Among all tumors in the central nervous system, spinal cord lesions account for approximately 12% in adults and about 5% in children. What is the cause of these pathologies and how are they treated?
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists ALEXANDER SERYAKOV MD, professor, oncologist, hematologist, radiologist (radiation therapist) of the highest category, leading oncologist of the SM-Clinic holding »
Most often, tumors localized in the spinal cord are detected in people aged 30 to 50 years. Mostly, in about 85% of cases, they affect the membranes of the brain and surrounding structures.
What is a spinal cord tumor
“Spinal cord tumors,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov, “are pathological neoplasms of a malignant and benign nature that are localized in the spinal cord.
They are rare. By location there are:
- intramedullary (18 - 20% of cases) - grow inside the spinal cord;
- extramedullary (80 - 82% of cases) - located near the spinal cord, developing from nearby tissues.
Among benign lesions, the most common are ependymoma (63%) and astrocytoma (30%). Much less common are non-malignant hemangioblastoma and malignant oligodendroglioma.
Types of back pain
The severity of pain varies from mild aching to severe or even unbearable pain, shooting, radiating to other parts of the body.
Acute back pain
Common causes of acute back pain
- intervertebral disc herniation, trauma, entrapment of the spinal cord roots by hernial protrusions. The acute period lasts 1-2 weeks, after which the pain gradually subsides and becomes less pronounced. Possible shooting in the lower limbs, arms and other areas of the body.
Blunt pain
Dull pain in the back
characteristic of spinal cord diseases - multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, myelitis. The symptom is characteristic of muscle (myofascial pain) diseases, spinal cord tumors.
Throbbing back pain
Pulsating pain in the back may indicate the presence of inflammation and is often found with spinal tuberculosis, vertebral osteomyelitis, and vertebral compression fractures. Throbbing pain can occur with diseases of the internal organs of the chest, abdominal cavity and pelvis (depending on location).
Sticking pain
Stiffness and stiffness of the spine combined with pain are a characteristic sign of inflammation of the intervertebral joints. This symptom is characteristic of rheumatic diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Unbearable back pain
Severe pain that is not relieved by analgesics is possible with acute inflammation of the intervertebral disc, spinal cord infarction, cauda equina syndrome (when fragments of the intervertebral hernia fall into the spinal canal, compressing the spinal cord and damaging bundles of nerve fibers). Burning casualgic pain, which is described by patients as a feeling of a hot wire in the back, can occur when the hernia is poorly located due to ischemia of the spinal cord roots. In such cases, only narcotic analgesics or paravertebral blockades with local anesthetics and hormones bring relief.
Causes of spinal cord tumors in adults
The true causes of tumor growth that occurs in the spinal cord have not been determined to date. Scientists have identified a number of risk factors that may increase the likelihood of tumor growth in children or adults, but definitely do not lead to the formation of pathology. These include:
- hereditary predisposition (features of genes passed on from parents to children);
- exposure to substances with carcinogenic effects (chemical dyes, petroleum products);
- development of lymphoma (this is a malignant lesion in the lymphatic system);
- the presence of Hippel-Landau disease (a tendency to grow tumors, both benign and cancerous, is inherited);
- development of neurofibromatosis type 2 (this is a disease associated with gene breakdowns in which multiple tumors are formed - schwannomas or meningiomas in the area of nerves and the nervous system);
- exposure to harmful environmental factors (chemical pollution, radiation exposure);
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle - smoking, drinking alcohol, poor nutrition;
- constant stress;
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- Excessive tanning (in a solarium, on the beach).
Often several factors influence at once and special conditions must be created for the tumor to begin to grow.
Symptoms of a spinal cord tumor in adults
There are no typical or characteristic symptoms only for a tumor; all signs can mimic other diseases, especially in the early stages.
Therefore, you should consult a doctor to determine or rule out the problem with the following complaints. Pain syndrome. The most common manifestation of a tumor is pain that occurs in the area of the spine where the tumor began to grow. In the early stage, the pain may be mild or more severe, but there are no significant neurological symptoms. As the tumor progresses, disturbances in sensitivity and movement occur, the pain becomes stronger against the background of coughing or sudden movements, sneezing, physical activity, at night and when moving, tilting the head.
Movement disorders. Muscle weakness is also possible, which occurs in combination with sensitivity disorders, the phenomenon of muscle atrophy, sharp and sudden contractions, twitching of muscle groups that are relaxed.
Sensitivity disorders. Sometimes there is no pain, but superficial sensitivity may suffer, while maintaining a deep tactile sense. The patient may not feel pain, temperature, or touch, but perceives pressure and vibration.
Problems with the functioning of the sphincters. Possible disturbances in urinary functions and, less commonly, bowel movements. This leads to retention of urine or stool.
Also, as the process progresses, scoliosis of the spine may occur, which is formed due to pain, motor dysfunction or destruction of the vertebral bodies.
It is impossible to identify spinal cord tumors externally; they are located quite deep in the spinal canal.
Symptoms
Signs of a spinal cord injury usually appear immediately and do not raise doubts when making a diagnosis. When the spinal cord is damaged, the following symptoms occur:
- Impaired consciousness (disorientation, loss of consciousness, coma);
- Pain in the area of injury;
- Headache;
- Vomit;
- Double vision;
- Breathing disorders;
- Confusion of speech;
- Numbness of areas of the body below the affected area;
- Paralysis;
- Incontinence of feces and urine.
The most dangerous is considered to be damage to the spinal cord in the cervical region, since in this case there is a risk of developing paralysis of the entire body. With this injury, brain function is disrupted and breathing may stop.
Muscle spasm due to spinal cord rupture
A symptom of spinal cord injury may be muscle spasticity. In this condition, pathological muscle tone is observed, which increases with tension and passive movement. Spasticity does not allow you to control muscles, move freely, or speak.
It is characterized by involuntary muscle twitching, which is associated with impaired nerve conduction due to spinal cord injury. However, the presence of spasticity may indicate that the connection between the muscles and the brain remains. Thus, when the spinal cord is ruptured, spasticity is a good sign that increases the chances of restoring normal function of the limb.
Make an appointment
Classification of spinal cord tumors in adults
There are many options for classifying tumors localized in the spinal cord.
It is possible to divide into groups according to a number of characteristics - the location of the tumor focus relative to the spinal cord, spine or meninges, features of the histological picture, as well as the specific location of the lesion. If we divide tumors by origin, they can be classified into two groups:
- primary is tumor tissue that developed from the cells of the spinal cord itself, its roots or membranes;
- secondary are tumors of a different localization that affect the spinal cord (including metastatic ones).
Based on the location of the tumor, they can be divided into several groups:
- extradural tumor - a lesion above the area of the dura mater;
- intradural – tumor under the dura mater;
- intramedullary - grows inside the spinal cord, originating from its cells.
Tumors can be located behind the spinal cord, in front, on the sides, affecting the cervical or thoracic, lumbar or sacral regions.
There is a very wide classification based on the origin and type of cells; tumors are determined based on biopsy data.
Vascular diseases of the spinal cord: treatment and diagnosis
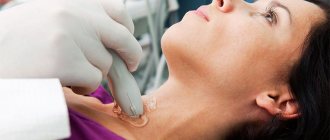
The diagnosis and treatment of vascular pathologies of the spinal cord is usually carried out by a neurologist. At the initial appointment, he collects a complete medical history, asks the patient about chronic and hereditary diseases, about troubling symptoms and the period in which they appeared. Based on the clinical picture, we can assume the presence of damage to any vascular system. The patient usually does not require laboratory examination. Most often they resort to the following instrumental diagnostic methods:
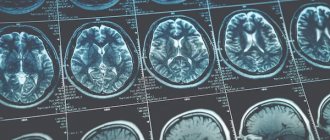
● magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spinal column. It is recognized as the most effective (sensitive) imaging technique for spinal cord disease. With its help, it is possible to diagnose soft tissue lesions (for example, neoplasms or abscesses), compression fractures, spinal cord parenchyma and other pathologies;
● myelography (with radiopaque agents). This technique is used less frequently than MRI, since it is invasive and not as informative. With its help, it is possible to detect lesions of the bone apparatus;
● electrophysiological studies. They are based on recording impulses of bioelectrical activity of the brain and nerve trunks. It allows you to accurately assess the degree of damage to the nerve pathways;
● spinal angiography. This is a lengthy examination in which the patient is given a large dose of contrast agent. It allows you to detect vascular disorders (in particular, aneurysms, occlusions and compressions, aneurysms);
● aortography. This diagnostic method is required in exceptional situations when there is a suspicion of an aneurysm, aortic occlusion or aortic valve insufficiency;
● echocardiography (EchoCG). Additionally, this non-invasive technique may be prescribed if the specialist suspects cardiac pathologies. With its help, intracardiac hemodynamics are assessed and many disturbances in the functioning of the muscular organ are detected;
● lumbar puncture. This is a procedure in which a specialist inserts a puncture needle into the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord (in the area of the spinal column). Further examination of the taken biomaterial allows us to detect signs of hematomyelia, excluding the infectious-inflammatory nature of myelopathy.
Detailed diagnostics are required to differentiate vascular diseases of the spinal cord from multiple sclerosis, spinal cord neoplasms, compression and infectious myelopathy. After a thorough examination, we proceed to prescribing the most appropriate therapy. Attempts at self-medication can lead to a number of negative consequences, so you should trust in the hands of professionals. Vascular diseases of the spinal cord are treated with two main methods - conservative and surgical. Let's take a closer look at the features of each method separately.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is a step-by-step process that allows you to determine the size and type of tumor and create a plan for its treatment.
First of all, the doctor is interested in the patient’s complaints, symptoms, and medical history. What is important is when the symptoms developed and how they changed over time. A full neurological examination is also carried out - determination of muscle tone, reflexes, muscle strength, spinal mobility, sensitivity.
To refine the pathology you need:
- MRI with contrast - this method helps to determine the condition of the entire spinal cord, its structures and determine the tumor;
- CT myelography is a technique for assessing the tumor border;
- diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor MRI;
- scintigraphy.
- direct angiography.
After clarifying the type, location and size of the tumor, a treatment plan is drawn up.
Modern methods of treatment
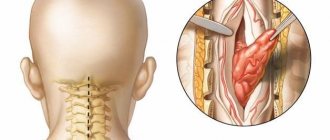
“The main type of treatment,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov, “is a neurosurgical operation in which the tumor is completely removed and decompression (removal of compression) of the spinal cord is performed.
Micro-neurosurgical techniques, intraoperative neuroimaging and neuronavigation are often used. For malignant tumors of the spinal cord, in addition to surgical treatment, the patient may be prescribed chemotherapy and radiation therapy (stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery using linear accelerators of the CyberKnife type).