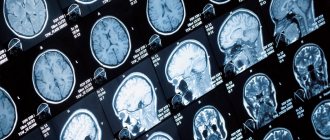
The most common symptoms of damage to the vascular system of the brain and neck are headaches, unsteadiness of gait or weakness in the arm or leg. If symptoms are present, the patient should be examined using MRI of the brain vessels. The purpose of diagnosis is to exclude congenital pathology, namely:
- arterial aneurysm;
- arteriovenous malformation (AVM).
Moreover, symptoms can go undetected for too long, up to 45 years.
The essence of the technique
The study is based on hydrogen atoms, which are affected by a magnetic field, forcing them to be an “exchanger” of energy. This is due to the fact that hydrogen atoms are part of any human organ, including liquids.
Hydrogen atoms rotate around a magnetic axis. When a person is placed in a tomograph, energy is absorbed by hydrogen atoms, and upon completion of magnetic resonance imaging, energy is released. The degree of release by different tissues is somewhat different, since their chemical composition and density play a role. The computer captures this emitted energy, amplifies and re-digitizes it in various degrees of gradation in brightness. Next, the information is displayed on the monitor and recorded on all supported media.
The study is harmless to the patient's health. This is the fastest diagnostic method that painlessly displays all structural and morphological changes in the vascular system of the brain, head and neck.
Indications for MRI of the brain
MRI of the brain is the most accurate study that is prescribed to identify and determine the nature of disorders of the normal structure and functioning of the brain. In our center, the diagnostic value of MRI increases thanks to the use of a high-field 1.5 Tesla expert-class MRI machine from Siemens and the work of qualified doctors with more than 7 years of professional experience.
What diseases does MRI of the brain show? The indication may be a disease or suspected pathology, including:
- Impaired cerebral circulation as a result of blockage of a vessel or its rupture;
- Chronic malnutrition of the brain due to a systemic disease such as atherosclerosis;
- Tumors and cystic formations with different growth patterns, including vascular: benign or malignant;
- Metastatic damage to brain tissue when the primary lesion is localized in other organs;
- Atrophic and demyelinating changes in the brain;
- Damage to the brain and its membranes of an inflammatory nature: encephalitis, meningitis, encephalomyelitis;
- Parasitic invasion with localization of the parasite in the brain;
- Identification or confirmation of abnormalities in brain development;
- Increased intracranial pressure, in order to identify the cause of the pathology;
- Head injury or multiple traumatic injuries with signs of brain damage to identify bruises, compression, concussion;
- Preoperative preparation to determine the boundaries of brain tissue damage;
- Dynamic observation of changes in pathological processes.
The list of diseases is diverse due to the fact that MRI of the brain shows changes of a different nature: both focal and widespread.
Symptoms that should prompt you to consult a doctor and undergo a diagnostic MRI:
- Headache. Prolonged or frequent pain that is difficult to relieve pain may be a sign of a serious pathology;
- Dizziness for no reason or accompanied by headache and nausea;
- Unreasonable nausea or vomiting, in the absence of pathology of the digestive tract;
- Loss of consciousness with convulsions (even once);
- Weakness in the legs when walking or in the arms in the absence of characteristic damage to the joints or peripheral nerves;
- Gradual deterioration of memory, decreased intelligence, impaired orientation in space, speech;
- A sharp deterioration in vision or hearing without pathology of the sense organs themselves.
Many of the listed symptoms may not occur separately from each other, but in various combinations, which may indicate a specific disease, which is shown by MRI of the brain. The main thing that needs to be done immediately when they appear is to carry out tomography and other diagnostic measures.
On the website of the Northern Capital Medicine center, you can sign up for an MRI of the brain yourself, having previously calculated the cost of the procedure using the MRI Calculator. This can also be done by telephone.
Diagnostics MRI of cerebral vessels
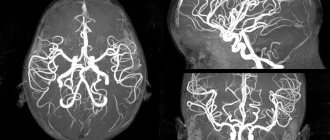
MRI of head and neck vessels is an informative neuroimaging method. Give a chance:
- assess the condition of the cerebral hemispheres;
- identify the presence of space-occupying formations;
- determine the presence and development of focal pathological changes;
- assess the condition of the cerebellum and brain stem.
During MRI of the vessels of the head and neck, the entire structure is analyzed with the exception of the skull bones. At the stage of such a procedure, the following occurs:
- assessment of the structure of the cerebral vascular system;
- the presence of an aneurysm in the substance is excluded or confirmed;
- confirmation or refutation of the pathological state of the structure of the vascular system.
Types of MRI of the head
Closed MR machine
Magnetic resonance scanning is most often performed on medium- and high-field tunnel-type tomographs. For claustrophobia, abdominal circumference more than 120 cm, in some other cases, diagnostics are performed using open devices.
Types of MRI of the head are distinguished by scanning area. During the procedure, the following is examined:
- brain tissue and membranes;
- space of the sella turcica, pituitary gland;
- intracranial vessels;
- eye sockets;
- paranasal sinuses;
- temporomandibular joints.
According to the characteristics of magnetic resonance imaging, they are classified into:
- native (performed without the use of amplifiers);
- with contrast (gadolinium preparations are administered to the patient’s body to increase the information content of the images);
- angiography (special programs are used to visualize the vascular bed).
Open MR machine
During the study, the radiologist can use various tomography modes (T1, T2, FLAIR, with fat suppression, etc.) and use special programs:
- for targeted examination of cranial nerves, cerebellopontine angle;
- if epilepsy is suspected;
- to exclude vasoneural conflict, etc.
Possible diagnosable diseases, pathologies
The diagnostic method will help confirm or refute:
- development of deviations due to previous traumatic brain injuries;
- any possible brain infections;
- tumor formations;
- stretching of the walls of the artery with subsequent deformation (most often, immediately after the bed);
- non-standard connection, as well as the location of the capillaries of the vascular system;
- autoimmune diseases;
- carotid artery syndrome;
- artery abnormalities;
- blockage of deep veins.
Such diagnostics can be carried out without the introduction of a contrast agent.
MRI of the vessels of the head and neck is relevant in cases where the patient has been experiencing for a long time:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- attacks of loss of consciousness;
- epilepsy attacks;
- other convulsive conditions.
The patient needs to contact a neurologist with this problem. The latter, using generally accepted medical techniques, will be able to determine how important MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck is for the patient.
MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and MRI of brain vessels: differences
When performing MRI of cerebral vessels, there is no direct possibility of assessing vascular structures. If a patient has a large aneurysm, most likely this will be visible during a routine native examination of the head.
As for the need to visualize vascular structures, for example, the demanded analysis of blood flow through the vascular system, excluding possible narrowings or other defective variants of the structure of the vascular bed, it is necessary to conduct an examination of the head. Also, if the patient has any ischemic conditions or strokes, with the help of additional brain diagnostics, it is possible to determine at the level of which of the arteries the “catastrophe” occurred.
How does an MRI examination of the brain differ from an MRI examination of the vessels of the head?
On a magnetic tomogram, brain structures are visible as numerous zones of darkening and clearing, forming certain signs. In a normal state, an MRI shows:
- soft tissues are visualized in gray on the images;
- sinuses - appear as black cavities;
- cerebral fluid inside the ventricles and in the subarachnoid space (dark on T1, white on T2).
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain allows you to study in detail the structure and localization of tissues, as a result of which you can identify:
- neoplasms (MRI detects tumors from 1 mm in size);
- necrotic areas;
- inflammatory processes;
- dystrophic, degenerative changes;
- congenital malformations (MRI reveals abnormalities of the brain and skull);
- contusions resulting from injuries;
- consequences of epileptic seizures;
- hydrocephalus (the pictures show a pathological accumulation of fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid system);
- pituitary diseases;
- dysfunction of the inner ear;
- strokes, etc.
If the purpose of the scan is to visualize the vascular system, angiography with contrast is performed. Then the images will show not soft tissues, but veins, arteries and capillaries.
MRI of the brain (left image) shows the focus of an ischemic stroke. MR angiography (right image) confirms the diagnosis: the image shows that the cause of the stroke was stenosis of a branch of the left middle cerebral artery
MRI of brain vessels allows you to diagnose:
- malformations - congenital anomalies of the connection of arteries and veins;
- thrombosis - the formation of blood clots in blood vessels;
- intracranial hemorrhages in the chronic stage as a result of injuries, cancer or other processes;
- aneurysms - bulging of the walls of blood vessels (most often arteries);
- areas of narrowing, bending, looping;
- atherosclerotic changes - deposition of plaques from a fat-like substance in the arteries;
- indirect signs of venous and arterial hypertension - increased blood pressure in the vessels;
- angiomas and brain tumors;
- dissection of the walls of blood vessels;
- venous stagnation;
- embolism - blocking of the vascular bed by various substrates (air bubbles, blood clots, etc.);
- vasculitis - inflammatory processes in the walls of blood vessels;
- angiopathy - pathology of the structure of the walls of blood vessels;
- strokes - ischemic (almost immediately after an attack), hemorrhagic (in the long-term period).
MRI of brain tissue and vessels complement each other, so they are usually performed in combination.
Decoding of received images
MRI of the head and neck vessels is a complex diagnostic method and requires special skills that only a radiologist and a neurologist can have. A few hours after MRI of the cerebral vessels, you can get a detailed answer from a specialist about the current situation. Also receive recommendations regarding treatment or further hospitalization of the patient.
The examination is carried out using modern equipment, so in addition to the conclusion, as well as photographs, the patient receives a CD with a recording of the examination. It is the use of the latter medium that makes it possible to find abnormal channels of the vascular system of small sizes.
Who is contraindicated for MRI?
There is a clearly defined number of contraindications that make MRI of cerebral vessels impossible or risky; it is customary to distinguish an absolute and conditional group. Relative contraindications include:
- Tendency to claustrophobia;
- Use of nervous system stimulants;
- Installed hearing aids in the inner ear;
- MRI is not recommended for those with prosthetic heart valves and insulin pumps;
- Kidney failure and heart disease are also relative contraindications.
The list of absolute contraindications is as follows:
- It is strictly forbidden to perform angiography on patients with pacemakers;
- The presence of metal implants makes the study unsafe and life-threatening;
- An installed clip in the vascular system is an absolute contraindication.
In addition, tattoos, provided there are metallic inclusions in the pigment, are also absolute contraindications. The patient is obliged to notify the doctor of the presence of all contraindications, and also to remove jewelry, accessories and piercings that contain metal from the body. MRI of cerebral vessels is not recommended for pregnant women, especially in the first trimester, especially if additional contrast is involved.
Examination with contrast
An MRI examination of the vessels and arteries of the neck using contrast is carried out exclusively according to the doctor’s indications. As a rule, injection of a dye into a vein is not required. At the time of examination, attention is first paid to the native part of the procedure. If at this stage any pathology or mass formation is detected, the radiologist may decide to carry out such a manipulation.
Despite such a simple procedure, there are a number of diseases that require the introduction of a contrast agent for better diagnosis. These include multiple sclerosis.
How often should the examination be carried out?
MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck is a completely safe diagnostic method and does not leave any traces in the body. It can be carried out countless times, namely as many times as the patient’s condition requires until a complete diagnosis is completed. For some, one study without follow-up is enough. A patient who needs a follow-up examination, for example, after removal of large tumors, undergoes MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck after 6-12 months.
Contraindications
MRI of the head and neck vessels has virtually no contraindications. The only exception is the presence of metals of a certain group in the body. These include products such as pacemakers or other electronics in a metal case. A complete exception may be the presence of titanium structures after osteosynthesis, fractures or joint surgeries. Each situation is considered individually. As a result, each patient can learn about the presence of contraindications.
Is brain imaging dangerous?
Not all patients understand the difference between magnetic and computed tomography, so in the comments you can find opinions about the dangers of both procedures. In fact, CT is a type of X-ray, and MRI is based on the properties of the magnetic field. Due to the absence of ionizing radiation, the second is considered safer and, according to indications, is prescribed even to pregnant women and small children.
Contraindications for MRI
Like any medical procedure, MRI has limitations. This method is absolutely prohibited for use if there are metal and electronic objects in (or on) the human body. Relative contraindications allow the appointment of MRI if symptoms require it, but subject to certain conditions. Among the restrictions are:
- weight above 120 kg;
- claustrophobia;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- conditions that prevent you from remaining still during scanning;
- heart disease during exacerbation;
- the presence of an insulin pump, neurostimulator, dental crowns, braces, infusion port system, artificial heart valve, analog hearing aid.
With magnetic resonance imaging with contrast, the risk may be associated with an allergic reaction to the substance injected. Although gadolinium medications rarely cause side effects, for patients with a history of dye allergy symptoms, diagnosis should be made after a preliminary test.
Also, MRI with contrast is not prescribed for people with severe renal and liver failure, pregnant women and after liver transplant surgery. Lactation is not an absolute contraindication, but since gadolinium passes into breast milk, you will have to wait until it is completely eliminated from the body for the next feeding. The mother should worry about the supply of food for the baby in advance.
What is more informative: MRI of head and neck vessels or computed tomography
CT angiography with the introduction of a contrast agent still remains a more informative procedure. This level of detail also has one significant drawback - the absorption of high load rays by the body. The latter can aggravate the development of cancer and completely excludes dynamic monitoring of certain pathological conditions.
The iodine-containing contrast agent administered during CT angiography is quite allergenic. Therefore, not everyone can conduct computer research. The examination itself is variable. At the time of assessing the clinical picture, the neurologist already understands which study will be more relevant for the patient: MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck or CT angiography.
Choosing a clinic, specialist and price of service
The mrt-mozga service is a full-fledged resource with a database of diagnostic clinics in Moscow (about 300 centers). The resource’s simple and intuitive interface will suggest the best offer. The patient can sort clinics according to various parameters: geolocation of the clinic, price, type of tomograph used, availability of contrast agent, operating hours, promotional offers. The information on the site is constantly updated and expanded.
You can make an appointment by calling 8 (495) 032-07-59 from 09:00 to 00:00. By taking advantage of the site's offer, you can not only make an appointment for free, but also get the best price offer.