Elbow joint
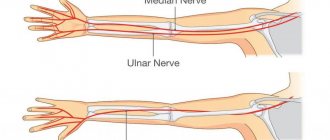
is a unique connection of three bones: humerus, radius and ulna. This is a complex combined joint, which includes three simple joints: humeroulnar, brachioradialis, proximal radioulnar. All of them are united by one common capsule and articular capsule (cavity). Inside the joint capsule, synovial fluid is constantly produced, which serves as a lubricant for the rubbing articular surfaces and nutrition for the anatomical parts. The ends of the bones are covered by a layer of periosteum, which helps protect and renew bone tissue, and also facilitates the supply of nutrients from the synovial fluid. All articular surfaces are covered with articular cartilage. The elbow joint is securely strengthened by ligaments and protected by a good muscular frame. These features allow you to perform four types of movements: extension and flexion, supination (rotation of the forearm in the elbow joint, in which it is possible to turn the hand with the palm up) and pronation (rotation of the forearm in the elbow joint, in which it is possible to turn the hand with the palm down). It is worth noting that the top end of the ulna has an olecranon process, shaped like a hook. The triceps brachii muscle is attached to it. A fracture of this process is a fairly common injury.
Types of damage
The following categories of diseases are characteristic of the elbow joint:
- Traumatic
Bruises. The most common injuries are to the olecranon, periarticular tissues, humeral condyles and ulnar nerve. - Ligament sprains
- Dislocations. There are: isolated dislocation and pronation subluxation of the radial head; dislocations of the forearm posteriorly, anteriorly, inwardly, outwardly; divergent dislocations with rupture of the proximal articulation and divergence of the bones of the forearm to the sides
- Fractures of the bones of the elbow joint according to the nature of the damage can be divided into: intra-articular;
- periarticular;
- closed;
- open;
- no offset;
- with displacement of fragments (displacement of bone fragments most often occurs with fractures of the olecranon)
- Epicondylitis (“tennis elbow”) is an inflammatory and degenerative disease that affects the tendons in the elbow joint due to chronic overload of the forearm muscles.
- Osteoarthritis is a dystrophic-degenerative disease of the cartilage and bone tissue of the joint.
Injections for pain: what does an elbow joint block give?
The concept of “therapeutic blockade” when used
In medicine, the therapeutic technique of injecting pain and analgesic drugs is called a blockade. The doctor injects the medicine directly into the damaged joint, muscle or bone tissue, depending on the location of the damage.
After administering the solution, the aching elbow stops bothering me. This method of treatment is more effective than ointments and tablets, because... the maximum amount of necessary substances enters the inflammation zone .
The blockade will allow you to do without surgical intervention.
Why does the inflammatory process develop:
- joint bruising
, which can occur during injuries. - Dislocations, fractures, bone deformations, stretching or rupture of muscle fibers and tendons are the reasons why the elbow is damaged.
- The elbow can deteriorate due to excessive stress on it during professional sports.
- Complications that occur due to arthritis, with the destruction of cartilage and bone tissue.
The therapist finds out what caused the injury. A general blood test, x-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging help identify pathology. Only after the examination is the procedure prescribed. Such a careful approach is necessary to select a medicine suitable for the disease. Anesthesia is administered to reduce the pain threshold.
Purpose of cutting:
- restore joint mobility;
- treat the damaged area with medications;
- prevent complications.
Drug blockade in action: how it affects the body
The elbow provides flexion/extension/rotation of the arm. This is a movable joint connecting the shoulder and forearm. When under load, due to physical stress, the connective tissues are stretched, microscopic tears occur in the tendons of the forearm, and therefore microcracks occur. Because of this, the elbow joint becomes inflamed, which leads to its pathology.
To eliminate the disease, an injection blockade is performed. The medicine is injected locally into the damaged area of the elbow through a syringe. It instantly affects the body, because... the anesthetic solution passes to the nerve fibers and settles on their surface. Pain conductors are “closed” (blocked), so painful sensations do not enter the brain. The drug method works if traditional methods of treatment are unsuccessful.
An injection with anesthetics or anti-inflammatory drugs is administered:
- into the soft tissue around the moving bone joints;
- into the intra-articular or intraosseous area.
The discomfort goes away after a few seconds. If the elbow is deformed or the integrity of the tendon is damaged, the blockade is one-time use. For arthrosis, arthritis, osteochondrosis, several injections are prescribed.
Classification of blockade procedures:
- Painkillers are used for piercing painful sensations, and local anesthetics are used. The pain decreases within a few minutes.
- Suppressing the inflammatory process ,
the injections include synthetic analogues of hormones. - Stimulating cellular nutrition. The goal is to activate metabolism and restore damaged cartilage.
The blockade will eliminate stiffness and discomfort. The advantage is that the session can be done multiple times, because... There are no negative manifestations with injections. Intra-articular injections do not cause infection. The positive therapeutic effect appears instantly.
How is the procedure performed?
The blockade is done in medical institutions. You should prepare for it. Before going to the doctor, take a shower. If a girl has long hair, she pins it up. There is no talking during the procedure.
The affected area is treated with an antiseptic. The articular sinus is pierced with a syringe filled with a solution, and the medicine is slowly injected directly into the joint, at the painful point of the elbow. After injection, the drug covers (envelops) the cartilage tissue with a protective film, so there is no joint friction and overload is eliminated.
After the procedure is completed, you cannot move your hand; the elbow should be at rest for three hours. You should not strain your limb or lift heavy objects. My general condition has improved, but I need to limit the load on my sore elbow.
What is good for joints
Blockade, as a therapeutic manipulation, cannot be considered a panacea for all ills; it is not the main method of treatment and will not eliminate the main cause of the pathology. Measures to prevent the disease include gymnastics and swimming.
Exercise will strengthen the elasticity of the muscles around your joints and protect them from damage. Physical exercise improves blood circulation, so cartilage tissue receives more active nutrition. The muscles are always toned and reduce the load on the joints. Spend a few minutes a day doing healthy exercises, and you will not be bothered by pain in the future.
Remember! During intense activity, the body loses moisture, primarily in the joints. The joint fluid becomes thicker, and lubrication of the joints deteriorates. Clean water will restore mobility to joints.
If it is not possible to quickly seek help from a medical facility, and the pain in the elbow becomes unbearable, folk remedies that are prepared at home will come in handy.
Massage your elbow, rubbing honey into it (you can add apple cider vinegar to it, the ingredients are taken in equal proportions). The procedure lasts 15 minutes. Rinse with warm water and wrap the sore spot with a warm thing.
Treatment with injection blockades will be effective if carried out in a comprehensive manner.
Additionally, physiotherapeutic and medicinal procedures are carried out. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Symptoms of pain
The main symptom of elbow disease is pain.
The following signs are typical for the traumatic group of injuries:
- Piercing pain at the time of injury
- Swelling and hematoma in the elbow joint
- Elbow deformity
- Restrictions in arm movements, partial or complete loss of limb function
- Or pathological mobility and the possibility of movements atypical for the elbow
- Numbness or tingling in the forearm, wrist, or hand
- Creaking or clicking noise when moving your elbow
- Any discoloration of the skin in the area of injury
- Palpable protrusion of bone fragments under the surface of the skin
If any of the above symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help from the traumatology department.
Pain in the elbow joint: causes
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, the human elbow joint is much more often exposed to injuries and stress than, for example, the knee joint. In addition, there are a number of diseases, one of the symptoms of which is pain in the elbow joint. This pathology may be caused by the following conditions:
- arthritis – infections, allergies or autoimmune diseases can cause arthritis. With arthritis, pain occurs in the elbow joint, a tumor forms around the joint, and its original appearance changes;
- arthrosis – pain in the elbow joint in this disease is caused by degenerative processes that occur in the cartilage tissue of the joint. Arthrosis is accompanied by destruction of the anatomical structures of the elbow joint;
- epicondylitis – pain in the elbow joint with epicondylitis is caused by an inflammatory process at the junction of the ligaments and epicondyle of the shoulder bone;
- injury to the elbow joint – pain in the elbow joint can be a consequence of previous fractures, bruises and dislocations;
- bursitis of the elbow joint - the occurrence of pain in this case is associated with an excessive amount of interarticular fluid in the synovial bursa of the joint.
Pain on the inside of the arm
The occurrence of acute pain in the arm on the inside of the elbow in the bend is most often associated with epicondylitis. The development of epicondylitis is caused by physical overload and severe stretching of the tendons. Normal movements are not accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the elbow, but increasing physical activity or frequent repetition of the same movements can lead to weakness and aching pain in the arm.
The risk group for developing this pathology includes people over 40 years of age whose activities require constant stress on their hands. Overexertion of the inner side of the arm causes the development of minor injuries and inflammatory processes, which, in turn, lead to the appearance of spasms, salt deposition, and the growth of scar tissue.
Pain in the elbow joint when flexing and extending
Pain in the elbow joint when flexing and extending may be associated with bursitis. The development of this disease is caused by an excessive amount and change in the composition of the interarticular fluid entering the synovial bursae of the elbow joint.
Bursitis can be acute or chronic. In addition to pain, the patient experiences redness of the skin in the elbow area, swelling, bumps and increased body temperature.
Elbow pain during exercise and heavy lifting
Such pain in the elbow joint may be a consequence of arthrosis. When you move your hand, a characteristic crunching sound occurs, but there is no intense inflammatory process.
The lack of timely treatment for arthrosis threatens its progression, as a result of which normal mobility of the arm is lost, the amplitude of permissible movements decreases, and other joints are affected.
Pain in the elbow joint when clenching a fist
If a patient feels pain when clenching his fist, osteochondrosis of the elbow joint can be suspected. The development of this disease is associated with metabolic disorders, dysfunction of the endocrine glands, old joint injuries, as well as previous surgical interventions on the elbow joint.
In patients with advanced stages of osteochondrosis, elbow deformity is observed, fingers become numb, and limb mobility is impaired.
Aching pain in the elbow joint
The appearance of aching pain in the elbow joint may indicate developing arthritis. The development of such a pathology is associated with frequent injuries to the elbows or hands, as well as ruptures of tendons and ligaments, various infectious diseases and disruption of the body’s immune system. In the absence of timely and proper medical care, patients may experience an increase in the size and density of the elbow and an increase in body temperature. The condition is accompanied by malaise, loss of appetite, development of fever and prolonged headache.
Acute pain in the elbow joint when pressing on the elbow
Acute pain when pressing on the elbow joint often manifests itself as severe injuries in this part of the body. In addition, similar pain in the elbow joint can occur due to bone cracks and rupture of muscles and ligaments. In the absence of the above prerequisites, pain in the elbow joint can be considered referred, initially arising in the spine and affecting the elbow.
This fairly common situation is most often encountered by patients who have been diagnosed with an intervertebral hernia. With this disease, patients' nerve roots are pinched, resulting in unpleasant sensations in the elbow joint. If the pain is reflected, there are no external changes in the joint, its mobility is not impaired.
Elbow pain due to cubital tunnel syndrome
Cubital tunnel syndrome is a neurological condition in which the ulnar nerve becomes compressed in the cubital tunnel. Such a violation is associated with microtrauma of the joints or individual anatomical characteristics of a person. In addition to pain in the elbow area, this syndrome is accompanied by numbness or tingling in the skin surrounding the joint, weakness in the limb, as well as pain spreading to other parts of the body (for example, the shoulder, little finger, ring finger).
If you have at least one of the above symptoms or pain in the elbow joint, you should consult a doctor, under no circumstances self-medicating, which, as a rule, only aggravates the problem.
Treatment Options
Treatment largely depends on the type and nature of the fracture in the elbow joint. For non-displaced fractures (for example, the olecranon), conservative treatment can be achieved by applying a fixing plaster cast for several weeks. If a joint has been displaced, then the issue of surgical intervention is decided. To do this, reposition the fragments (closed or open). With open comparisons, surgical fixation of fragments is required; this operation is called osteosynthesis. Osteosynthesis is the joining of bone fragments using special fixing agents (bone grafts or metal structures). If the fractures of the articular part of the humerus are fragmented, then it is possible to replace the elbow joint with a prosthesis. To restore the function of the elbow joint in case of deforming arthrosis, as well as in congenital and acquired deformities and contractures of other etiologies, osteotomy is currently performed. Osteotomy is a surgical operation that helps eliminate deformation of the elbow joint or improve the function of the musculoskeletal system through an artificial fracture with further fixation to give a functionally advantageous position. After any surgical intervention, the patient is prescribed rehabilitation measures drawn up by the attending physician individually for each person.
Signs and symptoms
Most often, the injury occurs due to a blow or fall on the hand. Most often, the symptoms are pronounced, so it is difficult for a person not to notice them. There may be a posterior dislocation of the joint, and this is the most common one. Occurs if a person falls on a straight arm or receives a blow to the elbow area. Anterior dislocation is diagnosed less frequently. It usually appears if there was a blow to the bent elbow.
The doctor can assume this type of injury based on the patient’s complaints. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, send for an x-ray. Based on the results of the study, it will be possible to confirm the guesses.
Symptoms:
- Intense pain. Often it turns out to be sharp, it is difficult for a person to bend his arm.
- Swelling of tissues. It gradually increases, especially if you do nothing.
- Numbness of the elbow. Sensation in the lower part of the limb may also be lost. This also usually indicates a dislocation.
- Increase in local body temperature. The skin in the damaged area will become hot.
- Weakening of pulsations of arteries in the limbs or complete absence.
If the listed complaints are present, the doctor will examine the hand and suggest a diagnosis. He may notice that the skin tone in the limb area has changed due to poor circulation. There may be a disturbance in the innervation of the hand.
Often the doctor is able to palpate the head of the radius from behind or in front, depending on the type of injury. An x-ray should confirm the fact that it has shifted. In some cases, rupture of the joint capsule may occur.
If an elbow dislocation has been confirmed, recovery will take some time. After starting treatment, the unpleasant symptoms should subside and the person will feel better. The main thing is to consult a doctor in a timely manner.