24.11.2016
Pinchuk Elena Anatolyevna
Deputy chief physician for medical work, kmn, neurologist, doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine
Lipovka Nadezhda Sergeevna
Head of the Department of Medical Rehabilitation, Physician of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Neurologist
Sobolev Arkady Igorevich
Doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine, neurologist
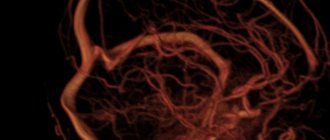
Normally, a person has elastic and strong blood vessels. However, high blood pressure and a number of other threatening factors make blood vessels fragile, as a result of which they are easily damaged. Such damage leads to a serious brain disease - stroke. Lesions may appear in different parts of the brain. One of the most dangerous places of occurrence is the brain stem. Hence the name of the disease – brainstem ischemic stroke.
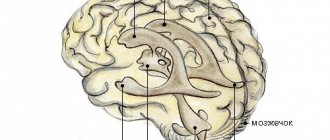
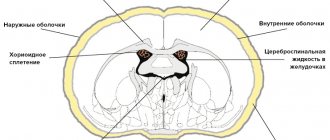
The brain stem is an important link between the brain and the spinal cord. It is through it that all impulses and commands enter the human body. A brainstem stroke is dangerous because hemorrhage in this area completely blocks the normal functioning of other parts of the brain: the cerebellum, the middle and medulla pons, the pons, and the entire thalamic region. A lesion in this area not only disables facial muscles, eye movement, but also important centers that are responsible for blood circulation, breathing, and thermoregulation. An atrophied brainstem disrupts the functioning of all human internal organs.
Causes of brainstem stroke
Brainstem stroke occurs for the same reasons as other stroke subtypes:
- Poor nutrition;
- Constant and prolonged stress;
- Increased blood cholesterol levels;
- Overweight;
- Abuse of hormonal drugs;
- Alcohol and smoking;
- Bleeding disorders;
Often, a stroke can occur against the background of existing diseases, such as hypertension, rheumatism, vascular atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus.
The danger of a brainstem stroke is that it develops very quickly and suddenly. Although it is accompanied by almost the same symptoms as ischemic stroke:
- Speech and articulation disorder;
- Dizziness, pale skin;
- Sweating;
- Fluctuations in body temperature;
- Rapid pulse, tachycardia;
- High blood pressure;
- Impaired functioning of the facial muscles, which leads to asymmetry and strabismus;
- Violation of movements, breathing, speech.
In some cases, paralysis may occur, affecting all parts of the body. However, a person does not lose his thinking abilities. Already in the process of treatment and recovery after a stroke, he is able to understand and evaluate what is happening.
If at least one of the above symptoms appears, you should call a doctor. The sooner a diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the victim’s chance of recovery. A brainstem stroke is diagnosed using MSCT and MRI, and a neurologist also checks the state of the cardiovascular system and respiratory function.
Causes and types of brainstem strokes
The causes of brainstem stroke do not differ from those in other localizations of blood flow disorders in the central nervous system:
- Arterial hypertension, which causes irreversible changes in the arteries and arterioles of the brain, the walls of blood vessels become brittle and sooner or later they may rupture with hemorrhage;
- Atherosclerosis, observed in the vast majority of older people, leads to the appearance of fatty plaques in the arteries supplying the brain, the result is plaque rupture, thrombosis, vessel blockage and necrosis of the medulla;
- Aneurysms and vascular malformations cause strokes in young patients without concomitant pathology or in combination with it.
To a large extent, the development of trunk stroke is promoted by diabetes and other metabolic disorders, rheumatism, heart valve defects, blood clotting disorders, including when taking blood-thinning drugs, usually prescribed to cardiac patients.
Depending on the type of damage, brain stem stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic. In the first case, a focus of necrosis (infarction) is formed, in the second, blood spills into the brain tissue when a blood vessel ruptures. An ischemic stroke has a more favorable course, but with a hemorrhagic stroke, edema and intracranial hypertension quickly increase, so mortality is much higher in the case of hematomas.
Video: basic about types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic
Treatment of brainstem stroke
The main therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the lesion - a blood clot or hemorrhage. Hematomas are removed surgically. If blood clots form, therapy is used to dissolve and prevent their formation. Drugs that thin the blood, regulate cholesterol levels, and control heart rate are administered. If respiratory function is lost, a special tube is inserted into the person's trachea to provide oxygen.
In most cases, a brainstem stroke leads to death, since most of the vital functions of the human body stop working. In order to avoid such a serious disease as a brainstem stroke, it is important to be regularly examined by doctors if you have other diseases of the cardiovascular system. It is also necessary to give up bad habits, lead a healthy lifestyle, and eliminate stressful situations from your life as much as possible.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 3/5 — 16 votes
Share article on social networks
Treatment of ischemic cerebral stroke in elderly people
Relatives of an elderly person who has suffered a cerebral infarction must understand that in a hospital setting, doctors will monitor the patient’s condition and will be able to provide him with the necessary therapeutic assistance in a timely manner. Patients in a state of deep coma with impairment of all vital functions will not be taken to a medical institution. Hospitalization will not help those who have repeated cerebrovascular accidents complicated by dementia and other mental disorders, as well as patients with incurable somatic diseases.
We recommend
“Care for bedridden patients after a stroke: how to achieve a quick recovery?”
More details Treatment of ischemic stroke follows certain rules:
- It is necessary to influence the activity of the cardiovascular system - with a pronounced decrease in myocardial contractility, cardiac glycosides are used, antihypertensive drugs, calcium antagonists (Nifedipine), beta blockers (Obzidan) and diuretics (Lasix), respiratory analeptics are administered (“Cordiamin”, “Sulphocamphocaine”).
- Correction of homeostasis is carried out by introducing electrolyte solutions (5% glucose solution, 0.9% sodium chloride solution, Ringer's solution, 4% sodium bicarbonate solution, polarizing mixture), low molecular weight dextrans (Reopoliglucin up to 400 ml), correction of hypokalemia, hypochloremia .
- To combat cerebral edema, 10 ml of 2.4% Euphyllin, 1 ml of Lasix, and, if necessary, Mannitol and urea are injected intravenously; antihistamines (Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen), novocaine; Hydrocortisone, dexamethasone, prednisolone, glycerin can be used orally.
This is how vegetative disorders are eliminated:
- at high temperatures, “lytic” mixtures are prescribed, including diphenhydramine, novocaine, analgin;
- neurovegetative blockade is carried out using droperidol, diphenhydramine, aminazine;
- It is advisable to rub the patient’s body with alcohol until red, which increases heat transfer;
- To reduce the temperature of large vessels, local cooling of the carotid arteries, axillary and groin areas is carried out, and wrapping with damp sheets is carried out.
In case of hemorrhagic stroke, blood clotting is increased and the permeability of the vascular wall is reduced using calcium preparations (10 ml of a 10% solution of calcium chloride intravenously or calcium gluconate intramuscularly), “Vikasol” (2 ml of 1%), 5–10 ml of a 3% solution of ascorbic acid, gelatin 10% – 20–50 ml intravenously, rutin, rutamin, e-aminocaproic acid (5% – up to 100 ml), “Ditsinon” (2 ml–250 mg) intravenously or intramuscularly; surgical treatment is possible - puncture stereotactic removal of the lateral hematoma after CT, various methods of surgical treatment of cerebral aneurysms.
Note that in case of ischemic stroke the following is done:
- increase blood flow to the brain by dilating regional cerebral vessels and reducing vasospasm, improving collateral circulation, using vasodilators (10 ml of 2.4% Eufillin solution intravenously), nicotinic acid (1% solution 1-2 ml intravenously), Stugeron ", "Trental" and others;
- improve venous outflow by administering cocarboxylase (50 mg) and Dietifen (10 mg);
- normalize blood coagulation and rheological properties with the help of heparin (5000–10000 units intravenously or intramuscularly for 3 days), “Phenilin” and other indirect anticoagulants (up to 2–3 months), acetylsalicylic acid, “Complamin”, “Prodectin”, "Trental" and others.
Increasing the resistance of brain tissue to low oxygen levels and improving brain metabolism is carried out through the use of tissue metabolism inhibitors (neuroleptics, regional hypothermia) ATP, vitamins and amino acids (cocarboxylase, glutamic acid, glycine, B vitamins, vitamin E), nootropics (Aminalon ", "Piracetam"), "Cerebrolysin", "Actovegin", hyperbaric oxygenation.
An elderly patient with ischemic stroke should be under constant monitoring, so it is necessary:
- every 1–2 hours, monitor indicators of circulatory restoration, check how the patient is breathing, taking into account the nature and frequency of respiratory movements;
- monitor the condition and appearance of the skin and determine the water balance daily;
- it is very important to adhere to bed rest with all the necessary procedures for caring for a bedridden patient;
- a sedentary state can provoke the appearance of pneumonia, constipation, urosepsis, thromboembolic complications, so special attention should be paid to the prevention of such conditions;
- prevent the development of contractures;
- establish a way of communicating with an elderly patient if speech disorders, tongue-tiedness appear, and perform speech therapy exercises;
- if swallowing is impaired, provide parenteral feeding and tube feeding;
- if there is a high temperature, care for the elderly patient as in the second period of fever.
Programs:
Assessment of rehabilitation potential
Movement restoration
Rehabilitation after stroke
Restoration of cognitive functions
Early (resuscitation) rehabilitation
Brain stem tumors
According to the previously existing opinion, any tumor of the brain stem was considered an infiltrative formation, diffusely growing into brain stem structures and, as a result, not subject to surgical removal. It has now become clear that in addition to diffusely spreading tumors (which, unfortunately, are the majority), there are limited nodular tumors in the trunk, the removal of which is quite possible. In such cases, to decide on the advisability of surgical treatment, the patient needs to consult a neurosurgeon. The dominant principle of trunk tumor removal is maximum resection of its tissue with minimal trauma to brain structures. In this regard, great hopes are placed on the development of microneurosurgical surgical techniques.
Unfortunately, about 80% of trunk tumors are inoperable. In relation to them, as well as as pre- and postoperative therapy, chemotherapy and radiation can be used. Chemotherapy is carried out using a combination of various cytostatic drugs. Radiation therapy achieves symptomatic improvement in 75% of patients. However, already in the early stages after treatment, many of them die. The technique of radiotherapy with an increase in the total dose of radiation has made it possible to slightly increase the life expectancy of children with stem tumors. In 30% of children, life expectancy after radiotherapy was 2 years.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is an innovative method for treating stem tumors today. It is possible to carry out 2 types of procedures: gamma knife and cyber knife. In the first case, a helmet is put on the patient’s head, irradiation is carried out from multiple sources so that their rays converge at one point corresponding to the location of the tumor. The effect is achieved due to the total impact of radiation sources, while the irradiation of healthy brain tissue is minimal, since each beam carries a small gamma energy. The procedure for targeting a tumor using a cyber knife is more automated. The robotic device itself directs the radiation to the area where the tumor is located, taking into account its movements due to the breathing or movements of the patient. However, so far these methods are effective mainly against benign tumors up to 3-3.5 cm in size.
Forecast
Benign tumors of the brain stem, due to their slow growth, can exist for up to 10-15 years, often having a subclinical course. But, unfortunately, most tumors in this area are malignant and cause death within several years or months from the onset of symptoms. Treatment in such cases only briefly prolongs the life of patients.
Signs of ischemic stroke of the brain stem
Main symptoms of brainstem ischemic stroke
- coordination of movements is impaired;
- dizziness (a feeling of movement or spinning);
- 30% of patients experience speech impairment, it becomes slurred and quiet;
- 65% of patients have problems swallowing;
- spontaneous uncontrolled movements of the legs and arms, mobility of the limbs is significantly reduced;
- breathing slows down, often patients cannot breathe on their own;
- blood pressure increases;
- the pulse becomes too rare or frequent,
- thermoregulation is disrupted - body temperature either sharply decreases or increases;
- control over spontaneous eye movements is lost, which leads to the development of strabismus and loss of the ability to focus on an object.
At the onset of brainstem ischemic stroke, its first manifestations may be impaired coordination of movements and unsteadiness when walking. Patients can move around and complain that they are suddenly forced to walk while holding onto the wall. After suffering a brainstem ischemic stroke, they still have consequences in the form of impaired swallowing - patients can only swallow soft food.