Main precedents of violations
Among them are congenital and acquired. Congenital ones include:
- Genetic failure of intrauterine development;
- Structural pathologies leading to disruption of connections between the hemispheres of the brain;
- The appearance of congenital neoplasms that can replace the ventricles of the brain;
- Arnold-Chiari and Dandy-Walker syndromes.
Acquired causes include:
- Consequences of traumatic effects on the brain and spinal cord;
- Intracranial formation obstructing normal outflow;
- Inflammatory and infectious processes in the tissues of the brain or spinal cord;
- Thrombotic formations.
The mechanism of occurrence of pathology
The main mechanism for the development of liquorodynamic disorders is a violation of the ratio of the volume of cerebrospinal fluid produced over the volume of its absorption. The process of cerebrospinal fluid production will depend on the state of the natural barrier between it and the bloodstream. As a result, through transfusion through the walls of biological barriers, plasma exits the blood into the cerebrospinal fluid.
Since the space where it is located is quite limited, when the quantity increases, compression of the structures of the central nervous system begins to occur. As a result of such changes, neurological symptoms appear. In some cases, a pathological clinic may develop against the background of normal cerebrospinal fluid production. But at the same time there is a violation of its outflow from the cavities of the brain. Another mechanism is the slowing down of the absorption of the substance into the brain structures.
Prevention of liquorodynamic disorders
Preventive measures include:
- Observation of pregnancy in the antenatal clinic. It is very important to register as early as possible.
- Timely detection of intrauterine infections and their treatment.
At 18-20 weeks, an ultrasound shows the development of the fetal brain and the state of the unborn child’s cerebrospinal fluid. At this time, it is possible to determine the presence or absence of pathologies.
- The right choice of delivery.
- Regular monitoring by a pediatrician. Measuring the circumference of the skull, if there is a need to conduct a fundus examination.
- If the fontanel does not close in a timely manner, it is necessary to conduct neurosonography and consult a neurosurgeon.
- Timely removal of tumors that block the cerebrospinal fluid pathways.
- Regular observation by a doctor and carrying out the necessary studies after suffering injuries to the brain and spinal cord.
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases.
- Prevention and therapy of chronic diseases.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- It is recommended to play sports and lead an active lifestyle.
It is easier to prevent any disease or take all measures to reduce the risk of developing pathology. If liquorodynamic disorders are diagnosed, then the earlier therapy is started, the greater the chance that the child will develop normally.
Symptoms of liquorodynamic disorders
The main complaint of patients with liquorodynamic disorders will be severe, sometimes unbearable headaches. A typical place for their localization is the parietal region. In some cases, they can radiate to the entire surface of the head. Often, the patient can accurately name the cause of the headache. Typically, this is sneezing, severe coughing, screaming, a sudden change in body position, in particular the head, etc. A headache can also be caused by prolonged uncomfortable posture, which leads to increased muscle tone in the cervical spine.
The pain symptom is accompanied by a feeling of nausea, as well as vomiting. The gag reflex is most often accompanied by a small amount of discharge, with the exception of recent consumption of food, the nature of the resulting masses does not have pathological signs.
Some people note visual impairment, which is manifested by decreased clarity, flickering spots and flashes of light. A severe manifestation of liquorodynamic disorders is dizziness, which can lead to falls. Upon examination, horizontal nystagmus and spasm of the muscles of the occipital group are revealed.
With a large volume of disorders, convulsions appear, they are clonic-tonic in nature. After an attack, pronounced muscle rigidity is observed.
Diagnosis of pathologies
Currently, there are several methods for diagnosing liquorodynamic disorders. The basis in this case is complaints and the clinical picture. In order for the doctor to make a more accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to initially talk with the patient, ask him about the complaints, the time of their appearance, duration, as well as the conditions against which they appear.
The accuracy of the diagnosis and the reduction of possible examinations are reduced after examining the patient; it is preferable to do this not during a period of calm and absence of a clinic, but at the moment of manifestation of the disease.
An examination is carried out, great attention is paid to checking nystagmus and palpation of muscles, especially the occipital muscles. After this, instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods begin.
Laboratory
The most common and economically less expensive is a general blood test. It indirectly determines the presence of an inflammatory process. This is necessary to confirm or, conversely, exclude a possible cause of the disease.
Cerebrospinal fluid examination. The method is less common and requires highly trained specialists for this manipulation. With its help, the nature of the contents contained in the cavity of the brain and spinal cord is clarified. In case of liquorodynamic disorders, an increase in protein content may be detected. A mandatory point is the complete absence of an inflammatory component.
There are many more instrumental diagnostic methods compared to laboratory ones, and in addition, they have greater diagnostic value. Among them are the following:
- Ultrasonography. It allows you to evaluate not only the structures of soft tissues, but also possible mechanical causes that create a violation of the outflow of fluid.
- Angiography is a method for determining the condition of the vascular component of the body. In cases of liquorodynamic disorders, examination of the vessels of the head and neck is of great importance. With its help, you can identify even small disorders that give a clinical picture of the disease.
- Echoencephalography. This is a non-invasive way to detect pathological changes in the transmission of nerve impulses at the level of the brain substance.
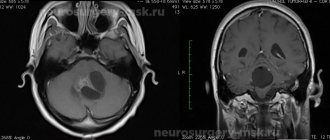
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging . These are ways to assess the state of brain structures, the volume of cavities and the sizes of component parts. Recently, the technique has become very popular due to the high accuracy of the resulting image compared to the previously common method of x-ray examination. Its significant disadvantage is high economic costs, as well as in some regions inaccessibility.
It is after a correctly developed diagnostic plan and the data obtained that the issue of selecting treatment is decided. It is useless to treat only symptoms, as this can lead to more rapid development of complications.
Diagnosis of liquorodynamic disorders
As everyone knows, a timely diagnosis is the first step on the path to healing. However, it is important to take into account that you need to seek professional help from an experienced doctor who will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment without causing harm to the patient’s health. As a rule, the diagnosis of liquorodynamic disorders is made using a lumbar puncture with the conversion of cerebrospinal fluid pressure. You will also be prescribed a computed tomography scan of the brain, ECHO-EG (echoencephalography), NMRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging), angiography and pneumoencephalography. Only after carrying out all these manipulations can the doctor make a correct diagnosis and begin treatment of the patient.
Treatment of diseases
It will largely depend on the cause that caused the clinical manifestations. Therefore, this therapy is also called etiopathogenetic. If the cause is congenital, associated with structural anomalies, then surgical intervention may be required to create artificial drainage systems or restore the outflow disorder. Such methods currently help cope well with hydrocephalus in the early stages of its course. Some congenital anomalies in the development of the brain or spinal cord, as well as bone structures, cannot be eliminated.
In case of thrombotic disorders that cause outflow disturbance, the use of anticoagulants, as well as agents that promote the resorption of blood clots, is required.
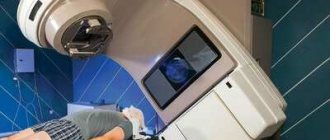
Tumor processes need to be treated using a comprehensive method. It will include surgery and, at the discretion of the specialist, chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
If the root cause is an infectious agent, anti-inflammatory treatment is prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen.
Since currently most liquorodynamic disorders can occur due to outflow disturbances due to changes in posture, much attention is paid to this method of treatment. In adults, it is quite difficult to completely correct the situation, and this may require complexes of surgical and physical methods; in childhood, you need to consult a specialist in order to select the most effective exercises aimed at improving the muscular corset of the spine.
Treatment of liquorodynamic disorders
The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chance of restoring lost brain functions. The type of treatment is selected based on the presence of pathological changes in the course of the disease, as well as the age of the patient.
In the presence of increased intracranial pressure, diuretics are usually prescribed: Furosemide, Diacarb. Antibacterial agents are used in the treatment of infectious processes. Normalization of intracranial pressure and its treatment is the main task.
To relieve swelling and inflammation, glucocorticoid drugs are used: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone.
Steroid medications are also used to reduce cerebral edema. It is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease.
As soon as liquorodynamic disturbances are detected, treatment should be prescribed immediately. After undergoing complex therapy, positive results are noticeable. This is especially important during the period of child development. Speech improves, progress in psychomotor development is noticeable.
Surgical treatment is also possible. It may be prescribed in the following cases:
- Drug treatment is ineffective.
- Liquorodynamic crisis.
- Occlusive hydrocephalus.
Surgical treatment is considered for each case of the disease separately, taking into account age, characteristics of the body and the course of the disease. In most cases, surgery on the brain is avoided so as not to damage healthy brain tissue, and complex drug treatment is used.
It is known that if the syndrome of liquorodynamic disorders in a child is not treated, the mortality rate is 50% up to 3 years, 20-30% of children survive to adulthood. After surgery, mortality is 5-15% of sick children.
Mortality increases due to late diagnosis.
Prevention of violations
This is one of the most important stages aimed at preventing not only liquorodynamic disorders, but also complications associated with them.
First of all, this is to prevent the development of the congenital form of this disease. If family members have hereditary pathologies, especially those related to circulatory disorders or developmental defects of various organs, it is necessary to consult a geneticist for advice. This is necessary to exclude the possible transmission of disorders associated with genetic mutations transmitted by inheritance.
As well as careful pre-conception preparation of a woman to prevent the development of inflammatory diseases at the stage of bearing a child.
Among the measures to prevent acquired conditions, the following should be highlighted:
- Prevention of infectious inflammatory diseases associated with damage to the nervous system.
- Monitor the state of the blood coagulation system, avoid hypercoagulation and stressful situations, as well as surges in blood pressure.
- Monitor your posture and prevent the development of osteochondrosis, especially in the cervical spine. To do this, you regularly need to carry out physical exercises aimed at strengthening your muscles. When working in a forced position of the body, take regular breaks to relax muscle fibers, as well as prevent stagnation.
What is this
CSF is produced by a special zone of the lateral ventricles of the brain, where blood vessels and epithelium are closely intertwined, forming villous plexuses in the lateral ventricles, which are also called “choroidal”; they produce cerebrospinal fluid from blood plasma due to the activity of two key enzymes: Na+/K+-ATPase and carbonic anhydrase. In fact, the action is vaguely similar to the work of the kidney, only the speed is lower: 0.35 - 0.4 ml/min., That is, 0.5 liters per day (complete renewal occurs 3-4 times a day).[1] Next, the cerebrospinal fluid passes inside the cavities of the brain, enters the central canal of the spinal cord and into the subarachnoid space around the brain, where the movement of this fluid becomes more directed upward, around the brain and downward, enveloping the spinal cord in the spinal canal. The cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed back by the arachnoid villi of the superior sagittal sinus, as well as by similar formations of the base of the brain and spinal roots due to the pressure gradient between the cerebrospinal fluid spaces and the contents of the sinus. All this allows the CSF to constantly circulate along the outer surfaces of the central nervous system and renew the cerebrospinal fluid.
Good cerebrospinal fluid is colorless, transparent and urine-like liquid, flowing out under pressure from 70 to 120 mm of water
.st. - this is about a drop per second during puncture. In the central nervous system there are only about 120 milliliters (+/- 30 ml)
Hydrocephalus
An increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity for several different reasons:
- Too much water is produced - with TBI, neuroinfections:
- Water does not come out well - impaired absorption of waste liquor: this usually happens after meningitis, SAH, sinus thrombosis due to clogging of the sewer with protein;
- Congestion - in the ventricles of the brain, aqueduct or holes of Luschka and Magendie completely interrupts the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, resulting in occlusive (non-communicating) hydrocephalus
- An obstruction to the flow of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space gives rise to communicating hydrocephalus - the cerebrospinal fluid still continues to flow there;
- Hydrocephalus may be due to impaired development of certain parts of the brain;
- When the brain atrophies, fluid replaces the vacated space, which is called replacement hydrocephalus. It is this hydrocephalus that occurs in Alzheimer's disease.
As CSF volume increases, the pressure may or may not increase.[2]
Consequences of liquorodynamic disorders
If you do not treat this disease in time, then after a short time after the onset of symptoms, adverse consequences may appear:
- Among them, the most common are cognitive impairment and memory impairment. A person may forget about events that happened to him recently. The ability to perceive information and remember gradually decreases.
- Children who have liquorodynamic disorders begin to develop worse than their peers, both mentally and physically.
- Constantly disturbing headaches prevent a person from performing his work duties normally. In many ways, the changes described above occur due to impaired nutrition of the brain substance. All brain cells, and in particular the cortex, are very sensitive to a lack of oxygen, and with prolonged or constant deficiency, their atrophy begins to occur. That is why adult children with severe manifestations of liquorodynamic disorders are forced to receive a disability group.
Causes of liquorodynamic disorders
As a rule, this disease occurs due to inflammatory processes that occur in the brain tissue. A spinal cord injury may also be involved - this fact plays an important role when compiling an anamnesis. Liquorodynamic disturbances can appear as a result of back injuries; very often patients suffer from intracranial hypertension after traumatic brain injury; the cause may be a tumor, as well as diseases (parasitic) of the central nervous system. Liquorodynamic disorders can develop in a person who has congenital pathologies in the formation of the brain, as well as the spinal cord.