note the appearance of nausea and repeated vomiting.
In the future, characteristic meningeal symptoms arise:
- stiffness of the neck muscles;
- Kernig's and Brudzinski's symptoms;
- loss of consciousness.
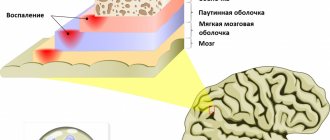
When a cerebral aneurysm ruptures, subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs. It may be accompanied by focal symptoms, which depend on the location of the formation. The most severe is hemorrhage into the ventricles, which often leads to the death of the patient.
With an aneurysm of the anterior cerebral artery, leg paresis develops, which is often combined with mental disorders. Damage to the middle cerebral artery leads to speech impairment and the development of hemiparesis.
If the pathology is localized in the area of the vertebrobasilar system, during the rupture of the aneurysm, swallowing disorders occur, nystagmus develops in combination with central paresis of the face and trigeminal nerve.
At the first sign of a possible aneurysm, you should immediately seek emergency medical help. It is important to maintain physical rest and avoid overexertion. Specialists will conduct an examination, diagnose, make an accurate diagnosis, and prescribe the necessary medications to reduce the risk of life-threatening complications.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of a carotid aneurysm in the neck are associated with its complications. An aneurysm may not cause any sensation and is discovered by chance during a medical examination or ultrasound of the neck.
- Visual impairment
Due to repeated detachments of small blood clots, ocular symptoms of a carotid artery aneurysm may develop: blurred vision, double vision, dilated pupils, loss of visual fields.
- Headache
A sudden and severe headache may be a sign of a ruptured carotid aneurysm, as well as other arteries in the brain. This pain is so severe that most patients describe it as “unbearable and most excruciating pain.” Headache is usually accompanied by nausea and vomiting, tension in the neck muscles, and loss of consciousness and coma often occur. Intracranial aneurysm rupture is accompanied by a very high mortality rate. Therefore, when such aneurysms are detected, they must be operated on as early as possible.
How is it diagnosed?
Since an arterial aneurysm can occur without significant symptoms, it is necessary to pay special attention to the first signs in women and men. A neurologist must diagnose the disease based on the examination, the diagnostic results obtained and the study of cerebrospinal fluid.
During a neurological examination, focal and meningeal symptoms are detected. Based on the location of complaints, it is possible to determine presumably where the pathological focus is located.
The neurologist obtains accurate information about the patient’s condition using the following studies:
- X-ray of the skull. A cerebral aneurysm is characterized by signs of bone tissue destruction.
- Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
- Angiography. Basic information about the location, shape and size of the brain aneurysm can be obtained.
- Lumbar puncture. The study reveals blood in the cerebrospinal fluid, which indicates the presence of hemorrhage.
Specialists carry out differential diagnosis of cerebral aneurysm. It is important to make an accurate diagnosis in a short time. This will avoid the adverse effects of a brain aneurysm. It is necessary to differentiate an aneurysm from tumor-like processes, cysts and abscesses.
Modern treatment of cerebral aneurysm
If an aneurysm is detected, treatment should begin immediately, without waiting for tragic consequences. The price of surgery for a cerebral aneurysm may seem high, but this is the cost of high-quality medical services, the masterly work of the best surgeons, the use of the latest technologies and a stay in a modern hospital. We provide our patients with the best conditions available in Moscow today.
The most effective way to treat an aneurysm is surgery - therapeutic angiography of the brain, which involves catheterization and, if necessary, stenting of blood vessels. The final cost of surgery for a cerebral aneurysm will depend on the specific technique and details of the operation, which will be determined only after undergoing a diagnosis of a cerebral aneurysm. The operation may involve covering the desired section of the artery with special microspirals. This is an endovascular minimally invasive operation that does not require opening the skull. However, the specific technique is determined by the surgeon after a thorough analysis of the patient’s condition, indications, type and size of aneurysm and all related factors.
Principles of treatment
Aneurysm treatment is carried out by a neurologist. The operation is performed only by a neurosurgeon. Surgical methods are aimed primarily at preventing aneurysm rupture, which can result in the death of the patient. Conservative therapy for this pathology is used to slow the progression of the disease.
Surgical treatment of a cerebral aneurysm involves two types of main operations: clipping and endovascular occlusion. Surgery prevents the aneurysm from rupturing. A radical method of treatment is the removal of arteriovenous malformation during a microsurgical operation.
Aneurysm clipping
Aneurysm clipping is an open operation during which the neurosurgeon blocks blood flow in a certain area of the vessel and applies a clip. At the stage of preparation for surgery, specialists prescribe a procedure that allows them to stabilize the patient’s condition and minimize the risk of possible complications. Preventive examination makes it possible to identify possible disorders and diseases that can lead to adverse consequences of surgical intervention.
The operation is performed using modern microsurgical techniques through a small trepanation hole. During surgery, the neurosurgeon prevents rupture of the wall of the malformation.
After isolating the neck of the aneurysm, the specialist places a clip on it. Additional control with Doppler ultrasound allows you to assess the state of blood flow and ensure the effectiveness of the operation.
Treatment of an aneurysm using the clipping method is considered quite complex and should only be performed by an experienced neurosurgeon. A qualified specialist will do everything possible to ensure accurate and technically correct application of the clip. Otherwise, dangerous complications and a long rehabilitation period cannot be avoided.
The clip is applied to the neck of the aneurysm vessel. The accuracy of the neurosurgeon’s actions is confirmed by conducting high-quality diagnostics (Dopplerography) during the procedure.
Endovascular occlusion
During endovascular occlusion of an aneurysm, the neurosurgeon blocks the lumen of the dilated vessel with a special implant. The operation is used when clipping is not possible, for example, when the aneurysm is spindle-shaped. During surgery, a specialist inserts a catheter balloon through the femoral artery using angiographic control. It closes the lumen of the aneurysm. You can also use a microspiral to perform thrombosis. The choice remains with the attending physician. The microspiral in the cavity of the affected vascular area forms blood clots, which clog the lumen of the vessel and shut off the aneurysms from the blood circulation.
Clipping of a cerebral aneurysm
Clipping of a cerebral aneurysm
Clipping is a surgical procedure performed to treat an aneurysm.
Most aneurysms resemble a ball, with a narrow neck at the beginning and a large, expanding dome. As the aneurysm grows, it becomes thinner and weaker. Its walls may become so thin that there is a high risk of aberysm rupture and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). The purpose of surgical clipping is to isolate the aneurysm from normal blood circulation.
An unruptured aneurysm does not cause symptoms and is usually discovered during routine testing. People with a family history of cerebral aneurysm should undergo follow-up CT or MRI angiography. The risk of aneurysm rupture is about 1% per year, but may be higher or lower depending on the size and location of the aneurysm. However, when a rupture occurs, the risk of death is 40% and the risk of disability is 80%.
Surgical solution
There are several treatments for cerebral aneurysm. A less invasive endovascular technique (coiling) may be preferable in older patients, with underlying serious chronic diseases, or in patients who have aneurysms in certain locations. In patients under 40 years of age, surgery with craniotomy and clipping provides longer-term protection against bleeding than endovascular coiling of cerebral aneurysms.
Surgical clipping is performed by a neurosurgeon. Many German neurosurgeons have specialized training in cerebrovascular surgery.
Before surgery to clip an unruptured aneurysm, a number of preoperative tests (eg, blood tests, ECG, chest x-ray) are performed. All nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and aspirin should be stopped one week before surgery.
The operation usually takes 3-5 hours, or longer if a complex craniotomy is planned.
Depending on the location of the aneurysm, the surgeon will make an incision in the skin to then make a small hole in the skull. The bone flap is raised and stored until the end of the clipping procedure.
The dura shell opens to expose the brain. Using a special operating microscope, the surgeon carefully opens the artery with the aneurysm.
Often the aneurysm is surrounded by connective tissue and must first be freed and isolated from other structures. A clip and clamp is placed across the neck of the aneurysm. The clip is then closed, pinching the aneurysm away from the parent artery. The dome of the aneurysm is pierced with a needle to ensure that no more blood enters the aneurysm.
After clipping the aneurysm, the dura mater is sutured. The surgeon replaces the bone flap and strengthens it. The muscles and skin are sutured together.
After surgery, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for observation and monitoring. After a day or two, the patient is usually transferred to a normal ward.
Patients typically remain hospitalized for 14 to 21 days and are monitored for signs of vasospasm.
What are the risks?
No surgery is without risk. Common complications associated with brain surgery include infections, allergic reactions to anesthesia, and brain swelling.
Aneurysms that are completely excised have an extremely low risk of regrowth.
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment of an aneurysm
The rehabilitation period takes place under the supervision of specialists. Professionals do everything necessary to prevent the occurrence of postoperative complications. The patient remains in the intensive care unit for several days under the constant supervision of specialists. Afterwards, the patient is transferred to a general ward, where strict bed rest must be observed for some time. The return to a normal lifestyle occurs gradually.
If the patient's well-being worsens after surgery, transcranial Doppler ultrasound may be prescribed. Rehabilitation is aimed primarily at preventing vasospasm and increased blood pressure. Specialists also monitor the general condition of the cardiovascular system and, if necessary, prescribe osmodiuretics to eliminate swelling of the brain tissue. Additionally, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out.
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment of an aneurysm necessarily includes a program to restore impaired body functions and further socialize the patient. The recovery period lasts at least 6 months. With the help of high-quality rehabilitation, it is possible, among other things, to eliminate the adverse consequences of surgical treatment.
Rehabilitation measures include physiotherapy, massage, and the implementation of an individually selected rehabilitation program. After endoscopic clipping, the patient can return to normal life within a few weeks.
How are endovascular interventions performed?
Endovascular interventions are performed under local anesthesia through a puncture in the vessel (usually an artery in the thigh or arm area is punctured). A conductor is inserted through a puncture in the vessel, through which catheters and other devices are delivered into the vascular bed, allowing for a therapeutic effect on the vascular wall. Endovascular procedures require hospitalization of the patient for several days. The patient spends the immediate period after the intervention (from several hours to 24 hours) in the intensive care ward.
Forecast for life
The prognosis of the disease depends on the location of the vascular protrusion and its size. The initial condition of the patient also has a huge impact. The mortality rate in case of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm exceeds 30-50%. Surviving patients sometimes retain the consequences of the condition in the form of movement restrictions, cognitive impairment and a significant decrease in quality of life. Mortality after recurrent hemorrhage exceeds 70%.
Therefore, it is so important to carry out surgical treatment in time, turning to a qualified neurosurgeon. The operation is postponed only if there are certain medical indications.
Successful neurosurgical operations are carried out at the Burdenko Research Institute. Patients with signs of an aneurysm or suspected aneurysm are admitted here. At the Institute of Neurosurgery, it is possible to carry out comprehensive diagnostics using the latest technology and further treatment of identified diseases.