You can familiarize yourself with other diseases starting with the letter “V”: Vegetative state, Ventricular, Vestibular ataxia, Vestibular neuronitis, Vibration disease, Viral meningitis, Viral encephalitis, Temporal lobe epilepsy, Intracerebral hematoma, Intracranial tumors of the cerebral hemispheres, Intracranial hypertension, Inflammatory myopathy, Inflammatory polyneuropathy, Congenital myopathy, Congenital paramyotonia, Secondary parkinsonism
Why is a vegetative state dangerous?
In vegetative states, the functions of the hypothalamus and brain stem are preserved, but the cerebral hemispheres suffer from severe dysfunction. This leads to impaired consciousness and the absence of the possibility of spontaneous mental activity. There are no signs of awareness, but the presence of unconditioned reflexes is noted. Vegetative states are characterized by periods of wakefulness accompanied by the opening and closing of the eyes. The disorder can be diagnosed clinically, but additional hardware diagnostic methods are prescribed, such as:
MRI;- Brain evoked potential study;
- Checking internal hemodynamics;
- EEG;
- PAT
As therapy, activities are carried out to stimulate the functioning of the hemispheres. In addition, the organization of high-quality patient care is required; nutrition, feeding, prevention of bedsores and possible complications.
The problem of persistent vegetative state in intensive care
M.A. Piradov
Research Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
The intensive development of resuscitation science is steadily leading to the emergence of an increasing number of people who survive, but are unable to care for themselves, as well as people who cannot be recognized as competent. According to global consolidated statistics, 6% of patients undergoing heart surgery using artificial blood circulation machines develop a so-called persistent vegetative state (apallic syndrome) in the postoperative period. In our country, for various reasons, this figure exceeds 10%. It should be noted that persistent vegetative state (PVS) can have a very different genesis - from traumatic brain injury and the mentioned postoperative complications, to cerebrovascular accidents and severe neurodegenerative diseases. PVS is the scourge of all prestigious clinics. In the most high-quality of them, patients with this pathology occupy up to 25-30% of the total bed capacity of intensive care units. Modern possibilities for correcting body functions, used in such departments, make it possible to maintain the existence of these patients for many years, but, alas, cannot return them to society. As a result, hospitals spend a lot of money on organizing care for patients in a vegetative state, and medical personnel are subject to a huge psychological and emotional burden, since many doctors and nurses understand the certain futility of their efforts. It is unnecessary to mention the moral state of relatives, who often tell doctors about “a living dead person in the house.”
In our country, as in many other countries, doctors have the legal right to stop resuscitation and other supportive measures only in exceptional cases, in particular when a diagnosis of brain death is made. Doing this in a persistent vegetative state is unacceptable.
Is it possible to predict the development of PVS at the beginning of resuscitation measures? In the vast majority of cases it is not possible. Moreover, when starting to save a person, the doctor has no right to act half-heartedly. Having done this once, he will involuntarily release the internal mechanism of self-control, which among resuscitators, like no other category of doctors, should be especially developed, and subsequently begin a priori to decide the fate of people, taking on the functions of a god, and not a doctor. Where is the way out of this situation? As paradoxical as it may sound, in the further development of resuscitation and medicine in general, primarily transplantology and implantology. Work has already begun around the world on transplanting specially treated groups of cells obtained from malignant tumors into certain areas of the brain. The first small successes have been achieved, confirmed using positron emission tomography. Next up are clinical studies related to stem cells, advances in genomics and other rapidly developing biological sciences. There are certain reasons to believe that in the near future the solution to the PVS problem will move forward.
The article was published on the website https://www.medolina.ru
General information about pathology
To vegetate means to live with the preservation of all biological functions, except intellectual and social. The term was introduced in 1972. In vegetative states, a personality disorder occurs, which results in disintegration of subcortical structures and the cerebral cortex. Special standardized scales have been developed that allow the degree of disorder to be determined using characteristic clinical signs. This is done by specialists such as resuscitators, rehabilitation specialists and neurologists. Accurate instruments to assess consciousness have not yet been developed. It has not even been established to what extent the impossibility of reacting to external stimuli reflects their perception or non-perception at the level of consciousness. It is not known whether a vegetative is able to understand the speech of others, their touch, and whether any internal processes occur in his consciousness.
Vegetative state: description
The term was introduced in 1972. The severity of the pathology is assessed using a special scale, but there are no exact methods that could determine the prognosis for the patient. In some cases, partial resumption of nerve conduction is possible, after which the functions of the cerebral cortex are gradually restored. However, if the tissue is damaged by trauma, the prognosis is poor.
A sign by which a diagnosis can be made is a lack of response to environmental signals. However, this condition does not give reason to believe that the patient does not perceive these stimuli. It is possible to predict the future for a patient only on the basis of data from additional examinations, as well as after monitoring the dynamics. If such a condition lasts more than 1 month, it is considered stable, which, however, does not give reason to exclude the possibility of a favorable outcome.
Causes
Cerebral dysfunction begins due to factors damaging the brain, which are the causes of the syndrome. Etiological factors are classified according to their mechanism of action:
Metabolic, causing acute intoxication and hypoxia. These may include the use of drugs, an overdose of which causes toxic damage to brain cells. In addition, such damage to cerebral structures can provoke acute dysmetabolic conditions, which include hepatic coma, uremia, hypo- and hyperglycemia caused by diabetes, as well as poisoning with neurotropic poisons;- Severe TBI, diffuse axonal damage, and brain contusions are considered mechanical factors. In fifty percent of cases, they cause a coma that turns into a vegetative state;
- Intracranial hemorrhages, brain tumors, meningitis, encephalitis and other infectious lesions are organic causes caused by changes in cerebral tissue.
Autonomic dysfunction in a child
Poor health in a child may be associated with a violation of autonomic regulation, but parents often look for hidden health problems. What should you do if your child regularly complains of headaches and fatigue? First of all, see a doctor and get examined.
Symptoms of VSD in children and their origin
Autonomic dysfunction or vegetative-vascular dystonia in a child usually manifests itself in many, often unrelated, symptoms. The nervous system and any of the organ systems are affected - for example, cardiovascular, endocrine, digestive. The appearance of symptoms is related to each other in time, but the pathogenetic connection may escape attention.
Possible symptoms of VSD in a child:
- Headaches caused by weather changes, headache after overwork at school, morning headache after waking up, migraine.
- Digestive disorders, without a morphological picture of the disease, functional disorders of the digestive glands.
- Dizziness and fainting, orthostatic collapse.
- Palpitations, shortness of breath during physical or psychological stress.
- Neurodermatitis, diathesis, excessive dry skin or sweating.
- Low-grade fever that persists for a long time for no apparent reason.
- Sudden rises in temperature during the day and normal temperatures at night.
Symptoms of autonomic dysfunction can be confusing even to doctors. Therefore, with the simultaneous appearance of several unrelated symptoms, with an unclear clinical picture, it is necessary to examine the state of autonomic regulation.
What diseases need to be differentiated from VSD:
- Heart diseases – myocarditis, arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy;
- inflammatory diseases of the lungs and bronchi, allergic bronchitis;
- acute and chronic infectious processes;
- gastritis, duodenitis, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, colitis;
- skin infections;
- neuropathy, neuralgia;
- head injury, circulatory disorders in the brain.
The presence of autonomic dysfunction does not exclude the presence of another disease, and often contributes to the intensification of its symptoms.
The psychological state of VSD also suffers. Children may suffer from night terrors, stuttering and speech problems, be overly excitable or inhibited, anxious or aggressive. Any weak link in the psyche with dystonia becomes even more vulnerable. Working with a psychologist helps the child adapt better, which subsequently improves his general condition.
Take care of your child and do not hesitate to consult a doctor. Paying attention to your health in childhood will make your future adult life easier!
Mechanism of development of the vegetative state
Under the influence of damaging factors, connections between the subcortical centers and the reticular formation are broken, which causes coma. When lost connections are restored, the functioning of the remaining synapses is strengthened, new interneuronal contacts are formed and neurotransmitters are reactivated, the coma is exited, which is characterized by an “awakening reaction,” that is, the patient opens his eyes. After this, a gradual restoration of consciousness begins. If recovery remains in the awakening phase, VS occurs. Experts suggest that it occurs during pathological processes of reintegration.
Characteristic signs of a vegetative state are extensive damage to the subcortical substance and diffuse necrotic changes in the thalamus and cortex. Atrophy of demyelination of subcortical structures also occurs, but much less frequently. According to some experts, the leading role in the mechanism of development of VS belongs to the activation of the process of removal of defective cells by the body.
Causes of a vegetative state
The syndrome is based on cerebral dysfunction resulting from exposure to various brain-damaging factors. Based on the nature of their action, the following types of etiofactors are distinguished:
- Mechanical
. Severe traumatic brain injuries: brain contusion, diffuse axonal damage. They cause coma with transition to a vegetative state in 50% of cases. - Metabolic
: hypoxia and acute intoxication. Hypoxic brain damage develops as a result of extensive ischemic stroke, cardiac arrest, asphyxia, significant arterial hypotension, and carbon monoxide poisoning. Toxic damage to cerebral structures is observed with an overdose of narcotic drugs, exposure to neurotropic poisons, acute dysmetabolic conditions (uremia, hepatic coma, hyper- or hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus). - Organic
. Caused by structural changes in cerebral tissue. Includes brain tumors, intracranial hemorrhages, infectious lesions (encephalitis, meningitis).
Symptomatic picture
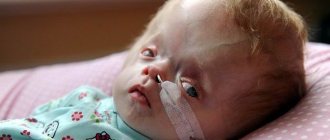
In a vegetative state the following is observed:
Preservation of vital functions: breathing, cardiovascular activity, digestion, chewing and swallowing reflex of tear production;- The ability to involuntarily move the eyes, blink, exhibit unfocused motor activity, grind teeth, grasp objects located near the hand, and respond to pain impulses is preserved;
- There are no signs of awareness of what is happening, no contact with the outside world;
- There are periods of wakefulness when a person lies with his eyes open. He is able to move his eyeballs slowly, but this is not a conscious gaze. When there are flashes of light and loud sounds, the patient reacts;
- In the absence of speech, the ability to produce isolated guttural sounds and deep sighs is retained, which can give untrained people the erroneous impression that they are emerging from a vegetative state. But that's not true. The first signs of exiting the VS are gaze tracking, gaze fixation, a state of small consciousness in which the patient can fulfill simple requests: clench his fingers, show his tongue.
The duration of a vegetative state can range from several months to 10 years. Persistent VS is diagnosed when symptoms persist for more than a month. Permanent is characterized by the persistence of symptoms for more than a year in a post-traumatic vegetative state and more than three months in a non-traumatic genesis.
Symptoms of a vegetative state
VS is characterized by the preservation of all vital functions: adequate cardiovascular activity, breathing, digestion. There is no contact with the environment and no signs of awareness of what is happening around. Conscious reactions to stimuli and purposeful motor acts are lost. The patient can make movements within the framework of unconditioned reflexes: exhibit non-targeted motor activity in response to a pain impulse, grasp an object touching the hand. Chewing and swallowing reflexes are preserved. The patient makes chewing movements, swallows food placed in the mouth, yawns, and grinds his teeth. Able to blink and move eyes involuntarily. Tear production is preserved.
A vegetative state is characterized by periods of wakefulness when the patient opens his eyes. Eye opening is observed with flashes of light and loud sounds. There is no speech, vocalization is observed - the ability to produce individual sounds. The painful effect sometimes causes groaning or sighing. Slow spontaneous movements of the eyeballs should be distinguished from conscious gaze tracking. Along with guttural sounds and sighs, they give the relatives of the vegetative a false impression of restoration of awareness.
The duration of the sun varies from several months to ten years. There are 2 stages. If symptoms persist for more than 1 month. talk about persistent VS. Duration of symptoms >3 months. with non-traumatic origin and >12 months. in case of traumatic it refers to permanent VS. Patients exit the vegetative state through a state of small consciousness. The first signs: fixation of gaze, following with gaze, fulfillment of simple requests (show tongue, clench fingers).
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist based on characteristic signs: lack of awareness, preservation of unconditioned reflexes, sleep-wake phases. To assess the metabolism of bioelectrical activity of the central nervous system and cerebral hemodynamics, hardware diagnostic methods are required:
The study of evoked potentials can demonstrate anatomical interruption of cerebral tracts. It is worth considering that the resulting picture will be heterogeneous;- Electroencephalography is capable of recording paroxysmal bursts, delta and theta rhythms, and occasionally an alpha rhythm close to normal may appear;
- Ultrasound scanning of intracranial vessels helps to clarify the state of vascular blood flow. With VS, there is difficulty in perfusion and impaired venous outflow;
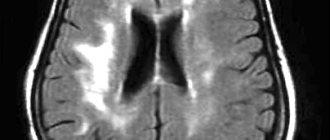
- Magnetic resonance imaging shows nonspecific changes in soft tissues: an increase in the volume of the ventricles and subarachnoid space, signs of atrophy. With a high degree of probability, the degree of atrophy makes it possible to make an expected prognosis about exit from the VS;
- PET allows you to detect the degree of decrease in metabolic processes in the cortex. In persistent vegetative states it decreases by 50%, and in permanent ones by 30-40 percent. During activation of the multifunctional area of the associative cortex, the exit from the VS begins.
To differentiate VS from coma, it is necessary to check the integrity of unconditioned reflexes, the change in sleep-wake phases and the presence of eye opening under light and sound influences. In coma, these signs are absent.
Therapy
Recent research has refuted the assertion that adult nerve cells are not capable of self-healing. To achieve this, the body has a mechanism for transforming stem cells and cerebral progenitor cells into neurons. The processes of surviving nerve cells grow and reserve areas of the brain are used. Treatment of vegetative-vascular conditions includes activation of the listed compensatory processes. It must be accompanied by the prevention of complications and quality care. Therapy includes:
Artificial nutrition that can fully provide the body with the necessary amount of microelements, vitamins, calories and proteins. Since tube feeding causes complications in the form of mucosal ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux, and aspiration, preference should be given to nutrition using a gastrostomy tube;- Pharmacological therapy and regular sensory stimulation designed to stimulate the restoration of consciousness. For this purpose, auditory, visual, painful, tactile, and olfactory stimuli are used with a gradual increase in intensity and time of exposure. This allows you to eliminate sensory hunger that prevents you from leaving the sun. In addition, recently a positive effect has been recorded from taking amphetamines. The search for a successful method of activating cerebral reintegration continues; in Japan and France, targeted electrical stimulation of the brain stem is now being tested;
- High-quality care, including maintaining adequate skin moisture, posture control, teeth brushing, and regular linen changes.
In addition, it is very important to carry out prevention and treatment of complications, which includes:
- Correct installation of catheters;
- Timely change of diapers;
- Massage;
- Changing the patient's posture;
- Planting with the help of orthopedic systems, designed to prevent secondary infections;
- Correction of muscle tone with medications;
- Passive movements to combat contractures;
- Treatment of contractures using tenotomy.
With permanent VS, it is necessary first of all to prevent complications. In case of persistence, brain stimulation is indicated.
Prognosis for vegetative states
It is possible to make any predictions only based on the cause of occurrence, the duration of the coma and the period of VS, the age and general condition of the patient. If the condition was caused by non-traumatic etiological factors, then recovery will take about 3 months, and at least a year if the factors that caused the vegetative state were traumatic. Cases of improvement were noted at a later date. In younger patients, motor activity returns more quickly. In most of the reported cases, restoration of brain function to the previous level does not occur. The consequence of VS is severe disability. If a vegetative is in this state for more than six months, then with good care and medical supervision, the survival rate is ¼ of all cases.