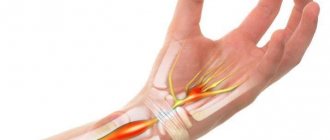
The concept of carpal tunnel syndrome is not universal for the wrist area; this condition can also manifest itself in other anatomical areas where the nerves lie quite superficially and close to the bone structures at the same time. The syndrome in question manifests itself in the form of a decrease or absence of sensitivity in the thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger, as well as impaired motor function in them.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common pathology and occurs in 1-3% of the population, mainly in people whose occupation is associated with fine, monotonous motor skills of the hand. Half of all those suffering from this syndrome are people whose type of employment involves using a computer. Also, this disease can be considered an occupational pathology in musicians, tailors, office workers, etc. The syndrome occurs in the active working population at an already mature age (40-60 years), and in 105 cases at a younger age. Scientists concluded that heavy PC users have a 15% higher risk of developing the syndrome, especially in women.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The median nerve in the hand area passes through a tunnel formed by the transverse ligament and the carpal bones of the hand. Compression of the nerve in the canal can be caused by:
- Traumatic injuries to the hand.
Bruises, dislocations, sprains, and fractures can cause swelling of the ligaments and muscles or even displacement of the wrist bones. All this can put pressure on the nerve in the canal and cause disruption of its function. With proper treatment, all these processes are reversible, but if help is not provided in time and correctly, then contractures of muscles and ligaments, as well as bone deformation, may be irreversible.
- Arthrosis, arthritis and other pathological joint processes of various etiologies and genesis.
The swelling and inflammatory reactions caused by these pathologies, including tissue necrosis, can also cause compression of the nerve. With the permanent occurrence of inflammation and the progression of degenerative-dystrophic processes, the articular surfaces of the wrist lose their properties and wear out, resulting in deformation and compression of the nerve in the canal by bone structures.
- Inflammation of the tendons or tenosynovitis.
Inflammation can be septic (caused by microorganisms) and aseptic (caused by stress, hypothermia, etc.). Septic inflammation can be provoked by diseases such as purulent wounds of the hand, including felons, improper technique for drawing blood from a finger, etc. Non-infectious inflammation can be caused by chronic traumatic stress, for example, frequent monotonous motor skills of the hand, static load on it, and temperature trauma.
- Diseases that lead to water retention in the body
, can cause swelling of the extremities and, as a result, lead to an increase in the volume of soft tissues and compression of the median nerve. Violation of the water-electrolyte composition can be caused by: pregnancy, taking hormonal contraceptives, menopause, kidney disease, etc.
- Rare, but do occur tumors of nervous tissue and median nerve
in particular. Most of these are benign neoplasms (schwannomas, neurofibromas, perineuromas), but there are also malignant ones arising from the nerve sheaths. With its growth, the tumor puts pressure on the nerve, which leads to its damage.
- Diabetes.
Under the influence of the enzyme protein kinase C, sorbitol and fructose accumulated during the disease begin to be destroyed in nerve tissues. Because of this, as well as due to a violation of the trophism of neurons and their processes, aseptic inflammation of the nerves and surrounding tissues occurs. Swelling increases, which in turn leads to compression of the nerves, including the median nerve.
- Acromegaly.
As a result of the prolonged and intense growth of a person suffering from acromegaly, processes of disproportionate growth of bone and soft tissue occur. The median nerve can be pinched in the narrowed carpal tunnel due to increased bone volume and narrowing of its lumen.
- Congenital malformations
. The transverse carpal ligament may be thickened from birth, and poor tendon lubrication production may occur. One of the factors predisposing to carpal tunnel syndrome may be an anatomical feature of the structure, the so-called “square wrist”.
Causes of tunnel neuropathies
The root cause of tunnel neuropathy is sports, household or professional microtrauma to the nerve trunk. Often the joints themselves are subject to various pathological changes (traumatic, inflammatory, degenerative), which also cause narrowing of the channels. Bone protrusions and tendon arches, as well as other similar formations that can injure the nerve in the tunnel, play a certain role in the development of tunnel neuropathies.
Narrowing of the canal can be caused by violation of the rules for intramuscular injections and other medical interventions. Often, compression of the nerves can be caused by prolonged exposure to a person’s usual position. For example, when sitting with your leg crossed over your knee, when compression of the nerve occurs in the popliteal fossa, when working for a long time at the keyboard and computer mouse, or while driving for a long time.
Aggravating and provoking factors for the development of tunnel neuropathies are endocrine disorders, leading to tunnel neuropathies in pregnant and lactating women or during menopause.
Often the pathology appears as a result of long-term use of oral contraceptives, diabetes mellitus, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, renal failure, alcoholism, acromegaly, hypothyroidism, fasting, hereditary predisposition or genetically caused increased trauma to the nervous tissue.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Feeling of numbness in fingers.
The syndrome in question, as a rule, develops gradually and the lesion mainly manifests itself unilaterally. Basically, the pathological process occurs in the limb that is the leading one; in right-handed people, the right hand, and in left-handed people, the left hand. The development of carpal tunnel syndrome occurs gradually. However, a two-way process can also be observed, with diseases of the endocrine system, pregnancy, etc. - Paresthesia
. They manifest themselves as tingling sensations and loss of sensitivity in the fingers. They appear in the morning, after waking up, and disappear within a few hours. But over time, these manifestations become more stable and intense and can already become permanent. This can lead to disruption of the normal function of the limb: strength, dexterity, etc., the patient has to change hands when performing actions, and give rest to the affected limb. Particular inconvenience is caused by manipulations requiring static tension of the limb.
- Pain.
When the disease manifests itself, a burning and tingling sensation may appear in the hand, which can be quickly eliminated by lowering the limb down and shaking it. Blood flow in the arm is restored and the pain goes away. As a rule, this occurs during sleep due to the static position of the hand, or during monotonous work performed by the limb. The pain is not specific to any specific joints and is widespread. As the disease progresses, pain can affect not only the fingers, but the entire hand and arm up to the elbow joint, which often makes diagnosis difficult. The patient is unable to perform his duties because the pain may occur during the daytime.
- Loss of dexterity and strength.
Over time, if the disease is not treated, the limb begins to lose strength and dexterity in movements. It is difficult for the patient to hold objects in his hands, especially small ones; they seem to spontaneously fall out. The ability to perform fine motor skills (grasp small things, position the thumb, etc.) is lost.
- Decreased sensitivity.
Over time, the patient may begin to notice that he has difficulty distinguishing the temperature of objects, and ceases to feel touches or even injections. A painful burning sensation and numbness appear in the hand.
- Amyotrophy.
In advanced forms of the syndrome, atrophy of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the arm may develop; muscles and ligaments not only lose strength, but also decrease in size. Over time, the hand becomes deformed and takes on a shape resembling a monkey's paw.
- Change in skin color.
Due to the fact that when the innervation of the hand is disrupted, the nutrition of skin cells also occurs, the color of the skin changes, they become lighter and unevenly colored.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
For an accurate diagnosis, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. In this case, the doctor conducts a number of specific tests, and laboratory and instrumental research methods can also be used.
Tests for carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Tinel test.
In the narrowest place of the carpal tunnel, on the side of the palm, when tapping, an unpleasant tingling sensation occurs. - Phalen test.
When the hand is bent to the maximum, pain and paresthesia appear in the wrist area within a minute or less. - Cuff test.
A blood pressure cuff is placed on the forearm and inflated as much as possible. Within one minute, if the test is positive and the syndrome is present, a feeling of numbness and tingling appears. - Raised hands test.
The upper limbs are raised vertically and held in this position for a minute. If the result is positive, unpleasant sensations appear within 30-40 seconds.
All of the above tests can be done at home, and if you have at least one positive test, be sure to consult a doctor.
The following instrumental research methods are used:
- electroneuromyography;
- X-ray examinations;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound.
To identify the causes of the disease, the patient is prescribed a blood and urine test:
- blood biochemistry;
- blood and urine test for sugar;
- analysis for thyroid-stimulating hormones;
- clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, antistreptolysin-O;
- blood test for circulating immune complexes;
- blood test for antistreptokinase.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
The most important thing in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is compliance with measures to prevent the development of the disease. Even with the best and highest quality treatment, you cannot do without preventive measures, because the effect may simply not be achieved.
- Preventive measures for carpal tunnel syndrome.
When the first signs of the disease occur, it is necessary to firmly fix the hand so that there is no possibility of movement in the joint and, as a result, injury to the nerve. The fixator can be applied by a doctor or purchased an elastic bandage at the pharmacy for temporary use. For two to three weeks, you must avoid activities that aggravate the symptoms of the disease. It is also recommended to apply cold to the wrist area for 2-3 minutes 2-3 times a day to reduce swelling. In the subsequent period, treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the pathological process and its severity. If this is necessary, then treatment is based on the treatment of the underlying disease (traumatic injury, hypothyroidism, diseases of the urinary system, diabetes mellitus, etc.) causing compression of the nerve in the canal. - Local treatment.
Includes the use of compresses and the introduction of medications into the canal cavity. These procedures can quickly relieve painful symptoms and relieve local inflammation.
- Drug therapy.
Drug therapy in each case is selected individually depending on the underlying or concomitant disease. In this case, B vitamins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vasodilators, diuretics, anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants, glucocorticosteroids, antidepressants, etc. are often prescribed. - Physiotherapy.
It can be used both during drug therapy and in the postoperative period during rehabilitation. In this case, the following is used: acupuncture; manual therapy techniques; ultraphonophoresis; shock wave therapy. Before using physiotherapeutic procedures, you should consult a specialist for any contraindications.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (carpal tunnel syndrome) is the most common form of compression-ischemic neuropathy encountered in clinical practice. In the population, carpal tunnel syndrome occurs in 3% of women and 2% of men [Berzins Yu.E., 1989]. This syndrome is caused by compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel under the transverse carpal ligament. The exact cause of carpal tunnel syndrome is not known. The following factors most often contribute to compression of the median nerve in the wrist area: • Trauma (accompanied by local swelling, tendon stretching). • Ergonomic factors. Chronic microtraumatization (often found among construction workers), microtraumatization associated with frequent repeated movements (among typists, with constant long-term work with a computer). • Diseases and conditions accompanied by metabolic disorders, edema, tendon and bone deformities (rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, acromegaly, amyloidosis, pregnancy). • Massive formations of the median nerve itself (neurofibroma, schwannoma) or outside it in the wrist area (hemangioma, lipoma).
Surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
If conservative therapy does not produce the desired effect for 6 months or more, then it makes sense to think about surgical resolution of the disease. The main goal of surgery is to relieve pressure on the median nerve by widening the carpal tunnel.
Most operations are performed under local anesthesia. The following methods are used:
- Open access:
The carpal ligament is dissected through a 5mm incision in the area of the carpal canal.
- Endoscopic surgery.
There are two types of endoscopic intervention, through two incisions and through one. In the first case, an endoscope is inserted into one incision, and an instrument is inserted into the second to cut the ligament. In the second case, both instruments are inserted alternately through one hole.
At the end of the surgical intervention, a plaster cast is applied to the arm to immobilize the limb. After the cast is removed, a course of physical therapy and physiotherapy is carried out. As a rule, complete restoration of hand function occurs within six months. After recovery, the patient can return to work, subject to a protective regime, so as not to provoke a relapse of the disease. In the modern world, where computer technology has already been introduced everywhere, the pathology we are considering is becoming more and more common. Timely and qualified assistance and prevention in the event of carpal tunnel syndrome allows one to achieve remission completely and with sufficient stability.
At-risk groups.
Among the risk factors that most influence the appearance of carpal tunnel syndrome are:
- Activities involving the performance of repetitive movements of the same type (risk group: programmers, guitarists, painters, tennis players, hairdressers, etc.);
- Elderly age;
- Endocrine diseases of the body (diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- Microtraumas of the ligamentous apparatus, joints;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- HIV, other autoimmune diseases.
Other causes of carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Tumors and edema;
- Increased physical activity;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Prolonged fasting;
- Wearing tight clothing;
- Injuries;
- Pregnancy;
- Unskilled surgical intervention.