Description of the disease
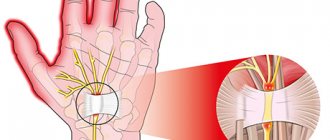
Vessels, nerves, synovial membranes, and tendons pass through the carpal (carpal) canal. The median nerve is also located here - the main nerve of the arm, running from the brachial plexus to the fingertips. Responsible for coordination of movement, fine motor skills of the hands, contraction and expansion of blood vessels from the action of external stimuli, regulates the functioning of the sweat glands. The width of the canal is limited on three sides by bones and the transverse ligament.
The carpal tunnel itself is quite narrow, which contributes to the formation of various pathologies. Any additional narrowing entails compression of the processes of nerve fibers and blood vessels, and blood supply is disrupted. Pathological processes proceed slowly, begin with a loss of physiological sensitivity, and lead to motor and trophic disorders. The picture of the disease has clear symptoms with a characteristic clinical picture, which makes it easy to make a diagnosis even at the initial stage.
Pathophysiology
There is a wide range of causative pathologies converging on two disease mechanisms, both of which lead to compression.
Reduced carpal tunnel size is caused by conditions such as:
- overuse injury (considered the most common association) or simply injury;
- osteoarthritis;
- acromegaly.
You can read about wrist sprains here.
Pathological conditions leading to an increase in the contents of the carpal tunnel:
- masses, eg ganglion cysts, primary nerve sheath tumors.
- deposition of foreign material, such as amyloid;
- hypertrophy of the synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis.
In general, the pathophysiology of CTS results from a combination of compression and traction mechanisms.
- The compression element of the pathophysiology includes a pathological cycle of increased pressure, difficulty in general venous outflow, increased local edema and disruption of the intraneural microcirculation of the median nerve. Nerve dysfunction increases, and disruption of the structural integrity of the nerve itself further propagates the dysfunctional environment—the myelin sheath and axon accumulate damage, and the surrounding connective tissue becomes inflamed and loses its normal physiological protective and supportive function.
- Repetitive traction and movement of the wrist aggravates the negative effects of surrounding structures, further damaging the nerve. Additionally, any of the nine flexor tendons that pass through the carpal tunnel can become inflamed and put pressure on the median nerve.
Idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome
- Idiopathic cases are more common in women (65-80%) aged 40 to 60 years; in 50-60% of cases the lesion is bilateral.
- The risk of bilateral involvement increases with the duration of symptoms.
- Idiopathic CTS correlates with hypertrophy of the flexor tendon synovium caused by connective tissue degeneration, as well as vascular sclerosis, edema, and collagen fragmentation. Histologic changes were thought to be suggestive of dynamic factors such as repetitive motion.
Symptoms of the disease
- 1. Reduced sensitivity of the hand.
First, patients begin to notice numbness in their fingers immediately after waking up. Over time, the periods of paresthesia increase, and feelings of burning, pain, cold or heat are added. Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by a simultaneous, radically opposite change in sensitivity. In one area it increases, but the other part of the palm does not feel anything.
- 2. Burning pain in the palms with shooting in the fingers.
Initially, the pain is felt in the area where the nerve is pinched, then it gradually begins to affect the entire arm: from the shoulder to the fingertips. This is accompanied by swelling of the wrist. As a rule, the dominant hand hurts: the right hand in a right-handed person, the left in a left-handed person, but bilateral symptoms also occur.
- 3. Muscle weakness and impaired motor activity.
As a result of prolonged pinching and inflammation of the nerve fibers, the hand loses muscle strength, and movement restrictions appear. It becomes difficult to operate small objects, such as buttoning buttons. The function of grasping and then holding objects weakens. Gradually, a decrease in the performance of the hand leads to muscle atrophy and deformation of the hand.
- 4. Lesions of the autonomic nervous system.
This is expressed in a pale and sometimes bluish color of the hand, dry skin, brittle nails, and cold hands.
Naturally, carpal tunnel syndrome affects the general physical and mental condition of the patient. He loses his ability to work, his quality of life decreases. Regular pain and a constant feeling of discomfort intensify at night, which interferes with normal sleep and causes insomnia.
A characteristic feature of this disease is that the patient can relieve discomfort on his own, without resorting to medications. To do this, just lower your hands down, move your fingers, shake your hands, stretch them, do massage, gymnastics. These manipulations help restore blood supply, but, unfortunately, not for long, since they do not get rid of the causes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, regardless of its location, include predominantly sensory disturbances ( pain , numbness , paresthesia ), motor disturbances (muscle fatigue/decreased muscle strength), and less commonly, trophic disturbances, which together form the individual picture of the disease. As a rule, tunnel syndromes debut with severe pain, including nociceptive/neuropathic components. The neuropathic component is caused by nerve damage, and nociceptive pain is caused by the inflammatory process and changes in the area of nerve channel conflict. Tunnel neuropathies are characterized by neuropathic manifestations in the form of allodynia (pain with non-painful stimulation), burning, sensation of electric shock (the so-called “electric shock”).
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include a combination of motor/sensory and autonomic disturbances at the level of the hand in the area of the median nerve. As a rule, sensory disturbances initially develop, manifested by numbness and paresthesia of the hand in the area of 1-3 fingers, which intensify with stress (drawing, working at the computer, driving a car, household chores), as well as at night and immediately after waking up. Motor disorders occur mainly at a later stage (after several years) and include atrophy of the thenar muscles, as well as paresis of 1-3 fingers: weakness of thumb abduction and flexion, palmar opposition. Carpal (carpal) tunnel syndrome can also manifest itself with vegetative manifestations ( swelling of the fingers / hands , neuropathic pain , Raynaud's syndrome , trophic changes in the skin ).
Patients often complain of changes in the shape of the hand, which is caused by wasting of the thenar muscles and is manifested by disturbances in fine motor skills: changes in handwriting, difficulty grasping small objects/fastening buttons. As weakness increases, the patient is unable to hold objects. In old age, the manifestations of carpal tunnel syndrome are more pronounced and are accompanied by severe wasting of the thenar muscles.
Diagnostics
It is easy to make a diagnosis of this disease; it is enough to interview the patient and conduct several tests, since carpal tunnel syndrome has clear distinctive features. Among them are the symptoms described above and preservation of the functions of the little finger, which is not affected when the nerve and vessels in the carpal tunnel are pinched.
The doctor also performs palpation and the following tests:
- Hoffman-Tinel test: tapping the area of the median nerve. With carpal tunnel pathology, the patient feels numbness, tingling, and burning in the palm of his hand.
- Phalen test: bending the hand at the wrist joint as much as possible, the patient feels pain and numbness in the palm.
- It is difficult to hold your arms raised above your head for more than 1 minute; pain and numbness of the limbs begin.
- It is impossible to connect (touch) the thumb with the little finger.
- To confirm the correctness of the diagnosis, determine the extent of the lesion and associated complications, additional examinations are prescribed:
- Electroneuromyography to evaluate the conduction of nerve impulses is the gold standard for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Ultrasonography helps detect damage and inflammation.
A neurologist, physiotherapist and hand surgeon can make a diagnosis and carry out treatment.
Forecast
With comprehensive and timely treatment, carpal tunnel syndrome in most cases has a favorable prognosis. In 10-15% of cases, compression of the median nerve does not respond to conservative treatment and surgery is required. A good postoperative prognosis is observed in cases where the disease is not accompanied by atrophy of the hand muscles/complete loss of sensitivity. After surgery, in most cases, hand function is restored by approximately 70% within a month. However, muscle weakness can persist for several months. Recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome rarely occurs.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
All measures taken are aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease - complete or partial elimination of compression of the median nerve. The treatment method depends on the severity of the syndrome. Choose between conservative and surgical treatment. It is also the doctor’s job to identify the cause of the disease in order to limit movements that worsen the symptoms.
Conservative treatment
Patients are prescribed to wear an orthosis, which holds the wrist joint in a position that is safe for blood vessels and nerves. It is recommended to wear it constantly, during the day and at night. According to statistical data, orthotics are effective in the early and middle stages of the disease. It is recommended to switch to a salt-free diet and limit fluid intake to reduce swelling.
Medicines are also prescribed:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids orally or by injection to relieve pain and restore joint mobility.
- Vascular drugs to improve blood supply to tissues.
- Diuretics to relieve swelling.
- Vitamin B6 to relieve symptoms and increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Physiotherapy helps to speed up the therapy process and achieve a positive result faster: electrophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy and other methods. A course of physical therapy and massage are often prescribed. The complex combination of these methods of therapy and the use of medications leads to remission in 59% of patients. The rest are forced, on average, after 1-2 years to turn to a hand surgeon for surgery.
Surgery
If conservative treatment is ineffective and the disease is advanced, surgery is prescribed. They are dealt with only by hand surgeons - highly specialized specialists who perform surgical procedures on the hand. The purpose of the operation is to release the median nerve and reduce pressure. There are two ways to open the carpal tunnel:
- An open surgical procedure in which an incision of about 3 cm is made on the wrist. Having gained access, the surgeon cuts the ligament, increasing the volume of the carpal tunnel.
- Endoscopy has a shorter incision length, which is up to 1.5 cm, but is performed in two places. They are necessary to insert a microchamber, which can be used to dissect the ligament.
Both types of surgery are performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes excision of tissue around the nerve and tendons with scarring, ovaries and cords is required. On average, the procedure is carried out within 20 minutes.
At first, the patient may feel pain in the scar area and physical weakness of the wrist. It will take several months until complete recovery; the period is individual in each specific case. Rehabilitation consists of gymnastics, massage, and physiotherapy. During the recovery period, many have to give up their type of activity if it affects recovery.
According to statistics, up to 90% of patients who undergo surgical treatment completely restore the physical activity of their hands and get rid of the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. Relapses occur in 8 - 12% of cases.
Alternative treatments.
You can relieve the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome without medication or surgery. To do this you need:
- Reduce the load on your hands and wrists, and eliminate activities that worsen the condition.
- Secure the arm with a splint, orthosis or elastic bandage to limit mobility.
- Relieve swelling with ice, limit fluid and salt intake.
- Perform hand exercises aimed at stretching the joints. We recommend exercising under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
If there is no improvement, then you should not delay consulting a doctor.
Treatment
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is aimed at preventing further entrapment of the median nerve. Patients are given anti-inflammatory and decongestant therapy to relieve pain and discomfort. Treatment of the underlying disease, manifested by carpal tunnel syndrome, is a mandatory condition, failure to comply with which can lead to frequent relapses and the development of complications.
When the first signs of pathology appear, it is necessary to fix the wrist. Patients are advised to apply cold to the lesion. If the cause of the pathology is work activity, it must be changed.
Drug treatment
To eliminate the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, experts prescribe:
Physiotherapy
- electrophoresis,
- ultraphonophoresis,
- shock wave therapy,
- reflexology,
- transcranial electroanalgesia;
- UHF therapy,
- magnetotherapy,
- laser treatment,
- ozokerite,
- mud therapy,
- neuroelectric stimulation,
- physiotherapy.
Surgery
Surgery involves excision of the ligament compressing the median nerve.
- Endoscopic surgery is low-traumatic and leaves no scars. Through a small size, a video camera and a special device are inserted into the median canal to cut the ligaments. After surgery, a plaster splint is placed on the wrist.
- Open surgery involves making a large incision in the palm along the line of the median canal. The ligament is cut to relieve pressure on the median nerve. The recovery period after open surgery lasts much longer.
Patients are encouraged to move their fingers the day after surgery. After 1.5 months, physiotherapy and occupational therapy are prescribed. During the rehabilitation period, massage and gymnastics are indicated. Patients should rotate their hands, stretch their palms and fingers. If necessary, you can take a pain reliever.
- Clenching your fingers into a fist.
- Rotate your fists to the sides.
- Clenching palms, spreading elbows.
- Pressure of one hand on the other.
- Squeezing a rubber ball.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome at home includes not only general and local drug therapy, but also the use of traditional medicine. The most effective and common folk recipes:
- Cucumber tincture relieves numbness in the fingers and normalizes blood circulation. It is used to rub sore fingers.
- Hands hover in a heated mixture of sea buckthorn berries and water.
- Sore wrists are rubbed with ammonia and salt.
- Pepper rubbing can help cure carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Lingonberry decoction is taken orally.
- An infusion of parsley root or white birch leaves has an anti-edematous effect.
- Bearberry increases diuresis and relieves inflammation.
- Mumiyo is rubbed into the skin over the lesion daily for several minutes.
- Mustard, sage, and turpentine baths irritate free nerve endings.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is not life-threatening and is a slowly occurring pathological process. The disease has a favorable prognosis for recovery, but due to neglect of their health, some people are in no hurry to visit a doctor. Over time, this leads to a decrease in motor activity, muscle strength, and impaired fine motor skills. If left untreated, irreversible processes will begin and the median nerve will atrophy. This will lead to the loss of functionality of the brush, which will no longer be possible to return.
Reasons for the development of the syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome disease develops under the influence of several factors. A decrease in the diameter of the carpal tunnel may occur due to compression of the nerve. Swelling of surrounding tissues and for both reasons simultaneously. The root cause is trauma, both one-time and microtrauma inflicted regularly due to lifestyle or work activity.
1. “Dangerous” professions.
Among the professions at risk:
- drummers;
- programmers;
- gamers;
- artists;
- pianists;
- secretaries;
- sign language interpreters;
- seamstresses;
- engineers;
- assembly line workers and others.
Most often, the syndrome is diagnosed in women over 40 years of age, mainly due to their professional choice and hormonal changes in the body. However, the disease can occur at any age.
2. Accompanying illnesses.
- A number of medical conditions increase the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome, including:
- Injuries, dislocations, fractures, causing hematomas and swelling.
- Neoplasms, tumors of ligaments and tendons.
- Frequent intratunnel pressure and swelling of the limbs.
- Chronic heart failure and other diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases and other endocrine pathologies.
- Obesity, regardless of the causes of its occurrence.
- Chronic arthritis, sclerosis, collagenosis and vasculitis.
- Tuberculosis and non-tuberculous bacterial infections.
- Kidney failure.
- Alcoholism, smoking, drug use.
3. External factors.
- Work in low temperature conditions. For example, fishermen, butchers, public utility workers.
- Working with heavy tools and vibrating devices. For example, builders, repairmen, industrial workers.
Any of the listed effects or a number of factors together causes a narrowing of the carpal tunnel and pathology develops. Most often, the disease develops according to the following scheme: trauma - aseptic (non-infectious) inflammation, spreading to the carpal tunnel - swelling of the subcutaneous fat layer. Then everything goes around in a new circle:
increasing pressure on nerves and blood vessels leads to even greater trauma and inflammation, causing progression of the disease and transition to the chronic stage.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tunnel syndrome increase as the nerve trunk is compressed.
- Clinical signs of the initial stage are unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the hand that occur after prolonged stress on this area of the body. Patients complain of trembling, itching and slight tingling in the limbs. At the initial stage, symptoms are temporary. When you shake your hands or change the position of your hands, the discomfort disappears.
- The narrowing of the canal is manifested by acute pain in the hand, which intensifies after exercise. The upper limb of patients becomes numb. Any movement of the hand in the wrist joint causes unbearable pain. Numbness, tingling and heaviness in the hands become unpleasant and irritating. Pain and paresthesia are localized in the area of the first three fingers of the hand. They occur at night or early in the morning. Numbness and decreased sensitivity of the limb deprives it of mobility.
- Significant narrowing of the tunnel is manifested by stiffness of the affected joint, hypotension and wasting of muscle fibers. At the same time, pain and numbness persist and intensify. Patients experience general symptoms: insomnia, irritability, depression. Cramps and constant pain unsettle me. A person can no longer lift a heavy object, dial a number on a cell phone, use a mouse on a computer, or drive a car. Fine motor skills are impaired and skin color changes. Patients experience weakness when flexing the hand, weakness in flexing the first and second fingers, especially the terminal phalanges. The sensitivity of the palmar surface of the first and second fingers is significantly reduced.
Pain syndrome is the main clinical sign of pathology. Patients complain of a burning or tingling sensation in the hands that occurs at night and disrupts sleep. Patients wake up to shake their arms. Blood flow to the fingers reduces pain. In advanced cases, pain appears not only at night. She torments patients around the clock, which affects their neuropsychic state and leads to impaired performance. Pain is often accompanied by a violation of autonomics and trophism, which is clinically manifested by swelling, hyperthermia and hyperemia of the wrist, palm and three first fingers.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is not life-threatening, but it does impair the quality of life. The intensity and duration of pain increases, insomnia and irritability occur, and diseases of the nervous system develop.