The procedure during which a special needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space is called a lumbar puncture (spinal, lumbar or spinal puncture, lumbar puncture or spinal puncture). The main purpose of the procedure is to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for further research, which will identify the exact causes of nervous diseases, infections and systemic pathologies. Lumbar puncture is also performed for therapeutic purposes. Before carrying out the procedure, it will be useful to know in what cases it is indicated and when it is prohibited. And when studying the technique of performing a lumbar puncture, the patient will understand that the manipulation is not dangerous to health. However, there is a possibility of some complications after it.
Basic information
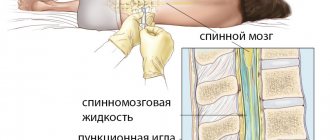
Spinal cord puncture is a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure during which cerebrospinal fluid is extracted from the subarachnoid space through a special needle.
There is an opinion that lumbar puncture is dangerous, since during it the spinal cord can be damaged. To understand that this is not so, you need to delve a little deeper into embryology.
During fetal development, the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, develops from the fetal neural tube. All components of the nervous system (neurons, peripheral nerves, subarachnoid cisterns, cerebrospinal fluid, etc.) have the same origin. Therefore, by the composition of cerebrospinal fluid from the caudal region of the back, the condition of the entire nervous system can be assessed.
The spinal cord ends at the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra
During fetal development, vertebrae grow faster than nerve tissue. For this reason, the spinal cord ends at the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra with the conus medullaris. Further, thin threads extend to the junction with the sacrum.
Thanks to this structure, it is safe to puncture the spinal canal in this place. According to doctors, the phrase “spinal cord puncture” is incorrect, since there is no spinal cord at the puncture site, only its membranes and cerebrospinal fluid are located here.
Reference. The volume of cerebrospinal fluid in an adult is approximately 120 ml. It is updated after 5 days.
Not all people understand why they take a spinal cord puncture. Lumbar puncture is done to achieve the following goals:
- Study of biological material in laboratory conditions for glucose, certain cells, proteins and other components.
- Determination of cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
- Removing excess cerebrospinal fluid.
- Introduction of drugs into the nervous system.
Now you know why a cerebrospinal fluid puncture is taken.
No ads 1
Lumbar puncture
- Before the procedure, the patient undergoes preparation: the lumbar area of the back is washed with water and antiseptic soap, the skin in the lumbar area is disinfected with alcohol, then with iodine and immediately covered with a sterile napkin. Next, the puncture site is numbed with local anesthetic.
- A lumbar puncture is made at the specialist's discretion in the space between the fourth and fifth or between the third and fourth spinous processes of the spine. Most often, the first puncture option is performed when treating children, and the second when treating adults. The guideline for choosing the desired interval is the curved line outlining the iliac vertebral bones.
- The patient is placed in a horizontal position on the couch on his side. His position at the moment should be as follows: bent legs tightly pressed to the stomach, head lowered and pressed to the chest. After the patient has taken the desired position, he is injected subcutaneously with a solution of novocaine, lidocaine or another anesthetic for pain relief.
As a rule, in order for the anesthesia to take full effect, you need to wait 10-15 minutes.
At the end of this period of time, the doctor carefully and accurately inserts a medical Beer needle with a 10-12 cm mandrel into the intrathecal space of the spine. The needle is inserted into the lumbar region exclusively in the sagittal plane with some upward displacement so that the puncture passes according to the location of the spinous formations.
When in contact with the interspinous and yellow ligaments, the needle experiences some resistance when moving into the spine. After this, it easily passes through the epidural tissue and again experiences difficulty passing only in the strong spinal membrane.
Lumbar puncture is almost always accompanied by a false sensation of the needle falling through, which can appear not only in the patient, but also in the doctor performing the procedure. This feeling should not be cause for concern as it is normal. After the needle has supposedly failed, it is necessary to advance it another 1-2 mm and remove the mandrin, which will immediately cause the cerebrospinal fluid to leak out of the needle. In adults, its outflow occurs at a depth of 4-7 cm, in children - 2 cm.
Liquor is a clear liquid that is released in small drops; if it does not flow out, the patient, at the request of the doctor, must cough or simply raise his head in order to slightly increase the fluid pressure inside the spine. A medical pressure gauge is used to measure its pressure.
When making a lumbar puncture, it should be taken into account that the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in an adult is approximately 120 ml, and the volume of secretion is 500 ml. per day. This way the liquid is completely renewed five times a day.
Indications for the procedure
As mentioned, a spinal tap may be performed for diagnosis or treatment. In the first case, the procedure is carried out when it is necessary to study the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid, identify pathogens in it, measure the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, as well as the patency of the subarachnoid (subarachnoid) space.
In the second case, the manipulation is carried out to evacuate excess cerebrospinal fluid and introduce medications (antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs) into the spinal canal.
Indications for lumbar puncture are divided into absolute and relative. In the first case, the procedure is mandatory, and in the second, it is recommended, but the decision is made by the doctor.
Lumbar puncture must be performed in the following cases:
- Infections affecting the central nervous system, for example, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Oncological formations in the membranes or structures of the spinal cord.
- Diagnosis of liquorrhea (leakage of cerebrospinal fluid) using radiocontrast agents.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding under the arachnoid membrane).
Relative indications include:
- Multiple sclerosis and other pathologies in which the myelin sheath of neurons is destroyed.
- Diseases characterized by systemic damage to peripheral nerves.
- Septic vascular embolism.
- Lupus erythematosus and other systemic connective tissue pathologies.
Meningitis is often preceded by an infection, and a lumbar puncture is performed to determine its cause.
During a lumbar puncture, the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the cerebrospinal fluid can be determined.
It is necessary to take cerebrospinal fluid for examination to determine intracranial pressure, the number of neutrophil granulocytes, and the presence of pathogenic bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae, meningococcus, pneumococcus).
A lumbar puncture is done to distinguish a stroke from other pathologies and to determine the cause of its development. A spinal puncture helps determine antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid, then doctors talk about multiple sclerosis. If tuberculosis is suspected, the cerebrospinal fluid is examined for sugar, neutrophils and lymphocytes. A spinal tap is performed to detect syphilis in asymptomatic cases.
Reference. By measuring cerebrospinal fluid pressure, hydrocephalus (water on the brain) can be detected. When evacuating 50–60 ml of fluid, most patients feel relief.
Lumbar puncture in newborns is performed if meningitis is suspected. The study will help identify the causative agent of infection (viruses or bacteria). The study will also help to identify the level of protein and red blood cells in a child, because their deficiency increases the risk of infectious diseases.
No ads 2
Lumbar puncture. Indications for use
Lumbar puncture or lumbar puncture with fluid collection (CSF) - insertion of a needle into the spinal canal at the lumbar level for diagnostic studies or administration of anesthesia. With the improvement of other diagnostic methods (MRI, CT and
Painless, unique technique
Cheaper than manual therapy
Soft, pleasant, children are not afraid of us
Free consultation from June 10 to June 20!
Using cerebrospinal fluid sampling, intracranial pressure is measured, subarachnoid hemorrhages, their degree and severity are determined, and puncture is also used for:
- diagnosis and treatment of pathologies after brain injury and treatment of spinal injuries;
- diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases;
- determination of sugar content;
- reducing intracranial pressure in the treatment of benign cranial hypertension or normal pressure hydrocephalus;
- administration of anesthesia, painkillers or chemicals, antibiotics;
- administration of contrast agents during radiography, myelography, encephalography or iodine-containing agents, oxygen, nitrogen, ozone, etc.
The spinal cord is protected by several layers of membranes (soft, arachnoid and hard), the space between which is filled with fluid. The epidural space, the space between the spinal cord and the spinal canal, is also filled with spinal substance. The fluid is taken, as a rule, from under the arachnoid layer. Normally, it should be transparent in color and slightly viscous in consistency.
Indications for cerebrospinal fluid collection
Lumbar puncture is performed:
- in the treatment of spinal diseases of chronic etiology and determination of subarachnoid hemorrhages in traumatic injuries of the spinal column, spinal cord, brain;
- in the treatment of infectious diseases of the central nervous system (encephalitis, meningitis, myelitis, tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.);
- for neurological diseases (multiple sclerosis, polyneuropathy, neuroleukemia, etc.);
- in the treatment of liquorrhea (leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose and ears after injury to the bones of the base of the skull or spine, after neurosurgical operations on the spine);
- in the treatment of dropsy of the brain (hydrocephalus) - excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain or in tumors of varying quality in the brain and spinal cord;
- in the diagnosis and treatment of arachnoiditis - serous inflammation of the arachnoid layer of the cerebral or spinal cord cortex.
Contraindications for lumbar puncture
Contraindications to cerebrospinal fluid sampling may include:
- intracranial hematoma or abscess of the brain or spinal cord (accumulation of pus in the brain matter) after traumatic injuries to the spine or skull;
- pronounced signs of pinching of the spinal cord, for example, with spinal stenosis, the treatment of which has just begun;
- compression of the spinal cord by an intervertebral hernia, the treatment of which requires surgery;
- combination of spinal injury with traumatic shock, severe bleeding and extensive soft tissue damage;
- bedsores, infectious, purulent and inflammatory processes in the lumbosacral region.
Lumbar puncture technique
Lumbar sampling of cerebrospinal fluid is performed with the patient lying on his side with his legs pulled up to his stomach, or sitting with his back slightly bent forward. The puncture site is treated with an antiseptic. Then a thin needle is gradually inserted into the intervertebral space, through which an anesthetic (Novocaine, Lidocaine) is injected. Next, a thicker puncture needle or Beer needle with a mandrel is inserted into the hole already made.
The manipulation is carried out strictly along the midline between the spinous processes of the vertebrae, making a slight upward slope and gradually moving inward through the muscular and ligamentous apparatus. A sign of a needle entering the subarachnoid space is a feeling of failure. If, on the contrary, an obstacle (bone) is felt along the path, then the needle is pulled back a little and its direction is slightly changed. The flow of fluid will indicate that the puncture was performed correctly.
The total amount of fluid required for the study of an adult is approximately 120 ml. After the procedure, the puncture site is sealed with a sterile napkin and the patient needs to lie on his stomach for 2-3 hours to restore the meninges and soft tissues. A lumbar puncture may cause a mild, dull headache or pain in the spine, which is caused by a decrease in intracranial pressure; it usually goes away 5-7 days after the procedure.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
When is spinal tap prohibited?
Before the procedure, you need to know in what cases lumbar puncture is prohibited.
Absolute contraindications:
- Marked swelling and increase in brain volume.
- Sudden increase in intracranial pressure.
- Neoplasms in brain tissue.
- Closed hydrocephalus is a pathology in which cerebrospinal fluid cannot independently enter the subarachnoid space due to obstacles.
If there are such contraindications, a child or adult is prohibited from having a lumbar puncture. Otherwise, the risk of axial herniation of the brain increases - this is a pathology in which part of the brain is displaced into the foramen magnum. Then the work of vital areas is disrupted, which threatens the death of the patient. Herniation can occur if the doctor uses a thick needle and removes a lot of cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal.
Carefully! If a lumbar puncture is necessary, and the likelihood of brain herniation is high, then a minimum amount of cerebrospinal fluid should be extracted. When symptoms of pathology appear, you must immediately inject the required volume of cerebrospinal fluid using a needle.
There are other contraindications for spinal puncture:
- Presence of pustules on the lower back.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Medicines that thin the blood (antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants).
- Blockade of the subarachnoid space.
- Bleeding due to local dilation and rupture of a vessel (aneurysm) in the brain or spinal cord.
- The period of gestation.
In the presence of such conditions, the doctor decides to perform the procedure, taking into account possible complications.
Technique for performing spinal cord puncture
The technique of performing a lumbar puncture is simple, but requires caution and knowledge of anatomy, so it is performed by an experienced doctor with the help of a nurse.
To perform a lumbar puncture, a special needle with a mandrel is used
First, the assistant prepares the kit for the procedure:
- gloves, mask;
- antiseptic solution that contains iodine;
- cotton wool;
- sterile underwear with a hole for the puncture site;
- Beer puncture needle with mandrin (rod for closing the lumen of the needle);
- test tubes with caps;
- adhesive plaster.
The nurse prepares the patient for the procedure and provides care after it.
Important. The main thing during a lumbar puncture is to correctly determine the puncture site. In some pathologies of the spinal column, it is impossible to pierce the spinal canal.
First, the doctor explains all the details of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection procedure to the patient. In addition, before the manipulation it is necessary to empty the bladder and intestines.
Lumbar puncture in the lateral position
In the ward, the patient must take a lying or sitting position. In the first case, the patient lies on the couch on his side, arching his back and pulling his knees towards his stomach (fetal position). In this position it is easiest to feel all the vertebrae, processes and even the distance between them.
In the second case, the patient sits on the couch and bends his torso forward to make it easier for the doctor to determine the puncture site in the lumbar spine.
Technique for performing lumbar puncture:
Symptoms and prognosis for spinal cord tumor
- The puncture point is determined, which is located between L3 – L4 (third and fourth lumbar vertebrae) or L4 – L5.
- The puncture area is wiped with an antiseptic three times, starting from the intervertebral area and continuing to increase the circumference.
- After the antiseptic has dried, the back is covered with sterile linen with a hole.
- An anesthetic injection is given; as a rule, Novocaine, Lidocaine or Ultracaine are used for this.
- The puncture needle is inserted into the previously determined space between the spinous processes at an angle, trying to adhere to the midline.
- The doctor punctures all layers in turn (for example, the yellow ligament, dura mater) until he penetrates the spinal canal. After passing through all the structures, the needle seems to fall into the spinal canal. If there is no such sensation, then you need to remove the mandrin; if the liquid leaks, then this indicates that the needle is already inside the canal. If the doctor has inserted the needle correctly, but the cerebrospinal fluid does not flow out, the patient is asked to cough or sit up to increase fluid pressure.
- Next, the liquid is collected in different test tubes of approximately 1 ml. The liquid should drain passively; do not extract it with a syringe.
- Then you need to measure the pressure, which is normally 100 - 150 mm Hg. Art. To get accurate results, you need to relax as much as possible. The pressure can be determined approximately: 60 drops of CSF is the norm. During inflammatory processes, the volume of cerebrospinal fluid increases.
- The needle is carefully removed, the puncture site is treated with an antiseptic and a sterile bandage is applied.
During a lumbar puncture, the needle is inserted between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae at a slightly inclined angle.
The procedure lasts approximately 30 minutes.
Lumbar puncture in newborns has its own characteristics:
- The child is held in a position on his side or sitting so that the lumbar region is flexed. In this case, you need to ensure that the cervical segment does not bend, because then the patency of the upper respiratory tract worsens.
- In very low birth weight premature babies, the puncture is made in the area between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae to avoid damaging the spinal cord.
- The depth of needle insertion is up to 1 – 1.5 cm.
Reference. With numerous lumbar punctures, adhesions appear, due to which the fluid may not flow out. Then the puncture is performed in an area slightly higher or lower.
The spinal puncture protocol is recorded in the medical history.
Technique for performing lumbar puncture.
No special preparation of the patient for spinal puncture is required. But first it is necessary to conduct a CT or MRI of the brain, evaluate the results and take into account contraindications.
For an experienced doctor, the lumbar puncture algorithm is not difficult. The patient's position is lying on the left side. The legs are bent as much as possible at the knee and hip joints, the knees are pressed to the stomach, the spine is bent, the chin is pressed to the chest, the hands are clasped around the knees.
Rarely, in some cases, for example in obese people, it is possible to perform a lumbar puncture in a sitting position. The body must be tilted forward as much as possible, with the spine bent.
A spinal puncture is done in the lumbar region. A typical point is the space between the spinous processes of the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae (L3-L4). It is also possible to do it in the intervals L2-L3, L4-L5. It is impossible to get a needle into the spinal cord, since in adults it ends at the level of the second lumbar vertebra (L2).
(c) Can Stock Photo
The puncture site is treated with antiseptics, after which local anesthesia with novocaine or lidocaine is applied in layers.
A lumbar puncture needle (Beer needle) is inserted along the midline between the spinous processes. When it passes the interspinous ligament, a sinking sensation occurs - this means that the needle has entered the epidural space. The needle is passed a little deeper through the dura mater and arachnoid membrane, after which the mandrel is removed and the cerebrospinal fluid begins to flow. If the needle rests on the bone, it must be removed, leaving the end in the subcutaneous tissue, then change direction and insert until the needle passes through the interspinous ligament. Having received the required amount of cerebrospinal fluid, the needle is removed and the puncture site is covered with a sterile napkin. (c) Can Stock Photo
After the procedure, the patient should lie on his stomach for at least two hours, as cerebrospinal fluid may continue to leak into the epidural space for some time. After the puncture, a headache may occur due to a decrease in intracranial pressure. This usually goes away without treatment in 5-7 days.
Sometimes, when performing a lumbar puncture, the needle can damage the epidural venous plexus, which will be accompanied by the release of cerebrospinal fluid mixed with blood. Receipt of travel blood may be mistaken for subarachnoid hemorrhage. To eliminate such errors, several methods exist to distinguish travel blood from true SAH.
- Having received blood-stained cerebrospinal fluid, you need to slightly pull the needle towards you. If travel blood is present, the fluid in subsequent samples will become lighter in color.
- If bloody cerebrospinal fluid gets on a white tissue, such as a gauze pad, then with true SAH the spot will remain uniformly colored, and in the case of travel blood, a rim of clear fluid will appear around the spot. This is called the double spot symptom.
- After centrifugation, the cerebrospinal fluid in SAH will always remain xanthochromic (reddish), and in the presence of travel blood it will become colorless.
Feelings during the procedure
Many patients are interested in the question of whether it is painful to perform a lumbar puncture. If the procedure is performed correctly, the patient does not feel any significant discomfort or pain. He can feel the needle passing through the hard membranes, but there is no painful reaction. Unpleasant symptoms do not appear, since the doctor administers an anesthetic solution before the puncture.
You may feel an electric shock if the needle hits a spinal nerve. Some patients experience headaches during the procedure.
[node:field_similarlink]
Rules of conduct after puncture
It is recommended to lie on your stomach for 3 hours after a lumbar puncture. It is also prohibited to lift heavy objects or subject yourself to physical stress. If these rules are followed, the patient will be able to avoid leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the hole.
If medications are administered into the subarachnoid space, the patient must remain in bed for at least 3 days.
Carefully. If there is an increase in temperature, numbness or fluid discharge from the hole after the puncture, you should visit a doctor.
Regimen after lumbar puncture
Some doctors believe that bed rest does not prevent the development of post-puncture syndrome, and therefore they are allowed to walk immediately after a lumbar puncture. However, most of the authors conclude that bed rest has a positive effect, and the position of the patient and the duration of bed rest are discussed (most stopped at 3-4 hours). The patient should be in a horizontal position, lying on his stomach. After a lumbar puncture, general cerebral symptoms may occur (nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness), in combination with the body’s autonomic reaction, it has a characteristic feature - deterioration when trying to get up. The patient needs to create peace, lower his head, offer plenty of warm drinks and (or) intravenous administration of plasma substitutes. When contrast agents or oxygen (air) are administered, bed rest can last up to three days.
Research results
As a rule, CSF is collected in 3 containers, which are then sent for general, biochemical and microbiological analysis.
Doctors pay attention to the color of the cerebrospinal fluid:
- Bloody - an admixture of blood in the fluid may indicate blood leaking into the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater.
- The yellowish color of the CSF indicates long-term development of hemorrhagic processes, for example, subdural hematoma (accumulation of blood between the brain and membranes), metastases in the meninges, blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways.
- Grayish-green – neoplasms in the brain.
- Transparent – the person is healthy.
The ventricular mass is carefully examined, doctors measure pressure, determine the amount of protein, glucose, etc.
Normal results of a cerebrospinal fluid test look like this:
- liquid color – transparent;
- protein level – from 150 to 450 mg/l;
- glucose concentration – from 4 to 60% of the blood level;
- there are no atypical cells;
- leukocytes – up to 5 in 1 mm³ of blood;
- neutrophils and red blood cells are absent;
- pressure – from 150 to 200 mm Hg. Art.
Important. If the cerebrospinal fluid pressure is higher than normal, then decongestant therapy should be performed. If this indicator is underestimated, then this indicates brain pathologies.
Red blood cells, neutrophils and pus indicate blood diseases. Atypical cells are found in brain tumors, and sugar levels decrease in bacterial meningitis.
Lumbar puncture will allow timely identification of many dangerous diseases and treatment.
No ads 3
What does a lumbar puncture show?
Normally, the cerebrospinal fluid should be colorless, transparent, the protein content ranges from 150 mg/l to 450 mg/l, the amount of glucose is up to 60% of the content in the blood, leukocytes no more than 5000 per 1 mm3, red blood cells, neutrophils are absent.
Any deviations from the norm may indicate certain pathologies.
In particular, the bloody color of the cerebrospinal fluid indicates subarachnoid hemorrhage, the yellowish color indicates a late-stage hemorrhagic process, and the grayish-green color indicates a malignant brain tumor.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Complication of spinal cord puncture
Consequences of puncture are rare (in 1–5 patients out of 1000):
- displacement and herniation of brain tissue;
- the appearance of symptoms of meningitis due to irritation of the meninges;
- neuroinfections as a result of violation of antiseptic rules by doctors;
- severe headache may be associated with impaired CSF circulation;
- severe pain along a certain nerve when the spinal cord roots are damaged;
- hemorrhages due to bleeding disorders or taking medications that thin the blood;
- epidermoid cyst;
- meningeal reaction - changes in CSF parameters after the administration of medications or contrast solutions.
These are the main complications that can occur after a lumbar puncture.
Indications for spinal cord puncture
A spinal tap is most often used when central nervous system infections such as meningitis and encephalitis are suspected. Multiple sclerosis is very difficult to diagnose, so a lumbar puncture is indispensable. As a result of the puncture, the cerebrospinal fluid is examined for the presence of antibodies. If antibodies are present in the body, the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is almost established. The puncture is used to differentiate a stroke and identify the nature of its occurrence. The cerebrospinal fluid is collected into 3 test tubes, and later the blood mixture is compared.
With the use of lumbar puncture, diagnostics help to detect inflammation of the brain, subarachnoid bleeding or determine herniated discs by injecting a contrast agent, as well as measure spinal cord fluid pressure
In addition to collecting liquid for research, specialists also pay attention to the flow rate, i.e. if one clear drop appears in one second, the patient has no problems in this area
In medical practice, spinal cord puncture, the consequences of which can sometimes be very serious, is prescribed in order to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid and thereby reduce intracranial pressure in benign hypertension, and is carried out to administer medications for various diseases, for example, chronic normotensive hydrocephalus.
Contraindications to lumbar puncture
The use of lumbar puncture is contraindicated for injuries, diseases, formations and certain processes in the body:
In any case, the doctor first conducts a series of tests to make sure that there is an urgent need to prescribe a spinal tap. Consequences
it, as already noted, can be very, very serious, since the procedure is risky, and it is associated with certain risks.
Spinal cord puncture and its consequences
The first few hours (2-3 hours) after the procedure should not get up under any circumstances, you must lie on a flat surface on your stomach (without a pillow), later you can lie on your side, for 3-5 days you should observe strict bed rest and do not take standing or sitting position to avoid various complications. Some patients experience weakness, nausea, spinal pain and headache after a lumbar puncture. The doctor may prescribe medications (anti-inflammatory and painkillers) to relieve or reduce symptoms. Complications after lumbar puncture may occur due to incorrect procedure. Here is a list of possible complications as a result of incorrect actions:
If the procedure was performed by a qualified specialist, all necessary rules were strictly followed, and the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, then its consequences are minimized. Contact our medical center, where only experienced doctors work, do not risk your health!
Lumbar puncture of the spinal cord (lumbar puncture, spinal, lumbar or spinal tap) is performed in the lower back, in the lumbar region of the spine. During surgery, a medical needle is inserted between the two lumbar bones of the spine (vertebrae) to either obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, numb the area for therapeutic or anesthetic purposes, or carry out treatment.
The procedure allows specialists to detect dangerous pathologies:
- meningitis;
- neurosyphilis;
- abscess;
- various central nervous system disorders;
- multiple demyelinating sclerosis;
- all kinds of cancer of the brain and spinal cord.
Doctors sometimes use a lumbar puncture to administer pain medications during chemotherapy.
Cost of the procedure
Prices for spinal puncture depend on the level of the clinic, the complexity and nature of the procedure.
In Moscow, the cost of lumbar puncture differs depending on the medical institution:
- Clinic "El. En." — 5400 rubles.
- "PENTA-CLINIC" - 3350 rubles.
- Medical - 2300 rubles.
- Central Clinical Hospital No. 2 of JSC Russian Railways - 1,700 rubles.
- Clinical Hospital No. 119 – 1500 rubles.
- Children's Clinical Hospital named after Semashko - 1450 rubles.
The higher the qualifications of the doctors, the better the equipment of the medical facility and the more complex the procedure, the more you will have to pay for it.
Reviews
Almost all patients respond positively to lumbar puncture. The procedure does not cause significant discomfort or pain, but provokes mental stress. In most cases, there are no complications after a lumbar puncture, although it all depends on the skill level of the doctor.
Irina, 45 years old: “I was treated several times in an inpatient setting for meningitis, and then a lumbar puncture was prescribed. It was scary the first time, but then I realized that there was nothing wrong with it. I felt a slight pain only during the anesthetic injection, then there was a sensation of interference in the lower back, but it became numb. The main thing is to find an experienced doctor, because you can remain disabled if you catch a nerve.”
Ekaterina, 34 years old: “I had a lumbar puncture twice for suspected meningitis. There were no serious complications after the procedure, although after the first time I had a headache. The second time I asked the doctor to make a puncture with a smaller needle, then I didn’t feel anything at all, and there was no headache.”
Igor, 44 years old: “I had to do a spinal tap 3 times. During the procedure, pain is not felt, only movement in the lumbar region was heard, this causes psychological discomfort. I tried to distract myself and stopped paying attention to it. There were never any complications after the study.”
Main conclusions
As you can see, lumbar puncture is an important and also informative diagnostic and treatment procedure. Most often it is prescribed for neuroinfections, suspected subarachnoid bleeding, malignant process, autoimmune pathologies of the nervous system. It is contraindicated in cases of severe cerebral edema, a sharp increase in intracranial pressure, the presence of a large tumor in the brain, etc. There are some features of performing a lumbar puncture for children and adults. To ensure that the procedure goes without complications, you need to contact an experienced specialist. After a lumbar puncture, the cerebrospinal fluid is sent for research, during which dangerous diseases of the nervous system can be identified and treated. Most patients who have had a lumbar puncture are satisfied with its results; they claim that there is no discomfort or pain during it.