According to WHO (World Health Organization), atherosclerosis is various changes in the inner lining of the arteries (intima). They can manifest themselves as accumulation of lipids, complex carbohydrates, fibrous tissue, blood components, calcification (deposition of calcium salts), which leads to damage to the medial layer of the vessel. In the international classification of diseases ICD-10, the pathology is coded I67 (“Other cerebrovascular diseases”).
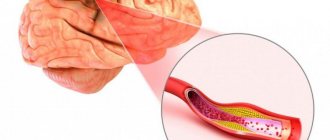
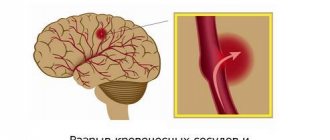
Vascular sclerosis occurs as a result of disturbances in lipid and protein metabolism in the body and is accompanied by the deposition of cholesterol, LDL and VLDL (low and very low density lipoproteins) on the walls of blood vessels. In this way, atherosclerotic plaques are formed (they are fibrous and cholesterol), gradually reducing the lumen of the arteries. The smaller their diameter, the less blood flows to organs and tissues, and ischemia occurs. Complete blockage leads to tissue necrosis. Another scenario is possible: an atherosclerotic plaque may break off and travel further in the bloodstream, where it will clog a capillary of a smaller diameter. As a rule, either an infarction occurs in the myocardium of the heart or a stroke in the brain.
The Yusupov Hospital offers complete diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular sclerosis using modern equipment. An individual approach to each patient and adherence to current treatment recommendations is the key to the professionalism of our specialists.
Causes of development of vascular sclerosis
The causes of sclerosis depend on risk factors. They can be modifiable, that is, we can influence them - lifestyle and laboratory parameters, or non-modifiable - age, gender and genetic predisposition.
Non-modifiable ones include:
- gender - men suffer more often, this is explained by the fact that in women estrogen has an angioprotective function;
- age - men over 45, women > 50 or with early menopause;
- cases of atherosclerosis in relatives.
Modifiable are:
- smoking;
- drinking excessive amounts of alcohol;
- lack of plant foods in the diet;
- low physical activity;
- stress;
- overweight;
- dyslipidemia;
- diabetes;
- arterial hypertension.
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels most often occurs in the following places:
- brachiocephalic trunk;
- carotid artery (common and external carotid);
- cerebral arteries (anterior, posterior and middle);
- vertebral artery and other small vessels.
Expert opinion
Author: Alexey Vladimirovich Vasiliev
Neurologist, Head of the Research Center for Motor Neuron Disease/ALS, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels is an insidious disease that is diagnosed in patients over 45 years of age. The initial stage proceeds almost unnoticed, so patients seek help in an advanced state. People who have relatives with atherosclerosis are susceptible to the disease, so they are recommended to undergo regular diagnostics to detect the disease at an early stage.
The disease occurs due to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques. Most often, BMS sclerosis is diagnosed in people who lead an inactive lifestyle, consume tobacco and alcohol, abuse fried foods and are overweight.
The disease develops in several stages. The initial stage is asymptomatic and very difficult to recognize. However, all stages are accompanied by various symptoms:
- Initial. Headaches and dizziness occur, which are most often attributed to overwork. It is worth considering that after sleep the symptoms disappear.
- Progressive. It is characterized by increased symptoms of the previous stage, the patient experiences emotional instability, and the person becomes depressed.
- Decompensation. It is the most complex form of the disease, in which stroke or paralysis occurs. The patient has memory loss and requires constant care.
The disease is most acutely tolerated by a person, as complications appear that end in complete loss of capacity or, even worse, death of the patient.
Types of sclerosis
Medical classification divides sclerosis depending on the location of damage to internal organs and the nervous system.
Sclerosis in the brain and lateral columns of the spinal cord is called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It can cause progressive paralysis of muscle tissue. This is a neurodegenerative disease in which peripheral and central neurons die.
An autoimmune disease that affects the nervous system is called multiple sclerosis. When it occurs, the nerve sheaths are damaged, and they lose the ability to transmit impulses to certain parts of the brain.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease characterized by the formation of plaques in blood vessels as a result of high cholesterol in the blood.
Pneumosclerosis affects the lung tissue, thereby inhibiting the oxygen supply to the body.
Cardiosclerosis affects the tissues of the heart muscle and valves. Scar tissue develops, the contractile function of the organ decreases, and the result is a cardiac aneurysm. Damage to the coronary arteries leads to attacks of angina pectoris and cardiac asthma.
Sclerosis of the brain and spinal cord leads to the death of nerve cells, neurites and their replacement with connective tissue. With this type of disease, paralysis, loss of sensitivity, and mental changes (madness, dementia) may occur.
Liver sclerosis (cirrhosis) is the replacement of glandular cells by connective tissue. Leads to dropsy and death.
Nephrosclerosis is a kidney damage in which the organ becomes smaller and denser, and decay products are retained in the body. Leads to urine bleeding and death.
Senile sclerosis is atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. It is not characterized by memory loss in older people. Memory impairment at this age is associated with the natural death of neurons, which directly affects a person’s mental abilities. The rate of death of neurons depends on the conditions of their existence: nutrition, oxygen supply, etc.
Sclerosis, depending on the location and causes of its occurrence, can have completely different symptoms, so diagnosing the disease is a complex process that requires high medical qualifications. Sclerotic changes in the body are irreversible. This is facilitated by improper blood supply, pressure changes, high physical and nervous stress, smoking, and stress.
Symptoms and signs of cerebral sclerosis
Symptoms and signs depend on the degree of mismatch between the brain's oxygen needs and the body's capabilities, as well as on the duration of this pathological condition. Brain tissue consumes up to 25% of all oxygen entering the body and up to 70% of glucose, since the brain does not have glycogen reserves from which other tissues take it. There is an assumption that if you hold your breath for 10 seconds, the brain is able to use all the oxygen that is currently in its tissues. And with sclerosis of its vessels, oxygen deficiency gradually increases, leading to the appearance of the first symptoms that need to be paid special attention to:
- having trouble sleeping, waking up more tired;
- headaches become more frequent or appear for the first time. Most often as a migraine;
- memory deteriorates, you become absent-minded, it is difficult to concentrate on a task;
- constant lethargy and depressed mood.
Initial stage of the disease
At the initial stage, all previous “bells” become more pronounced and intensified. In addition to the above, dizziness, ringing in the ears and flickering of “spots” before the eyes occur, and a feeling of heaviness in the head appears.
At this stage, about 90% of patients complain of migraine headaches. They differ from ordinary ones in that they can appear at any time of the day. Their occurrence is provoked by physical or mental work, stress, and being in a stuffy room. In addition to the characteristic pulsating or pressing pain sensations, fear of light and noise is added. Conventional painkillers do not relieve the condition.
Second stage
It is characterized by a combination of complaints similar to the initial stage, but the condition is aggravated by the appearance of neurological microsymptoms:
- reflexes of oral automatism come to life;
- the innervation of facial muscles is disrupted, the tongue deviates in the direction of damage;
- coordination and oculomotor disorders occur;
- the speed of reflexes decreases, there may be convulsions or even paralysis (complete/partial);
- active movements slow down, muscle tone increases;
- Memory lapses increase, negative character traits become sharper, and psychosis is possible.
Diagnosis of cerebral vascular sclerosis
The Yusupov Hospital has all the necessary equipment to carry out a full range of diagnostics. Experienced neurologists pay close attention to each patient, listen to their complaints and collect anamnesis in order to make the correct diagnosis. To clarify this disease, it is necessary to find out the presence of associated factors:
- bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol and other drugs;
- relatives with the same disease;
- diabetes mellitus, myocardial infarction;
- cerebrovascular accidents, damage to the great vessels of the head;
- transient ischemic attacks in the past.
Laboratory examination methods use a blood test to identify the following indicators:
- dyslipidemia;
- hyperglycemia;
- hypercoagulation;
- increase in atherogenicity coefficient.
During physical examination, a reliable method for determining carotid artery sclerosis is auscultation in the bifurcation area (where the common carotid artery divides into two large branches - the internal and external carotid arteries). If stenosis is present, a systolic murmur will be heard using a phonendoscope.
The most informative instrumental studies include:
- Doppler ultrasound (duplex scanning) of the vessels of the head. The bottom line is that with the help of ultrasound you can find out the speed of blood flow using the Doppler effect. It is performed in two modes - two-dimensional (B-mode) and transcranial duplex scanning. Their difference is that B-mode allows you to study blood flow in vessels that are not located inside the skull. Transcranial scanning is used additionally when examining brain tissue for the presence of tumors;
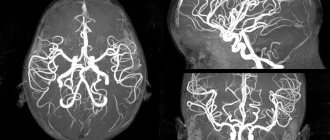
- angiography - visualization of blood vessels by introducing a special contrast agent into the bloodstream, which will be visible on x-rays;
- MRI and CT examination. They make it possible to identify cerebral circulatory disorders (ischemia, strokes), vascular malformations (aneurysms, dissections), as well as neoplasms. MRI is preferable because there is no radiation exposure and the method is non-invasive. But with the help of CT, you can detect minimal changes and obtain a three-dimensional image of internal organs, arteries and veins, joints and bones.
Treatment
When discussing the treatment of multiple sclerosis, patients are primarily interested in how curable multiple sclerosis is. Currently, there is not a single case of complete cure for this disease. But the use of preventive therapy makes it possible to delay the development of new symptoms, and also significantly reduce the number and frequency of relapses of the disease. In this case, immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibody drugs, and chemotherapy are actively used.
When determining a plan for how to treat multiple sclerosis in an individual case, the doctor takes into account the specific symptoms of the disease and prescribes exactly the medicine for multiple sclerosis that can alleviate their manifestation. However, for symptoms of multiple sclerosis, not only pills for a specific manifestation are used. If the patient goes to a specialized medical center, he is also prescribed physiotherapeutic methods of therapy, as well as a specially designed diet . Supportive treatment with folk remedies can also be practiced. Thanks to the constant work of researchers on the problem of treating multiple sclerosis, something new in the treatment of the disease regularly appears.
When the disease relapses, patients are often prescribed large doses of corticosteroids, which reduces the duration of the relapse.
Doctors are very careful about making predictions about the course of multiple sclerosis. But there are statistics that indicate that the prognosis is more favorable if the disease began before the age of 35; a woman is sick; the intervals between illnesses are long; After relapses, complete recovery occurs.
With multiple sclerosis, it is important to avoid infections, since even an acute respiratory infection can provoke an exacerbation of the disease. Patients should not be allowed to overheat, become overtired , or eat too much. Stress also has a negative impact on the patient's condition.
Treatment of cerebral vascular sclerosis
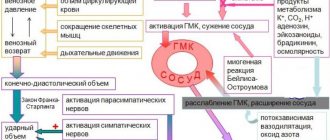
Treatment tactics are aimed at eliminating vessel occlusion (if possible), stimulating the development of collateral circulation and preventing the progression of sclerosis with possible complications.
Treatment begins with adjusting the patient’s lifestyle - quitting smoking and drinking alcohol, increasing physical activity, correcting nutrition and monitoring blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Additional, but no less important, treatment methods include physiotherapy: balneotherapy, massage and other procedures prescribed by a doctor.
Physical activity should be appropriate for age and level of physical fitness, be regular and strictly dosed. It increases the supply of oxygen and blood circulation throughout the body. Physical exercise will help reduce cholesterol levels and weight if it is overweight.
Sclerosis of cerebral vessels
Sclerosis of cerebral vessels ( cerebral atherosclerosis ) is a disease that occurs relatively frequently. In the process of its development, damage to vessels of the muscular-elastic type occurs. In this case, pockets of lipid deposits gradually form in the inner lining of blood vessels in the brain. They can be either single or multiple. As the disease develops, the vessel gradually becomes deformed and narrows. Sometimes complete obliteration of the vessel occurs. As a consequence, there is a chronic, slowly increasing lack of supply to the organ that is fed through the brain vessel affected by sclerosis.
Most often, the symptoms of this disease, as well as damage to the blood vessels of the lower extremities, appear in people after the age of twenty, but the disease is most common among people over the age of 50.
As a rule, the manifestation of the disease is determined by a hereditary factor. However, the disease begins to develop under the influence of factors that stimulate its manifestations. These are too frequent psycho-emotional stress , diabetes mellitus , arterial hypertension , alimentary obesity , physical inactivity , and smoking .
Symptoms of the disease can be different and depend on where the disease is localized and where the process spreads. Diagnosis is based on the presence of damage to individual vessels.
To treat the disease, methods are used to stop the progression of the disease, as well as to activate the development of circulatory blood flow pathways.
As a therapy, it is practiced to ensure regular muscle activity, for which special exercises are used. Particular attention is paid to the patient’s nutrition. His diet should contain equal amounts of vegetable and animal fats, since weight gain with this disease is undesirable. If a person already has excess weight , then he should get rid of it.
In addition, it is important to provide systematic treatment of diseases that accompany sclerosis. A sharp drop in blood sugar, as well as a drop in blood pressure, should not be allowed.
Drug therapy
The following groups of drugs are prescribed. Our specialists at the Yusupov Hospital will select the most suitable combination based on your medical history and examination.
- statins;
- antiplatelet agents;
- nootropics to improve cerebral circulation;
- antihypertensive drugs and drugs that lower blood sugar (if there is a concomitant pathology).
Statins are drugs that reduce certain fractions of lipids (in particular low- and very low-density lipoproteins), which are deposited on the walls of blood vessels. Antiplatelet agents increase blood clotting to prevent the accumulation of red blood cells on the atherosclerotic plaque. Thus, these two groups of drugs protect against recurrent sclerosis and the risk of stroke.
Nootropic drugs, in turn, have a stimulating effect on the integrative function of the brain. By regulating energy processes in cells, they fight hypoxia and also improve blood supply to the central nervous system. Taking nootropics improves the trophism of nervous tissue, which leads to increased brain activity, activation of operational and long-term memory and restoration of hemodynamics after a stroke or brain injury.
Antihypertensive therapy aims to lower blood pressure below 140/90 to prevent complications.
Commentary by doctor E.V. Popova about PED
Ekaterina Valerievna will talk about what types of DEDs exist, how different DEDs differ, and what influences a doctor’s choice in prescribing a particular drug for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Let's consider the indications for prescribing DMTRS for various types of MS.
The role of PITRS
The clinical effect of DMTs in multiple sclerosis develops, as a rule, from 1 month to six months from the start of use. To assess the effectiveness of the drug, treatment results are reviewed over a period of 6 months to 1 year.
Patients who have been prescribed DMT for the first time often ask the following questions:
Why take the drug if I don't feel better?
The mechanisms of action of DMTRS are such that a noticeable effect from therapy usually occurs within 1-6 months. The duration of this period is individual and depends on a number of factors, such as the nature of the disease, the patient’s condition before the prescription of drugs, concomitant therapy, individual reactions to the drug, etc. In addition, it is worth remembering that the effect of treatment for PED is not manifested by any specific sensations, but by a long-term absence of exacerbations.
Do I need PEDs if I have never had an exacerbation?
There are cases when the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is made to a patient who has never had any manifestations of the disease. This most often occurs when lesions are detected by MRI before symptoms appear. The patient is then diagnosed with radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS). On the other hand, the patient could only experience one clinical episode—clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). And, since the symptoms of MS are nonspecific and can occur in various neurological diseases, the patient may not realize that he has had an exacerbation. In both cases, according to the decision of the attending physician, the patient may be prescribed DMT therapy. This approach is justified.
Can it get worse while taking DED?
As a rule, DMT therapy stops the development of exacerbations of MS. More often, during treatment, various side effects of the drug may appear. Subjectively, these sensations may be regarded by the patient as a deterioration of the condition. Over time, these reactions may become less pronounced and no longer bring such pronounced concern to the patient. In each case, it is necessary to discuss the occurrence of side effects of the drug and options for their correction with your doctor.
I felt the effect of therapy/I felt better, when can I stop taking the drug?
If a good result is obtained from the prescribed therapy and exacerbations do not occur, treatment with DMT should not be stopped. Some patients stop treatment for MS on their own, and most typically experience a return of MS symptoms within two years or less of stopping treatment. Long-term drug treatment often causes anxiety among patients. You can compare DMTs with drugs to lower blood pressure or normalize blood sugar, which are also taken for a long time. This treatment should be regarded as helping the body with what it cannot cope with on its own. In any case, you should consult your doctor.
What are the risks of long-term use of DMTs?
With long-term use of prescribed drugs of the DMT group, mandatory monitoring of clinical blood parameters is carried out, the function of the liver, kidneys and other vital organs is assessed. If serious deviations in any of the indicators are determined, the drug may be temporarily discontinued or replaced by the attending physician. If no changes are detected during regular monitoring, there is no risk to the body.
Side effects interfere with my daily life, is it possible to stop the drug?
The criteria for changing treatment for DMT are:
- planned pregnancy;
- poor tolerability of therapy;
- change in the type of course of multiple sclerosis;
- low effectiveness of therapy.
The listed situations are quite rare, with the exception of possible pregnancy and adverse reactions. As a rule, adverse reactions are more likely to bother the patient at the beginning of therapy. Over time, they become less pronounced or disappear completely. If the attending physician confirms the severity of side effects, and the therapy prescribed to reduce their severity does not help, the drug should be changed.
What are the treatment tactics for PED during a planned pregnancy?
During pregnancy and childbirth, as well as during breastfeeding, taking DMT drugs is not recommended. Continuation of therapy should definitely be discussed with your doctor, who will assess the benefits and possible risks of therapy. After breastfeeding ends, the patient usually returns to her previous therapy. The drug for each patient must be selected individually, taking into account the form of multiple sclerosis and the characteristics of the course of the disease. The choice should also depend on the presence of certain symptoms and tolerability of certain medications. PEDs can preserve the health of the patient and prolong the period of working capacity and activity of patients with multiple sclerosis
Diet for cerebral sclerosis
Diet No. 10C is prescribed, which consists of reducing the intake of animal fat, easily digestible carbohydrates and cholesterol, as well as salt to 5–7 grams per day. It is recommended to eat plant foods and seafood. The diet should include ingredients that contain B vitamins and vitamin C, dietary fiber, potassium, magnesium (vegetable oils, vegetables and fruits, seafood, cottage cheese). Ready meals should be fresh. Boiled food is preferred, sometimes baking is allowed. The food temperature is normal. Approximate composition of KBZHU: 2200-2600 kcal, proteins - 90-100 g (50% animal), fats - 70-80 g (40% vegetable), carbohydrates - 300-350 g (50 g sugar). Low numbers are recommended for comorbid obesity. Consume up to 1.2 liters of water per day, table salt - up to 7 g.
It is prohibited to consume any types of fatty, salty and spicy foods: fatty meats, fish, poultry, canned food, sausage, caviar, smoked and salted fish, butter and puff pastry, fatty dairy products, rice, semolina, pasta, various salty and spicy foods. snacks and sauces.
A sample menu for one day would look like this:
First breakfast: low-fat cottage cheese with a small handful of nuts and dried apricots, a protein omelet, weak tea.
Second breakfast: fresh apple.
Lunch: fresh cabbage soup, steamed meat balls (chicken), vegetable sauté, compote.
Snack: rose hip decoction, apple or pear.
Dinner: tomato and seaweed salad, baked fish and boiled potatoes, tea with lemon.
At night: a glass of 1% kefir.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment of carotid artery stenosis is recommended for patients with stenosis greater than 60% (NASCET). For this pathology, two types of surgical interventions are possible: carotid endarterectomy and carotid angioplasty. Surgical treatment is determined by the attending physician based on medical history, examination data and possible risks.
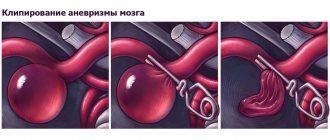
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is an open surgical procedure aimed at removing the inner wall of the carotid artery affected by atherosclerotic plaque. Technique of the operation: under anesthesia, an incision is made in the neck in the projection of the carotid artery. It is released and opened at the site of narrowing. A temporary shunt is placed to ensure blood flow to the brain. Then the inner part of the vessel wall with the atherosclerotic plaque is removed. Afterwards, plastic surgery of the artery is performed and the wound is sutured layer by layer.
Carotid angioplasty with stenting (CAS) is a minimally invasive X-ray surgery that involves installing a stent at the site of the narrowing. A stent is a tube made of a special metal mesh. The first stages of stenting are the same as for angiography: preparation, local anesthesia, puncture of the artery, insertion of a catheter and injection of a contrast agent. After installing a guiding catheter, a special metal filter is inserted into the affected carotid artery. Its essence is to delay possible microemboli that can break away from the plaque and enter the brain vessels. Then a stent is inserted along the guide, it is inflated by a balloon catheter, and it restores the normal diameter of the artery, serving as its frame. Thanks to this, proper blood supply to the brain is restored. The entire manipulation is carried out under X-ray control - everything is visible on the monitor. At the end of the operation, the filter and catheter are removed, leaving a stent inside. Over time, it epithelializes and becomes one with the wall.
After surgery, it is recommended to avoid intense exercise for six weeks. You should stop driving for three weeks.
Prevention of cerebral vascular sclerosis
Prevention consists of leading a healthy lifestyle, namely giving up bad habits, maintaining a work-rest schedule and a balanced diet. If you have diseases that can lead to sclerosis (diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension), you should follow the instructions of your doctor.
All patients who have undergone surgery for carotid artery stenosis should be periodically observed by a neurologist and a vascular surgeon, and at least once a year undergo an outpatient examination with mandatory Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head.
You can undergo examination and treatment for cerebral vascular sclerosis in Moscow at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic’s doctors use the latest equipment to detect the disease at the initial stages. An individual approach to each patient consists of developing a personal treatment plan. Therapy is carried out in accordance with the latest European recommendations for the treatment of atherosclerosis. You can sign up for a consultation and ask all your questions by phone.
Treatment and prevention of sclerosis
Treatment of sclerosis must begin at the earliest stages of the development of the disease; the processes in the body with this pathology are mostly irreversible. Hormonal medications are prescribed, means to improve the functioning of nerve impulses, enhance immunity and normalize metabolism.
To prevent sclerosis, proper nutrition, organization of work and rest, limiting foods containing high cholesterol, and an active lifestyle are necessary. It is necessary to drink clean water. When you are sick, it is useful to eat apples, garlic, parsley, horseradish, seaweed, raspberries, rowan berries, apricots, barberries, quinces, and pomegranates.
Argo's assortment includes Rejuvenating Oil, which is aimed at rejuvenating the entire body, strengthening the immune system, normalizing cholesterol levels, and improving blood supply to all internal organs. Rejuvenating oil is an effective means of preventing any type of sclerosis in the body.