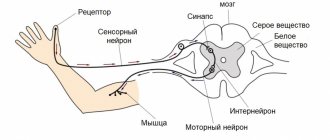
Neuritis of the facial nerve is a partial or complete dysfunction of the facial nerve. The facial nerve is the nerve that is responsible for the facial muscles of the face. With facial neuritis, symptoms appear suddenly or develop within 48 hours. Often this is first noticed by the patient's family members (deviation of the nasolabial fold or slurred speech). Patients often noted that they noticed these symptoms in the morning. Other common symptoms of neuritis are numbness or burning in half the face, facial asymmetry or drooping corner of the mouth on one side, increased sensitivity to loud sounds, watery or dry eyes, difficulty eating, headache, pain behind the ear, changes in taste.
This disease affects 1 in 5,000 people in the United States each year. Facial neuritis can occur at any age. Neuritis of the facial nerve occurs more often in pregnant women, patients with diabetes, after influenza or acute respiratory infections, or simply hypothermia.
Cause of facial neuritis
The cause of Bell's palsy is unknown. However, the most common theory is about the viral etiology of the disease. According to this theory, under certain circumstances, a virus like HSV-1, which usually lives within nerve cells, is activated. The virus begins to actively multiply and produce toxic substances. As a result, inflammation of the nerve occurs and disruption of the conduction of electrical impulses along the nerve fiber. Most patients with sudden loss of facial nerve function on one side are diagnosed with Bell's palsy.
However, this diagnosis must be made by a doctor, such as a neurologist. There are many other causes of facial paralysis. The doctor will look at how quickly the symptoms began, whether there are other symptoms such as fever, headache, hearing loss, dizziness, weakness or numbness in the arms and legs, difficulty swallowing, and hoarseness. The doctor will also need to find out about pre-existing medical conditions, medications, and family history. In addition, a full inspection is required.
Other causes of facial neuritis are: ear infections and tumors, trauma, Lyme disease, brain tumors, stroke, etc.
If the symptoms progressed slowly over 3-6 months, the presence of constant headaches was noted, or there was a transient nature of the symptoms, then this is not Bell's palsy.
The prognosis for neuritis of the facial nerve is quite good. If the dysfunction was incomplete (a certain range of muscle movements was preserved), then the likelihood of a complete recovery is very high. In this case, 95% of patients will have complete recovery of nerve function. In a small number of patients, minor disturbances (asymmetry when smiling or twitching) may persist.
With complete paralysis, it is possible to achieve up to 80% recovery, that is, practical restoration of functions in full. Approximately 17 percent of patients experience persistence of some dysfunction. This may be some weakness of the facial muscles, twitching of the lip or eyelid. A small percentage of patients (4 percent) may have more significant dysfunction, such as persistent facial muscle weakness or twitching.
Typically, most patients begin to regain function within 3 weeks. The earlier recovery begins, the better the final result. If paralysis does not recover within 3 months, then another pathology is likely.
Paralysis
Polio
Encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis
Syphilis
Stroke
17950 September 17
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Paralysis: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition _
Paralysis is a complete loss of movement in one or more parts of the body, loss of muscle strength in a muscle or group of muscles, and inability to perform movements. In some cases, the term is used to describe muscle contractility disorders. Paralysis is not an independent disease, but only one of the symptoms of many organic pathologies of the nervous system.
A condition in which voluntary movements are not completely lost is called paresis.
Types of paralysis
Any damage to the nervous system can lead to impaired motor function. There are organic, functional and reflex paralysis.
Organic paralysis is formed due to the fact that the nervous system (at any level) is affected by tumors, injuries, infections or any other factors.
Functional paralysis in most cases occurs as a result of the formation of a so-called stagnant region of inhibition in the brain, which prevents the muscles from receiving the command to contract. During the development of the disease, no pathological changes occur, reflexes remain normal, muscle tone is maintained at the proper level. Reflex paralysis is caused by damage to the peripheral motor neuron and can be caused by damage to any part of the nerve pathway. From an anatomical point of view, a distinction is made between paralysis caused by damage to the central nervous system (brain or spinal cord) and paralysis associated with damage to the peripheral nerves.
The variety of causes of paralysis is reflected in pathomorphological changes, which can have a very different nature and location.
Paralysis is divided according to severity, persistence and prevalence. It can be complete or partial, irreversible or transient, localized or widespread.
None of these clinical types is an independent pathology, however, there are certain types of paralysis that represent independent diseases. These include Parkinson's disease (shaking palsy), polio (infantile paralysis), Bell's palsy, bulbar palsy, pseudobulbar palsy, familial periodic paralysis, brachial plexus palsy, cerebral palsy and others.
Destruction, degeneration, inflammation, formation of foci (plaques), sclerosis, demyelination are the most typical types of pathological changes in nervous tissue that are detected during paralysis. According to their development, acute and flaccid paralysis are distinguished. In the first case, the symptoms increase very quickly, in the second, immobilization develops gradually.
The following classification of paralysis is distinguished, based on the prevalence of the process:
- monoplegia - paralysis of one limb on one side of the body;
- paraplegia - paralysis of two limbs of the same type, for example, both arms;
- hemiplegia – paralysis develops in the limbs on one side;
- tetraplegia – all four limbs are affected simultaneously;
- Ophthalmoplegia is paralysis of the muscles that provide motor activity to the eyes.
With central paralysis, motor function as a whole usually suffers, but not individual muscles.
Paralyzed muscles are spastic (convulsively tense), but do not undergo atrophy (it can only be a consequence of inactivity), and there are no electrophysiological signs of degeneration. In paralyzed limbs, deep tendon reflexes are preserved or enhanced. When peripheral motor neurons are damaged, instead of increasing muscle tone, it decreases. Individual muscles are affected, in which atrophy and an electrophysiological reaction of degeneration are detected. In a paralyzed limb, deep reflexes are reduced or completely disappear, and clonus are absent.
Psychogenic paralysis, which is not based on organic damage, can imitate one of these options or combine features of both. Central paralysis can appear in its pure form or be combined with features of peripheral paralysis. As a rule, it is accompanied by sensory and trophic disorders, as well as changes in vascular tone.
Peripheral paralysis is often accompanied by sensory impairment.
Possible Causes of Paralysis
There are different causes of paralysis, but they all boil down to damage to the nervous system caused by injury, tumor, abscess or inflammation. In addition, paralysis can occur as a result of demyelinating diseases associated with the destruction of the protein that ensures the conduction of nerve impulses along the fibers - myelin. Such diseases include: multiple sclerosis, multiple encephalomyelitis, etc.
Causes of paralysis can also be:
- myasthenia gravis – a disease characterized by pathological muscle fatigue;
- myopathy – congenital or acquired metabolic disorders in muscle tissue;
- poisoning with botulinum toxin (botulism), alcohol, industrial poisons, mercury, organophosphorus compounds, salts of heavy metals, nerve poisons;
- epilepsy;
- diseases associated with dysfunction of motor neurons, resulting in pathology of muscle function and paralysis of the limbs;
- damage to a large nerve trunk;
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (progressive degeneration of the central nervous system);
- acute cerebrovascular accident;
- immunoinflammatory diseases, in particular Guillain-Barré syndrome;
- congenital or hereditary degenerative diseases of the central nervous system;
- neoplasms (benign and malignant, including metastatic);
- injuries, if they are associated with damage to motor pathways or directly to motor centers;
- infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, polio, viral encephalitis, tick-borne encephalitis, meningitis);
- some medications (for example, muscle relaxants “turn off” the diaphragm, which is practiced during abdominal surgery);
- radiation exposure;
- hypothermia.
Which doctors to contact for paralysis
To determine the cause of paralysis, you should contact a general practitioner or. In case of infantile paralysis, it is necessary to urgently show the child. The doctor will conduct the necessary examination, consult with specialized specialists, and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Diagnostics and examinations for paralysis
The first and most common manifestation of paralysis is usually the inability to move and control the musculoskeletal system due to a lack of strength in a muscle or an entire group of muscles, namely:
- a complete lack of muscle strength in the muscles of the upper limbs, as a result of which it becomes impossible to perform actions such as grasping an object, lifting, bending and straightening the arm;
- complete lack of muscle strength in the muscles of the lower extremities, which is accompanied by a lack of active movements in the affected limb;
- drooping of the head forward, which is observed with paralysis of the posterior muscles of the neck.
In addition, there may be slurred speech, deviation of the tongue to the side when sticking it out of the mouth, and retraction of food while eating.
In some cases, there is a disturbance in the movement of the eyeballs, which is manifested by a lack of coordinated eye movement, resulting in the development of strabismus or so-called gaze palsy. With some paralysis, the function of the pelvic organs is impaired, which is accompanied by automatic reflex emptying of the bladder and fecal incontinence.
The symptoms of paralysis depend on its type:
- when the facial nerve is damaged, severe headaches appear;
- with bulbar palsy, immobilization of the tongue develops;
- with paralysis of the diaphragm, breathing stops;
- with spastic paralysis of the larynx, spasm of the upper respiratory tract occurs;
- a symptom of upper obstetric palsy (Duchenne-Erb palsy) in children is dysfunction of the muscles of the shoulder girdle;
- with distal obstetric paralysis (Dejerine-Klumpke palsy), paralysis of the hypothenar, thenar, lumbrical and interosseous, long flexor muscles of the hand and fingers is observed, as a result of which the hand is in the “clawed paw” position or hangs down.
During a neurological examination, a differential diagnosis is made between central and peripheral paralysis.
To do this, the volume of active and passive movements, superficial and deep reflexes, the presence of pathological reflexes, muscle tone, identification of atrophies, hypotrophies, fascicular and fibrillar twitches are checked. After a general examination, laboratory and instrumental research methods are prescribed. To detect signs of poisoning, a toxicological blood test is necessary. A general blood test can reveal signs of inflammation.
The first signs and clinic of the disorder
The first sign of the disease is a feeling of numbness in half of the face. There is a feeling that the lips and tongue “do not obey”, difficulties arise in conversation, it is impossible to smile normally, frown or even close your eyes.
Pain behind the ear gradually appears - this symptomatology can increase over 1-2 days or appear rapidly (2 hours before complete paralysis). Paralysis usually comes on suddenly and develops within 48 hours.
A feature of the disease is the rapid increase in symptoms. As inflammation of the facial nerve develops, the following symptoms appear:
- distortion and weakness of facial muscles;
- the palpebral fissure widens to such a state that the eye cannot be closed. The folds on the forehead above the eye are smoothed out;
- the pain from the ear moves to the corner of the mouth, the nasolabial fold is smoothed out, so saliva flows from the corner of the mouth;
- numbness and heaviness of the facial muscles are felt, their sensitivity is not lost;
- there is a loss of taste.
There is no facial expression on the affected side, and strong muscle contraction sometimes occurs on the opposite side. Typically, signs of paralysis appear clearly in the morning.