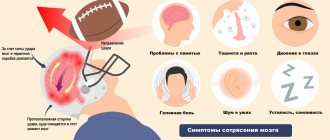
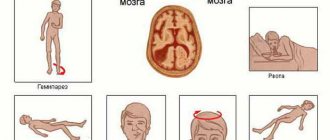
How does dizziness manifest?
We recommend
“How to care for a bedridden elderly person” More details
During dizziness, it seems to a person that not only his head is spinning, but that he himself is spinning, or that the objects around him are spinning. When dizziness occurs in older people, nausea may occur, a feeling similar to intoxication and other unpleasant symptoms may occur, including loss of consciousness and falling.
Old people begin to blur before their eyes not only from external influences, but also due to the occurrence of diseases. Perhaps any person over the age of sixty has at least once felt suddenly dizzy. If this happens regularly, it becomes a serious problem that interferes with a normal life. In order to properly deal with the disease, it is important to determine the causes of its occurrence.
Causes of dizziness in older people
Why might an elderly person feel dizzy? Most often, this is an age-related manifestation, caused by problems with the vestibular apparatus, neurological abnormalities, vascular diseases, and damage to nerve cells. Here are some of the most common causes of dizziness in older people:
- Consequences of injury.
- Sudden changes in pressure.
- Chondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Brain tumor.
- Diabetes.
- Arrhythmia.
- Ischemic disease.
- Damage to the eardrum.
- Meniere's disease (fluid accumulation in the inner ear).
- Benign tumor of the auditory nerve (neurinoma).
- Depression, fatigue, lack of sleep.
But the main thing that causes dizziness in older people is:
1. For 30–35% of cases - BPPV (benign positional paroxysmal vertigo). In older people, this is usually a consequence of degenerative changes in the area of the inner ear. The receptors of the vestibular apparatus are irritated by microscopic deposits (otoliths), resulting in dizziness. More often, older people feel such symptoms when they wake up in the morning.
2. Diseases of the cerebral vessels, so-called cerebrovascular diseases, and atherosclerosis. A characteristic manifestation of these ailments is insufficient blood supply to the brain due to partial damage to blood vessels. This is a very dangerous condition, and dizziness with it is the most harmless symptom.
3. Poor blood circulation in the brain (stroke). According to statistics, stroke occurs in 450 thousand people in the world every day, and over 80% of them are old people. One of the manifestations of a stroke is dizziness, which can recur in a person even after undergoing a course of treatment.
4. Drug abuse (polypharmacy). Taking a large number of drugs at the same time increases the risk of adverse symptoms. It is impossible to list at once all the pills that cause dizziness in older people. Typically these are heart medications, blood pressure medications, painkillers (analgesics), antibiotics, beta blockers, diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, tranquilizers and antidepressants, sleeping pills, anti-seizure medications.
We recommend
“Lonely elderly people: how to help them” More details
5. Dizziness in elderly people with normal blood pressure is rare; rather, the cause of mild weakness and faintness is too high or too low blood pressure.
6. Weakened (due to old age) vestibular apparatus. This can cause not only a feeling of unsteadiness, but also dizziness in older people.
7. There are a number of concomitant diseases for which you have to take a large number of medications (diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease). Then the cause of dizziness in the elderly can be both medications and the disease itself.
8. Many older people have a very difficult time psychologically and emotionally experiencing the changes in the body that come with age. They are afraid of losing consciousness or falling if they suddenly feel dizzy. Attacks of anxiety and even panic can cause so-called psychogenic dizziness, and with them comes chills, arrhythmia, general weakness, lack of air and faintness.
A serious problem that requires treatment is severe dizziness in older people with a weak vestibular system. Objects seem to be moving in a circle; a person cannot clearly perceive their outlines. This is a common occurrence in older people with hypertension. There are also other symptoms:
- spots before the eyes;
- feeling of blindness;
- feeling that the head has become heavy;
- feeling as before loss of consciousness;
- weak legs and arms, apathetic state.
Sometimes isolated manifestations of such symptoms occur, then this most likely means that the person is simply overtired. After rest, the unpleasant feeling will pass.
However, such signs should not be ignored if they occur after a stroke or, for example, during menopause. This has serious health consequences. An elderly person may become frightened during an attack, faint, or injure himself - all this is very unsafe.
Even one of the listed symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. The reasons for poor health must be found out. Let a therapist, endocrinologist, or neurologist examine you. The process can be complex and lengthy; you will have to examine the central nervous system and other organs and take the necessary tests.
Recommended articles on this topic:
- Boarding home for the elderly: features and rules of choice
- Low blood pressure in older people: causes, symptoms and treatment
- Health of the elderly: old age is not a problem
What are the causes of dizziness in older people?
Dizziness in older people is a fairly common phenomenon that is directly related to age, vestibular disorders, neurological changes, vascular problems, and destruction of nerve cells. The main point here can be considered poor blood supply, ischemia and atherosclerosis.
Not only disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus lead to dizziness. Neurological diseases also lead to it, for example Parkinson's disease and other diseases of a neurotic nature. The influence of somatic ailments such as diabetes mellitus and cardiac arrhythmia is also possible.
Often, dizziness in older people is provoked by changes of an emotional and psychological nature. Limitations in their physical condition and transition to a different social status cause psychological maladaptation in them. If an elderly person suffers from phobias and other disorders of consciousness, this has an even more negative impact on the situation.
Most people whose vestibular apparatus does not work well feel the circular movement of objects in space. If the problem is serious, then there may be a disturbance in the perception of the outlines of objects that surround the person. This often happens with hypertensive patients. Along with these symptoms, the following may occur:
- spots in the eyes, feeling of blindness
- heaviness in the head
- faintness
- feeling of cottony limbs and apathy towards everything that is happening
If the manifestation of these signs is one-time in nature, then this can only indicate fatigue. Once you rest, the discomfort will disappear on its own.
But if these signs appear during menopause or after a stroke, then you should pay more attention to them. They can negatively affect human life. He begins to experience fear when an attack occurs, loses consciousness, and may fall and get injured. All this is unsafe for an elderly person.
If you have at least one of the above symptoms, go to the doctor. Don't waste time. Visit a therapist, neurologist and endocrinologist to determine the true cause of the disorders. This takes time because it is difficult to make a diagnosis right away. A thorough study of the central nervous system, collection of tests and the results of numerous examinations are required.
First aid for severe dizziness in an elderly person
Here's what to do if there are complaints of weakness and dizziness in older people:
- put the person horizontally as soon as possible;
- ensure air flow into the room;
- eliminate possible sources of noise: loud music, radio, TV;
- remove too bright light (but there should be enough lighting).
If the person is dizzy but not vomiting, give the person water or tea with sugar. You can wipe your face with a damp cloth (not too cold). Atropine (0.1% solution, 8–10 drops) helps well. If the patient's condition does not improve within an hour, call an ambulance.
Often, older people immediately experience dizziness and nausea, and black spots appear before the eyes. At the same time, the person turns pale, body temperature drops. Such symptoms can be heralds of a hypertensive crisis, and if you do not quickly call an ambulance, it will lead to myocardial infarction.
It is also worth paying attention if a person experiences speech impairment, numbness in half of the face, headaches, or fainting. All these are signs of a cerebral stroke, and if doctors are not called urgently, the life of the pensioner will be threatened.
We recommend
“Interests of older people: how to improve the life of a pensioner” Read more
Diagnosis of dizziness in older people
The success of treating dizziness in older people depends on correct diagnosis. Often the cause of dizziness is changes in the functioning of the brain. In this case, it is necessary to conduct appropriate research. Surveys of this kind are carried out according to the following scheme:
- Determine what type of dizziness is.
- Find the reasons for its appearance.
- The presence of neurological or ENT symptoms is determined.
- Additional methods are used to study the patient’s condition, depending on what pathologies were identified during the examination and interview.
1. History taking and external examination.
First you need to make sure that you really have dizziness. Old people often mistake one condition for another and may mistake nausea or blurred vision for dizziness.
An examination is very important; you need to take a closer look at how the person’s coordination of movements is, and whether the reflexes work normally. You should understand why weakness and dizziness occur in older people, what factors influence the development of the disease, and how it progresses.
If the head begins to feel dizzy gradually, this is classified as dizziness of central origin, and if suddenly and quickly, this is classified as peripheral. The latter are characterized by tinnitus and poor hearing (these symptoms are called local disorders). Central vertigo is accompanied by damage to the cortex and brain stem. A general serious condition with frequently recurring vomiting are signs of vestibular disorders.
To identify the diagnosis, the patient is asked to change the position of the head, for example, tilt it to the left or to the right. If the head becomes more dizzy when bending over, then we are talking (most often) about benign dizziness in older people, the cause of which is a weak vestibular apparatus.
Through a survey, they will find out what autoimmune or inflammatory diseases, intoxications (medicines or alcohol), and head injuries have been suffered. Check to see if the person being examined has nystagmus. Nystagmus is an oscillatory movement of the eyes independent of the patient. They study the spontaneous form of nystagmus (caused by gaze), when a person first looks straight ahead and then moves his eyes to the side.
Another diagnostic method is the Hallpike test. The patient is placed on the couch in a sitting position, he looks to the right, turning his head about 45 degrees. Holding the person by the shoulders, he is asked to quickly lie on his back so that his head hangs off the couch. The same is repeated by turning the head to the left.
An otolaryngologist examines the outer, middle, inner ear, eardrum, removes wax plugs, checks for infections (acute or chronic), and finds the consequences of injuries.
2. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
CT and MRI are prescribed to ensure the absence of neoplasms and demyelinating processes. Structural pathologies (congenital or acquired) are identified. It may be necessary to take an X-ray of the skull (if there is an assumption that the person has new or old fractures).
We recommend
“Adaptation of older people: in modern society and boarding homes” Read more
The cause of weakness and dizziness in older people may be vascular dysfunction. In case of such suspicions, Doppler ultrasound of the cervical and cephalic great vessels is performed.
A complete blood test will help rule out the possibility of infection. If a pathogen is found, antibodies are determined for it.
If there is concomitant hearing impairment, the patient undergoes pure-tone audiometry. A person drinks Glycerol, after which one can notice better speech perception and recognition of low-frequency sounds. If such signs are found, then we are talking about Meniere's disease, which, as a rule, is accompanied by dizziness.
Dizziness against a background of apathy, hypochondria, accompanied by a decrease in mental activity and causeless painful health, indicate that the patient has a diagnosis of a psychiatric or neurological nature.
Dizziness in older people
Dizziness
Dizziness, like love, is subject to all ages. However, older people, who already face many health problems, are almost three times more likely to suffer from it. Thus, over the age of 60, 30% of older people experience dizziness, and about 50% over the age of 85. [1][2]
Dizziness is one of the most common causes of falls in the elderly. [3] As we age, our bones become more fragile, which is why many of these falls result in severe injuries. Particularly dangerous is a hip fracture, which can leave a person permanently bedridden. After all, the older the patient, the higher the risk, unfortunately, that the fracture will not heal.
The main causes of dizziness in older people are:
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which occurs in 30-35% of cases. [4] In older adults, it often occurs due to degenerative changes in the inner ear. Microscopic deposits (otoliths) when turning the head can irritate the vestibular receptors and cause dizziness. Such dizziness can, for example, overtake an elderly person in the morning after waking up. [4]
- Cerebrovascular (“vascular”) diseases of the brain, including atherosclerosis. Almost all “vascular” diseases lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain due to damage to blood vessels. Dizziness in this case is one of the least dangerous manifestations of such conditions.
- Stroke. Statistics say that every day about 450,000 people suffer a stroke in the world, more than 80% of them are elderly. 5 One of its first signs is dizziness, which may persist after treatment.
- Polypharmacy , that is, taking a large number of medications at the same time. Moreover, the more drugs a patient takes, the higher the likelihood of developing side effects. [6] Dizziness may occur as a result of taking certain non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor drugs, loop diuretics, ototoxic antibiotics and some other drugs. [7]
- High or low blood pressure often manifests itself as general weakness and a feeling of impending fainting [8]
- Age-related changes in the vestibular system , which, in addition to dizziness, often lead to a feeling of unsteadiness in older people. [9]
- Concomitant diseases (for example, Parkinson's or Alzheimer's diseases, diabetes mellitus and spinal diseases). Dizziness, in this case, can be caused both by the diseases themselves and by the simultaneous use of a large number of medications intended to treat them.
- Psychological and emotional factors are of particular importance for older people. Many of them painfully experience age-related changes, experience fear of falling due to dizziness, anxiety and even panic attacks. Such psychogenic dizziness is often accompanied by lack of air, weakness, presyncope, chills, arrhythmia, etc. [4]
Treatment of dizziness in older people
It is especially important for older people to pay close attention to the body's alarm signals and be sure to report them to the doctor. In addition to drug therapy, the prevention of dizziness and special vestibular exercises are important, which, by the way, are also useful for healthy people over 60 years of age. However, exercises can only be performed under the supervision of medical personnel and in the absence of contraindications. Psychotherapy can provide significant support, especially in cases where dizziness is caused by emotional disorders. [9]
It is important for older people suffering from dizziness and their loved ones to know the rules of emergency treatment for dizziness, as well as information about dizziness prevention and proper nutrition.
Be sure to contact a specialist if you or your elderly relatives need qualified help.
Bibliography:
1. Zamergrad M.V. Age-related aspects of dizziness // Neurological Journal. – 2014. –T. 9. -No. 3. – P. 21-28.
2. Parfenov V. A., Antonenko L. M. Treatment and rehabilitation of major diseases manifested by vestibular vertigo // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. – 2015. – T.7. — No. 2. – 56-60.
3. Drapkina O.M., Chaparkina S.M., Ivashkin V.T. Dizziness in the practice of an internist // Cardiovascular therapy and prevention. – 2007. – No. 6 (4). – pp. 107-114.
4. Zakharov V.V. Dizziness in the elderly // Pharmateka. – 2012. – No. 9
5. Mukh E.A., Nazarenko N.V. Prevention of stroke in the elderly: an integrated approach in the conditions of the department of hospital-replacement therapeutic technologies // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences - Vol. 5. - No. 3.
6. Belozerov E.S. and others. Drug complications, St. Petersburg, 2001. - 448 p.
7. Babiyak V.I., Bazarov V.G., Lantsov A.A. On the problems of vestibular pathology // News of otorhinolaryngology and logopathology - 2000. - T. 2. - No. 22. - P. 67–73.
8. Freeman R. Treatment of orthostatic hypotension. Semin Neurol 2003; 23:435–42.
9. Zamergrad M.V. Balance disorders in the elderly // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. – 2012. – No. 1. – 101-105.
Co-author, editor and medical expert:
Volobueva Irina Vladimirovna
Born 09/17/1992.
Education:
2015 - Sumy State University, specializing in General Medicine.
2017 — Completed an internship in the specialty “Family Medicine” and also defended her master’s thesis on the topic “Peculiarities of the development of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children of different age groups.”
Anti-dizziness medicine for older people
What drug treatment is used for dizziness in older people? Since the diagnosis is so common, there are a number of drugs that make attacks less frequent and have a beneficial effect on the brain. These are so-called nootropics, that is, drugs that accelerate neural processes in the brain. They are excellent for helping with memory loss, complications of mental activity, sclerosis and dementia. In addition, they can be prescribed to improve blood circulation, to combat prolonged fatigue, insomnia and depression.
Nootropics have a wide spectrum of action and are completely safe for the body. They can be given to children and prescribed to absolutely healthy people for whom maximum concentration at work is important. But you should not try to choose a drug for yourself; let a doctor prescribe it. The main nootropics are Glycine, Phenotropil, Piracetam, Cinnarizine, Bilobil.
We recommend
“Boarding home for the elderly: how to place an elderly relative there” More details
Any of these medications improves blood circulation in the vessels of the brain, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, fights hypoxia, and establishes neural connections in the central nervous system. Some drugs have a sedative effect. Medicines in this group improve cellular metabolism and activate energy processes inside cells. This increases the ability to perceive and remember information and learn. Nootropics are used to treat dizziness in older people because they improve mood and sleep, and make a person more active.
Here is a more detailed description of some nootropics:
- Piracetam is on the first step in popularity. Many people experience sleep disturbances when taking the drug, so it is not prescribed for use in the evening, only before lunch.
- Cinnarizine. It is prescribed not only as a nootropic, but also as an anti-allergy remedy. It should be borne in mind that the drug causes drowsiness, dry mouth, and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Glycine is good because it does not cause adverse reactions. A very popular drug among students, especially during study periods. The main component is gamma-aminobutyric acid, which accelerates brain function and is important for metabolic processes.
- Phenibut. Its main component is the same gamma-aminobutyric acid. This medicine may cause you to feel sleepy, especially when you first start taking it.
How else to treat dizziness in older people? Nootropics based on herbal components are also used:
- Vinpocetine. The basic component is the small periwinkle. It has a beneficial effect on brain function, improves blood circulation in areas of blood vessels susceptible to ischemia (relaxes their walls). Helps lower blood pressure.
- Bilobil. The main herbal component is ginkgo biloba. Supplies the brain with oxygen and glucose, making blood vessels more resilient in case of oxygen deficiency. Improves attentiveness, memory and learning abilities. Has a weakening effect on numbness of the limbs.
All of the above remedies and others like them should be taken for at least three months. Only after a month will the first changes be noticeable. The frequency of administration is usually one to three times a day. The treatment regimen must be prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment of dizziness in older people with folk remedies
Along with drug treatment, it is permissible to use traditional medicine recipes. It is better to consult a doctor first so that the effect does not turn out to be the opposite. Some simple remedies:
- Sage. Brew 4 tbsp in 0.5 liters of boiling water. l. sage flowers. Leave for half an hour, you can mix with honey. Drink before meals. The decoction is a good tonic.
- Common parsley. Grind the seeds of the plant in a coffee grinder, brew 1 tsp in a glass of boiling water. crushed mass, leave overnight. In the morning, strain and take four times a day in equal parts, before meals. It stops dizziness well in older people.
- A collection of peppermint leaves, lemon balm, linden flowers and mistletoe. The herbs need to be brewed with boiling water and allowed to brew. It helps well with a weakened vestibular apparatus.
- Red clover. Brew 1 tsp in half a glass of boiling water. dried flowers, let it brew. Take 50 ml twice a day 40 minutes before meals. Helps cleanse the walls of blood vessels, activates life processes, and reduces dizziness.
- Elecampane root. Brew a pinch of crushed root in a glass of boiling water, let it brew for half an hour and strain. Take 4 times a day in equal parts. Tones, destroys infections and parasites, has a beneficial effect on the vestibular system and stops dizziness.
- Simple kelp (sea kale). Eat 1 tsp once a day. dried plant with water. Strengthens the immune system, helps cleanse toxins, normalizes the central nervous system, and stops dizziness.
We recommend
“Centers for pensioners: what they are and how to get there” Read more
- Veronica grass. Brew 1 tbsp in 250 ml boiling water. l. dried plant, infuse. Take the infusion warm, 80-100 ml before meals. Acts as a sedative and relieves dizziness.
- Onion. Scroll it through a meat grinder. The dizziness goes away if you breathe over the resulting mush. Mix chopped onion and honey in a glass jar in equal parts and leave in a cool place for 5 days. The remedy stops severe dizziness in older people and gives strength.
Basically, soothing herbal decoctions are used as herbal remedies:
- Chamomile tea with mint. Brew a tablespoon of dried herbs in a glass of boiling water and strain after 15 minutes. If you are not allergic to honey, you can add one teaspoon to your tea.
- Calming drink. Brew chamomile, mint and valerian (one teaspoon each) in 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 12 hours. The best option is to prepare the decoction overnight, strain it in the morning, add honey and apple cider vinegar (one teaspoon each). Drink before meals.
- Dried ginger root is an excellent folk remedy for treating dizziness in the elderly. The root is taken in powder form three times daily before meals. Dry, powdered garlic is also a good tonic. You can take both remedies at once.
- Hawthorn relieves spasms and has a strengthening effect on the walls of blood vessels. A self-prepared infusion is much more effective than a pharmaceutical alcohol preparation. To prepare, brew one tablespoon of dry herb in 200 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour.
- Dizziness stops after two weeks of taking plantain infusion.
You can also prepare tinctures:
- From garlic. Pour half a liter of alcohol into 300 g of garlic in a glass container and leave in a cool place for 15 days. Method of administration: add 20 drops of tincture to half a glass of milk. The product cleanses the body of toxins, fights infections, improves the functioning of the heart muscle, and relieves dizziness.
- From chestnut. Crushed chestnut buds are poured with half a liter of Cahors (preheated to 70 degrees) and kept for 15 minutes in a water bath. When it cools down, add two tablespoons of honey and a little vanilla powder. Take 50 ml before meals. Improves general condition and activates the activity of brain vessels.
Juice treatment:
- Carrot. Drink 0.5–1 glass three times a day before meals. Strengthens the immune system, relieves dizziness. An excellent remedy is a mixture of carrot, pomegranate and red beet juices (in a ratio of 3:2:2). Take the same way, 0.5–1 cup three times a day before meals. Improves the overall well-being of older people.
- Pineapple. Pineapple is a very strong antioxidant, rich in minerals and vitamins. Its juice rejuvenates the body and has a strengthening effect on the walls of blood vessels. Relieves dizziness in older people and is good for anemia.
- Juice from salad. Drink 25 ml 4 times a day if dizziness occurs due to heart failure or disorders of the central nervous system.
- Juice of young zucchini (possibly with the addition of carrot). It is taken in cases where dizziness occurs due to cardiac problems or high blood pressure.
Dizziness in the elderly - treatment with folk remedies
Simple remedies:
- Red clover. 1 tsp dry flowers pour ½ cup boiling water. Insist. Drink the decoction twice a day, 50 ml 40 minutes before meals. Increases vital activity, cleanses the walls of blood vessels, eliminates dizziness in older people.
- Sage. 4 tbsp. sage flowers pour ½ liter of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes. Drink before meals. Add some honey. Increases vital activity.
- Elecampane root. Finely chop, pour 1 pinch of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes. Strain. Take equal parts 4 times a day. Gives strength, cleanses from parasites and infections. Stabilizes the vestibular apparatus and stops dizziness.
- Common parsley. Grind parsley seeds in a coffee grinder. 1 tsp Pour the powder into a glass of boiling water overnight. Strain in the morning. Take in equal parts 4 times a day before meals. Stops dizziness.
- Simple kelp (sea kale). 1 tsp Eat dried seaweed and drink water once a day. Increases immunity, removes toxins, normalizes the functioning of the central nervous system, and eliminates dizziness.
- A mixture of lemon balm leaves, peppermint, mistletoe and linden flowers. Pour boiling water over and leave. This infusion is good for poor functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
- Onion. Grind the onion in a meat grinder. If you breathe in the vapors of onion pulp, the dizziness will go away. Fill ½ glass jar with chopped onion. Add honey, filling the jar, stir. Place in the refrigerator for five days. Take 2 tbsp daily. in the morning before meals. Will give strength and eliminate severe dizziness. You can also rub onion on your temples if you feel dizzy.
- Veronica grass. Pour 1 tbsp into a thermos. dry veronica grass. Pour 250 ml of boiling water. Let it brew. Take 80-100 ml warm before meals. Relieves nervous excitement, eliminates dizziness.
- Hawthorn (flowers). 5 tbsp. pour 1 liter of hawthorn flowers. boiling water Leave for an hour. Add honey. Drink instead of tea. Helps with dizziness that occurs due to a diseased heart and blood vessels.
Tinctures:
- Garlic tincture. Grind 300 gr. garlic, put in a glass container, pour in ½ liter of alcohol. Place in a cool place for 15 days. Take with milk: 20 drops per half glass of milk. Removes toxins, eliminates infections, normalizes heart function. Eliminates dizziness.
- Hawthorn tincture. 150 gr. hawthorn buds, 50 gr. linden honey and 0.7 liters of cognac. Add 1 gr. cinnamon and vanilla. Leave for several days. Take 1 tbsp. in 10 minutes before meals. Normalizes heart function, improves the condition of blood vessels, and eliminates dizziness.
- Chestnut tincture. Grind the chestnut buds. 2 tbsp. l. raw materials pour ½ liter of Cahors heated to 70 degrees. Keep in a water bath for 15 minutes. Cool. Add 2 tbsp. l. honey and a little vanilla. Take 50 ml before meals. Normalizes the general condition, stimulates the functioning of brain vessels.
Socalation:
- Carrot juice. Take 0.5-1 glass three times a day before meals. Increases immunity, eliminates dizziness.
- A mixture of carrot, red beet and pomegranate juices. Mix in proportion 3:2:2. Take 0.5-1 glass three times a day before meals. Improves the general condition of older people.
- Pineapple juice. Powerful antioxidant. Contains vitamins and minerals. Strengthens blood vessels, promotes rejuvenation. Helps with anemia and dizziness in older people.
- Juice of young zucchini (you can add carrot juice to it). If the cause of dizziness is high blood pressure or lack of cardiac activity, take this juice.
- Juice from salad. If the cause of dizziness is a disruption of the central nervous system or a lack of cardiac activity, take 25 ml of juice four times a day.
Other treatments for dizziness in older people
Dizziness in older people is best treated by a combination of medications, folk remedies and the following methods:
- Physiotherapy. Properly selected exercises strengthen the spine and stimulate the functioning of blood vessels. Regular exercise can sometimes give more significant results than taking medications.
We recommend
“Gymnastics for the elderly: the best exercises for various diseases” Read more
- Physiotherapy. Modern technologies in this area are multifaceted; water, sound, light, magnetic, and laser treatments are available. Regular implementation of these procedures has a very beneficial effect on the nervous system.
- Reflexology, in particular acupuncture. It normalizes the functioning of the central nervous system, relaxes muscles and activates blood circulation.
- Psychotherapy. The likelihood of dizziness in older people is significantly reduced if measures are taken to relieve nervous tension and anxiety.
Entering into old age will be much easier if you take care of your health in advance. The physical capabilities of the body directly depend on compliance with the daily routine, proper nutrition, intensity of exercise, and abuse of bad habits. Think about what is easier - to prevent the disease or to treat it later? Provide your body with normal functioning, do not neglect examinations if you are already about sixty. Be active, walk more, look at the world positively. Then you definitely won’t have to deal with bouts of dizziness.
Dizziness in the elderly: non-drug treatment
A good result in the treatment of dizziness in the elderly is achieved by combining therapy with medications, traditional medicine and, in addition, methods such as:
- Exercise therapy. Simple, properly selected physical therapy exercises improve overall well-being and have a good effect on the spine, and therefore on the functioning of blood vessels. Sometimes constant training gives better results than drug treatment.
- Reflexology (eg acupuncture). Acupuncture has a beneficial effect on the central nervous system, relaxes the muscle frame, and improves blood circulation.
- Physiotherapy. There are many new technologies in the field of physiotherapy. They treat with water, light, sound, magnets, laser. All these procedures have a positive effect on the nervous system if taken regularly.
- Psychotherapy
Read material on the topic: Exercises for older people