Causes of heaviness in the head
Physiological factors
The most common causes of heaviness in the head are fatigue and lack of sleep.
Your eyes get stuck together, you want to quickly put your head on the pillow and fall asleep - this situation is typical for overwork. Symptoms that develop periodically after exercise usually do not pose a threat to a person. After a good sleep, the discomfort disappears. When such violations bother you too often, you should pay attention to your health status. Heaviness in the head occurs in many people under the influence of sea motion. Seasickness is diagnosed in every third adult and is manifested by dizziness, a feeling of “fog in the head,” and nausea. In most cases, symptoms are mild and can be managed without medication. Heaviness with pressing pain in the head also occurs with motion sickness in land transport.
Tension headache
This type of cephalalgia is sometimes manifested not by classic pressing or squeezing pain, but by heaviness in the head. The symptom occurs some time after waking up and may disappear after a few hours or last the whole day. Unpleasant symptoms are of moderate intensity and are not combined with acute pain or dizziness. In strength and character, the heaviness is similar to the feeling of a hoop squeezing the head.
Arterial hypertension
With high blood pressure, heaviness is observed in the occipital area of the head, which is aggravated in a lying position, when bending over, or straining. Discomfort becomes more noticeable during physical activity and stress. If the patient does not follow the recommendations for taking medications, does not control blood pressure, heaviness in the head bothers him every day. The spread of discomfort to the frontal area and the appearance of sharp pain is a sign of an incipient hypertensive crisis.
Heaviness in the head
Infectious processes
Most bacterial or viral infections in the prodromal period are manifested by low-grade body temperature, which provokes heaviness in the head. Symptoms are complemented by moderate pain in the joints and muscles, and drowsiness. Patients describe their condition as malaise or weakness. After 1-2 days, when the full picture of the disease unfolds, the severity is often replaced by classic cephalgia.
ENT diseases
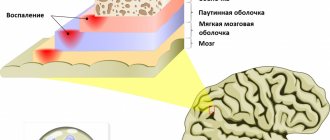
The appearance of heaviness in the head during inflammatory otolaryngological pathologies is caused by general intoxication and malaise, accompanied by an increase in temperature. The symptom can occur with more serious damage to the organ of hearing, which is due to the spread of the process to the vestibular analyzer. Severity is usually accompanied by dizziness, nausea, and lack of coordination. The main ENT causes of discomfort:
- Sinusitis.
Heaviness in the frontal zone is observed with frontal sinusitis or ethmoiditis, which is associated with the accumulation of inflammatory exudate in the paranasal sinuses. Symptoms intensify when the head is tilted forward and pressure is applied to the bridge of the nose. The patient is also concerned about nasal congestion, mucopurulent discharge, and fever. - Eustachite.
Heaviness in the head in those suffering from inflammation of the auditory tube is due to the involvement of the structures of the middle ear in the process. In addition to this symptom, the patient complains of noise and ringing in the ears, and notices hearing loss. A pathognomonic sign of eustachitis is a feeling of resonance of one’s own voice. - Meniere's disease.
The disease is characterized by paroxysmal heaviness in the head, occurring simultaneously with dizziness and episodic unilateral loss of hearing. The patient experiences a feeling of rotation of surrounding objects or a feeling of “sinking” of his own body.
Pathologies of the cervical spine
Damage to the vertebrae or neurovascular structures located in this area is a typical cause of heaviness in the head in middle and older age. Symptoms appear against the background of osteochondrosis and cervical spondyloarthrosis. Patients complain of heaviness and dull pain in the head, which is accompanied by pain in the back of the neck. When making sharp turns or staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time, the pain becomes shooting, burning.
Paroxysmal heaviness in the back of the head, headaches and impaired coordination of movements develop with vertebral artery syndrome, which occurs as a basilar migraine. Occasionally, heaviness in the head is caused by congenital structural anomalies - Klippel-Feil syndrome, platybasia, basilar impression. In this case, symptoms mainly manifest in childhood.
Neurasthenia
A painful heaviness in the head that begins at the end of the day is a characteristic manifestation of asthenic neurosis. Patients experience an unpleasant feeling of pressure on the head from all sides, as if they were wearing a heavy and tight helmet. The clinical picture is complemented by dizziness. Its peculiarity is that surrounding objects seem motionless to a person, and rotation occurs “inside the head.”
In addition to physical symptoms, emotional disturbances are noted. Patients are characterized by increased nervousness, irritability and excitability. They react negatively to extraneous noise, loud speech, and large crowds of people. The patient feels that being around strangers makes the heaviness in his head intensify. Characterized by difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings at night and disturbing dreams.
Rare causes
- Withdrawal syndrome:
after using drugs, alcohol. - Intoxication
: heavy metals, organic solvents. - Polycythemia.
- Injuries
: concussion or contusion of the brain, subcutaneous hematoma in the scalp.
Features of the condition and symptoms
It is necessary to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms so that it is easier to identify the cause of the swelling in the head.
Pressure, swelling of the head is often accompanied by a feeling of fogginess and numbness of the limbs. All this leads to a deterioration in cognitive function and, in some cases, causes memory loss and disorientation. People with a chronic feeling of fullness are characterized by impaired concentration and decreased ability to work. They learn worse and absorb new information, and also suffer from chronic fatigue.
Common neurological symptoms are also accompanied by other signs of pathologies:
- spots before the eyes;
- cardiopalmus;
- sweating and increased fatigue;
- dizziness and nausea, leading to vomiting;
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- increased nervousness, aggressiveness;
- sensitivity to weather changes.
If a person has the feeling that his head is about to burst, he needs to pay attention to additional symptoms, which will depend on the cause of the condition. With infectious lesions of the brain or the body as a whole, high fever, chills and muscle pain appear.
The most dangerous infection, meningitis, is accompanied by unbearable headaches and stiff neck muscles. This condition is also characterized by frequent vomiting.
With hypertension, floaters often appear before the eyes and numbness in the arms or legs.
With circulatory diseases, symptoms worsen in a horizontal position. Also, pain and a feeling of fullness appear after prolonged work with the head down. It is especially dangerous to be in stuffy, unventilated rooms.
Diagnostics
Patients who experience heaviness in the head require consultation with a neurologist. The specialist receives valuable information during the initial examination, determining the neurological status and conducting simple tests to assess autonomic innervation. During a conversation with the patient, the fact of dependence on alcohol or psychoactive substances can be revealed. Diagnosis of the causes of heaviness in the head involves the appointment of instrumental and laboratory methods, of which the most commonly used are:
- CNS study.
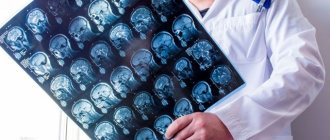
Standard examination in neurology includes echoEG, which is used to measure intracranial pressure and identify space-occupying pathological formations. To clarify the diagnosis, EEG, CT, and MRI of the brain are prescribed. REG and extracranial ultrasound data have diagnostic value. - X-ray of the spine.
Images of the cervical spine in two projections make it possible to determine bone deformation, narrowing of joint spaces, and developmental anomalies. Bones and neurovascular bundles are visualized in detail during either MRI. - ENT examination.
Heaviness in the head accompanied by dizziness requires a standard otoscopy and a hearing test using audiometry. For diagnostic purposes, specific tests are performed: acoustic impedance measurement, electrocochleography, vestibulometry. - ECG.
Unpleasant symptoms may be associated with cardiac problems, for rapid diagnosis of which electrocardiography is recommended. If abnormalities are detected on the cardiogram, the diagnosis is clarified using 24-hour blood pressure monitoring and echocardiography. - Blood analysis.
When heaviness in the head is combined with an increase in body temperature, it is necessary to examine the hemogram. The results of the analysis indicate an inflammatory process (leukocytosis and increased ESR), and also help diagnose polycythemia (with an increase in the number of red blood cells).
Massage of the cervical-collar area
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To eliminate heaviness in the head, a positive emotional attitude is of great importance. It is necessary to protect yourself as much as possible from stress and external irritants, normalize your daily routine, and not overwork yourself at work. Doctors advise establishing a drinking regime and limiting coffee consumption to 1 cup per day. Regular walking before bedtime, fortified meals, and a change of environment help reduce signs of neurasthenia.
Self-administration of painkillers to relieve heaviness and pain in the head is the wrong approach, since the symptoms manifest themselves in dozens of different diseases. Trying to eliminate discomfort, the patient does not solve the problem, so there is a risk of disease progression and complications. If heaviness in the head is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, visual and hearing impairment, this is an indication for emergency medical attention.
Conservative therapy
To eliminate heaviness in the head associated with tension cephalgia or neurasthenia, psychotropic medications are recommended. Antidepressants - selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors - have a good effect. Additionally, muscle relaxants and sedatives are prescribed. To remove symptoms, restorative treatment is carried out with calcium glycerophosphate and hopantenic acid.
If the cervical spine is affected, tablets of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are taken, injections of chondroprotectors and B vitamins are given. To quickly relieve discomfort, ointments with an analgesic and warming effect are indicated. If the pathology is accompanied by vertebral artery syndrome, therapy is enhanced with neuroprotective drugs and medications that improve cerebral circulation.
For neurasthenic cephalgia and heaviness in the head, physiotherapeutic treatment is effective. Reflexology, aromatherapy, and electrosleep are effective in normalizing the functioning of the nervous system. To get rid of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, electrophoresis with drugs, magnetic therapy and electroanalgesia are used. ShVZ massage and manual therapy are performed strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Causes of pressure in the head
Most often, the head compresses against the background of vascular pathologies - problems with arterial and intracranial pressure, spasms, circulatory disorders, oxygen starvation of brain tissue. Less often, unpleasant symptoms arise due to back diseases, lifestyle, errors in the body’s thermoregulation, and intoxication.
Squeezing his head - what does it mean:
- hormonal imbalance - occurs in women during pregnancy and PMS, during menopause, against the background of long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- increased meteosensitivity - any changes in atmospheric pressure can provoke the appearance of pressing sensations inside the skull, headache and dizziness, weakness, weakness, pain and aching in the joints;
- trauma, brain tumors, damage to the skull bones;
- frequent stress;
- overwork, physical stress, chronic lack of sleep;
- pinched occipital or trigeminal nerve;
- exhaustion due to long-term diets:
- if, with squeezing sensations, the head shoots and bursts, then these are clear signs of a psychosensory disorder;
- with osteochondrosis, strong and constant tension in the neck muscles, pain from the back of the head rises to the top of the head.
Pressing pain appears due to osteochondrosis
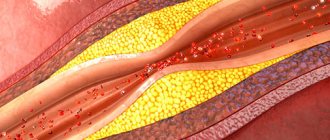
Often the head is compressed in people who smoke and abuse alcohol, are addicted to fatty, spicy, fried foods - this lifestyle reduces the tone of blood vessels due to the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on their walls, the brain begins to suffer from oxygen deficiency, a feeling of vacuum and heaviness arises in the head
An unpleasant sensation, as if something is moving in the area of the back of the head or the top of the head, occurs with encephalopathy, against a background of severe anxiety, fear, advanced forms of VSD, the head becomes heavy, a gait appears like a drunk, the person may lose consciousness.
How to determine the cause of its occurrence based on the nature of the pressing pain
The head can be pressed and pulled over the entire plane, or the pain is localized in a specific area, radiating to the temple, eyes, bridge of the nose, ear or neck. Some specific manifestations of discomfort allow us to draw a preliminary conclusion about the possible cause of its occurrence.
Characteristics and features of pressing pain:
- with very high blood pressure, unpleasant sensations are localized in the parietal part, the pain syndrome is severe, patients characterize it as a hoop on the head, often accompanied by nausea, increased heart rate, dizziness, and tinnitus;
- increased intracranial pressure causes pain that presses on the forehead and eyes, accompanied by severe loss of strength and blurred vision;
- glaucoma - intraocular pressure increases, vision deteriorates, puts pressure on the temples and above the eyebrows;
- meningitis - severe constant pain, there is a feeling that the head is burning from the inside, unpleasant sensations cover the eyes, accompanied by an increase in temperature to critical levels, confusion and loss of consciousness;
- long-term or chronic diseases of the nasopharynx - with sinusitis, sinusitis, pain occurs, which is localized in the upper center, or in the forehead and bridge of the nose;
- migraine - before an acute attack of pain, black or luminous spots begin to flash in the eyes, discomfort is accompanied by vomiting, nausea, a person cannot tolerate strong odors, light, stuffiness, unpleasant sensations cover one side of the head, temple and eyes;
- if you are overcooled, in a draft, or if you are constantly in a room in the summer with the air conditioner running, your head will become stiff in the forehead area, a burning sensation will appear in your eyes, and a lot of mucus will come out of your nose.
Prolonged sinusitis may cause a squeezing headache.
Oxygen starvation against the background of iron deficiency anemia - the head hurts from above, but can cover the temples, forehead and back of the head, the person complains of frequent attacks of dizziness, weakness, decreased attention, flickering of spots before the eyes. With this pathology, the hands and feet are constantly cold, the quality of sleep deteriorates, and the skin becomes pale.
If the head is compressed from the front, this is one of the first signs of the flu, unpleasant sensations arise against the background of intoxication with toxins of pathogenic microorganisms, the vessels begin to increase in diameter, and the surrounding edematous tissues burst.