Intercostal neuralgia
This is a pain syndrome caused by damage to the peripheral nerves of the chest. Appears due to inflammation, irritation or pinching of the nerve roots in the intercostal space. Intercostal neuralgia is not a disease - it is a syndrome that can appear against the background of various pathologies. Vertebrogenic thoracalgia (as intercostal neuralgia is called) is a general concept that refers to pain that occurs in the chest area. They can appear for no particular reason, or can serve as a sign of various diseases.
Symptoms may resemble pain from a heart attack, pneumonia or pleurisy, diseases such as pancreatitis and others. A characteristic symptom is an increase in pain when coughing, laughing, moving, bending the body and decreasing at rest and with muscle relaxation. This is a distinctive feature of intercostal neuralgia, which allows it to be differentiated from symptoms of heart disease or other pathologies. But you shouldn’t take risks and try to diagnose yourself. The cost of a mistake can be higher than the prolonged pain syndrome.
The principles of treatment and symptoms of intercostal neuralgia in men and women are similar. The main manifestation is pain:
- Paroxysmal, occurring on its own.
- Monotonous, aching.
- Intensified by movement, deep breathing and exhalation, laughter, coughing.
- Occurs when pressing on individual points on the front of the chest or side.
- A burning sensation in the area where the nerve is damaged.
- Numbness, “pins and needles” sensation.
The pathology is more common on the left side of the body, and in women, intercostal neuralgia is a fairly common companion to pregnancy. During this period, the growing fetus puts pressure on the organs in the abdominal cavity, which can lead to pinched nerves.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia
The main symptom of the disease is paroxysmal severe pain that prevents you from breathing or moving. This symptom of intercostal neuralgia can be localized on the right or left in the chest or on the ribs, extending to the shoulder blades, back or arm. With severe inflammation of the nerves, there may be redness, numbness, and loss of sensitivity of the skin. When palpating the ribs, the pain intensifies.
If you experience these symptoms, then you need to make an appointment with your doctor. Remember that similar sensations can also be accompanied by other diseases - including very dangerous ones! Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis and select treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia can be carried out in the department in St. Petersburg, or, as prescribed by our specialists, at home. Highly qualified doctors, professional equipment and modern working methods allow us to detect health problems in the early stages and prescribe effective therapy as quickly as possible.
Types of disease
- Left-sided With left-sided intercostal neuralgia, the pain is localized in the left side of the body, which is why it is often confused with heart pathologies. Painful sensations occur not only in the heart area, but can also radiate to the side, hypochondrium, chest or shoulder blade on the left side. To exclude the presence of heart disease, in this case some additional diagnostic procedures, such as, for example, an ECG, may be prescribed.
- Right-sided intercostal neuralgia on the right side does not differ from the left-sided side in terms of pain intensity and treatment options. The only exception is the localization of pain - it is felt on the right side of the chest.
- Bilateral In this case, severe pain is felt on both sides of the chest. This is the most severe type of disease. The treatment methods used here are the same as for unilateral neuralgia.
Neuralgia is not a fatal disease, but it can make life very difficult. No need to endure pain, consult a doctor.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia
It is imperative to treat this disease; the main thing is to see a good doctor who can confirm or refute the diagnosis. When choosing a clinic, choose Union Clinic. Doctors at our medical center have been successfully treating patients for more than 20 years. Also at the Union Clinic you will receive a full examination and qualified assistance from experienced doctors.
For neuralgia, drug treatment is prescribed, but in case of severe intense pain, our neurologists can additionally prescribe instrumental methods - laser, ultrasound or reflexology, which will quickly relieve pain.
The clinic has promotions and discounts on an ongoing basis, which makes it possible to save money during treatment. You can make an appointment by phone or by filling out a special form on the hospital’s official website on the Internet. Immediately after filling out the application, administrators will contact you to clarify additional information.
Causes
Intercostal neuralgia can be caused by various reasons. Basic:
- Poor posture, injuries, intervertebral hernias, osteochondrosis.
- Hypothermia, which led to poor circulation.
- Infectious and other diseases that lead to nerve damage. For example, destruction of the nerve sheath in multiple sclerosis.
- Neoplasms that compress nerve roots.
- Muscle spasms, prolonged tension during sudden movements or prolonged uncomfortable body posture.
- Operations.
- Pathologies of internal organs.
Causes of intercostal neuralgia on the right
Since intercostal neuralgia is a syndrome of a number of pathologies of the spine and nervous system, its causes are degenerative, inflammatory or tumor in nature, and are always associated with a specific disease.
| Causes: | Factors causing intercostal neuralgia: |
|
|
Diagnostics
Intercostal neuralgia can be a symptom of many diseases - from cardiovascular pathologies to diseases of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and chest. It is impossible to independently determine the cause only from existing complaints. A consultation with a neurologist and a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary to ensure that there are no diseases of the heart, lungs, or digestive system.
Particular attention is paid when diagnosing and treating intercostal neuralgia on the left side. Acute pain in the heart may be a sign of a heart attack. Symptoms usually differ - for example, with heart problems, cold sweat appears and shortness of breath bothers you, the pain does not decrease with rest when the muscles relax. But making a diagnosis based only on symptoms is wrong. The doctor is responsible for the life and health of the patient, which means he needs confidence in the diagnosis and correctness of treatment.
The procedure for examining a patient with suspected intercostal neuralgia is as follows:
- Questioning the patient about complaints and the characteristics of their occurrence.
- Examination to find the location of the pain.
- Setting up a preliminary diagnosis.
- Carrying out examinations to confirm intercostal neuralgia, its causes and prescribe the treatment that will be required in a particular case.
The following diagnostic methods can be used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography is a study that will provide detailed and highly accurate images of tissues and pathology in them.
- ECG – monitoring of heart function to exclude cardiovascular diseases.
- Ultrasound of the heart or other internal organs, diseases in which may have similar symptoms.
- X-ray of the lungs to exclude pneumonia, pleurisy and other diseases in which there are complaints of chest pain.
Diagnostic methods are selected individually depending on the nature of the pain and its location, and the patient’s condition. In some cases, other specialists are involved in diagnosis and treatment - a cardiologist, gastroenterologist, pulmonologist.
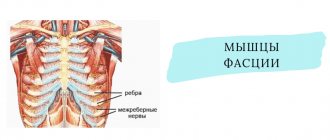
What is intercostal neuralgia?
Neuralgia literally means “pain along the nerve,” i.e. in the intercostal nerves. This is not an independent disease, but a designation of a pathology that occurs in the spine for various reasons . The resulting pain is intense and painful, with a predominant localization in the sternum.
Dystrophy of cartilage tissue or osteochondrosis does not cause intercostal neuralgia. The spinal disease itself is not accompanied by paroxysmal, persistent pain, but its complications may well be the cause of this pathology.
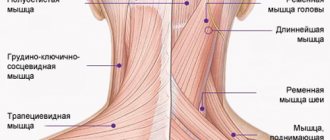
There are radicular and reflex neuralgia . In the first case, the spinal nerve roots are irritated, and pain in the spine radiates to the sternum. And with reflex pathologies, pain appears when the intercostal muscles tense and contract. According to the location, the disease is divided into right-sided and left-sided.
Intercostal neuralgia can be radicular and reflex
In any case, intercostal neuralgia is a sign of developing pathologies of the spine , so it is very important to promptly recognize its symptoms on the right and left. Deciphering such signals given by the body is important for further diagnosis and prescribing appropriate treatment.
Treatment
The goals of therapy for intercostal neuralgia: reduce pain, eliminate the cause of pinching or inflammation.
For this purpose, drug treatment is prescribed using:
- Muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms.
- Neuroprotectors for the protection and restoration of nerve cells.
- Painkillers and injection therapeutic blockade with various drugs. It has a strong analgesic effect, relieves swelling and eliminates muscle spasms.
Drug treatment of intercostal neuralgia is complemented by physiotherapy. The following physiotherapeutic procedures can be used:
- Exercise therapy is an individually selected set of exercises to relax spastic muscles, improve blood circulation and lymph flow in the problem area. Exercise therapy is effective for the treatment and prevention of neuralgia, but it can only be done if there are no contraindications. It is important not to cause harm, which is possible with home exercises. What exercises will be effective, how exactly to do them, the number of repetitions - all this will be advised by a physical therapy doctor. The safest and most effective classes are under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor in individual or group classes.
- Laser therapy uses light energy to increase blood circulation, relax muscles, and reduce pain and inflammation.
- Magnetotherapy - the effect of an electromagnetic field on the body leads to the elimination of congestion, improvement of blood circulation, and reduction of pain syndromes.
- Diadynamic therapy, galvanization, exposure to interference currents and other procedures with electric current of varying power and frequency. They have a healing effect on soft tissues, improving blood circulation and lymph outflow, relaxing muscles and providing an analgesic effect.
- Electrophoresis is a procedure that improves the penetration of drugs into soft tissues and accelerates their action.
- Therapeutic massage and manual therapy are methods of influencing the body with the hands of a doctor. They allow not only to reduce or completely relieve pain, but also to treat the causes of intercostal neuralgia - pathologies of the spine, functional blocks in its work. What exactly to use - acupressure, segmental or other types of massage - is decided by a chiropractor or massage therapist.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture) – injections with thin needles into biologically active points on the body to relieve pain and normalize the functioning of internal organs.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia on the right or left side of the chest, in the side with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures is carried out in several procedures. A full course usually consists of 10-15 sessions. Appointments are always individual.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia
Treatment of a disease such as intercostal neuralgia is aimed, first of all, at eliminating the causes that cause it, relieving pain and alleviating the patient’s condition. During the acute period of the disease, it is recommended to adhere to bed rest. It is advisable for the patient to lie on a hard, flat surface, preferably on an orthopedic mattress, or with a shield under the mattress.
Light, dry heat will help alleviate the patient’s condition with intercostal neuralgia; for this you can use sand heated in bags, an electric heating pad, mustard plasters, pepper plaster on the painful area, or a woolen scarf. The patient should avoid sudden movements, bending and turning the body, prolonged sitting, and heavy lifting.
Wearing a corset helps, but not for long, to avoid the development of muscle weakness.
Drug treatment
To treat intercostal neuralgia, it is necessary to carry out active anti-inflammatory measures. When treating intercostal neuralgia, the patient may be prescribed drug treatment with drugs from the following groups:
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs that relieve pain and have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect;
- muscle relaxants, reducing muscle spasms;
- calming nervous system, herbal remedies;
- B vitamins - milgamma, neurorubin, neurobion and other drugs that restore damaged nerve structures and improve the passage of impulses.
For local treatment, the doctor may prescribe ointments and gels with NSAIDs - fastum-gel, dolobene and others. Preparations are also prescribed - solutions and ointments that do not contain non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, but have
analgesic effect - finalgon, capsicam, menovazin.
There is also a relatively new dosage form for the treatment of this pathology - transdermal patches, which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
Non-drug treatment
After acute pain has been relieved, non-drug treatment methods can help quickly restore the functions of the affected areas, such as:
- therapeutic massage that provides muscle relaxation, relieves pain, improves metabolic processes in the paravertebral muscles, and reduces swelling;
- vacuum therapy – cupping massage to further enhance soft tissue drainage;
- manual therapy to normalize intervertebral connections, eliminate pinched nerves;
- Exercise therapy to strengthen the muscular corset of the spinal column;
- physiotherapy: electrophoresis, phonophoresis, electrical myostimulation of muscles, magnetic therapy, laser therapy;
- acupuncture;
- hirudotherapy.
Intercostal neuralgia, which often occurs during pregnancy, is a fairly serious problem that requires increased attention to the patient. The cause of intercostal neuralgia in the second half of pregnancy is an increase in pressure caused by a restructuring of the usual arrangement of organs on the chest, ribs, intercostal spaces, and nerves. The doctor must competently select such an individual complex treatment regimen in order to avoid complications for the mother and child. Properly selected and timely treatment of intercostal neuralgia leads to a fairly rapid recovery and does not cause long-term problems for a pregnant woman.
Treatment with folk remedies
To alleviate the patient's condition with intercostal neuralgia, traditional medicine methods are also used, which have a good effect, in combination with the treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Ointments based on snake and bee venom have long been known; after rubbing them into the affected area, the application site must be insulated with a woolen scarf. It will also help to treat intercostal neuralgia using a pepper patch, before using which you need to wipe the skin with an alcohol solution or cologne and then wipe it dry. The patch should be removed when intense burning occurs.
An effective remedy is rubbing an alcohol solution of mumiyo into diseased areas and taking 20 grams of mumiyo orally before meals.
It must be remembered that for a successful recovery it is important not only to relieve pain, but much more important is to identify the cause of the disease and its comprehensive treatment.
Prevention
The following recommendations help to avoid the appearance of intercostal neuralgia:
- Moderate physical activity to strengthen the muscle frame and maintain their elasticity.
- Maintaining correct posture.
- Healthy eating.
- Daily routine and alternation of work and rest time.
- Protection against hypothermia.
You should not endure the pain of intercostal neuralgia and worry about its causes - consult a doctor to be sure that there are no serious pathologies and for quick relief of symptoms.
Types of intercostal neuralgia
Typically, intercostal neuralgia affects one intercostal nerve on one side of the body. But sometimes the disease forms a wider pathological zone, occupying two or three intercostal spaces, and several nerve roots on one side are affected.
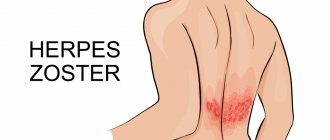
In addition to unilateral lesions, there is bilateral intercostal neuralgia, which can be caused by diseases with a pronounced decrease in immunity, such as herpetic neuralgia caused by HIV infection in the AIDS stage, or other diseases, for example, radiation sickness.
Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Hepatitis
Jaundice
Vomit
30177 05 April
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
The right hypochondrium is one of nine areas into which the anterior abdominal wall is conventionally divided. This area belongs to the so-called “upper floor” of the abdominal cavity.
In the right hypochondrium there are the liver, gallbladder, hepatic angle of the colon, and swollen loops of the small intestine can also be projected into this area. The organs listed above belong to the digestive system.
The liver is a parenchymal (spongy) organ with a very good blood supply. The outside of the liver is covered with a capsule in which nerve endings are located. The liver is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and plays a vital role in detoxification of the body.
Harmful substances that enter the liver are subjected to “chemical” processing, which makes them less toxic to the body and promotes faster elimination through the gastrointestinal tract and urine.
In addition, liver cells produce bile necessary for digesting food, primarily fats. Bile enters the gallbladder, located on the lower surface of the liver, where bile accumulates, which is released from it into the duodenum during the next meal.
From above, the liver is adjacent to the diaphragm - a kind of muscular partition between the abdominal and thoracic cavities. From below, from the side of the abdominal cavity, the diaphragm is lined with peritoneum (which covers the entire abdominal cavity and organs located in it from the inside), and from above, from the side of the lungs, by the pleura, which lines the pleural cavity from the inside and covers the lungs from the outside. Both the pleura and peritoneum have good innervation, which is important to know to understand the causes of pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium. The peritoneum also covers the gallbladder and intestinal loops.
Types of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
The pain in the right hypochondrium can be acute, sometimes “dagger-like”, which makes you think about a serious illness. This pain is characteristic of hepatic colic and is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, increased sweating, increased heart rate and a drop in blood pressure.
In chronic diseases and the gradual development of acute diseases, the pain is often dull, bursting in nature, or is described by the patient as “heaviness, discomfort” in the area of the right hypochondrium.
Pain syndrome can be spontaneous, or it can be provoked by food intake, alcohol, physical activity, change in body position, etc.
Possible causes of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
There is only one mechanism for the development of pain: stimulation of pain receptors. As mentioned above, the peritoneum has good innervation. Also, a large number of nerve endings are localized in the wall of hollow organs (intestines, gall bladder). Therefore, inflammatory processes in these organs naturally manifest themselves as pain.
Pain also occurs when the liver capsule is stretched. This can occur due to an increase in the volume of the organ (which in most cases is associated with tissue swelling), due to the accumulation of any fluid (most often blood) under the capsule (with a traumatic rupture of the liver), or damage to the capsule.
Unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium are caused by excessive distension of the intestinal loops by intestinal contents or gases. In addition, since the organs of the chest are located close to the right hypochondrium, in case of development of pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura), the pain syndrome can also be localized in the right hypochondrium and imitate diseases of the abdominal organs.
Diseases that cause pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Among acute diseases accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning first of all those that require emergency surgical intervention.
These include
acute calculous cholecystitis
and
renal colic
.
Both conditions are a consequence of cholelithiasis
. Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) develops against the background of an already advanced process of stone formation or, conversely, is the cause of the formation of stones. With renal colic, a calculus (stone) becomes wedged into narrow segments of the biliary tract, which is accompanied by severe pain, impaired bile outflow, and in more severe cases – jaundice (yellowing of the sclera and skin).
Other diseases of the biliary tract, such as
biliary dyskinesia
,
chronic cholecystitis
, cause recurrent pain in the right hypochondrium, usually associated with an error in diet.
Another disease classified as an “acute abdomen” that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium is appendicitis.
(inflammation of the appendix).
Despite the fact that the classic position of the appendix corresponds to the right iliac region, an abnormal position of the appendix in the right hypochondrium is quite common, especially in children.
Overdistension of intestinal loops can develop as part of
intestinal obstruction
.
Swelling of the liver tissue is characteristic of hepatitis (inflammation of the liver parenchyma). Hepatitis can have a variety of origins: viral hepatitis A, B, C, etc., autoimmune, toxic, incl. alcoholic. These diseases are usually accompanied by pain, as well as weakness, nausea and vomiting, yellowing of the skin and sclera, change in the color of urine and feces.
Subcapsular hematomas of the liver (accumulation of blood between the liver tissue and its capsule), as well as ruptures of the liver capsule, are usually traumatic in nature.
Among the diseases of the chest that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning pleuropneumonia (inflammation of the lung tissue and pleura), heart failure, intercostal neuralgia and herpes zoster. The latter is characterized by the appearance of blistering-type skin rashes, which are preceded by severe pain.
Which doctors should you contact if you experience pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium?
If sudden, progressively increasing pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium, you should contact a doctor to exclude acute surgical pathology. If the pain is not acute, the examination can begin at or. If necessary, the patient can get advice from a hepatologist (a specialist in liver diseases) and other specialized specialists.
Diagnostics and examinations for pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
After a detailed survey and comprehensive clinical examination, the doctor, as a rule, needs laboratory and instrumental confirmation of the diagnosis. For this purpose, the following studies are used:
- A clinical blood test with determination of the leukocyte formula, based on the results of which one can suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and determine its severity.