Hospitalization and treatment under the compulsory medical insurance quota. More details after viewing the pictures.
Brain tumors can be benign or malignant; the latter are aggressive in nature and pose a significant threat to life. Neoplasms form inside the skull due to abnormal disturbances in the cellular genetic apparatus, which leads to uncontrolled growth of tissue structures. Atypical cells are formed from normal ones as a result of mutations, exposure to physical, chemical or other factors. These can be various cells of brain tissue, for example, neurons, glial cells and others. Often, metastasizing cells formed from cancer of other organs enter the brain, which leads to the formation of secondary malignant tumors. The main treatment involves surgical removal of pathological foci, additionally radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed, as well as drugs to relieve negative clinical manifestations.
Causes of tumors
At the moment, medical science does not fully understand the reliable causes of the formation of cancer. Doctors name factors that increase the risk of tumor formation. An important role is played by the age and gender of a person. Some types of cancer, such as meningiomas, are more often diagnosed in women over 45-50 years of age. This is due to the characteristics of the female endocrine system and hormonal levels. For example, during pregnancy, some neoplasms progress more intensively. Brain tumors in men, as a rule, have a more severe course and complex prognosis, because in this case the tumors are highly malignant.
Other provoking factors include:
- adverse environmental impacts: radiation, hazardous industries, living in contaminated areas, etc.;
- constant contact with toxic elements;
- infection with viruses that can contribute to the development of cancer;
- genetic characteristics (the presence of certain genes in the human genome that increase the risk of developing a brain tumor);
- head injuries of various nature and origin;
- treatment with drugs, for example, hormones, chemotherapy;
- bad habits;
- consumption of low-quality food saturated with carcinogenic elements.
These factors can influence the formation of diseases both separately (for example, heredity) and in combination.
Most Common Brain Tumors: 5 Things You Should Know
June 22, 2016
A diagnosis of a brain tumor can sound ominous. Although the symptoms of most brain tumors are the same, not all tumors are cancerous.
In fact, meningioma is the most common brain tumor, accounting for about 30 percent of them. Neurosurgeon of Anadolu Medical Center Prof. Serdar Kahraman says that meningiomas are often benign tumors: You may not even need surgery.
Here are five key facts you need to know about meningioma:
- Meningiomas can grow in different places.
These tumors arise from cells in the lining of the brain and spinal cord. So, technically speaking, they are not brain tumors at all, since they are not the result of mutated brain cells.
But they continue to grow inside your skull, which means there is cause for concern. If the meningioma grows or causes swelling that presses on the brain or other structures in the skull, it can cause symptoms similar to a brain tumor.
- The symptoms meningiomas depend on their size and location.
Dr. Kahraman, says: “Meningiomas are present with typical symptoms of a brain tumor, such as headaches, vision problems or seizures. A severe headache by itself is rarely a symptom of meningioma or any other brain tumor.”
Large meningiomas can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to hydrocephalus ("water on the brain"), which can affect gait and memory. Tumors elsewhere can affect your sense of smell, vision, hearing, or even the function of your pituitary gland.
- A diagnosis of meningioma may occur when a doctor is looking for something else.
Dr. Kahraman says, “The diagnosis of a brain tumor is often incidental—that is, a doctor discovers a tumor on a CT or MRI while examining an individual for another reason, such as a traumatic brain injury or another neurological problem.”
When your doctor diagnoses meningiomas, you will receive additional tests to find out how the tumor is likely to behave. Based on this data, the neurosurgeon will recommend removing the tumor or simply watching it to see if it is growing.
- Most meningiomas do not spread.
It can come as a shock to anyone to be diagnosed with meningioma - especially large ones - but these tumors are usually benign. This means that the tumor cells are not likely to spread to other parts of the body.
However, meningiomas can grow quietly for many years without causing any problems - and can reach surprisingly large sizes.
- Treatment of meningioma: surgery - or not
Sometimes, believe it or not, your doctor may recommend monitoring a meningioma, especially if it is small and not causing problems. From time to time you will undergo regular MRI diagnostics for monitoring.
Otherwise, the main treatment for meningioma is surgery to remove the tumor, either by craniotomy or another procedure. Your doctor will carefully check what the surgery will involve, how the surgeon will be able to access the tumor, and what the patient can expect after the surgery.
How does a neurosurgeon operate on meningiomas? It all depends on the location. Dr. Kahraman says, “Depending on where the tumor is located, each approach will be different. Tumors located close to the surface are generally easier to operate on than those located along the base of the skull."
Base of the skull tumors are those located deep in the skull, behind the nose or eyes. This can be a challenging task and requires skill and some experience in this field of surgery.
“There are a number of new techniques in brain tumor surgery, even for tumors located deep in the skull, and some of them are less aggressive.”
"The new system we're using involves a tube with a camera that gently moves into the brain tissue so we can reach the tumor with a smaller incision, so patients can recover faster," he says.
After treatment, you will probably return to your normal activities, but will need regular MRI scans to make sure the tumor is not coming back.
In many cases, the tumor does not return, Dr. Kahraman says: “After 10 years, about 90 percent of patients who had meningiomas do not return, provided, of course, that the tumor was completely removed, including some of the brain tissue lining the tumor "
Regardless, if you have been diagnosed with meningioma or any other tumor, the best thing you can do is learn as many facts about the disease itself, be informed, and work with the most experienced neurosurgeon and team you can find.
Types of tumors
Neoplasms that form in the brain can be:
- Benign – tumor tissue does not contain cancer cells. Neoplasia of this type is characterized by clear edges and slow growth. They are much easier to treat surgically, but can become malignant, that is, turn into cancer;
- Malignant tumors contain abnormal cells that can divide uncontrollably and metastasize to other organs. In this case, the disease is difficult to control; in the later stages, surgery is impossible. Treatment in this case is difficult, has a high cost and, as a rule, poor prognosis.
Brain glioma
Glioma
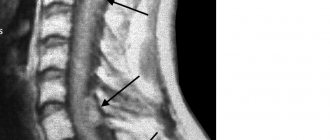
This type of tumor is diagnosed more often, accounting for approximately 60% of all types of cancer that form in the brain. The tumor is formed from glial cells. In most cases, this is a primary neoplasm, most often formed in the area of the chiasmata or ventricles, but it can also affect the brain stem; pathogenesis rarely extends to the bones of the skull, however, in rare cases this is possible. The size of gliomas is usually up to 14 cm. Metastases are rare, growth is usually slow, but due to penetration into adjacent tissues, the boundaries of the lesion are difficult to distinguish.
Three varieties are known
- astrocytoma – diagnosed more often than others (it accounts for about 50% of gliomas);
- oligodendroglioma – up to 10% of cases;
- ependymoma – less than 7%.
According to the World Health Organization classification, there are 4 stages of glioma:
- The first stage is benign. It is characterized by slow growth. Example: giant cell astrocytoma.
- Second stage. Features: borderline malignancy with slow tissue growth, easily progresses to stages 3 and 4. In this case, only one symptom of cancer is identified - cellular atypia.
- Third and fourth stage. In this case, the tumor has all the signs of cancer, for example, necrotic changes in glioblastoma multiforme.
Brain astrocytoma
Removal of a large GRADE II WHO astrocytoma of the right temporal lobe (before surgery)
This malignant neoplasm of varying degrees of aggressiveness is diagnosed quite often. The beginning is given by degenerated glial cells - astrocytes (hence the name - astrocytoma). There are:
- Common astrocytomas: protoplasmic, fibrillary and hemisrocytic.
- Special astrocytomas: cerebellar, piloid, microcystic and subependymal.
Astrocytomas are distinguished by the stage of malignancy:
- The first stage (benign tumor) includes piloid or pilocytic astrocytoma of the brain.
- Second stage of malignancy: fibrillary tumor is also an ordinary neoplasia, second degree of malignancy.
- The third stage is already cancer. It includes anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain.
- The most life-threatening are glioblastomas (giant cell glioblastoma and gliosarcoma), which are classified as stage 4 and are characterized by rapid growth and the ability to metastasize.
In addition to the ones mentioned, there are other types of astrocytomas, for example, ependymoma (develops from ventricular cells), oligodendroglioma (forebrain) - grow quite slowly without the formation of metastases, and glioma of the brain stem.
Meningioma of the brain
Removal of a large middle cranial fossa meningioma before surgery
Pathogenesis begins with pathogenic cells in the superficial membrane that surround the brain tissue. The neoplasm is oval in shape, grows slowly, and is therefore considered benign. Meningiomas are diagnosed in 15% of cases (of all brain tumors). The risk of degeneration into cancer is about 3-4%. The clinical signs that appear are caused by increased intracranial pressure and tissue compression. With malignancy (degeneration of somatic cells into carcinogenic ones), meningiomas become aggressive. Usually more than one lesion forms and may spread to the spinal cord. After surgical treatment, there is a high probability of relapses. As a rule, pathology is diagnosed by chance, because symptoms appear only when the lesion reaches a large size. There are no early signs of the disease.
Note. Meningiomas often form in females.
Other types of brain tumors
There are quite a lot of types of neoplasms. Here are some of those that are diagnosed relatively often (besides those mentioned above):
- medulloblastoma is a brain cancer that originates from the structures of the cerebellum;
- germinoma - formed from germ cells, most often it is detected in the first half of a person’s life;
- Craniopharyngeoma - develops in the pituitary gland at the base of the brain;
- Shawnoma – formed from degenerated Schwann cells;
- tumors in the pineal gland area.
Types of surgeries to remove brain tumors
When a tumor is discovered in the brain, in most cases, immediate medical intervention is required to prevent irreversible damage to one of the most important organs in our body. Surgical intervention, i.e. removal of the detected tumor is considered the most effective of all methods of treating brain tumors. However, surgery is not always possible, and its implementation depends, among other things, on the location of the tumor and its characteristics.
The Center for Advanced Neurosurgery at the Herzliya Medical Center employs doctors who specialize in the treatment of brain tumors and have special skills in performing complex neurosurgical operations. Once you have been examined and fully diagnosed, they will be able to determine which treatment is most effective for you and will administer it in the best possible way.
When will the decision be made to undergo brain surgery to remove the tumor?
As already mentioned, brain surgery is considered the best option when there is a dangerous tumor in the brain, since this way the tumor can be removed completely, or at least most of it. A brain tumor, even if it is not cancerous, can press on tissue and important areas of the brain, interfere with the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and cause multiple symptoms. Thus, removing the tumor can lead to significant improvement in your condition, leading to almost immediate relief of symptoms and even their disappearance. All of the above becomes even more significant when it comes to a malignant tumor that affects healthy tissue and has the ability to spread to other areas of the brain. This process in many cases will be significantly slowed down or even stopped completely after the tumor is removed.
Although this is a procedure that is considered particularly effective, it is important to remember that not every case can remove the tumor. The brain is a complex and sensitive organ, so any significant damage to healthy tissue can cause serious and irreversible damage to the functioning of the body. Therefore, the decision to operate will be made only if the tumor can be completely removed, or at least a large part of it.
The decision to undergo surgery or choose another type of treatment (chemotherapy, radiation therapy, etc.) will be made after a thorough diagnosis of your health condition, as well as checking the characteristics of the tumor. First, you will undergo an imaging test—in most cases, a head CT or MRI—which will be performed at the Advanced Imaging Institute at Herzliya Medical Center Hospital. It will then be decided whether a biopsy, a semi-invasive procedure in which a small sample of tissue is removed from the tumor, is necessary. This sample will be sent to the hospital's histopathology laboratory for analysis, and the laboratory will be able to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant, and the degree of malignancy if the tumor is malignant.
This stage is extremely important. Only after it is completely completed will your doctor be able to determine which treatment is most suitable for you, how to give it and when.
How to prepare for surgery to remove a brain tumor?
Once it has been decided that surgery is the best treatment option, the medical staff will need to make a decision regarding the type of surgery you will have. There are several ways to surgically remove brain tumors; The following are the most common of them:
- Craniotomy: Surgery that is performed through an opening in the skull, near the location of the tumor. This operation allows the surgeon direct and relatively convenient access to the tumor, which makes it possible to remove it to the maximum extent. This operation is performed under general or local anesthesia (local anesthesia is used when there is a need to test brain function during the operation itself), and usually requires a long recovery.
- Minimally invasive craniotomy: This procedure is relatively innovative and is performed through several tiny holes in the skull, resulting in a shorter post-operative recovery period and reduced risk. The surgeon will use micro-instruments to remove the tumor without “invading” the brain completely
- Brain surgery through the paranasal sinuses: Over the years, surgical techniques have been developed that aim to cause the least possible harm to the patient. This is a brain surgery performed through the paranasal sinuses - natural openings through which you can access different parts of the brain without making deep cuts in the skin or penetrating the cranial bone. Many operations, such as pituitary gland operations, are regularly performed using this method
- Catheter surgery : There are two main reasons for placing a catheter in the brain: to effectively administer chemotherapy drugs to a specific area of the brain, and to effectively drain cerebrospinal fluid (to prevent fluid from accumulating in the head, a phenomenon known as hydrocephalus). In both cases, the procedure is performed under full anesthesia and is performed through small holes in the skull. When it comes to installing a catheter to drain fluid from the brain cavity, the distal end of the catheter is installed in the abdominal cavity, where the fluid is drained.
It is important to remember that each of these operations can last several hours and that the recovery process lasts a relatively long time. Operations are performed using modern neurosurgical equipment, such as a computerized navigation system, surgical microscope and much more. After the tumor has been removed, and especially if the tumor is malignant, you will be invited for follow-up visits every few months to assess the success of the operation and to ensure that the tumor has not re-grown in the area where the tumor started or in surrounding areas.
At the advanced neurosurgery center at Herzliya Medical Center, you have at your disposal the best doctors who have performed many operations to remove brain tumors, even in particularly complex cases. Doctors demonstrate the highest success rates, working in accordance with international standards. You can choose the doctor who will operate on you, and even schedule the operation at a time convenient for you.
Should you undergo surgery to remove a tumor in your brain?
the Center for Advanced Neurosurgery at Herzliya Medical Center today and choose from a long list of excellent, experienced physicians the surgeon who will operate on you.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms are usually divided into general and focal. In the latter case, the symptoms depend on where the tumor forms.
General symptoms
The clinical picture is caused by an increase in pressure inside the skull and the toxic effect of metabolites of pathogenic cells on healthy tissue. Common signs include:
- headache not relieved by conventional analgesics;
- various visual impairments, for example, fog, doubling, glare, decreased visual acuity and others;
- loss of appetite, poor health, nausea and vomiting that are not caused by food poisoning;
- changes in the usual emotional state: mood swings, depression or aggressiveness, and others;
- symptoms of an epileptic nature;
- weakening of the brain: it is difficult for a person to concentrate, mental activity is disrupted, there is a loss of concentration, memory problems, etc.
Important. Early signs of cancer are often misunderstood by sick people. They seek help when clinical signs significantly impair quality of life. In this case, the brain tumor is diagnosed late, which significantly complicates treatment and worsens the prognosis.
Focal symptoms
Signs of this type arise due to changes in the functioning of cerebral structures, so the clinic depends on the location of the neoplasm:
- when the hemispheres are damaged, tactile sensitivity decreases, muscles in the opposite part of the body weaken (in the presence of pathogenesis in the right hemisphere, problems arise on the left side);
- disease in the temporal lobe leads to a deterioration in the ability to speak, memory suffers, and the perception of smells changes;
- pathological changes in the cerebellum lead to disturbances in gait and coordination of movements;
- damage to the frontal lobe causes mental and cognitive changes;
- neoplasia in the parietal lobe changes tactile sensations and fine motor skills;
- damage to the occipital zone negatively affects vision, and hallucinations are possible.
Important. The presence of these signs (of any type and intensity) is a good reason to seek medical advice. Early detection of pathologies improves the prognosis of treatment.
Brain surgery
The Scientific Center for Neurology provides highly specialized care for the following pathologies:
- meningiomas of various locations
- tumors of the skull base (except for transnasal removal of pituitary adenomas)
- posterior fossa tumors
- glial tumors of the brain
- cranial nerve neuromas
- symptomatic cysts of intracranial localization
- neuralgia of the trigeminal and hypoglossal nerves, hemifacial spasm, Meniere's disease (with neurovascular conflicts)
- disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (hydrocephalus)
- Arnold-Chiari malformation
- vascular pathologies of the brain
- intracranial hemorrhages (n., epidural, subdural, subarachnoid, intracerebral hemorrhages)
Brain tumors The gold standard for diagnosing brain tumors is an MRI of the brain with intravenous contrast. The clinical picture of brain tumors depends on the size, location and degree of impact of the tumor on the surrounding neurovascular structures. Brain tumors are divided into the following types:
- Neuroepithelial tumors
- Tumors of the cranial and paraspinal nerves
- Tumors of the membranes
- Metastatic tumors
Each of the presented groups has tumors of varying degrees of malignancy in its structure, depending on the histological pathomorphology of the tumors. Depending on the degree of malignancy of the tumor, the most effective treatment methods are selected or combined:
- observation
- surgical removal (as much as possible/complete)
- irradiation (radiotherapy/radiosurgery)
To decide on the choice of tactics for patient management, it is necessary to have the following data: the patient’s condition at the time of making the decision, MRI/SCT with or without contrast enhancement (depending on the pathology), results of examination by specialists (depending on the location of the tumor). Any tumor of the central nervous system, regardless of histology, size and degree of malignancy, has a number of manifestations that can and should be eliminated by neurosurgeons:
- growth of tumor tissue within the intracranial space leading to compression of vital structures, which in turn can lead to disability or death
- existing mass effect, which can lead to the death of the patient.
The Scientific Center for Neurology offers highly qualified neurosurgical care using the most modern equipment. We have at our disposal:
- modern neurosurgical microscopes
- neurosurgical multifunctional tables
- endoscopic stand with a set of instruments for various types of interventions, 3D endoscopy available
- neuronavigation
- intraoperative monitoring (all types of intraoperative neuromonitoring)
- transcranial magnetic stimulation and identification of functionally important areas of the brain
- all types of MR and CT diagnostics
- one of the most powerful neurorehabilitation departments for patients with neurological deficits.
| Exterior view of the operating room during use of neuronavigation and endoscopic stand | |
| Construction of a surgical plan for a patient with a tumor in the motor cortex, using data from preoperative neurophysiological cortication of brain areas responsible for limb movements | |
| The process of endoscopic brain surgery |
The department specializes in endoscopic intracranial neurosurgery (through small burr holes and minal incisions, with minimal risk of damage to surrounding structures)
| View of the incision in a patient operated endoscopically for a tumor of the base of the anterior cranial fossa 1 month after surgery | |
| External view of the incision 1 month later in a patient after endoscopic removal of an epidermoid cyst of the left temporal lobe. | |
| The appearance of the incision after endoscopic removal of an acoustic neuroma (identical to the incision for trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm). |
| Photos of patients who have successfully undergone treatment in our clinic: |
| Patient with frontal lobe meningioma before and after surgery | |
| Patient with colloid cyst of the third ventricle before and after surgery | |
| Intraoperative picture during endoscopic removal of a colloid cyst of the third ventricle | |
| Patient with a glial tumor of the temporal lobe (before, after) surgery | |
| Temporal lobectomy in a patient with a temporal lobe tumor and drug-resistant symptomatic epilepsy. Discharged without neurological deficit | |
| A patient operated on for meningioma of the base of the anterior cranial fossa. She was discharged without neurological deficit. | |
| Patient with parasagittal meningioma of the middle third of the falx. On the left before removal, on the right control after 14 days | |
| A patient with PCF meningioma and facial nerve paresis. Pictures above before surgery, below after (control after 6 months) | |
| Patient with neuroma of the 8th nerve MRI before (left) and after (right) surgery with complete preservation of facial nerve function | |
| MRI of the patient before (left) and after (right) removal of meningioma of the sphenoid bone platform and dorsum sella |
Diagnostics
The initial examination involves an oral interview and a physical examination. The doctor assesses the patient’s general condition, determines the nature of clinical manifestations, their duration and intensity, evaluates coordination, reflexes, psycho-emotional state, and so on. Next, the patient will have to undergo a thorough diagnosis, which may include the following types of studies:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound (echoencephalography);
- angiography - X-ray contrast study of the condition of the blood vessels of the head;
- examination of eye function and level of vision;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging – obtaining high-precision layer-by-layer images, which allows you to identify all the nuances of the disease and determine the method of tumor removal;
- magnetic resonance spectroscopy – study of the functioning of pathogenic tissues at the biochemical level;
- positron emission tomography (PET) of the head shows the characteristics of metabolic processes in the painful focus, which makes it possible to talk about the rate of development of the disease;
- biopsy - tissue collection for histological examination; in this case, the material is obtained after tumor removal.
Also of great diagnostic importance is the study of cerebral fluid, in which pathological cells are located. The stereotactic biopsy method is the most informative in terms of determining the type of carcinogenesis and its characteristics.
Brain tumor removal
Therapy for neoplasms is complex, always complex and quite expensive. For example, in Russia, surgical treatment of a brain tumor is estimated at approximately 350 thousand Russian rubles. You can find out the final cost of treatment in one of the best oncology centers in the Russian Federation after consulting a neurosurgeon. Prices abroad are much higher. In Germany, for such therapy you will need to pay about 28,000-30,000 US dollars, in Israel it is several thousand cheaper, so it is important to take this fact into account when choosing a clinic. You need to pay attention to the nuances. For example, the equipment in foreign clinics is often better, although the treatment methods and results are not fundamentally different, but in the event of an unfavorable outcome, Western specialists will not have to deal with paying local insurance, so they easily take foreign patients who pay for everything themselves.
Note. The main treatment is a radical surgical operation; other methods used in combination act as auxiliary ones (chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other methods).
Brain cancer can only be removed through surgery. It is performed for nodular tumors and is impossible for diffuse neoplasms due to deep infiltration into nearby structures. In such circumstances, brain tumor surgery is performed to remove some of the abnormal tissue, relieve pressure inside the skull, and prevent dropsy. The size of the tumor and the stage of the cancer play a decisive role in deciding whether to remove the tumor.
Radiotherapy involves repeated exposure of cancer cells to radiation, which leads to blockade of division and death of the latter. With significant doses of radiation, pathogenic cells stop developing and most of them die.
At the same time, treatment involves the use of chemotherapy through oral and intravenous administration of cytostatics (toxic substances for pathogenic cells). These therapies have many negative effects. Recently, medicine has been producing more and more unique chemical drugs that selectively target tumor cells, which can significantly reduce the negative impact of poisons on the body.
At the same time, medications are prescribed to eliminate unfavorable signs that can be caused by both the tumor and side effects from the proposed treatment.
Surgery
Surgeries to remove tumors in the brain are the only effective treatment. This type of treatment is very complex. The possibility and effectiveness of the operation depends on many factors, among which important are the stage of cancer, the nature of the spread of pathogenic tissues, the presence of metastases and secondary foci, as well as the localization of pathogenic formations in brain tissue.
Any neurosurgical operation is quite complicated, because the doctor must remove a malignant tumor located between healthy brain tissue. Therefore, treatment of this kind is traumatic, and in some cases impossible. For example, cancer removal is not carried out if the tumor is large, when it affects vital parts of the brain, or if the disease is at a terminal stage. In addition, the person’s health status, the presence of chronic diseases, their stages, the patient’s age and other features are taken into account.
In each specific case, the choice of technique and method of tumor removal is selected individually. At the moment, doctors have a lot of specialized surgical equipment in their arsenal, for example, tomographs, laser and ultrasound equipment. This significantly increases the efficiency of operations to remove tumors.
Most often, surgical removal of brain cancer involves trepanation and resection of the skull. The methodology is as follows:
- At the beginning of the operation, the surgeon dissects the skin layers above the cranial vault (a scalp incision is made).
- After turning away the cut skin, the doctor moves the muscle layers aside.
- At the next stage of the operation, the required part of the bone tissue of the skull is removed so that the brain tumor becomes accessible for manipulation.
- Then the pathological focus is excised and the extracted bone tissue is installed in its original place (this is called trepanation). If part of the skull is not returned to its original place, then such an operation is called resection.
- At the final stage of the operation, the soft tissues covering the skull are restored and sutures or staples are applied.
After resection, the hole in the skull is closed with a special material or mesh. Removing pathogenic tissue reduces intracranial pressure, freeing up space for swollen tissue afterwards. In addition, craniotomy is necessary if the tumor process has spread to bone tissue. After removal, the extracted biological material is sent for histological analysis.
Treatment of brain tumors
In our hospital, a comprehensive approach is used to treat brain tumors: surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
The task of neurosurgeons during brain surgery is to reduce the volume of the intracerebral tumor, as well as to collect tumor cells for histological examination in order to verify the tumor process with further radiation and chemotherapy treatment. Some tumors are completely removed. Tumors that grow into important functional centers of the brain, central vessels and nerves are removed partly due to the high risk of damage to healthy areas and the occurrence of irreversible neurological consequences.
The operations are performed under general anesthesia. The patient is placed on the operating table on his back or side, depending on the ease of access to the tumor.
A craniotomy is performed. Part of the skull bone above the tumor is removed. To remove a tumor, neurosurgeons use special devices, endoscopic techniques, microsurgical instruments, and a surgical microscope.
In cases where the localization of the tumor causes liquorodynamic disturbances and increases intracranial pressure, special ventriculoshunting operations are performed. This allows you to normalize intracranial pressure. Radiation therapy is used immediately after surgery. Sometimes it is more important than surgery and is the only method of choice. The goal of radiation therapy is to kill the remaining malignant cells and prevent them from growing further. In our hospital, in the radiology department, irradiation of the area of the brain affected by the tumor is carried out using a modern remote cobalt radiotherapy device “TERABALT”. The dose and duration of the course depend on the type of tumor, its size, and the age of the patient.
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment of tumor cells. Taking into account the type of tumor, the chemotherapist selects the necessary drug that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier of the brain and have a detrimental effect on malignant cells. Chemotherapy is prescribed in courses.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy have their own side effects. But sometimes there is no other choice to improve the patient’s health.
SPECIALISTS
Sorvilov Igor Vasilievich
Head of the Department of Neurosurgery, neurosurgeon of the highest qualification category
Voloshin Yuliy Nikolaevich
neurosurgeon of the highest qualification category
Bastron Alexey Yuryevich
neurosurgeon of the highest qualification category
Life forecast
Without surgery, treatment of malignant tumors is ineffective, and the prognosis is extremely negative. After removal of a tumor, life expectancy depends on the stage, level of malignancy, type of carcinogenesis and the degree of its germination into other structures. As a rule, after partial removal of the tumor, brain cancer comes back again, so surgery in this case prolongs the patient’s life for a very short time. The patient will live no more than a year if the relapse is aggressive, and only 25% of patients will live more than two years. After removal of the pathological focus at the first stage of malignancy, life expectancy in 80% of patients is estimated at more than 5 years (in the case of complete removal of carcinogenic tissue). The most dangerous are the late stages of the disease. The prognosis for life at the quadruple stage is not very encouraging - a person will not live longer than a year.