Our treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy in adults is always highly effective. This is due not only to the completeness of the diagnosis, but also to the use of modern methods of restorative medicine. Our advantages allow us to treat encephalopathy as fully as possible, depending on the cause of its formation and the individual characteristics of the development and functioning of the body.
Using only proven and only effective therapeutic techniques, we achieve maximum results in the shortest possible time. Side effects of treatment for cerebral encephalopathy are expressed in the form of a healing effect for the entire body, which contributes to a significant improvement in the quality of life.
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy
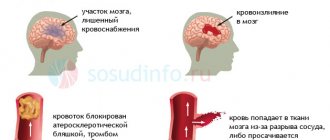
Encephalopathy of the brain is a severe and complex pathology that occurs due to the death of brain neurons. It can develop in unborn children (congenital encephalopathy), but more often the disease appears with age due to injuries, somatic diseases, infections, and the use of narcotic and psychoactive substances. Encephalopathy is often detected in those who suffer from alcohol addiction, are constantly located (or work) in an area of increased radiation, have brain injuries, malnutrition of the brain, etc. Cells die due to lack of oxygen, cessation (weakening) of blood flow, toxic effects, injuries, and it is important to identify the problem in a timely manner and begin active rehabilitation therapy.
Alcoholic encephalopathy requires special treatment. A quick cure should not be expected; rather long-term specific therapy is required. In the Preobrazhenie Clinic, over more than 20 years of successful work, unique techniques have been developed that can not only reduce the treatment time for alcoholic encephalopathy, but also achieve significantly better final results. This is explained by the fact that under the influence of our specific procedures, brain tissue is restored more fully and much faster.
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy in the clinic is carried out using the latest technologies of restorative medicine using neurometabolic therapy.
In the vast majority of cases, unlike other methods, we achieve restoration of brain function, and our patients return to their normal lives.
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy in the clinic
The Preobrazhenie Clinic uses advanced developments and unique techniques for the treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy of the brain in adults. We are ready to help adults and adolescents from 14 years of age, regardless of what stage of the disease is diagnosed and what is the cause of the pathology. Our specialists use not only well-known classical treatment methods, but also have developed their own proprietary methods.
Treatment for alcoholic encephalopathy varies depending on its severity. Treatment usually includes medications to relieve symptoms, reduce the severity of existing problems, and address the underlying cause.
Alcoholic encephalopathy is an acute and urgent condition. If the disease is detected, we recommend immediate active neurometabolic therapy in a hospital setting. Often, a delay of even a few hours can become critical for the patient’s health.
It is necessary to carry out measures as quickly as possible that will prevent the formation of Korsakov psychosis, which can become decisive in the future fate of a person. It is necessary to take all measures to restore mental and neurological functions as quickly as possible. It is at the initial stage of the formation of this condition that the onset of alcoholic dementia can be prevented.
At home (help at home, detoxification at home, etc.) it is very dangerous to provide medical care to such patients. It must be remembered that in 90% of such cases, home care ends in tragedy.
Features of the approach
It is necessary to understand that in severely malnourished patients with alcoholism, administering glucose solutions intravenously, performing hemasorption and plasmapheresis is extremely risky and dangerous. These procedures deplete the amino acid and vitamin reserves of the human body, which in turn accelerates the formation and manifestation of Wernicke encephalopathy. In patients who had no signs of the disease, these actions lead to the emergency development of the disease, which often ends in sudden death or leads to lifelong disability.
Taking these unfavorable factors into account, we prescribe special neurometabolic therapy that ensures the safety of the patient’s health. Individual therapy promotes rapid digitalization and prevents the formation of severe consequences after drinking alcohol. Due to the fact that patients’ memory function suffers, especially in the initial and crisis stages, they require special care and round-the-clock monitoring, preferably in a specialized clinic.
Our specialist can recommend not only maintaining a daily routine, but also a special diet to eliminate the underlying causes. In some cases of the disease, when the brain does not receive enough oxygen, the doctor prescribes intensive neurometabolic therapy and physical therapy.
There are no recommendations or universal programs that could be recommended in all cases. In each specific case, our doctors individually develop a technique for each person individually.
The brain is a vulnerable and complex organ, and the disease progresses differently in everyone. The first task is to restore blood flow and the functioning of diseased brain cells. It is necessary that encephalopathy does not develop further. It is also important to eliminate the root cause of the disease as quickly as possible and consider a maintenance therapy program.
Advantages of treating alcoholic encephalopathy in the clinic
- We use advanced techniques for diagnosing and treating encephalopathy;
- We offer inpatient and outpatient treatment;
- We employ experienced doctors who have practiced not only in Russia, but also abroad. We adopt the experience of foreign colleagues;
- comprehensive treatment is provided - our clinic is famous for its results, our patients really recover and return to a healthy life;
- reasonable prices for treatment. We do not prescribe unnecessary procedures, do not perform abstract therapies, and do not use cheap drug substitutes. We prescribe exceptionally effective programs to restore brain function using licensed original drugs;
- comfortable conditions for placement in a hospital. If encephalopathy is severe, stage III is identified. It is better to stay under the supervision of doctors at the Preobrazhenie Clinic for a while.
We extend a helping hand to you, we are ready to help you. Call by phone. We help even in the most difficult situations, when previous treatment did not help or was ineffective.
Why is hospitalization required?
The most important thing is to save a person’s life and minimize the toxic effects of alcohol. Without complete, active specific therapy, patients die much more often. In any case, it is impossible to provide the entire necessary range of activities at home. Even if it costs a lot. In such situations, a person must be observed simultaneously by several doctors of different specializations. And at home, 24-hour monitoring, at least 3 specialists, and this is a very big luxury. As a rule, after an acute attack of illness at the time of another binge, a person sharply degrades. This usually manifests itself in unfunny, offensive, obscene jokes, statements, and anecdotes told. Nystagmus and optic nerve palsy begin to form, which persists and develops as a consequence of the disease. Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy provides some relief of symptoms, but does not go away completely.
As usual, treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy is effective and does not bring complete relief to about 50% of patients. Impaired motor function does not disappear completely, the gait continues to be slow, clumsy, and they spread their legs wide apart when walking.
Treatment methods for alcoholic encephalopathy developed at the Transfiguration clinic for the most part bring more than 30% of patients almost complete restoration of motor and mental functions. Concomitant diseases are also compensated. Only in the most severe cases, and this is less than 20%, treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy does not bring complete relief. The remaining 50% of cases have a completely positive effect, with complete restoration of all functions.
After hospitalization
Alcoholic encephalopathy disrupts gait and forms horizontal nystagmus, which is the main symptomatology. This is accompanied by alcoholic dementia and complex somatic pathology. Recovery of the vestibular apparatus is usually slow, as is the regression of ataxia. It takes several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the condition. However, in very severe cases it is not always complete.
Apathy, lethargy and confusion begin to decrease gradually, while long-term memory takes much longer to fully recover. Long-term memory and learning ability (Korsakoff's syndrome) may remain as a long-term effect.
It should be emphasized that patients with alcohol dependence, exhaustion and Korsakoff psychosis are not divided into separate diseases. This is one disease, the sources of which can be various reasons.
Oculomotor disorders, ataxia, global disorientation and amnestic syndrome are successive phases of regression in the context of a single pathological process. Korsakoff psychosis is one of the components of alcoholic encephalopathy.
Types and causes of encephalopathy
- Traumatic encephalopathy - occurs due to injuries and other damage to the brain. Trauma causes neuronal damage. Typically found in athletes or military personnel who have been injured.
- Glycine encephalopathy is a genetic, hereditary disease. When producing abnormally high levels of the amino acid glycine. Appears in children soon after birth.
- Hashimoto's encephalopathy is a rare type associated with Hashimoto's autoimmune disease. In this case, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.
- Hepatic encephalopathy is the result of liver disease. The liver does not remove toxins that accumulate in the blood. Often combined with alcoholic encephalopathy.
- Hypertensive encephalopathy is the result of chronic, severely elevated blood pressure that has not been treated for a long time. Causes brain swelling and damage.
- Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy is a type of brain damage caused by a lack of oxygen. Usually leads to irreversible changes in the brain. Reasons: the child in the womb is exposed to alcohol, nicotine; carrying out xenon therapy, other influences.
- Toxic-metabolic encephalopathy is the result of exposure to infections, toxins, or organ failure. Imbalance of electrolytes, hormones and other active substances in the body.
- Infectious encephalopathy - transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases). Prions are proteins that begin to mutate and inhibit brain function.
- Uremic encephalopathy is the result of kidney disease. When toxins accumulate in the blood. It manifests itself from mild confusion in consciousness to deep coma.
- Alcoholic encephalopathy or Wernicke's encephalopathy is the result of prolonged alcoholism. Doesn't heal quickly. In the absence of proper treatment, it leads to the formation of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
Diagnostics
To diagnose encephalopathy, our doctor carries out a differential diagnosis by analyzing the mental and neurological status of the patient.
If our doctor suspects that you have another condition, he or she may do additional tests to determine the cause and severity of your condition. Research may include:
- examination by an experienced doctor;
- pathopsychological examination - to clarify the mental and neurological status;
- blood tests - identifying aggravating diseases, bacteria, viruses, toxins, hormonal and chemical imbalances. The choice of tests is based on the results of the examination;
- CT or MRI to detect injuries to the spine or brain. It is used only based on the results of an in-person examination, on the recommendation of a doctor.;
- electroencephalogram – exclusion of epilepsy (latent epilepsy). It is used only based on the results of an in-person examination, on the recommendation of a doctor.
Treatment and consequences of toxic encephalopathy
Organic damage to brain tissue due to the action of neurotropic poisons does not go away without leaving a trace. It is hardly possible to restore lost neurons, so changes in the psyche and neurological status are often permanent, leading to disability. Dangerous consequences are considered:
- Psychoorganic syndrome with loss of intellectual abilities;
- Coma and death;
- Bleeding in the brain;
- Irreversible mental disorders - hallucinations, depression, asthenoneurotic syndrome;
- Convulsive syndrome;
- Paralysis and polyneuropathy.
Treatment of toxic encephalopathy should be started as early as possible, at the very first symptoms of trouble. In addition, an integrated approach is important, taking into account the nature of the toxin, the degree of brain dysfunction, and the condition of the patient’s other organs.
In severe encephalopathy, tactics are aimed at stabilizing the condition; in all cases, infusion therapy and quickly limiting contact with a toxic substance are indicated. Patients are observed in toxicology or intensive care units, where there is every opportunity for intensive care.
The first action that should be taken is to stop contact with the neurotropic poison (for exogenous toxins). In the case of encephalopathy due to liver or kidney damage, it is impossible to immediately stop the action of toxic agents, so active detoxification therapy begins.
The basic principles of treatment of severe brain damage due to intoxication are:
- Conservative or surgical methods of detoxification, introduction of specific antidotes;
- Infusion of solutions and forced diuresis (has limitations in case of renal failure);
- The use of agents that enhance the breakdown of toxic substances - glucose, vitamin C, oxygen mixtures, sodium hypochloride);
- Transfusion of albumin, fresh frozen plasma to normalize the rheological properties of blood and hemostasis;
- Administration of glucocorticoids and diuretics to combat cerebral edema;
- The use of drugs that improve metabolic processes in the brain - cerebrolysin, nootropil, ATP, nicotinic acid, vitamins C and B;
- Anticonvulsant treatment - diazepam, magnesia, hexenal;
Removal of neurotropic poison is carried out by administering saline solutions into a vein, glucose, and accelerating urine excretion with diuretics. Cleansing enemas and gastric lavage are indicated to stop further absorption of the toxin. If necessary, hemodialysis, hemosorption and plasmapheresis are performed.
Symptomatic therapy includes the use of anticonvulsants (clonazepam, diazepam), tranquilizers, and antipsychotics for psychosis. To restore blood flow in the brain, vascular agents and antihypoxants (Cavinton, Nootropil, Actovegin, B vitamins, etc.) are indicated. If necessary, antihypertensive drugs, antiarrhythmics, and specific antidotes are prescribed if available.
Among conservative treatment methods, psychotherapy is of great importance. It is especially indicated for alcoholism and drug abuse, as well as depressive disorders. In addition, physiotherapy methods are used (massage, darsonval, medicinal baths).
Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, the patient takes multivitamin complexes, antioxidants, omega-3-based drugs, and nootropics. As indicated, he continues to take antidepressants and work with a psychotherapist.
The prognosis for encephalopathy of toxic origin is very serious, regardless of what poison caused it, since the damage is irreversible. The risk of developing cerebral edema, coma, and persistent psychoorganic syndrome requires extremely early initiation of treatment and dynamic monitoring of the patient after stabilization.
Alcoholic encephalopathy
Alcohol or toxic encephalopathy is often otherwise referred to as Wernicke encephalopathy (WE). This is an acute condition that requires emergency medical care to prevent a sharp decline in intelligence and, often, death of the patient.
According to Wikipedia, “Wernicke encephalopathy and WKS are most often observed in people who abuse alcohol. Errors in diagnosing WE and therefore in treating the disease result in death in approximately 20% of cases, while 75% are left with permanent brain damage associated with WKS. Of those affected, 25% require long-term treatment to receive effective care.”
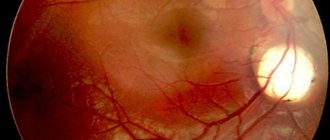
In 1881 Carl Wernicke identified a disease with symptoms that were characterized by an acute mental health disorder. It was accompanied by swelling of the optic nerves, hemorrhages in the retina, oculomotor disorders and coordination disorders in gait.
The most common causes of the disease are acute brain damage associated with the toxic effects of alcohol, drugs and other psychoactive substances. In addition, such disorders were observed in people working in hazardous industries and with eating disorders with an acute degree of exhaustion. It should be noted that recently this disease can often be observed in people who have undergone procedures such as plasmapheresis and hemadsorption without any particular need for it. It should be noted that this form of the disease often begins to develop against the background of xenon therapy. Unfortunately, this procedure is now often recommended for people with alcohol and drug addiction. This stimulates the development of very serious diseases and aggravates the patient’s condition.
Alcoholic encephalopathy can present with various symptoms, so a full diagnosis can only be made with a comprehensive examination.
The main symptom of alcoholic encephalopathy is a change in a person’s mental state.
Main signs of alcoholic encephalopathy
- change in mental state;
- dizziness, noise in the head;
- absent-mindedness, confusion, forgetfulness;
- depression, bad mood, grouchiness;
- hot temper;
- fast fatiguability;
- sleep disturbance;
- slow thinking, sleepy state;
- Difficulty pronunciation, speech problems.
If you have at least one of the listed signs, you should check your health and identify the existing disorder in time. It is necessary to establish whether encephalopathy develops after head injuries, whether there are vascular pathologies of the brain, coronary artery disease, whether there was heavy metal poisoning, etc. People with addiction to psychoactive substances, even those who previously suffered from alcoholism, need to be examined regularly. At the first visit, our competent and experienced doctor can identify all the main symptoms of encephalopathy and carry out a diagnosis.
Features of the manifestation of alcoholic encephalopathy
- The depression of consciousness is increasing. These consequences often lead to the death of the patient. And it was death that was often evidence of the disease.
- Focal vascular lesions of the gray matter of the brain are formed.
- Oculomotor disturbances occur, bilateral optic nerve paresis is formed, leading to horizontal double vision, convergent strabismus and nystagmus. Gaze paralysis.
- Behavior changes and becomes clearly inappropriate. Asks questions and answers inappropriately. Obscene, offensive jokes.
- Impairments in motor functions occur.
- An imbalance of the vestibular apparatus occurs, and a person loses stability when walking. In later stages of the disease, miosis (constriction of the pupil) and absence of pupillary reactions are formed. Retinal hemorrhage often occurs.
- Ataxia appears in a standing position and when walking. Even in the initial stage, it can be so pronounced that the patient is unable to stand and move without support. In the initial stages, this may be manifested by a peculiarity of gait, when a person, when walking, steps on his foot starting from heel to toe.
- With significantly pronounced impairments of a person’s movement in space (locomotor functions), cerebellar tremor in the arms and legs is quite rare.
- In some cases, the so-called “Chanted Speech” may appear.
Toxic encephalopathy of the brain: what kind of disease, main causes
The toxicogenic effect of most neurotropic poisons is based on their negative impact directly on neuronal membranes and the mechanisms of nerve impulse transmission. Violations of energy and plastic metabolism play an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease. In addition, some toxins inhibit the hematopoietic and circulatory systems, breathing, which also causes toxic hypoxic encephalopathy. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, cells localized in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum and hippocampus are especially sensitive to the influence of pathological factors, which causes the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Major neurotoxins
The main causes of toxic encephalopathy include:
alcohol and volatile solvents: destroy cell membranes, receptors, cause changes (irreversible with long-term exposure) in energy metabolism;- psychoactive substances (opiates, cannabinoids, amphetamines, cocaine, ephedrine, hallucinogens, some drugs, etc.): pathologically affect the reuptake system and the production of norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin
- heavy metals (mercury, lead, manganese, arsenic, thallium, etc.): have a direct destructive effect on the structures of the central nervous system and also affect the functioning of the peripheral nervous system.
Accordingly, the risk of toxic brain encephalopathy is especially high among people working in hazardous industries. These are, for example, chemical, construction, metallurgy, and agriculture, where insecticides and pesticides are used. The disease is often diagnosed in alcoholism and drug addiction. The pathology is less common among artists; those who use neurotoxic paint solvents are at risk.
Development of alcoholic encephalopathy
Against the background of alcohol withdrawal (hangover), especially at the time of alcoholic psychosis (delirium), alcoholic encephalopathy develops especially rapidly. Changes in a person can be observed within a few hours. Therefore, we often encounter a situation where people around us are surprised to observe a sharp change in the behavior and condition of the patient.
Alcoholic encephalopathy Wernicke-Korsokov can develop simultaneously in a severe and acute form. However, most often ophthalmoplegia and ataxia precede the onset of the disease several days, sometimes 10 or 20 days, before the onset of the main symptoms.
Alcoholic encephalopathy Wernicke-Korsokov is very often accompanied by other diseases. Most often this is due to the toxic effects of alcohol not only on the brain, but on the entire body as a whole. For example, in one variation or another, patients suffer from polyneuropathy, impaired liver function, heart disease, genital diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, endocrine and other disorders. The clinical picture may be supplemented by the manifestation of spastic spinal ataxia.
Consequences of alcoholic encephalopathy
In the chronic stage of the disease, a person ceases to recognize odors. This is due to toxic damage to the diencephalic region of the brain.
Cardiovascular changes occur, tachycardia, shortness of breath on exertion, and postural hypotension appear. However, only minor changes may occur on the ECG. Quite often such people die suddenly. The cause of their death is often determined to be cardiovascular collapse. However, having become more fully acquainted with its history, such a judgment will be fundamentally incorrect. The true cause of such deaths is the sudden development of alcoholic encephalopathy, a disorder of brain tissue. The tissue of the area of the brain that is responsible for regulating cardiovascular functions is damaged.
It has been proven that with Wernicke-Korsokov alcoholic encephalopathy, a fairly high cardiac output occurs, which does not correspond to the volume of oxygen consumed. Fainting and motor impairment may occur. This is a consequence of an imbalance in the functions of the peripheral nervous system, which are usually more specific to a defect in sensory regulation.
Can encephalopathy be prevented?
Yes, alcoholic encephalopathy is preventable. First of all, it is necessary to avoid excessive alcohol consumption or eliminate it altogether. In this case, we recommend undergoing special anti-alcohol therapy. You should also exclude from use the main toxic substances that cause the formation of toxic encephalopathy.
Toxic substances causing toxic encephalopathy include:
- Drugs,
- IQOS,
- Various types of hallucinogens,
- Other psychoactive substances.
A healthy lifestyle will significantly reduce risk factors for brain diseases.
Prognosis for the treatment of alcoholic and toxic encephalopathy
The prognosis depends on the cause and extent of the disease. Most cases are reversible and can be cured. However, one should take into account the fact that any encephalopathy can be fatal. Therefore, treatment of alcoholic and toxic encephalopathy is mandatory.
The therapeutic effect in our clinic is achieved by introducing the latest technologies of restorative medicine. Treatment of brain diseases will improve your condition and improve your quality of life.
Symptoms of toxic encephalopathy
Symptoms of the disease depend on the substance causing the poisoning.
- Alcohol.
With excessive consumption, brain cells are destroyed, nerve connections are destroyed, fatigue appears when performing a standard set of functions, weakness appears, consciousness, memory, speech are impaired, and the temperature rises. - Manganese.
There is drowsiness, lethargy, muscle tone decreases, and dull pain appears in the limbs. There are disturbances in intellectual activity, the emotional background is unstable, with severe poisoning, widening of the palpebral fissures is observed, unnatural crying or laughing for no reason with trembling lips and tongue is possible. - Mercury.
With mercury poisoning, the heartbeat quickens, heaviness in the stomach appears, tachycardia, arms and legs specifically tremble, a blue border appears on the gums, and increased sweating is noted. - Lead.
The appearance of a purple border on the gums, the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth, salivation, vomiting, severe pain in the abdominal area, malaise, general weakness, headache, memory impairment. - Petrol.
Complaints of abdominal pain, tachycardia, shortness of breath, fever, the person is sweating, and muscle weakness is observed. - Arsenic.
Arsenic acts rapidly, affecting all body systems. Symptoms appear after 20 minutes: headache, nausea, vomiting, general weakness, abdominal pain, loose stools, dehydration, thirst, garlicky breath. - Medications.
Possible vomiting, blurred vision, breathing, speech, headache, mental changes.
Outcome of the disease
The outcome of the disease can be expected to be different. Complete or almost complete recovery with conventional therapy can be expected in less than 20% of patients. In other patients, complete recovery cannot be achieved. Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy with our methods results in complete recovery in 50% of cases, incomplete recovery in about 30%. We observe a weak result in only 20% of patients, in very severe and advanced cases, which usually occur after undergoing hemadsorption and plasmapheresis procedures.
Depending on the outcome, many of our patients return to everyday life. But, in more severe conditions, in most cases we ensure that the patient can live outside a medical institution, at home, and continue treatment under supervision. Very rarely, due to the fact that the condition is sometimes characterized by significant memory loss, the patient, after discharge, must be placed in a specialized rehabilitation center. Since the patient lacks the ability to sequentially distribute events over time.
In the final stage of the disease, the manifestation of oculomotor disorders and ataxia often decreases significantly, sometimes it is difficult to recognize them at all. However, an increase in degradation or dementia associated with the use of alcoholic beverages can be noted.