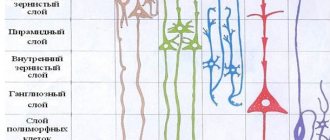
Functions of the temporal lobes
Dominant hemisphere (usually left).
language recognition and understanding;
medium-term memory;
long-term memory;
memorizing audio information, selecting words;
memory of complex events and facts, processing of visual and audio information;
emotional balance.
Non-dominant hemisphere (usually right):
recognition of facial expressions, recognition of voice intonation, rhythm;
music;
remembering visual information.
Temporal lobe
Side view
Three-dimensional image of the surface, side view.
3D image of the bottom surface.
3D image - active brain, side view.
For many years, the temporal lobes have not received the attention they deserve from human psychologists. They are rarely discussed at psychiatry meetings, and very few neurologists realize the enormous contribution this region of the brain makes to our existence and to our experience of life as we experience it. Until we were able to map the temporal lobes and their functions, the action of the temporal lobes remained a mystery. Many professionals believed that the main function of the temporal lobes was to serve as a kind of “cushion” for the brain. However, the results of scans carried out in our clinic indicate that the temporal lobes play an important role in processes such as memory, emotional balance, memorization and socialization.
The most valuable things we retain in life are the images that we store in the memory banks of our brain. All of our stored experiences determine our sense of personal identity and connectedness to others.
Our experience plays a huge role in making us who we are. The temporal lobes, located in both hemispheres of the brain, just behind the eye sockets and under the temporal bones, store memories and images, helping us to recognize ourselves as ourselves.
In the dominant part of the brain (the left hemisphere for most people), the temporal lobes are heavily involved in language recognition and understanding, medium- and long-term memory, complex memories, language use and word selection, emotional balance, and visual and auditory processing.
Language is one of the main factors that distinguishes humans from animals. It allows us to communicate with other people and to describe and preserve our thoughts and actions for future generations. Receptive language, the ability to perceive and recognize speech and written text, requires stable functioning of the temporal lobes. The ability to clearly hear your child say, “I love you,” or listen and be afraid of scary stories, is located in this area of the brain. The dominant temporal lobe helps process sounds and written words into meaningful information. The ability to read, remember what you have read, and integrate information received is largely determined by the functions of the dominant temporal lobe. Problems in this part of the brain lead to difficulty using language, misunderstandings, and difficulty recognizing written text.
I often tell patients that their memories bring them both their greatest joy and their deepest disappointments. Memories can make us strong and confident (remember when you felt most confident), or they can bring us to our knees (remember the worst mistakes you made). Memories influence your every action and behavioral algorithm. Essential elements of memory are integrated and stored in the temporal lobes. When this part of the brain is damaged, memory is usually impaired.
Memories can undermine our chances of success and effectiveness. Among my patients was a couple with severe marital problems. The husband suffered from depression and attention deficit disorder. His wife was tough and vindictive. In the end, it was her memories that destroyed their relationship. Soon after they began treatment, the husband's problems were diagnosed and he was prescribed medication. He felt much better. Everyone except his wife noticed this improvement. Because his more positive behavior did not match her experience, she did not notice the progress and continued to behave as before. She constantly blamed him. She didn't want anyone to help her. Eventually this marriage fell apart. And it was her own memories, not reality, that killed him.
In our research, we also discovered that the dominant temporal lobe plays an important role in maintaining emotional balance. The ability to maintain a stable and positive frame of mind, regardless of the ups and downs that we encounter in daily life, is extremely important for the development of a stable character and a stable personality. The optimal mode of operation of the temporal lobes strengthens peace of mind, while disruption of their activity entails frequent mood swings and unpredictability of behavior and reactions.
The non-dominant temporal lobe (usually the right one) helps recognize facial expressions, voice intonation, hear rhythm, listen to and perceive music, and assimilate visual information.
Recognizing familiar faces and facial expressions, and the ability to accurately perceive and judge voice, tone, and intonation are all essential social skills. The ability to understand whether the other person is happy to meet you, or scared, or bored, or in a hurry, is of great importance for effective contacts with others. The Italian ophthalmologist Caglino in 1867 described a patient who, after a stroke, lost the ability to recognize familiar faces, but could still read small text well. Since the 1940s, more than a hundred cases of prosopagnosia (the inability to recognize familiar faces) have been described in the medical literature. Patients suffering from this disorder are often either unaware of it (damages of the right hemisphere often result in an inability to recognize or admit the existence of the disease), or are ashamed to admit that they do not recognize close relatives and friends. Most often, these problems are associated with decreased activity in the right temporal lobe. Recent research suggests that recognizing facial expressions is an innate ability and not something acquired early in life (babies are good at understanding their mother's facial expressions). However, when problems arise in this part of the brain, social skills suffer.
The temporal lobes help us perceive the world of sights and sounds. This area of the brain allows us to become excited, relaxed, or delighted when listening to great music. The temporal lobes are often called the “interpretive cortex” because they interpret what we hear and integrate it with our existing memory, thereby helping us extract meaning from incoming information. The temporal lobes are also responsible for feelings of strong conviction, inner insights, and knowledge of the truth.
Activity rate
As you know, the temporal lobe is located at the level of the imaginary temple of glasses - that is, on a line below the level of the ears. The temporal lobes, combined with the activity of the limbic system, make life emotionally rich. Their unity allows us to talk about the emotional brain, which is known for passionate desires and sublime experiences. These experiences make us feel the peak of pleasure or leave us in deep despair.
Normally, with balanced activity of the temporal lobes and limbic system, a person has full self-awareness, relies on personal experience, experiences a variety of uniform emotions, is inclined to experience spiritual experience, and is aware of everything. Otherwise, all of the listed activities of the human brain will be disrupted, and, therefore, problems in communication and everyday life will not be avoided.
Problems related to both temporal lobes:
memory problems, amnesia;
headaches, abdominal pain for no obvious reason;
unaccountable and unreasonable anxieties and fears;
abnormal sensory perceptions, visual or sound distortions;
the feeling of having already seen (deja vu) or never seen (jamais vu);
periods of dizziness and loss;
excessive fixation on religious or moral issues;
hypergraphia, verbosity when writing;
convulsions.
Temporal lobe dysfunction is more common than previously thought. You may have noticed that many of the symptoms listed were previously thought to be psychological, when in fact they are caused by biological causes. The temporal lobes are located in a very vulnerable part of the brain in the temporal fossae (cavities), behind the eye sockets and behind the temporal bones. On the anterior wall of the cavity there is a protruding sharp edge of the sphenoid bone, which often injures the frontal lobes even with mild head injuries. (It would be better if the Lord put some protection on this edge.) Because the temporal lobes are located in a cavity surrounded on five sides by bony protrusions (front, back, right, left and below), they can suffer a blow to the head from almost any angle.
Problems related to the temporal lobes have a variety of origins. Most often they arise due to a hereditary predisposition, as a result of head injuries, poisoning or infections. Due to their location relative to the bones of the skull, the most vulnerable areas of the brain are the temporal lobes, prefrontal cortex and cingulate gyrus. It is these areas that play the most important role in human thinking and behavior.
Dummy base of the skull (thick arrow points to the temporal sockets, in which the temporal lobes are located, thin arrow points to the sharp sphenoid bone).
Blaine
Blaine (age 60) came to see me because his wife heard me speak at a national conference and thought he had a temporal lobe problem. Blaine suffered from memory loss. His mood often deteriorated and he was aggressive. In addition, with his corner vision, he often saw shadows and heard an unpleasant buzzing noise, for which he consulted a doctor, but to no avail. Outbursts of rage seemed to arise in him without any reason. “I explode over little things. Then I feel very ashamed,” he said. At age five, Blaine fell head first into a pile of bricks. At school he was not good at reading, he often got into fights. The SPECT scan revealed significant abnormalities in the left temporal lobe: decreased activity in the anterior and posterior parts of the lobe and excessive activity in the deep lobe. Seeing this picture, I realized that many of Blaine's problems were related specifically to disturbances in the left temporal lobe, which, apparently, were the result of his fall in childhood. I prescribed him Depakote, an anticonvulsant drug that also stabilizes the activity of the temporal lobes. When we met three weeks later, Blaine was happy. The buzzing and shadows no longer appeared, and since he started taking the medicine, he has never lost his temper. “For as long as I can remember, for the first time in my life in all three weeks I never yelled at anyone.” Four years have passed and Blaine is still able to control his emotions.
Blaine's Brain
3D image of the bottom surface. Note decreased activity in the left temporal lobe (see arrow).
3D image - active brain, bottom view. Note increased activity deep in the left temporal lobe (see arrow).
Typically, disturbances in the left temporal lobe include aggression (inward or outward), dark or violent thoughts, increased sensitivity to slights, mild paranoia, difficulty finding words, difficulties with listening and reading, and emotional instability. Let's take a closer look at this.
Aggression caused by disorders in the left temporal lobe can manifest itself in relation to others or in relation to oneself in the form of aggressive thoughts directed at oneself. Aggressive behavior is a very complex problem. However, according to the results of a survey conducted in our clinic, 70% of patients who attacked another person or caused some kind of material damage through aggressive actions had impaired activity in the left temporal lobe. It seems that damage or dysfunction of the left temporal lobe makes a person more susceptible to irritability, angry and aggressive thoughts (we will talk about this in much more detail in the chapter on violence). One of my patients with left temporal lobe dysfunction (apparently hereditary, since his father often had fits of rage) complains of frequent and vivid thoughts of violence. He is very ashamed that such thoughts come into his head. “It happens that I’m just walking down the street,” he says, “and if one of the passers-by accidentally touches me with his sleeve, I immediately want to shoot him or beat him to death. It scares me". Fortunately, in the scan, along with abnormalities in the left temporal lobe, we found good condition in the prefrontal cortex of his brain. Therefore, he is able to control his behavior and his own impulses that may arise against the background of aggressive thoughts. Another similar case. Misty (45 years old) came to see me complaining of angry outbursts. One day, in a grocery store, a woman accidentally “bumped” into her. In response, Misty started yelling at her. “I don’t understand where this anger comes from,” she says.
I have been going to a psychotherapist for sixteen years. I just flare up out of the blue. The most monstrous thoughts come into my head. If you knew what these thoughts are, you would hate me.” At four years old, Misty fell from the second tier of her bed and remained unconscious for a minute or two. The anterior and posterior parts of her left temporal lobe were clearly injured. Taking Depakote daily in small doses did a great job of taming the “monster” inside her.
I often see how aggressiveness caused by disturbances in the left temporal lobe is expressed in suicidal behavior. In our study, we noted left temporal lobe abnormalities in 62% of patients who seriously contemplated or attempted suicide. After I gave one of my lectures in Auckland, a woman approached me in tears. “Dr. Amen,” she said, “I understand that everyone in my family had problems associated with disorders in the left temporal lobe. My paternal great-grandfather committed suicide. My father's parents also committed suicide. My father and two of his three brothers also committed suicide. My son attempted suicide last year. Can you help us? I was able to examine three members of her family. Two were found to have abnormalities in the left temporal lobe. Treatment with Depakote helped them.
With regard to suicidal behavior, the role played by the left temporal lobe in it is confirmed by one sad episode. For many years I wrote a column for our local newspaper about the connection between behavior and brain function. One of them was devoted to suicidal behavior and disorders in the left temporal lobe. A week after publication, a woman came to me. She said that her daughter, who was twenty years old, committed suicide a few months ago. She herself could not recover from the grief that befell her completely unexpectedly. “She was the epitome of the perfect child. One can only dream of such a daughter,” she said. “She was an excellent student, polite, helpful, and a pleasure to communicate with. Then suddenly everything changed at once. Two years ago, while riding a bicycle, my daughter had an accident. She hit a tree branch, flew over the handlebars and hit the ground on the left side of her face. When they ran up to her, she was unconscious, but quickly came to her senses. She has changed since then. She became gloomy, irritable, and easily became angry. She began to complain about the “bad thoughts” that came into her head. I took her to a therapist, but it didn't help. One evening I heard a loud sound. She shot herself right on the front lawn.”
Her tears made me cry too. I knew that her daughter could be helped if she could find a doctor who could understand that her “minor head injury” had caused damage to her left temporal lobe. Taking an anticonvulsant drug would have prevented her from committing suicide. Interestingly, in recent years, psychiatrists have often resorted to anticonvulsant drugs to treat a large number of psychiatric diseases. I fully admit that often we actually treat physiological disorders of the brain, which are commonly called psychiatric diseases.
People with left temporal lobe dysfunction are hypersensitive to neglect and appear to suffer from a mild form of paranoia. Unlike patients with schizophrenia, who sometimes become completely paranoid, people with impaired function of the left temporal lobe often seem to be laughing at them, discussing them, although they have no reason for such suspicions. Such sensitivity can cause serious complications in the family and at work.
When the left temporal lobe is malfunctioning, reading difficulties and language problems are often noted. The dominant temporal region is largely responsible for the ability to read, remember what has been read, and integrate new information. Recent estimates indicate that nearly 20% of the U.S. population has reading difficulties. When examining patients with dyslexia (who have difficulty reading), we often find that they have decreased activity in the posterior part of the left temporal lobe. Dyslexia can be inherited or develop as a result of injury to this part of the head. Here are two illustrative examples.
Carrie
Carrie (40) is a psychologist. She came to see me two years after she received a head injury in a car accident. Before the accident, she had an excellent memory, she read quickly and remembered what she read well. She always said that reading was one of her greatest academic strengths. After the accident, she began to have problems with her memory, she had to deal with irritability, and it became more difficult to read. She said that she had to read certain pieces of text several times to understand what was written there. She was able to remember what she read for a very short time, just a few minutes. A SPECT scan revealed that she had anterior and posterior injury to her left temporal lobe (a typical finding in trauma). I referred her to our biofeedback specialist to increase activity in her left temporal lobe. Within four months, she regained her reading skills, improved her memory, and regained control of her emotional states.
Based on our experience, we can state that disorders in the left temporal lobe are more often manifested by discomfort caused by external factors (anger, irritability, aggression). At the same time, disorders in the right temporal lobes are more often associated with states of internal discomfort (anxiety, fearfulness). Among our patients, the left-sided dichotomy is particularly distressing. One possible explanation is that the left hemisphere of the brain is involved in understanding and expressing information expressed through language. When the left hemisphere is affected, people strangely express the discomfort they experience. When the non-dominant hemisphere is affected, discomfort is more often expressed in non-verbal ways.
Mike
Problems associated with dysfunction in the non-dominant (usually right) temporal lobe often affect social skills, especially the ability to recognize facial expressions and vocal inflections. The case history of Mike (30 years old) provides a clear example of the manifestation of impaired function of the right temporal lobe. Mike came to my appointment because he dreamed of a date. He had never gone on a date in his life. He himself was infuriated by his inability to approach a woman and make an appointment with her. At the reception, Mike said that he was unable to figure out what his problem was. His mother, who came with him, had her own ideas. “Mike,” she said, “judges situations wrong. He's always been different. Sometimes he is too assertive, and sometimes, when another person shows interest in him, he, on the contrary, withdraws into himself. He also does not perceive the sound of my voice. I can be very angry with him, but he doesn't attach any importance to it. Or he may think that I am angry with him, while I do not even have this in my Thoughts.
As a child, Mike always wanted to play with other kids, but he never knew how to make friends. It was very painful for me to see his disappointments.” The scan revealed that Mike had reduced function in his right temporal lobe. The left temporal lobe was functioning normally. What helped Mike best was an intensive social skills course. He worked with a psychologist who taught him to recognize different facial expressions, tones of voice and taught him the basics of how to interact with people. Six months after his first visit to our clinic, Mike went on his first date.
Impaired function in one or both temporal lobes can cause a wide variety of symptoms. These include: disturbances in perception (sensory illusions), memory problems, the feeling that you have already seen and experienced this, although this could not be (deja vu), inability to recognize familiar faces and places, attacks of unreasonable panic or fear, attacks of dizziness and confusion, excessive preoccupation with religious or moral issues. An extremely common symptom of temporal lobe dysfunction is illusions.
Most often they appear like this:
with peripheral vision a person sees shadows or bugs;
objects begin to change size and shape (one patient told how, before his eyes, lampposts began to turn into animals and run away; another saw how the figures in the picture began to move);
a person hears the buzzing of bees or the crackling of a radio, although neither the bees nor the receiver are near him;
the person begins to smell or feel a strange taste in the mouth;
a person feels as if insects are crawling on his skin.
Temporal lobe dysfunction often causes headache or abdominal pain of unexplained etiology. Recently, the anticonvulsant drug Depakote gained another use: it began to be prescribed for migraines. Often, when headaches or abdominal pain are caused by dysfunction of the temporal lobes, patients benefit from anticonvulsant medications. Many patients who suffer from anxiety, worry, or panic attacks develop secondary associations with panic, causing them to develop fears or phobias. For example, if, when you first felt an attack of panic or horror, you were in a park, then you may well have an anxious feeling every time you enter this park.
Often with dysfunction in the temporal lobes there is an excessive fixation on religious and moral issues. In my practice, I encountered a six-year-old boy who drove himself to the point of physical illness by worrying about everyone who would go to hell.
Another patient spent a week in church praying for the souls of his family. He came to see me with complaints about outbursts of anger that arose in him, often directed against family members. These outbursts arose in response to what he perceived as serious moral transgressions. Another patient came to me because he was spending so much time thinking about the “mysteries of life” that he was unable to work and was already a candidate for dismissal.
Damage to the temporal lobes often results in a condition called hypergraphia, a tendency to write compulsively and verbosely. The above raises the question of whether Ted Kaczynski3, known as the Unabomber, suffered similar violations. Such suspicions are suggested by his long, inarticulate manifesto, penchant for violence, and departure from “civilization.” However, he had such a hatred of technological progress that we were unlikely to be able to give him a SPECT scan. Some of my patients with temporal lobe dysfunction spend hours writing. One patient sent me letters of 20–30 pages, describing her life to me in great detail. As I learned more about hypergraphia and began treating it with anticonvulsants, her letters became clearer and were reduced to two or three pages containing the same information. By the way, many who suffer from disorders in the temporal lobes develop a condition opposite to hypergraphia; It becomes difficult for them to extract the necessary words from their minds and put them on paper. I know one doctor who speaks brilliantly in front of an audience, but is unable to formulate his thoughts enough to write a book. His scans revealed decreased activity in both temporal lobes. After he began taking small doses of Depakote daily, his thoughts became freer and he could write for hours without interruption.
3 Kaczynski was an American mathematician who fought against industrial society. To attract public attention to the problem of industrialization, he began sending letters with bombs by mail to universities and airlines. — Approx. lane
Harriet
Memory problems have long been considered a classic symptom of temporal lobe dysfunction. Amnesia resulting from head trauma is often caused by injury to the internal tissues of the temporal lobes. Serious memory problems can arise as a result of previous infectious diseases. Harriet turned out to be an extremely graceful 83-year-old lady who suffered encephalitis fifteen years ago and lost her memory. True, she remembered well the events that took place before her illness. As for what happened after that, Harriet's memory contained only scattered fragments of memories. An hour after lunch, she felt quite full, but could not remember whether she had eaten or not. Harriet told me, “I donated my brain to the medical school in the hope that my problems might help someone else. But I don't think they can use my brain. Unless they give it to students who will dissect it. Besides, I would like to know what my problem is. And be sure to write it down. I won’t remember anything from what you tell me.” Harriet's scan revealed large areas of lesions in both temporal lobes, and especially on the left. It seemed as if the virus had literally eaten away part of her brain.
Alzheimer's disease, a devastating, progressive form of dementia, is one of the leading memory problems in older adults. Unfortunately, for many, this disease robs them of years of well-deserved rest, and leads their loved ones to physical, emotional and financial exhaustion. SPECT is an effective diagnostic method in such cases. Before functional diagnostic methods became available to doctors, the only reliable way to make this diagnosis was an autopsy. SPECT scans show decreased perfusion typical of Alzheimer's disease in both temporal lobes and decreased activity in the parietal lobes. Sometimes this picture occurs three to six years before symptoms appear. Some new drugs to treat the disease appear to be able to slow its progression. During the scan, we observed that their action improves perfusion in those parts of the brain that are responsible for memory and thinking, including the temporal lobes. The illustrations show the brain of a patient with Alzheimer's syndrome, who became forgetful, often could not find his way when leaving the house, began to forget basic things, for example, forgot how to dress himself and began to show more and more aggression towards his own wife.
Harriet's brain. Consequences of encephalitis
3D image of the bottom surface. Note the decreased activity in both temporal lobes (see arrows).
Alzheimer's disease
Three-dimensional image of the surface, top view. Note the markedly decreased activity in the parietal lobes (see arrows).
3D image of the bottom surface. Note the markedly decreased activity in the temporal lobes (see arrows).
They say that Fyodor Ivanovich Dostoevsky suffered from “spasms of the temporal lobes.” He considered his illness a “holy experience.” One of his biographers, René Fülep-Miller, quotes Dostoevsky as saying that epilepsy “arouses in me feelings of which I was hitherto unaware, imparting to me sensations of bliss, abundance and eternity.” In his novel “The Idiot,” Dostoevsky writes: “He thought among other things about the fact that in his epileptic state there was one degree almost just before the seizure (if only the seizure came in reality), when suddenly, in the midst of sadness, spiritual darkness, pressure, moments like his brain would ignite, and with an extraordinary impulse all his vital forces would be strained at once. The feeling of life and self-awareness almost increased tenfold in these moments, which lasted like lightning. The mind and heart were illuminated with extraordinary light; all his worries, all his doubts, all his worries seemed to be pacified at once, resolved into some kind of supreme calm, full of clear, harmonious joy and hope, full of reason and final reason. But these moments, these glimpses were still only a premonition of that final second (never more than a second) from which the real seizure began. This second was, of course, unbearable. Thinking about this moment later, already in a healthy state, he often said to himself that all these lightning and glimpses of higher self-awareness and self-awareness, and therefore “higher being,” are nothing more than a disease, a violation of the normal state, and if so, then this is not the highest being at all, but, on the contrary, should be ranked among the lowest. And yet, he finally came to an extremely paradoxical conclusion: “What is it that this is a disease?”, he finally decided, “What does it matter that this tension is abnormal, if the very result, if the minute of sensation, remembered and considered already in a healthy state, turns out to be extremely harmony, beauty, gives an unheard of and hitherto unforeseen feeling of completeness, proportion, reconciliation and alarmed prayerful merging with the highest synthesis of life?
Bryce
Lewis Carroll, according to some accounts, also suffered from “temporal lobe phenomena,” which are well reflected in the visual images of Alice in his book “Alice in Wonderland.” Seven-year-old Bryce, to whom his mother began to read Alice, became very excited. He said he felt like Alice. “Strange things are happening to me,” he told his mother. “I see all sorts of things.” In broad daylight, he observed how objects change their shape, often decreasing in size. At night he saw greenish ghosts. Bryce exhibited many symptoms of anxiety. His mother, fearing that Bryce was “going crazy” (and his cousin had been diagnosed with a schizophrenia-like condition), brought him to see me. After hearing about his symptoms, I suspected that one or both of his temporal lobes were overactive. A SPECT scan revealed abnormalities in the right temporal lobe and increased activity in the basal ganglia. I prescribed Dapakote (an anticonvulsant drug effective in treating temporal lobe lesions) as well as psychotherapy to reduce anxiety. Within two weeks, Bryce's strange symptoms stopped, and within six months, his anxiety also decreased.
Bryce's brain. Temporal lobe epilepsy
3D image of the bottom surface. Note the area of increased activity in the deep right temporal lobe (up arrow) and basal ganglia (down arrow).
Ellen and Jack
Ellen and Jack have similar medical histories. Both were slightly withdrawn. Both experienced attacks of dizziness and causeless panic. For both of them, religious experience occupied a fairly significant place in their lives. Ellen (32 years old) had deep religious experiences that almost paralyzed her life. She was unable to work and was socially isolated. Jack was very interested in her “periods of deep spiritual enlightenment,” but he could not understand what it meant. Ellen was brought to see me by her parents, who were concerned about her social isolation. Jack wanted to be examined for panic attacks. In both cases, scans revealed marked hyperactivity of deep areas in the temporal lobes. Much of their symptoms went away after they started taking Depakote. At the same time, while continuing to take this drug, both remain deeply religious people. True, they no longer remain immersed in their thoughts for a significant part of the time, as they once did.
Jim
As with Ellen and Jack, Jim suffered from dizziness and panic attacks. He also had periods of “religious thoughts” during which he felt “the presence of the devil” and became insecure and fearful. His fear of the devil haunted him and made him withdrawn. The family believed that he was suffering from paranoia. Jim's brain scan results showed an interesting difference from Ellen's and Jack's. In Jim, the abnormalities were found in the left, not the right, temporal lobe. Based on my experience, I believe that disturbances in the left temporal lobe are where particularly negative or gloomy thoughts manifest themselves. After Jim started taking Depakote, the “presence of the devil” ended.
Limbic system
The limbic system models the emotional impulse: negative or positive emotions are its derivatives. Thanks to its influence, a person has a certain emotional mood. If its activity is reduced, optimism and positive feelings prevail, and vice versa. The limbic system serves as an indicator for assessing current events.
These areas of the brain have a strong charge of negative or positive memories entered into the register of the limbic system. Their importance is that when looking at events through the prism of emotional memory, the ability to survive is stimulated, the resulting impulse stimulates action when it concerns starting a relationship with the opposite sex, or avoiding a dysfunctional boyfriend who is recorded in memory as having brought pain.
The emotional background, negative or positive, creates the sum of emotional memories that affect stability in the present, views, and behavior. The deep structures of the limbic system are responsible for building social connections and personal relationships. Based on the results of the experiments, the damaged limbic system of rodents did not allow mothers to show tenderness to their offspring.
The limbic system functions like a mental switch, instantly activating emotions or rational thinking. When the limbic system is calm, the frontal cortex becomes dominant, and when it is dominant, emotions drive behavior. In people with depression, the limbic system is usually more active and the cerebral cortex is depressed.
Anatomical parts of the brain
There are 5 separate anatomical parts of the brain, which were formed phylo-ontogenetically in different ways. Let's start with the oldest parts, gradually moving to the younger parts of the brain.
- Temporal lobe of the brain: structure and functions
- The structure of the hemispheres
- Sinuses and processes of the dura mater of the brain
- Frontal
Medulla
This is the most ancient part of the brain, which is a continuation of the spinal cord. The gray matter here is presented in the form of the nuclei of the cranial nerves, and the white matter forms the pathways up and down.
Here are important subcortical centers for coordination of movements, regulation of metabolism, balance, breathing, blood circulation, and protective unconditioned reflexes.
Back of the brain
Includes the pons and cerebellum. The cerebellum is also called the small brain. It is located in the posterior cranial fossa and weighs 120-140 grams. It has 2 hemispheres, which are connected to each other by a worm. The bridge looks like a thick white cushion.
The hindbrain regulates balance and coordination in humans. There are also a large number of nerve pathways that carry information to the higher and lower centers.
Midbrain
Consists of 2 upper (visual) tubercles and 2 lower (auditory). Here is the center that is responsible for the reflex of turning the head in the direction of noise.
Divisions of the brain
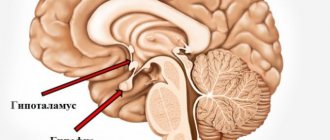
Intermediate part
It includes the thalamus, which acts as a kind of mediator. All signals to the cerebral hemispheres pass only through the thalamic pathways. The thalamus is also responsible for adaptation of the body and all types of sensitivity.
The hypothalamus is a subcortical center that regulates the activity of the autonomic nervous system, and therefore all internal organs. It is responsible for sweating, thermoregulation, lumen and tone of blood vessels, respiratory rate, heartbeat, intestinal peristalsis, formation of herbal enzymes, etc. This part of the brain is also responsible for the body’s sleep and wakefulness, eating behavior and appetite.
In addition, it is the central organ of the endocrine system, where nerve impulses from the cerebral cortex are transformed into a humoral response. The hypothalamus regulates the functioning of the pituitary gland by producing releasing factors.
Terminal (cerebral hemispheres)
These are the right and left hemispheres, which are united into one whole by the corpus callosum. The telencephalon is the most recent part of the human brain in evolutionary terms and occupies up to 80% of the total mass of the organ.
Important Acute mental reaction to stress
The surface has a large number of convolutions and grooves, which are covered with cortex, where all the higher centers for regulating the body’s activities are located.
The hemispheres are divided into lobes - frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. The right hemisphere is responsible for the left side of the body, and the left hemisphere is responsible for the opposite. But there are centers that are localized only in one part and are not duplicated. As a rule, for right-handers they are located in the left hemisphere, and for left-handers, vice versa.
Sinuses and processes of the dura mater of the brain
The following are considered to be the processes of the dura mater:
- A large crescent-shaped continuation, or the crescent-shaped process of the largest hemispheres of the brain, is located between both large parts of the brain;
- A small falciform process, or a falciform process near the cerebellum, extends into the cavity between the cerebellar hemispheres, joining the bone tissue of the occiput from the internal occipital indentation to the large foramen of the occiput;
- Cerebellar tentorium - located between the parts of the cerebral hemispheres at the back of the head and the cerebellum;
- The plate is located above the sella turcica; in the middle there is a hole through which a funnel runs.
Sinuses (lacunae) of the dura mater of the brain, formed due to the splitting of the dura mater into two strands, are essentially channels through which blood from the veins is drained from the head into the internal dual veins.
The hard shell plates that form the lacunae are tightly reinforced and do not move. Therefore, these sinuses are visible in the section. They are not equipped with valves. This structure of these tanks allows venous blood to flow freely from the brain, completely independent of pressure surges inside the skull. On the inner walls of the bone tissue of the skull, in the areas where these recesses of the hard shell are located, there are proper tentories. In medical practice, the following names of the dura sinuses are used:
- The superior vertically dividing sinus is located longitudinally along the entire upper-outer border of the falx of the cerebral hemispheres, from the edge resembling the cockscomb of the ethmoid bone to the indentation of the occiput inside. In the anterior parts, this tank is equipped with anastomoses with veins of the paranasal space. Its termination at the rear is included in the transverse manifold.
- The lower vertically dividing lacuna is located inside the lower spacious border of the falx of the cerebral hemisphere. It is much smaller than the top one.
- The straight sinus is located vertically in the splitting of the cerebellar membrane in the direction of the attachment of the falx of the cerebral hemisphere to it. This collector combines the posterior ends of the superior and inferior sagittal sinuses.
- located in the part of the separation of the cerebellar plate from the dura mater of the brain. On the inner side of the scales of the bone tissue of the back of the head, an extensive groove of the transverse sinus is related to this depression.
- The occipital lacuna lies at the bottom of the cerebellar falx. Descending longitudinally from the inside of the occipital border, this tank is located to the posterior border of the large opening of the occiput, where it diverges into two grooves that frame this opening at the back and on both sides.
- The sigmoid collector is double, located in the sigmoid branch on the inside of the skull, characterized by an S-shaped appearance. In the area of the opening of the great veins, this tank flows into the jugular vein.
- The cavernous sinus is double and lies on the vault of the cranium away from the sella turcica. The carotid artery and some intracranial arteries pass through this cistern. The recess has a very intricate structure in the form of interconnected caves, which is why it got its name.
- The sphenoparietal lacuna is double, refers to the spacious posterior border of a small wedge-shaped bone fragment, in the cleft it connects in this place with the dura mater of the brain.
- The upper and lower stony recesses are double and lie longitudinally along the upper and lower borders of the triangle of bone tissue in the temporal region.
Important Gray matter of the brain: what it consists of and what it is responsible for
In some areas, all these cisterns form connections - anastomoses - with the external veins of the skull through connections of vessels. In addition, the sinuses of the TO connect to the diploic arteries, which are located in the spongy structure of the bones of the base of the skull and are included in the superficial vessels of the head. Thus, blood from the veins of the brain flows through the branches of its vessels located on the surface and in the depths into the sinuses of the brain and then into both internal large veins.