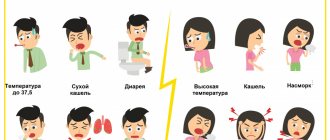
Photophobia symptoms
Photophobia can manifest itself in the following signals:
- squinting eyelids even in conditions of
In this article
Photophobia symptoms
- Causes
- Photophobia as a symptom
- Diagnosis and treatment of photophobia
dim lighting;
Photophobia is often accompanied by headache and dizziness, the effect of sand in the eyes, and a gradual deterioration in visual function. The presence of photophobia can be determined independently by these symptoms, but you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and prescription of corrective therapy.
Symptoms
Manifestations of photophobia are determined by the very name of this pathology. This disorder is primarily characterized by a complete intolerance to bright light in the eyes.
Moreover, strong discomfort with this disease is caused by both artificial and natural light sources. When entering an open, well-lit space, the patient in this case involuntarily squints, trying to cover his eyes with his eyelids or his hand. After all, at this moment he experiences pain in the eyes or even a headache.
In cases of extreme severity, patients react acutely not only to bright lighting, but it becomes impossible for them to tolerate any light at all. Sometimes such a disease is hereditary and can be explained by the high sensitivity of the eye to excessive light intensity, even in the absence of any pathologies.
Such patients are usually recommended to wear special glasses with dark lenses to protect their eyes from the discomfort caused by daylight and to adapt to the performance of daily duties.
Causes
- Photophobia can occur for non-pathological reasons:
- a congenital structural feature of the eye with the absence of coloring pigment;
- dilated pupils when using eye drops;
- use of certain medications;
- prolonged work at the computer, which overloads the eyesight and causes dry mucous membranes;
- prolonged stay in the dark;
- the presence of a foreign body in the organs of vision (in this case, photophobia usually affects one eye and is accompanied by cutting sensations);
- exposure to excess sunlight on the retina.
For such reasons, fear of bright light does not indicate the presence of a disease.
But in some cases, photophobia is a sign of the disease, which, in combination with other signs, indicates the true cause of the pathology:
- the presence of an ophthalmological disease (keratitis, conjunctivitis, etc.);
- acute infectious diseases (measles, rubella, meningitis);
- cold viral infections;
- in rare cases - neurological disorders, depressive disorders, chronic fatigue.
Getting rid of photophobia in such situations can only be done by identifying and treating the underlying disease.
Photophobia as a symptom
By analyzing the compatibility of symptoms, you can guess what pathology caused the appearance of photophobia, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
- Photophobia and lacrimation
Their simultaneous appearance may indicate a mechanical injury, a foreign body or substance entering the eye; inflammation or erosion of the cornea; conjunctivitis; influenza or acute respiratory disease; aniridia and other developmental anomalies of the eyeball; inflammation, melanoma or retinal detachment; retinopathy; hemophthalmos; hyperthyroidism; uveitis; migraine; encephalitis, meningitis.
In addition to lacrimation and photophobia, each of these diseases is characterized by a whole list of other symptoms that help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment.
- Photophobia and eye pain
They can be combined with burns, ulcers, mechanical damage to the cornea, spring catarrh, acute glaucoma, endophthalmitis.
- Photophobia and redness of the eyes
The simultaneous appearance of these signs may indicate injury or burn of the cornea, keratitis, uveitis, conjunctivitis.
- Sun sensitivity and fever
Increased sensitivity to light in combination with a rise in body temperature may indicate meningitis, endophthalmitis, encephalitis, trigeminal neuralgia, hemorrhagic stroke, brain abscess, purulent uveitis.
- Photophobia and headache
This combination is typical for brain abscess, migraine, encephalitis and meningitis, stroke, tension headaches, acute attacks of glaucoma, acromegaly.
- Fear of light and nausea
Typically, nausea combined with photophobia indicates increased pressure inside the eyes or skull, which is typical for diseases such as meningitis, migraines, hemorrhagic stroke, and brain abscess.
- Photophobia and pain in the eyes
Cutting sensations in the eyes with fear of bright light are characteristic of conjunctivitis, keratitis, astigmatism, trigeminal neuralgia, uveitis, blepharitis, ulcers and burns of the cornea.
Causes and treatment methods for photophobia
Some people experience increased eye sensitivity to light. This condition is usually accompanied by uncomfortable sensations: pain and burning in the eyes, as well as involuntary closing of the eyelids. Photophobia itself is not a disease. Often it indicates the presence of various pathological processes in the body.
What is photophobia of the eyes?
Increased sensitivity of the organs of vision to a light source in a child or adult is usually called photophobia. This condition is characterized by a painful reaction of the visual organs to any source of both natural and artificial light. Involuntary closing of the eyelids, itching and burning in the eyes, as well as increased lacrimation are the most characteristic symptoms of photophobia. In addition, additional unpleasant phenomena such as headache, dizziness, vomiting and nausea, and in severe cases, even loss of consciousness may occur.
When the retina is exposed to light, a person’s unconditioned reflex of involuntary squinting is triggered. There is a certain indicator of the lighting intensity at which this mechanism does not work, and a person comfortably perceives the rays of light. This parameter may vary somewhat in each specific case, but, as a rule, it has an average statistical value. If the lighting intensity exceeds the permissible norm, blinding and involuntary squinting of the eyes occurs, which is not a deviation. However, if this reaction is observed under normal lighting intensity, we can talk about a phenomenon such as photophobia. Ophthalmologists claim that there is no such disease as photophobia. In fact, the presence of increased sensitivity of the visual organs to light may indicate various pathological conditions in the human body that are not necessarily associated with the visual system.
Photophobia of the eyes in adults and children should not be confused with such a serious disease as heliophobia (fear of being in the sun). This is an obsessive condition associated with dysfunction of the nervous system. It has nothing to do with the patient's visual system. In this case, the help of a qualified psychiatrist is required.
Signs of photophobia:
• Involuntary closing of the eyelids;
• Increased lacrimation;
• Itching, burning, pain and stinging in the eyes;
• Headache, dizziness;
• Vomiting, nausea, loss of consciousness (in severe cases).
As a rule, these symptoms are characteristic of both adults and children. They are observed only in direct contact with a light source. When you are in a darkened room, the discomfort disappears.
Photophobia of the eyes in an adult: causes of occurrence
Increased sensitivity of the visual organs to light can occur for a variety of reasons. The most common include inflammatory, infectious and other diseases of the visual organs.
What inflammatory eye diseases cause photophobia?
• Conjunctivitis (inflammation of the uvea of the eyes);
• Keratitis (inflammation of the cornea);
• Iritis (inflammation of the iris).
Photophobia can also be triggered by damage to the organs of vision of various types: sunburn, as well as erosion, ulcers and mechanical damage to the cornea, including those caused by the penetration of a foreign body or wearing incorrectly selected contact correction devices. In the absence of timely assistance from an ophthalmologist, these conditions pose a threat to eye health.
The causes of photophobia may be associated with some common diseases, such as influenza, acute respiratory infections, migraines, acute attacks of glaucoma, etc. The sensitivity of the visual organs to light is also affected by taking certain medications. In addition, a discomforting symptom may occur due to adverse environmental influences, for example, during a long stay in an area with excess ultraviolet radiation.
If the eye is exposed to excessively bright light, photophobia may also occur. This is often observed during welding work without protective glasses, as well as when looking sharply at the sun or the penetration of a large number of sun rays reflected from the snow (snow ophthalmia). In addition, high sensitivity of the organs of vision to light often occurs against the background of constant drying of the cornea and increased visual stress. This is especially true for patients whose work involves being at a computer.
Sometimes photophobia can be congenital. In this case, the human eye reacts too actively to artificial or daylight due to an insufficient amount or complete absence of a special pigment in the body (melanin). In addition, the presence of this symptom may indicate the occurrence of various pathological conditions in the body.
What diseases are photophobia symptoms of?
• Various diseases of the nervous system;
• Diseases of the thyroid gland;
• Infections (rabies, measles, rubella);
• Various hereditary diseases (color blindness, etc.);
• Intoxication (mercury poisoning, etc.).
Photophobia of the eyes in children often develops against the background of increased visual stress and fatigue of the visual organs. This may be a consequence of stress, lack of sleep, excessive time spent with various electronic devices (computer, smartphone, etc.), as well as pathologies in the structure of the visual organs. In some cases, the provoking factors are incorrectly selected vision correction products. Children are more often susceptible to viral and infectious diseases, so photophobia is often a consequence of these ailments. This is especially true for viral and infectious conjunctivitis. In rare cases, the cause of increased sensitivity of the eyes to light in a child is “pink disease” - an autoimmune childhood disease that is accompanied by photophobia, high blood pressure, anorexia, increased sweating, and pink discoloration of the skin of the feet and palms.
Diagnosis of the disease and clinical picture
If signs of photophobia persist for more than three days, you need to consult an ophthalmologist and undergo a comprehensive examination of the visual organs: ophthalmoscopy, examination of the condition of the cornea, as well as additional diagnostic methods to determine the cause of the pathology. This applies to both adults and children. If during the examination the ophthalmologist determines that the cause of photophobia is not related to a malfunction of the visual system, the patient will be prescribed additional examinations: MRI or CT scan of the brain, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and others. In some cases, additional consultation with a neurologist may be required.
Before treating photophobia, it is necessary to determine what disease it is a symptom of. Only in this case will a specialist be able to prescribe a therapeutic course of treatment. Often, elimination of the primary cause - the underlying disease - leads to the disappearance of the high sensitivity of the visual organs to light. In some cases, when it is impossible to eliminate this cause, the patient is advised to make small adjustments to his daily life to prevent photophobia. On sunny days, it is advisable to go outside only in safety glasses with a high-quality UV filter and a hat with a wide brim.
Photophobia may be temporary. For example, it occurs when a foreign body enters the eye. In this case, a moisturizing ophthalmic solution, as well as antiseptic or anti-inflammatory drops, can help. However, it should be remembered that the use of medications is permissible only under the supervision of a physician.
In some situations, photophobia is an individual characteristic of the human body and is in no way associated with any disorders or pathological processes. In this case, wearing wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses is recommended.
A person needs to seek help from a specialist as soon as possible if:
• Aversion to light and pain in the eyes appear even at low levels of illumination;
• When exposed to light, vision becomes blurred and this condition persists for 2 days;
• Headaches appear, the organs of vision become very red;
• There is a need to wear sunglasses indoors.
How to prevent symptoms of photophobia?
Following some simple preventive measures will prevent the appearance of photophobia (photophobia) in children and adults. Ophthalmologists recommend, whenever possible, reducing the time spent at a computer or tablet, even for educational purposes. It is necessary to follow a daily routine. It is important that sleep is complete and stable: at least 8 hours for children and at least 7 hours for adults. It is imperative to go to bed at the same time. In addition, you should walk in the fresh air, preferably at least 1 hour a day.
One of the preventive measures for the appearance of photophobia is maintaining personal hygiene of the visual organs. This will reduce the risk of penetration of various bacteria and microorganisms that cause eye diseases, which in most cases provoke photophobia. Another important factor is a balanced diet that provides the necessary amount of vitamins and microelements. To avoid the development of photophobia due to visual fatigue, people with high visual stress should regularly perform simple eye exercises. Ophthalmologists advise taking short breaks every half hour when working at a monitor for a long time.
People who are forced to spend long periods of time outdoors due to the nature of their work are recommended to wear sunglasses. As a rule, this applies to builders, drivers and representatives of other professions who often stay outdoors during the daytime.
Come for a diagnosis at the Kazakh Research Institute of Eye Diseases at the address: Almaty, Tole bi street, 95a (corner of Baitursynov street). Telephone; +7 (727) 279 54 36
Diagnosis and treatment of photophobia
Therapy for photophobia is based on finding and eliminating the cause of this symptom. The following types of studies help to detect a disease that has manifested itself as photophobia:
- ophthalmoscopy - when performed, the doctor examines the fundus of the eye using a special device;
- biomicroscopy - an ophthalmologist examines areas of the fundus and the vitreous body through a slit lamp for changes;
- perimetry - this method allows you to establish the boundaries of the patient’s field of vision;
- tonometry - a test during which the doctor measures the pressure inside the eyes;
- gonioscopy - involves examining the corner of the eye where the iris borders the cornea;
- pachymetry is a diagnostic test in which the doctor determines the thickness of the cornea;
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision - helps to examine areas of the eye when ophthalmoscopy is not possible;
- fluorescein angiography - during this, the doctor examines the patency of the vessels that feed the ocular structures;
- optical tomography - it is used to detect changes in the tissues of the retina;
- electroretinography is a research method aimed at analyzing the functioning of the retina;
- culture for viruses, bacteria - helps to establish the source of the eye infection.
These diagnostic methods allow the ophthalmologist to name the exact cause of the development of photophobia and other associated symptoms. If ophthalmological examinations show the absence of eye diseases, but photophobia is present, consultation with a neurologist is required. This specialist may prescribe additional diagnostic tests: MRI of the brain, Dopplerography of the cervical vessels, electroencephalography.
If, along with photophobia, signs of hyperfunction of the thyroid gland or diabetic retinopathy were detected, an endocrinologist is involved in treatment. For symptoms indicating a tuberculosis process in the cornea, call a phthisiatrician.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist in case of photophobia is mandatory, but prophylactic wearing of sunglasses, which will significantly reduce the dose of ultraviolet radiation affecting the organs of vision, will help ease its course.
Diagnosis of photophobia of the eyes
If symptoms of photophobia persist for more than two days, you should seek medical help. Initially, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination of your vision organs in the office of an ophthalmologist. As a rule, it includes various diagnostic methods aimed at identifying the cause of the pathology: examination of the condition of the cornea, ophthalmoscopy, and others. If the specialist determines that the cause of photophobia is not related to a dysfunction of the visual system, the patient will be scheduled for further examination by a neurologist, who will most likely give a referral for an MRI or CT scan of the brain. In some cases, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and other examinations may be required. This approach is aimed at identifying the primary cause of photophobia. Only in this case can the patient be provided with qualified medical care to eliminate high sensitivity to light.
If it is impossible to eliminate the cause of the primary pathology, for example, with autoimmune thyroiditis, a person is recommended to make small adjustments to his daily life to prevent photophobia. On sunny days, direct contact with ultraviolet rays should be avoided. To do this, you should go outside wearing a wide-brimmed hat and safety glasses. These recommendations are also relevant if photophobia is in no way related to any pathological processes and is an individual feature of the human body.
If photophobia occurs temporarily, for example, due to a foreign body entering the eye, you should use a moisturizing ophthalmic solution, antiseptic or anti-inflammatory drops. This will help alleviate the symptoms somewhat. However, the use of medications is permissible only under the supervision of a physician.
Symptoms of photophobia for which you should consult a doctor:
- Increased lacrimation and pain in the eyes are observed even with low lighting levels;
- Vision becomes blurred when in contact with a light source;
- Discomfort persists for 2 or more days;
- Headaches and dizziness appear;
- There is a need to wear sunglasses indoors.