04.12.2015
Maltseva Marina Arnoldovna
Head of the consultation department - neurologist, specialist in the field of extrapyramidal pathologies, doctor of the highest category
Shabunina Ekaterina Mikhailovna
Neurologist, category 2
Prolonged headaches may indicate the patient is developing a dangerous disease - a malignant brain tumor. Let's consider the main characteristics of pain due to brain tumors and the features of combating them.
What to look out for in case of brain cancer
A cancerous brain tumor does not metastasize, that is, secondary foci. However, already in the early stages of the development of the process, the patient begins to feel its signs. The following symptoms of trouble should alert you:
- progressive impairment of speech function;
- disturbances in coordination of movements;
- constant fainting;
- chronic headaches. Remember that headaches with a brain tumor are constant. They do not subside after taking analgesics, which are usually found in our home medicine cabinet. This phenomenon should be more alarming than others;
- the occurrence of hallucinations of various types. Most often, a person feels the constant presence of a certain odor.
Symptoms of a brain tumor
Symptoms that develop with brain tumors are divided into four main groups. The first group consists of growing tumors. They can cause an increase in intracranial pressure, leading to headache, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting. Typically, a severe headache develops in the morning and subsides by mid-day. Vomiting occurs suddenly, which was not preceded by a feeling of nausea. Intracranial pressure increases with tumors localized in the cerebellum, fourth ventricle and pons. Often the neoplasm spreads to the entire ventricle.
A group of focal symptoms is caused by damage to local brain structures. Severe symptoms occur with massive tumors localized in the motor cortex, base of the brain, or Broca's area. The following signs indicate damage to the motor cortex: myoclonic seizures, generalized convulsive epileptic seizures and paresis of one half of the body. Hallucinations, oral automatism reflexes and other psychotic disorders are typical for damage to the temporal lobes of the brain. When the tumor is located in the right hemisphere, the headache occurs in the right half of the head.
Tumors that are localized in the deep parts of the brain and affect the visual pathways are characterized by the development of visual impairment. When the tumor is located at the base of the brain, neurologists find classic symptoms of damage to the cranial nerves. A tumor located at the jugular foramen causes cranial nerve palsies. For cerebellar tumors, in addition to headache, the development of the following symptoms is typical:
- nystagmus (involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyes of high frequency);
- ataxia (disorders of coordination of movements);
- diplopia (double vision).
Symptoms of the third group are caused by long-term endocrine effects, which are characteristic of tumors of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Damage to local parts of the brain is typical for pituitary tumors. They extend upward to the area that lies above the sella turcica and to the optic chiasm, as well as into the sphenoid sinus located below.
If the pituitary tumor grows laterally, the cavernous sinuses are affected. It can spread to areas behind them, sometimes to the middle or posterior cranial fossa. The tumor can also affect the III, IV and VI cranial nerves. Intratumoral hemorrhages lead to severe headaches, sudden visual disturbances and a decrease in the production of hormones by the pituitary gland.
The nature of headache during a tumor
Headache during brain tumors is significantly different from others. Not only is it permanent and does not go away after strong enough painkillers. It is oppressive in nature. In some cases it is quite intense. The headache intensifies in the following cases:
- exercise stress;
- sharp bends of the body;
- cough;
- abdominal muscle tension.
The headache is also worse in the morning. This occurs as a result of the fact that huge amounts of fluid accumulate in the brain tissue overnight.
Such pain also has warning signs. Usually they are nausea. In addition to such characteristics as intensity and duration, the patient can also describe his sensations this way:
- the pain seems to “pulsate” in the head”;
- after waking up the sensations are the strongest;
- confusion of consciousness and speech is often noted;
- migraine symptoms are completely absent;
- Sometimes the painful sensation is complemented by dizziness, decreased sensitivity of certain parts of the body, mental disorders, and signs of depression.
Diagnosis of a brain tumor
To make a diagnosis and determine the stage of a brain tumor, the following studies are prescribed:
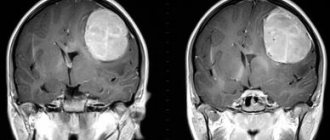
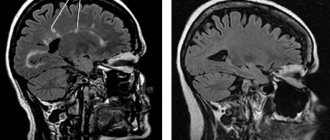
- MRI. Measures the size of a brain tumor. Before scanning, a contrast agent is injected to improve image quality.
- Biopsy (tissue sampling). To make a definitive diagnosis, surgical removal of the brain tumor is performed. A small amount of tissue is used for examination under a microscope.
- CT scan. Computed tomography allows you to visualize the brain in a 3D projection, which makes it possible to accurately determine the size and location of the tumor.
Among the effective methods for diagnosing the oncological process, PET, cerebral arteriogram, spinal tap or lumbar puncture, and myelogram should be highlighted. The results obtained make it possible to determine the size and type of tumor in order to develop effective therapy.
What to do for headaches
If you notice any alarming symptoms, the first thing you should do is visit a doctor. Under no circumstances should you buy painkillers for yourself. There is no need to trust your precious health to healers.
Remember that only early diagnosis of brain tumors will significantly increase the likelihood of successful treatment.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 4 votes
Share article on social networks
Treatment measures for brain tumors at the Medscan clinic
Conservative therapy for brain cancer is prescribed to reduce the pressure on cerebral tissue. This is necessary to reduce symptoms and normalize the general condition of the patient’s body. The doctor prescribes painkillers and antiemetics, psychotropic and sedatives.
Drug treatment of a brain tumor is aimed at temporarily alleviating the patient’s condition. The main way to combat a brain tumor in oncology is surgical removal (gamma and cyber knife). Small tumors are removed using stereotactic radiosurgery.
Oncology care: an interview about a tumor that disguises itself as a headache (sometimes arms and legs go numb)
In any case, the patient decides whether he is ready for surgery or not. Much depends on the experience of the surgeon, the equipment of the clinic, and preoperative planning. It is highly likely that if the left temporal lobe is operated on in a right-handed person, speech function may be affected, but this is an acquired function, so patients have the opportunity to learn to speak again by working with a speech therapist.
How long does it take for a person to recover after brain surgery?
— This is a very delicate point that depends on many factors. It is possible to operate on a patient in such a way that he will be in a coma for a month, or it is possible so that he will be awakened by the anesthesiologist immediately after the end of the operation, transferred to the department three hours later, the next day he will be able to walk, and on the fifth to seventh day he will be discharged from the hospital .
In most cases, our patients are transferred to the department either on the day of surgery, or the next morning, spending several hours in intensive care, or the next day.
— What are the features of immune and targeted therapy for brain tumors?
— There is an immune theory of the appearance of tumors: the patient’s immunity begins to work incorrectly, because some pathological cells that carry genetic errors are constantly being formed in the body. The body finds them and kills them using its own immunity. For some reason, the body cannot identify an individual tumor cell, it begins to divide, and a tumor develops.
There are methods that are being developed in several countries, including here in Novosibirsk at the Research Institute of Fundamental and Clinical Immunology, when after surgery in a patient with a brain tumor the main markers of tumor cells are released, which are presented to the blood cells responsible for immunity. The latter, “immunized” by the tumor, are left immune. This is the most simplified and superficial description of the idea of immunotherapy for tumors in general and brain tumors in particular. This is one of the modern trends in oncology.
Targeted therapy is targeted, affecting a certain type of malignant cells of the same type with identical defects in the genome, and malignant brain tumors are very polymorphic in their structure: they have many genetic mutations, so they are often difficult to fight. For example, targeted therapy is effective for patients with certain types of breast cancer, when there is one type of genetic defect. Therefore, it is still difficult to create targeted drugs for brain tumors. Unfortunately, at present, malignant brain tumors - primarily we mean glioblastomas - are among the most aggressive and difficult to treat.
— Many famous people died from malignant tumors, including glioblastomas. For example, Zhanna Friske had a tumor. Actress Anastasia Zavorotnyuk was also diagnosed with it. In your opinion, can the appearance of glioblastomas be influenced by IVF, as was discussed in the media?
— Pregnancy itself is an additional stress, especially in cases where additional medicinal preparations for this process are carried out. However, this issue requires separate study before making a direct cause-and-effect relationship between these procedures and the development of malignant tumors.
Cancer pain
A cancer patient often experiences pain: acute pain after surgery, acute pain during complications of chemotherapy and chronic pain during radiation damage to soft tissues, acute pain when taking blood tests and administering medications, chronic pain from a developing tumor and growing metastases. Each pain has its own emotional coloring: burning, dull, spastic.
The patient may simultaneously have several types of pain: dull pain in the lumbar spine affected by metastases, which becomes acute when the body position changes. And then there was an acute burning pain due to medicinal stomatitis that developed after chemotherapy and spastic pain due to damage to the intestinal mucosa. At the same time, temporary headaches associated with fatigue or increased blood pressure, which are common for all people, are not completely excluded.
Cancer pain is associated with the presence of a tumor, primary or secondary - metastases. Metastases grow into surrounding healthy tissue, involving them in the cancer process and destroying nerve endings that signal trouble to the brain. Not all organ metastases cause pain. Thus, damage to the lung tissue is painless until the process involves the pleural layers, which will hurt during inhalation. Pain in the liver or kidney will appear when the capsule covering the organ is involved in the cancer process.
Metastases in the bones will hurt when the process spreads to the abundantly innervated periosteum - there are almost no nerves inside the bone, and therefore there will be no pain either. Metastases in the brain push back tissue, but pain will appear only with severe compression of the brain, plus additional production of cerebrospinal fluid and disruption of its outflow will increase intracranial pressure.