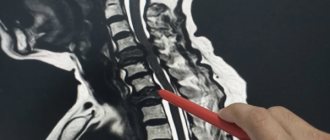
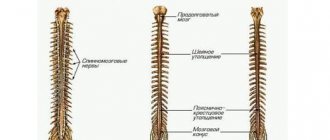
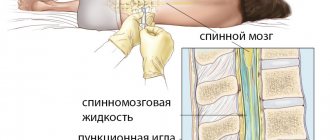
2.Why are bone marrow biopsies and spinal taps performed?
A bone marrow biopsy and puncture is performed to:
- Find the cause of changes in red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets in patients with thrombocytopenia, anemia, or abnormal white blood cell counts.
- Identify blood disorders such as leukemia, anemia, or factors affecting the bone marrow (multiple myeloma or polycythemia).
- Make sure that Hodgkin lymphoma or another type of lymphoma has not spread to the bone marrow.
- Look for infections or tumors that may have spread to the bone marrow.
- Find the best treatment methods for bone marrow diseases.
- Collect bone marrow samples for medical procedures such as stem cell transplants or chromosomal analysis.
Are errors possible?
Aspiration biopsy of the thyroid gland is a fairly accurate diagnostic method. However, in rare cases errors may occur:
- A false positive result is when there is no malignant tumor, but laboratory specialists thought that there was one. The probability of such an error is 3%.
- False negative results occur in less than 5% of cases. However, tumor cells are not detected in the laboratory, but in fact the patient has a malignant tumor.
The reasons for errors can be different: the inexperience of the doctor who performed the puncture, the laboratory employee, the peculiarities of the histological structure of various neoplasms. Nodules less than 1 cm in diameter may be difficult to penetrate with a needle, and nodules larger than 4 cm may not be able to collect tissue samples from all parts of the nodule.
If your attending physician has doubts about the diagnosis, get a second medical opinion from specialists at the international clinic Medica24.
3.How is a biopsy performed?
These procedures are performed by a hematologist, oncologist, internist, pathologist, or specially trained physician. In adults, a sample of bone marrow fluid is usually taken from the back of the pelvic bone. In rare cases, a fluid sample is taken from the chest or the front of the pelvic bone. In young children, samples are obtained from the front lower part of the lower leg, just below the knee. A bone marrow biopsy is taken only from the pelvic bone. The puncture is performed using a needle. A biopsy uses a special instrument that is screwed into the bone.
Rehabilitation period
After the procedure, the woman remains in the clinic for one and a half to two hours under the supervision of specialists. Then the attending physician conducts a follow-up examination. After this, the patient can leave the fertility center accompanied by her spouse or another person.
Please note: driving after anesthesia is not recommended. On the day of the puncture, you should avoid any other activity that requires quick reaction and concentration.
For 2-3 days after the procedure, patients may notice:
- scant bloody discharge from the vagina of a spotting nature;
- feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- slight increase in temperature;
- headache;
- weakness.
Be sure to contact your doctor right away
if you have the following symptoms:
- body temperature is more than 37.5°C;
- strong pain;
- profuse bleeding from the genital tract;
- dizziness;
- nausea or episodes of vomiting;
- difficulty urinating.
After the manipulation, the patient needs to adhere to some recommendations:
- avoid serious physical activity and stressful situations;
- Eat a high protein diet. In particular, you can include in the menu dishes from lean meat and river fish, as well as various dairy products;
- minimize the consumption of foods that cause increased gas formation;
- exclude intimate contacts;
- do not take hot baths, or visit a bathhouse or sauna;
- take any medications, including painkillers, strictly in consultation with your doctor.
4. Bone marrow biopsy results
Bone marrow biopsy results are usually ready within a week.
The following indicators are considered the norm:
- Bone marrow has normal amounts of fat, connective tissue, and iron. Normal ratio of adult and growing bone marrow cells.
- There are no signs of infection.
- There are no cancer cells such as leukemia, lymphoma or multiple myeloma.
- There is no spread of cancer cells from other affected areas.
Deviation from the norm:
- Bone marrow cells with pathology.
- The ratio of the number of different cells is disturbed.
- Bone tissue with pathology.
- Too much iron or too little iron (iron deficiency anemia).
- There are signs of infection.
- Cancer cells (leukemia, lymphoma, or multiple myeloma) are present.
- The bone marrow is replaced by scar tissue.
Depending on the results of a bone marrow biopsy or spinal tap, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations, select or adjust a treatment regimen, or, conversely, make sure that everything is in order with your health.
Fine needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis of cancer
Find out the cost of PTAB Thyroid gland
Sign up through your personal account
Biopsy (puncture) is a diagnostic method in which cells or tissues are taken intravitally from the human body and then examined microscopically.
In the structure of mortality in Russia, cancer is in second place after cardiovascular diseases. Cancer statistics in Russia show that approximately 1,500 patients with cancer are registered in our country every day. In total, at least 2.5 million patients with various forms of cancer are registered in oncology clinics in Russia.
The main reason for increased mortality from cancer in Russia is late diagnosis. An important reason for the late detection of malignant neoplasms is that people do not consult a doctor on time due to lack of knowledge in this area or insufficient funds. This leads to the fact that in Russia every third cancer patient dies within a year from the moment of diagnosis. For example, in the United States, more than 80% of patients pass the five-year survival mark.
In the majority of cancer patients, the pathology preceding thyroid and breast cancer is usually benign neoplasms. Nodules in these groups of patients can be detected by ultrasound. The widespread use of high-resolution ultrasound devices makes it easy to diagnose nodular formations, including small ones (up to 1 cm in diameter).
The main goal of a diagnostic search for nodal pathology is to identify patients with neoplastic changes in the mammary and thyroid glands, since it is this category of patients that is primarily subject to surgical treatment and, if necessary, radiation therapy, etc.
It is no secret that it is almost impossible to reliably determine the type of tumor (benign or malignant) using ultrasound; moreover, ultrasound is a rather subjective method in which the human factor (ultrasound diagnostic operator) is present. Significant variability in ultrasound diagnostic indicators depends on two main factors - the level of qualification of the diagnostician and the technical parameters of the ultrasound scanner used.
The insufficient information content of the used methods for studying diseases of the thyroid and mammary glands, combined with the need to clarify the diagnosis, forced clinicians to actively use invasive manipulations with morphological verification of the process.
Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) is the most accurate, highly informative, safe method used in many diagnostic algorithms for focal diseases of the thyroid, breast and other superficially located structures.
The study of punctate allows not only to recognize the nature of the process (benign or malignant), to clarify the histogenetic affiliation of the neoplasm, but also to identify cancer in the early stages of development, when clinical manifestations of the disease are not yet present.
In patients operated on for thyroid cancer, if tumors are detected in the surgical site, a puncture biopsy provides a clear differential diagnosis between tumor recurrence, hyperplasia of the remaining gland tissue, or postoperative changes such as granuloma.
Main indications for TAPB:
- Single or multiple nodes in an organ, when their benign nature is in doubt.
- The presence of altered lymph nodes, when it is necessary to determine the source of metastasis.
- Focal formations of the mammary glands with characteristic signs of a tumor process, various cysts (atypical, simple). When a cyst is punctured, a therapeutic function is also performed, since its contents are removed as much as possible.
- Neoplasms of the salivary glands, soft tissues of the neck, in some cases, median or lateral cysts of the neck.
- Recurrence of the primary tumor
According to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE), fine-needle aspiration biopsy of nodules measuring 10 mm or less is not indicated unless ultrasound findings are suspicious for thyroid cancer and there is no high risk of cancer according to medical history. However, all these recommendations are not absolute and in certain situations leave the clinician the right to decide on the need for fine-needle aspiration biopsy, even in cases where nodular formations do not meet the above criteria.
Main contraindications to TAPB:
- blood diseases (blood clotting disorders can lead to bleeding, which may require urgent hospital treatment);
- the patient has mental illness, since TAPP can provoke an exacerbation of the underlying disease.
Methodology for performing FNAB of nodal changes in the thyroid and mammary glands
The fine-needle aspiration biopsy method is simple, as is drawing blood from the patient's arm. It has virtually no contraindications and can be performed on an outpatient basis without anesthesia. The introduction of anesthetics causes a deterioration in ultrasound visualization of the area under study, a change in the cellular pattern, and the anesthesia itself is as painful as the puncture. The patient is in a supine position. The skin surface is treated with a solution of 70% ethyl alcohol. An injection (puncture) is made through the skin into the tumor-like formation of the organ and the contents of the formation are aspirated. As a result of puncturing the formation under study with a needle, tissue fragments are collected. The movement of the needle and all manipulations are visually controlled on the screen of the ultrasound machine. After the tip of the needle is inside the formation, the doctor performs aspiration (sampling) of the contents of the node several times with a syringe. To obtain a sufficient amount of biological material, 2 - 3 injections are performed in different areas of the formation. The needle is then removed and the resulting material is applied to glass slides. The slides are sent for examination to the cytology laboratory. Next, these slides are specially stained, and a cytologist examines their contents under a microscope. By carefully examining the cellular material taken through a biopsy, the doctor will be able not only to determine the malignancy or benignity of the pathology, but also to identify the degree of damage to the organ. When planning surgery, the need for a biopsy increases. After the study, a written conclusion is issued. The duration of a puncture biopsy depends on the number of lesions being punctured. No special preparation is required to perform a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. The TAPB procedure is well tolerated by patients. A hypoallergenic sterile patch is glued to the injection site, which can be removed after 20 minutes. 5-10 minutes after the biopsy, the patient can lead a normal life.
Side effects and possible complications of TAPP
The occurrence of moderate pain at the site of TAPE is associated both directly with tissue damage in the manipulation area, and sometimes with the possible development of delimited hematomas, which resolve safely. Discomfort, pain in the neck, and headaches can be triggered by throwing back the head during TPA if the patient has cervical osteochondrosis.
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy is today the most valuable and informative method for preoperative differential diagnosis of various nodular formations. This is the only method that allows one to reliably confirm or refute the malignant nature of the process. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is critical in determining treatment strategy.
Using fine-needle aspiration puncture biopsy, you can obtain reliable and accurate information about changes in the tissues of the mammary and thyroid glands in order to identify the disease at an early stage and begin effective treatment.
FAQ
Is a fine needle aspiration biopsy really appropriate for me?
Fine needle aspiration biopsy is the only non-surgical method for determining whether a nodule in the organ being examined is benign or malignant.
The large tumor must be removed. In this case, am I also indicated for a fine-needle aspiration biopsy?
Yes, it is indicated to determine the extent of surgical intervention. Sometimes a node may have tumors of different histological structures. Knowing this in advance, the surgeon plans and carries out more competent treatment accordingly.
Should fine needle aspiration biopsy be ultrasound guided?
Yes, definitely! Tumors are often located close to blood vessels, neurovascular bundles and other organs. In order to avoid their traumatization during biopsy, the latter should be carried out under ultrasound control.
Can a node “degenerate” into a malignant one after a biopsy?
NO!!! Fine-needle aspiration biopsy does not cause malignancy (degeneration into a malignant neoplasm)!
Can a biopsy cause the tumor to spread?
There is no data in world practice to prove tumor spread after fine-needle aspiration biopsies.
The life of each of us depends only on ourselves. How to get maximum pleasure and minimum suffering from it? - try to maintain your health, strengthen your immune system, carry out the necessary prevention and treatment in a timely manner, and, accordingly, diagnosis.
Make an appointment for ultrasound diagnostics and an appointment with an oncologist-mammologist at the Clinic in Severny by calling +7.
Author of the article: ultrasound doctor Irina Yurievna Novikova.
Anesthesia
The method of pain relief during follicular puncture is selected for each patient individually. In this case, the patient’s psycho-emotional state, her individual characteristics, and the level of pain threshold are taken into account. If there is increased anxiety or fear on the eve of a puncture, it is recommended to take tranquilizers - drugs that balance the functioning of the central nervous system.
When puncturing follicles, the following types of anesthesia are used:
- General anesthesia. The drugs are administered intravenously or inhaled. Under their influence, a woman loses sensitivity to pain, relaxes and temporarily loses consciousness.
- Sedation is the introduction of a woman into a shallow sleep. There is no discomfort or pain.
- Local anesthesia is used only if there are contraindications to general anesthesia. In most cases, an anesthetic is injected into the cervix, which numbs the posterior vaginal vault, the area where the piercing will be done.
- Combined - simultaneous use of local and intravenous anesthesia.
When the ovarian puncture is carried out in a natural cycle, that is, the contents of one follicle need to be taken, then anesthesia is not required.
A little anatomy
Content:
- A little anatomy
- Indications for manipulation
- Contraindications for puncture
- Technique of pleural puncture
- Features of the procedure for different types of effusion
- Pleural puncture in children
- Laboratory test results
- Complications of pleural puncture
The serous membrane that lines the lungs and the surface of the chest is called the pleura. In the normal state, between its two sheets there is from one to two milligrams of straw-yellow liquid, which is odorless and viscosity, and is necessary to ensure good sliding of the pleural sheets. During physical activity, the amount of fluid increases tens of times, reaching 20 ml.
At the same time, some diseases can also lead to changes in the composition and increase in the contents of the pleural cavity. Diseases of the cardiovascular system, post-infarction syndrome, cancer, lung diseases, including tuberculosis, and even injuries can cause disruption of the outflow of pleural fluid, which provokes the so-called pleural effusion.
An increase in the volume of fluid in the pleural cavity (effusion), the accumulation of air in it that does not escape due to a mechanical obstruction (pneumothorax), as well as the appearance of blood caused by various types of injuries, tumors or tuberculosis (hemothorax) can lead to respiratory or heart failure. In order to clarify the diagnosis and in cases where the patient’s condition is rapidly deteriorating and there is no time left for a detailed examination to save his life, doctors make the only right decision - performing a pleural puncture.
Technique for follicle puncture
Ovarian puncture is a surgical intervention that is performed in compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis in an operating room. The patient is asked to change into sterilized or disposable clothing. Before a woman is put under anesthesia, her blood pressure is measured and some indicators of the cardiovascular system are recorded. After the onset of anesthesia, the gynecologist treats the puncture site with an antiseptic solution. The cervix is exposed in the speculum and fixed with bullet forceps. The inferior speculum is then removed and a hollow needle attached to an ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina. Using ultrasound, the doctor locates the ovary and follicles, pierces them successively and sucks out the contents.
The average duration of a puncture is 15-20 minutes.
The follicular fluid along with the eggs is transferred to the embryology laboratory. Before fertilization, the oocytes undergo a thorough check. The next stage is the interaction of eggs and sperm. When there is not enough genetic material, fertilization is carried out using the ICSI or PIXI method. In some cases (with massive adhesions in the pelvis, abnormal location of the ovaries), it is impossible to obtain eggs using transvaginal puncture. In such cases, the woman is offered laparoscopy.
Laboratory test results
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The puncture material is examined for tumor cells and pathogenic microorganisms. It also determines the amount of protein, enzymes and blood components.
The accumulation of excess proteins in the pleural cavity indicates the inflammatory nature of the fluid as a result of pneumonia, tuberculosis, pulmonary embolism, lung cancer or diseases of the digestive tract, as well as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus erythematosus.
The cause of insufficient protein content in the effusion can be heart failure and a number of other diseases, including sarcoidosis, myxedema, glomerulonephritis.
Blood cells in the effusion are a consequence of injuries or tumors of the pulmonary artery. The detection of tumor cells indicates the presence of metastases and new malignant formations.
Bacteriological analysis of effusion allows us to identify the causative agents of infectious pleurisy.