Alcoholic encephalopathy is a neurological disease caused by the negative effects of alcohol on the brain. The disease is accompanied by damage to brain cells and the resulting disruption of the nervous system and the body as a whole.
Alcoholic encephalopathy is characteristic of the last stage of alcohol dependence. With the development of this disorder, the patient experiences somatic (bodily) changes and the functioning of the nervous system is disrupted.
In this material we will consider this disease, its manifestations, types and methods of treatment.
Content:
- Why do alcoholics develop encephalopathy?
- Classification of the disease
- What does diagnostics include?
- How is the treatment carried out?
2.1. Acute alcoholic encephalopathy2.2. Chronic alcoholic encephalopathy
Alcoholism affects all vital organs and, first of all, the brain.
Alcohol literally destroys its cells, which leads to serious disorders and changes. One of the complications of addiction is alcoholic encephalopathy. This disease manifests itself at the end of the second - beginning of the third stage of alcoholism. It requires serious treatment, as it can lead to the most unfavorable consequences:
- severe mental disorders;
- dementia;
- complete or partial loss of memory;
- pseudoparalytic syndrome;
- of death.
Treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy must be carried out in a specialized hospital. At home, it is impossible to completely eliminate the signs of the disease and normalize the patient’s condition.
Alcoholic encephalopathy
Alcohol or toxic encephalopathy is often otherwise referred to as Wernicke encephalopathy (WE). This is an acute condition that requires emergency medical care to prevent a sharp decline in intelligence and, often, death of the patient.
According to Wikipedia, “Wernicke encephalopathy and WKS are most often observed in people who abuse alcohol. Errors in diagnosing WE and therefore in treating the disease result in death in approximately 20% of cases, while 75% are left with permanent brain damage associated with WKS. Of those affected, 25% require long-term treatment to receive effective care.”
In 1881 Carl Wernicke identified a disease with symptoms that were characterized by an acute mental health disorder. It was accompanied by swelling of the optic nerves, hemorrhages in the retina, oculomotor disorders and coordination disorders in gait.
The most common causes of the disease are acute brain damage associated with the toxic effects of alcohol, drugs and other psychoactive substances. In addition, such disorders were observed in people working in hazardous industries and with eating disorders with an acute degree of exhaustion. It should be noted that recently this disease can often be observed in people who have undergone procedures such as plasmapheresis and hemadsorption without any particular need for it. It should be noted that this form of the disease often begins to develop against the background of xenon therapy. Unfortunately, this procedure is now often recommended for people with alcohol and drug addiction. This stimulates the development of very serious diseases and aggravates the patient’s condition.
Alcoholic encephalopathy can present with various symptoms, so a full diagnosis can only be made with a comprehensive examination.
The main symptom of alcoholic encephalopathy is a change in a person’s mental state.
Main signs of alcoholic encephalopathy
- change in mental state;
- dizziness, noise in the head;
- absent-mindedness, confusion, forgetfulness;
- depression, bad mood, grouchiness;
- hot temper;
- fast fatiguability;
- sleep disturbance;
- slow thinking, sleepy state;
- Difficulty pronunciation, speech problems.
If you have at least one of the listed signs, you should check your health and identify the existing disorder in time. It is necessary to establish whether encephalopathy develops after head injuries, whether there are vascular pathologies of the brain, coronary artery disease, whether there was heavy metal poisoning, etc. People with addiction to psychoactive substances, even those who previously suffered from alcoholism, need to be examined regularly. At the first visit, our competent and experienced doctor can identify all the main symptoms of encephalopathy and carry out a diagnosis.
Features of the manifestation of alcoholic encephalopathy
- The depression of consciousness is increasing. These consequences often lead to the death of the patient. And it was death that was often evidence of the disease.
- Focal vascular lesions of the gray matter of the brain are formed.
- Oculomotor disturbances occur, bilateral optic nerve paresis is formed, leading to horizontal double vision, convergent strabismus and nystagmus. Gaze paralysis.
- Behavior changes and becomes clearly inappropriate. Asks questions and answers inappropriately. Obscene, offensive jokes.
- Impairments in motor functions occur.
- An imbalance of the vestibular apparatus occurs, and a person loses stability when walking. In later stages of the disease, miosis (constriction of the pupil) and absence of pupillary reactions are formed. Retinal hemorrhage often occurs.
- Ataxia appears in a standing position and when walking. Even in the initial stage, it can be so pronounced that the patient is unable to stand and move without support. In the initial stages, this may be manifested by a peculiarity of gait, when a person, when walking, steps on his foot starting from heel to toe.
- With significantly pronounced impairments of a person’s movement in space (locomotor functions), cerebellar tremor in the arms and legs is quite rare.
- In some cases, the so-called “Chanted Speech” may appear.
From the editor: Human brain contusion
Why do alcoholics develop encephalopathy?
Due to constant drinking
In high doses, metabolic processes in the human body begin to proceed incorrectly, and an acute deficiency of vitamin B1 develops. Gradually, metabolic disorders spread to the brain. Its capillaries become thinner, and severe swelling may develop.
The likelihood of developing a disease is very high if an alcohol addict often takes surrogates for alcohol or independently prepares “hot drinks” from various technical liquids containing alcohol. Indeed, in this case, acute intoxication occurs many times faster.
Diagnosis and treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy
Diagnosis of the pathology usually does not cause difficulties and is based on data on chronic alcohol abuse and the uniqueness of the symptoms, which are assessed by a psychiatrist or narcologist. The fact of alcohol abuse can be indicated by the patient’s relatives, data from blood tests for alcohol and its surrogates.
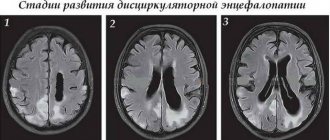
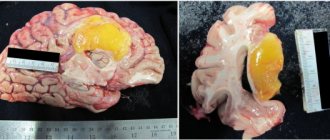
An objective examination shows an enlarged liver, signs of pancreatitis, increased blood cholesterol, liver enzymes, and decreased blood clotting. For differential diagnosis, electroencephalography, MRI or CT scan of the brain is performed.
MRI of the brain of a healthy middle-aged man suffering from alcoholic encephalopathy
The diet of patients with alcoholic encephalopathy should be rich in proteins and vitamins, sufficiently high in calories, but sparing, since the disease is usually accompanied by digestive disorders due to pacreatitis, erosive gastroenterocolitis, hepatitis or cirrhosis.
Drug therapy includes:
- B vitamins, ascorbic acid, PP in high doses;
- Nootropics, drugs for improving cerebral blood flow (piracetam, encephabol, cinnarizine, actovegin);
- Metabolic agents and antihypoxants (mildronate, antioxycaps, omega-3 based drugs);
- Anticonvulsants for convulsive syndrome (carbamazepine, Relanium);
- Antihypertensive drugs for high blood pressure.
Concomitant pathology requires symptomatic treatment. Thus, for infectious complications, antibiotics are indicated, in the case of hepatitis and cirrhosis - hepatoprotectors, for pancreatitis - enzymes (mezim, pancreatin), antiproteases (contrical).
In the case of acute severe alcohol intoxication, intensive care may be required in intensive care with fluid infusion and diuretics to quickly eliminate toxins and alcohol. If there is a risk of cerebral edema or its increase, diacarb, mannitol, furosemide, administration of glucose with insulin, and anticonvulsants are indicated. In the intensive care unit, artificial ventilation of the lungs is established; hemodialysis and long-term parenteral nutrition are often required.
The most important action that a patient with alcoholic brain damage must take is to completely stop drinking any alcohol-containing drinks. After stabilization of the condition, together with a narcologist, you can choose the optimal withdrawal route for a given patient - implantation of teturam-containing drugs, hypnosis, various coding methods using intravenously administered medications.
During the entire rehabilitation period, vitamins B, C, PP, antioxidants and metabolic agents are indicated. Proper nutrition should be observed, and antidepressants and sedatives are often prescribed (not alcohol!).
It is important that the patient does not lose sight of the narcologist for at least the next few years, during which he needs to visit a psychotherapist, undergo preventive examinations in his clinic, engage in auto-training, etc.
Usually, responsibility for rehabilitation falls on the closest relatives, who monitor the patient’s lifestyle and health.
The most characteristic consequences of alcoholic encephalopathy are considered to be polyneuropathy, mental disorders, decreased intelligence and memory, lack of self-criticism, difficulties in self-care and the inability to work.
Relatively mild forms of pathology are better amenable to correction, patients can subsequently adapt to living conditions, but dynamic observation and complete abstinence from alcohol are prerequisites for those who want to at least partially get rid of the manifestations of the disease.
Classification of the disease
Alcoholic encephalopathy is usually classified into:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Let's look at the symptoms of each type in more detail.
Acute alcoholic encephalopathy
It starts with warning symptoms. The patient complains of insomnia, loss of appetite, and increased fatigue. He cannot eat foods containing high amounts of protein and fat. He always tries to eat dishes rich in quickly digestible carbohydrates. As a result, metabolic failure becomes even more pronounced, as does a deficiency of vitamins and microelements. A little later, pain begins in the stomach, in the right hypochondrium, nausea in the morning, heartburn and diarrhea.
Gaye-Wernicke encephalopathy, one of the acute forms of the disease, usually begins with delirium. The patient sees hallucinations, constantly mutters something, and behaves inappropriately. Periodically he experiences painful cramps. The face may swell greatly, which seems unnatural given the overall thinness.
At a certain moment, the pulse skips a beat, body temperature rises, and blood pressure drops.
An alcoholic may fall into a coma. A fatal outcome cannot be ruled out. According to statistics, most often it occurs two weeks after the first signs of encephalopathy appear. If events develop favorably, the so-called psychoorganic syndrome occurs. It manifests itself:
- mental helplessness;
- memory loss;
- complete loss of volitional abilities;
- inability to adapt to new conditions;
- apathy.
Mitigated encephalopathy is the second acute form of the pathology. It is characterized by:
- constant depressed mood;
- sleep disorder;
- high level of anxiety;
- sudden memory loss.
After drug correction of the condition, the patient may suffer from amnesia symptoms for a long time. It is difficult for him to remember moments from the past. Even what happened to him yesterday, he cannot always retell and describe.
The hyperacute form is another type of acute alcoholic encephalopathy. It is characterized by rapid progression and is therefore very dangerous. Often results in death.
Before a person encounters a dangerous disease, he may notice warning signs within three weeks. Afterwards, severe psychosis develops, consciousness is impaired, and body temperature rises to 41°C. In just a few days the person falls into a coma and dies. If he manages to survive, he is faced with pseudoparalytic syndrome. The latter is characterized by a euphoric mood, absurd delusions of grandeur in the absence of progressive paralysis.
Chronic alcoholic encephalopathy
The chronic form of encephalopathy can manifest itself as Korsakoff psychosis and alcoholic pseudoparalysis. The first one is encountered more often by female representatives. The disease is characterized by memory loss, difficulties with spatial orientation, and poor motor reactions and speech. The patient may also experience neuritis.
Pseudoparalysis occurs more often in men. The patient develops dementia, loses many knowledge and skills, and suffers from constant sudden mood swings. His hands are shaking, his speech is impaired.
Varieties and subspecies
There are encephalopathy in the acute stage and chronic. Chronic can develop for years, going through all stages. At first, the patient suffers from a slight malaise, then neuropathy begins, turning into encephalopathy. The acute form progresses quickly. Often, relatives and close people do not have time to get their bearings, not to mention the patient himself. Within a few weeks, the health condition deteriorates sharply, followed by coma and death.
The acute form of encephalopathy is called Gaye-Wernicke. The duration can be completed within one week.
Gaie-Wernicke symptoms:
- General physical weakness. Constant sleepiness and lack of strength.
- Dyspnea. Feeling like there is not enough air. This condition is associated with the destruction of blood vessels in the lungs, which leads to hypoxia in the future. The diaphragm muscles weaken.
- Arrhythmia. Heart rhythms either speed up or slow down. There is a pressing sensation in the chest.
- Migraines and headaches. They may not go away even after sleep. A person suffers constantly, unable to adequately assess what is happening.
- Trembling in limbs. Joint weakness. Hand tremors. Legs feel like cotton wool.
- Loss of coordination. Muscle spasms lead to spontaneous movements of the arms and legs.
- The extremities are constantly cold, sometimes wet.
- Insomnia and sleep disturbance. A person cannot get enough sleep. Often there is no deep stage of sleep.
- Body temperature fluctuates. More often in the direction of increase.
- At the last stages of development, a person falls into a coma.
From the editor: Tips and exercises for developing attention
One of the main symptoms of Gaie-Wernicke is the lack of relief and satisfaction from drinking alcoholic beverages, which do not bring any pleasure. Chronic encephalopathies develop over a long period of time, so they may not be noticed by the patient or others. Korsakov's psychosis does not occur very often. Women are more prone to it. This is probably due to the behavioral characteristics of the female population, as well as to the characteristics of the body itself.
Symptoms of Korsakoff psychosis:
- False memories are created. A person remembers something that never happened. This indicates a serious malfunction of the brain.
- Disorientation in space. The vestibular apparatus suffers. A person tends to often fall out of the blue.
- Polyneuritis of the extremities.
This stage lasts a relatively short time. It happens quickly and clearly. Despite the fact that the syndrome is chronic, it rarely goes beyond one year. Alcoholic pseudoparalysis usually affects middle-aged men. This disease is also associated with long-term alcoholism, which was not stopped or treated.
Symptoms of alcoholic pseudoparalysis:
- Manic delirium. A person constantly talks about something non-existent or fictitious. He is haunted by memories and phobias.
- Memory disorder. The brain is no longer able to retain information. Due to the fact that many neurons have been destroyed, memory lapses appear.
- Tremor of the limbs.
- Changes in facial expressions. Nerve fibers in muscle tissue are destroyed, causing sagging. The face expresses nothing.
Encephalopathy is the final stage, which is caused by the destruction of brain cells, which are no longer able to control the functioning of the entire body as a whole. The most common cause is heart failure, followed by cerebral edema and inevitable death.
How is the treatment carried out?
The amount of medical care that needs to be provided to a patient directly depends on the form of the disease and the severity of the patient’s condition. To speed up the cleansing of the body from toxic compounds and to put metabolic reactions in order, intensive infusion therapy is carried out. Medications that help with psychosis are administered intravenously to a person using a drip. With their help, a narcologist can:
- remove existing metabolic disorders;
- restore normal breathing;
- prevent the development of severe diseases of the kidneys, liver, heart, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract;
- remove hyperthermia.
Additionally, the addict is prescribed symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating the symptoms of emerging pathologies of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system, etc. The treatment regimen necessarily includes taking vitamin and mineral formulations, since without them it is impossible to normalize metabolism.
It is very important that the treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy is carried out by a highly qualified narcologist. If the patient and his relatives ignore the first dangerous “bells” signaling brain damage, then the disease will not be long in coming. Starting treatment at the beginning of the pathological process allows doctors to achieve excellent results, which is why it is so important not to delay seeking medical help.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
What is encephalopathy?
Alcoholic encephalopathy is a disease in which brain cells are destroyed. The cause of the pathological process is alcohol abuse. In most cases, the disease develops before or after the transition from the second stage of alcohol dependence to the third.
The first signs of the anomaly may appear after 7–20 years with regular drinking. But in some cases, it may take much less time for the disease to develop. Sometimes the disease manifests itself even with periodic consumption of alcoholic beverages. Intake of industrial alcohol and other drink substitutes increases the likelihood of pathology.
The anomaly is based on a metabolic disorder, which is characteristic of alcohol dependence. Regular consumption of ethyl alcohol leads to vitamin B1 deficiency. This effect is associated not only with a deterioration in the absorption of nutrients in the intestine. A lack of vitamins and minerals is caused by liver dysfunction, as well as a monotonous diet.
The patient's condition is further aggravated by a lack of vitamins B6 and P. Their deficiency causes malfunctions of the digestive system. At the same time, the permeability of brain vessels increases, which often leads to swelling of the organ.
The number of deaths due to the disease ranges from 30 to 70%.
To prevent complications, it is recommended to start treatment at an early stage of the pathological process. If timely measures are not taken, the patient may face various psychological disorders.
The treatment of alcoholic encephalopathy is carried out by the narcological hospital.