The brain is one of the most important organs, the central computer of the body. His research was always fraught with difficulties and precautions. However, with the advent and implementation of magnetic resonance imaging, diagnosing brain pathologies has become faster and easier. MRI is a non-invasive test. It is based on the use of high-frequency pulses, magnetic fields, a computer system and special software that allow you to obtain the most detailed image of the brain. “Treatment and Diagnostic Center on Vernadsky” offers MRI at a cost that is one of the lowest in the capital.
Types of MRI examinations
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head is performed with or without a contrast agent. In the first case, the subject is injected with special substances (usually based on gadolinium salts), which make it possible to create a contrast between different tissues. In some cases, the contrast agent may cause allergic reactions. The type of study (with or without contrast) is determined by the specialist.
MRI of the brain with or without contrast
MRI of the brain with contrast is not required in all cases. Statistically, every third patient needs contrast injection, since in most cases the standard magnetic resonance imaging protocol is sufficient. In our diagnostic center, we first perform a regular MRI of the brain, and then, if indicated, we offer to repeat the study with a contrast agent. This strategy helps reduce examination costs and avoid unnecessary contrast administration.
We strongly recommend not to refuse contrast if there are indications for its use and there are no contraindications. After all, contrast agents significantly increase the accuracy of diagnosis, help determine the disease without a biopsy and other complex procedures, allow you to make a prognosis and choose the best treatment tactics. MRI with contrast can influence the outcome of the disease and the success of treatment, and reduces the risk of misdiagnosis.
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging
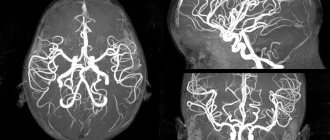
- Pathologies and diseases of cerebral vessels.
- Head injuries and bruises, which are accompanied by internal bleeding.
- Speech impairment and hearing loss.
- Tumors of the brain, cerebellopontine angle.
- Paroxysmal states.
- Infectious diseases of the central nervous system (abscess, meningitis, HIV infection).
- Pituitary adenoma.
- Abnormal development of the blood vessels of the head (thrombosis, aneurysms).
- Epilepsy.
- Systematic headaches of unknown origin.
- Sinusitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Neurodegenerative diseases.
- Pathology of the base of the skull.
What can be revealed when using a computer method?
This type of diagnosis allows doctors to detect the following problems in patients:
- Damage of various kinds.
- Vascular diseases.
- The presence of neoplasms of benign and malignant nature.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Congenital anomalies.
Computer research can be carried out on people who have a variety of metal inserts and structures (heart engine, valves, etc.), which significantly expands the scope of the presented method, in contrast to MRI of the brain. This technology does not have an adverse effect on such patients and is in no way capable of harming their health or life.
Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
Relative:
- severe claustrophobia;
- the presence of non-ferromagnetic implants, insulin pumps, heart valve prostheses;
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- drug or alcohol intoxication;
- presence of tattoos containing metallic compounds in the ink;
- heart failure.
Absolute:
- the presence of metallic foreign objects in the patient’s body;
- hematopoietic anemia (with magnetic resonance imaging with contrast);
- use of electronic devices such as pacemakers, etc.
In what situations is it prohibited to do a CT scan of the brain with contrast?
Despite the numerous privileges of the described examination, there are special restrictions for carrying out diagnostics with the introduction of an additional amplifier for a certain category of people:
- The presence of individual intolerance to the components of the contrast drug.
- The presence of chronic renal failure and myeloma.
- Problems with the thyroid gland.
- Severe stage of diabetes mellitus.
- The patient's condition is described in a clinical sense as severe (coma, connection to a ventilator, etc.).
Preparing for an MRI of the brain
Usually, there is no need to do any complicated steps before the examination. Sometimes the specialist may ask the patient to refrain from eating and drinking before the procedure. The person being examined must remove all metal jewelry. In many centers, the patient is given a loose shirt, in some they are allowed to remain in their own clothes, provided that they are loose and free of metal parts. Before a brain MRI, women should inform their doctor about the possibility of pregnancy. The patient is also obliged to inform the doctor about recent operations and diseases, allergies and the presence of metal implants. If the person being examined suffers from claustrophobia or is very worried before the procedure, he may ask the doctor for a sedative.
CT scan of the brain with contrast - subtleties and nuances
The presented diagnostic method allows medical workers to obtain a more detailed picture of the required organ or area. The only difference from a standard study is that before the procedure begins, the patient is given an intravenous contrast agent. Often, the drug has an iodine base, so in some people this medication can cause a number of negative effects - nausea, gag reflex and pain in the head.
The main task of such a component is to highlight internal structures so that they can be clearly visible in the resulting images from the tomograph. Using this method, a specialist obtains data on the size and shape of blood vessels. Colored blood cells gradually circulate in the tissue, which clearly highlights the presence of various pathologies, such as cysts or neoplasms. A sufficiently qualified doctor, when analyzing a CT scan of the brain with contrast, can in some cases describe the histological structure of the tumor, based on the reaction of the contrast reagent along with nearby soft tissues.
How is an MRI of the brain performed?
- An MRI machine is a cylinder with holes at both ends. The patient sits on a movable table that is placed inside the device during the MRI procedure.
- The length of the tunnel depends on the specific type of apparatus. Some devices only partially surround the table. Tomographs can also be open on the sides. They are used for patients with severe claustrophobia. In closed-type devices, the table slides in completely.
- During the examination, the patient is secured with belts. The less it moves, the more accurate the diagnostic results.
- During magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, devices with wires that receive and send radio waves are placed around the head.
- Patients are often given earplugs. This helps protect your hearing from the loud noise that comes from the MRI machine when it is in operation.
- The table is placed inside the tomograph, and the specialist moves to an adjacent office, which houses a computer system that processes the data. The device takes a series of pictures. Each one takes a few minutes to shoot. As a rule, an MRI of the brain without contrast takes about 20–30 minutes, with a contrast agent – approximately 45–50 minutes.
- An MRI machine takes layer-by-layer images of tissue. During a head scan, data is collected from approximately 20 levels, each 4–5 mm thick. The higher the magnetic field strength of the tomograph and the thinner the sections, the more accurate the research result.
Why is an MRI of the brain done with contrast agent?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is the most accurate method for diagnosing diseases of the central nervous system, with high levels of sensitivity, specificity and information content. However, there are pathologies that can be difficult to identify even with MRI (most often these are tumors and inflammatory diseases of the brain and spinal cord, such as multiple or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). In such cases, the study is carried out with contrast.
The principle of action of contrast agents is based on their ability to accumulate in those areas of the brain where there are inflammatory processes, tumors and other pathologies. In this case, healthy tissues practically do not absorb the contrast. The main component of the contrast is the rare earth metal gadolinium in the form of nanoparticles, which has the ability to enhance the signal received by the MRI unit from the tissues of the human body. As a result, areas with a high contrast content, corresponding to a particular pathology, are highlighted in the images, accurately indicating the location, size and shape of the lesion. In addition, contrast can highlight and emphasize the characteristic features of a tumor or disease, facilitating diagnosis and increasing the accuracy of MRI studies.
MRI of the brain with contrast is indicated for suspected tumors and demyelinating diseases. Some types of MRI studies are performed with contrast only, as is the case with magnetic resonance imaging of the pituitary gland. However, most often the indications for the use of a contrast agent arise during routine MRI of the brain.
Prices for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in Moscow
Various factors influence how much an MRI costs in each case. The price may change depending on whether the specialist will use a contrast agent, whether the results will need to be recorded on disk, etc. The approximate cost of magnetic resonance imaging is indicated on the page.
You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Diagnostic and Treatment Center on Vernadsky. To do this, call us by phone at any time convenient for you. You can also leave an online application through a special form presented on the website.
Table of approximate radiation exposure values for CT (MSCT)*
*The table shows average and approximate values, which may vary up or down depending on:
- Research protocol;
- Number of scanning zones;
- CT scanner;
- Patient weight;
- Patient's height;
- The ratio of muscle and fat tissue in the patient;
- Goals and objectives of diagnostics.
The tomograph is equipped with a dosimeter, which allows you to determine the level of effective radiation exposure in each specific study. This value is indicated in the conclusion and in a special report file on a DVD or flash drive given to the patient based on the results of the study.
Is MRI safe?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe, harmless method, which is based on the principle of the influence of a magnetic field on the human body. Unlike X-rays used in CT scans, magnetic radiation does not have a negative effect on humans. The only inconveniences that may appear during the examination:
- The hum of the tomograph is too loud
- The need to lie still throughout the examination (15-60 minutes)
MRI in our center
Power 1.5 Tesla
High image quality
Study for patients up to 250 kg
Burn to disc for free
Why is MRI not recommended for pregnant women in the first trimester? For reinsurance! In fact, scientists have not found evidence of harm from magnetic radiation to the expectant mother or fetus, but in order to save the patient from worries, it is advisable to abandon diagnostics for a while.
It is important to remember about MRI contraindications, in which tomography is impossible.
Key benefits of brain MRI
Among the most prominent advantages of this method, doctors include:
- Maximum level of safety - since during the examination the device does not emit toxic radiation.
- Non-invasive technique - for MRI, as well as for CT with contrast, you do not need the use of medical equipment.
- Painless - thanks to the non-invasive testing method, the patient will not feel pain or discomfort during the appointment.
- There is no need for recovery - since magnetic rays during MRI of the brain with contrast do not have a toxic ability.
- Possibility of performing magnetic tomography a large number of times.
- The device can show even minimal deviations from the norm, as well as the initial stages of the development of serious diseases, which makes it possible to promptly identify the disease and begin its treatment.
- The use of MRI of the brain with contrast allows obtaining high quality and accurate images.
Disadvantages accompanying MRI of the brain
Numerous advantages do not change the fact that MRI and CT with contrast have some limitations. Each method has its own prohibitions, both absolute and temporary.
The patient is prohibited from scanning the body with contrast if there are electrical devices, metal structures and other inserts inside the body - since resonant equipment can disrupt their functioning, which will lead to negative consequences, and in some situations, death.
The relative limitations of brain MRI with contrast include:
- Women carrying a child, in particular during the early stages of pregnancy, a magnetic scanner may have an adverse effect on the future development of the fetus.
- The presence of ferromagnetic inserts in the body means there is a risk of receiving false information.
- The patient is afraid of confined spaces - the doctor may introduce sedatives before the session.
- Possibility of a heart attack.
- The patient's serious condition.
Also, it is worth noting in what cases it is prohibited to conduct a magnetic assessment method with a contrast agent:
- Carrying a child, in particular the first months of pregnancy, since the contrast component can easily penetrate the placenta and negatively affect the future development of the fetus.
- Allergic reaction of the patient - during MRI of the brain with contrast, a person may develop individual intolerance to contrast substances.
- Hematopoietic anemia, as well as renal failure in the chronic stage.
- Problems with the urinary system - after all, in order for the contrast drug to leave the body during an MRI of the brain with contrast, stable functioning of the excretory structure is necessary.
Preparatory activities before CT scan of the brain
Before the procedure, many patients begin to worry and think about what may need to be done before the session begins. It is worth understanding that special preparation for the described method, as well as for MRI of the brain, is not required from patients. The only thing you need to adhere to is to stop eating food and drinking any liquid a few hours before taking it.
Also, doctors advise leaving all accessories and jewelry at home or removing them before visiting the tomograph tunnel. You will need to wear comfortable and comfortable clothing so that it does not cause discomfort or constrict your limbs. It should be without metal parts. In some clinics in the capital, medical staff provide their visitors with personal gowns. If a person suffers from claustrophobia, that is, is afraid to be alone in a closed space for a long time, then he should be told about this problem in advance. The examination for such patients is carried out in a standard manner, but before the scan begins, the doctor will administer a sedative to the patient.
Preparing for an MRI with contrast
Preparing for an MRI with contrast injection does not require any additional preparation. The only exception is the abdominal examination procedure. In this case, the patient will need to avoid eating foods that cause increased gas formation for several days. Approximately five hours before the MRI, you should refrain from eating and drinking liquids. It is best to come to your MRI procedure in loose clothing. Before entering the MRI room, you must remove all jewelry and leave all metal objects behind. This will help prevent errors during an MRI examination.
How often should an MRI be done?
This is a more correct question, which should be asked, first of all, to the attending physician. However, there are some general patterns:
- For herniated discs, it is advisable to undergo an MRI every 2-3 years
- For stroke – once every 1-3 years
- For the initial diagnosis of multiple sclerosis - 1 examination every six months, for an already established disease - 1 session per year
- In the presence of stable tumors - 1 examination every six months to a year
- In the presence of unstable tumors - 1 examination every 3 months to six months
- After surgery to remove a tumor - 2-4 examinations in the first year, then - once a year
Too frequent, randomly performed MRI examinations are only a blow to your wallet, but not to your health. To save money, do not neglect consulting a doctor!
MRI of the brain - description
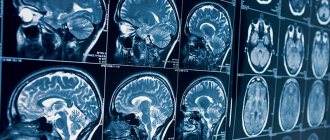
It's time to consider in detail another diagnostic method, which is also quite often used by many doctors to scan specific areas of the body. MRI of the brain - allows you to carry out various checks of the patient’s condition, showing the most detailed and high-quality photographs. The presented testing is based on the functioning of a magnetic field with a specially specified frequency, which interacts with hydrogen elements located in the patient’s body. This method has much in common with computer examination. The device also contains sensors and scanners that send data to the PC. An MRI machine for the brain consists of a ring capable of generating magnetic vibrations while the patient is inside the tunnel. All changes occurring in the body are recorded by special mechanisms, as a result of which doctors receive an informative picture of the presence of pathologies, if any. Photographs are obtained in section, as well as in 3D projection.
What is MRI of the brain based on?
The diagnostic effect of brain MRI is based on nuclear magnetic resonance. In response to the powerful radiation created by the generator, the hydrogen atomic nuclei contained in the tissues line up along the electromagnetic field lines and begin to vibrate. Each atom becomes like a spinning mini-spinning top, emitting energy waves.
Different structures emit different amounts of energy - some give it out more intensely, while others less so. The difference is recorded by a device that takes pictures (slices) in different projections.
To do this, the patient is placed inside a tomograph in which generators maintain a high-frequency electromagnetic field. Special radio emitters generate pulses, and coils record the energy sent by vibrating atoms.
The resulting slice images are combined into a three-dimensional matrix using a special computer program, in which dark or light unhealthy areas are visualized against a gray background.
Can the procedure be done often?
The MRI procedure of the brain can be performed as many times as necessary to establish a diagnosis. Of course, no doctor will prescribe the procedure several times a week - changes in the body do not occur that often. In a hospital setting, the study can be carried out 2-3 times a month or more often (for example, when monitoring a postoperative condition). The only limitation may be the cost of the procedure and the time required to prepare it. There are no other restrictions.
Meanwhile, there is a certain category of doctors who are confident that the appearance of data on the dangers of magnetic resonance imaging is just a matter of time, and the fact that they have not yet appeared is due only to the novelty of this technology. They are not even convinced by the fact that over the course of 20 years there have been no evidence of deterioration in the health or well-being of patients, changes in any vital parameters or the appearance of residual effects - both positive and negative. All this directly indicates that today there is not even a tendency towards the probable occurrence of side effects after MRI.
When is a brain MRI prescribed?
The presented examination method, which allows you to obtain maximum information, is prescribed by doctors in the following situations:
- Probability of oncology formation.
- Constant pain in the head area.
- The presence of dizziness and fainting.
- Previously suffered a stroke.
- An MRI of the brain with contrast will help understand the cause of the loss of hearing and visual ability.
- Damage and swelling.
- Reduced degree of memorization of various events.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Inability to perform a computed tomography scan with contrast.