Previous Next
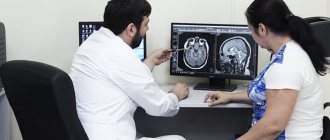
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is a modern examination method that can provide important information for the diagnosis of tumor, inflammatory and demyelinating diseases of the brain and meninges. For doctors, MRI of the head is primarily valuable for its high information content. With its help, it is possible to immediately obtain all the necessary data for an accurate diagnosis and prescription of effective therapy. It also allows you to quickly monitor the results of the treatment and adjust the therapeutic regimen if necessary.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
What is magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
The brain can be considered one of the most difficult organs for the early detection of pathologies, anomalies and disorders. Not every hardware diagnostic method can handle it. Thus, thick cranial plates do not allow examining the head structures of an adult using ultrasound of the head. Radiography shows the condition of the skull bones well, but it is impossible to obtain detailed results of the condition of the white and gray matter, the vascular bed and the pituitary gland. Therefore, magnetic resonance imaging plays an invaluable role in diagnosing brain pathologies.
This method uses harmless magnetic fields and radio waves and allows you to see the area under study in three dimensions. During the examination, the patient's body is exposed to electromagnetic waves. This causes the vibration of a hydrogen atom in the brain cells, which is picked up by the tomograph's computer, digitized and turned into a series of three-dimensional images. The examination procedure itself is absolutely safe, since it does not involve radiation exposure, unlike CT. Since the brain is 80% water, there is a very strong resonance effect, and MRI images of the brain have very good tissue contrast. The information content of the method is so high that it allows identifying possible pathological changes up to 1 mm in size.
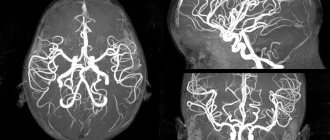
MRI of head and neck vessels with contrast
To study the vessels of the brain and neck, several methods involving the introduction of iodinated contrast into the arterial bed were previously used. This is a rather complicated and painful procedure, with a lot of side effects. While contrast is injected into the arteries, doctors take X-rays or CT scans.
MRI of the head and neck vessels or magnetic resonance angiography is a completely different method for diagnosing diseases of the arteries and veins. Thanks to the presence of angio-mode, the tomograph is capable of taking pictures only of the vascular bed without the use of contrast and associated painful manipulations, such as inserting a catheter into the femoral artery. The patient only needs to remain still while lying inside the tomograph.
However, MR imaging can also be done with contrast. However, unlike CT scans, MRI contrast agents do not contain iodine, are safe and have virtually no side effects. MRI contrast is injected with a regular syringe into the cubital vein in the middle of the study (the duration of the procedure increases by 15 minutes). Contrast agents tend to accumulate in inflamed or tumor tissues, highlighting and highlighting them in images, which facilitates diagnosis and increases the information content/specificity of magnetic resonance imaging.
Indications
Attending physicians, as a rule, prescribe a referral for an MRI of the brain in order to exclude a whole range of serious medical pathologies - brain tumors and cysts, stroke, infectious lesions, an aneurysm in the wall of one of the blood vessels in the brain. A person himself can understand that he needs to sign up for an MRI of the brain if:
- severe headaches;
- headache is accompanied by dizziness, numbness of the fingers, changes in visual acuity, and coordination problems;
- severe headache makes you wake up at night or in the morning;
- the head hurts even when a person coughs or sneezes, as well as after sports training or sexual intercourse;
- after unsuccessful treatment or if the results of other examination methods are in doubt;
- surgery is ahead or diagnostics is required after head injuries.
In most medical centers, you can get an MRI of the brain for a fee without a doctor’s referral. Examination with an MRI machine does not pose a threat to health, and magnetic resonance diagnostic technology makes it possible to detect any disorders in the brain at the stage when they are just beginning.
Medical experts advise making it a rule to do an MRI of the head on an annual basis if:
- you are 50 years old or older and the headaches are different from those you had in your youth;
- have had head injuries, especially if you play sports;
- you suffer from vascular or hormonal disorders, obesity;
- are at risk for cancer.
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
What will magnetic resonance imaging of the brain show?
Head tomography data allows for high-quality differential diagnosis of the following pathologies:
- demyelinating diseases, including multiple sclerosis;
- volumetric formations of benign or malignant origin;
- cysts and pseudocysts;
- degenerative changes in brain structures, for example, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease;
- inflammation of the meninges, including meningitis and encephalitis;
- leukoaraiosis of the brain;
- hydrocephalus;
- epilepsy.
| MRI image of a healthy brain | brain cyst on MRI | brain cancer on MRI |
When is an MRI of the head and neck prescribed?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head and neck is used in the diagnosis of the following diseases:
- Primary headaches (cluster headache, tension headache, migraine) as a method to exclude organic brain damage;
- Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis);
- Volumetric formations of the brain (cysts, abscesses, tumors);
- Metastases to the brain, cervical vertebrae;
- Vascular diseases (atherosclerosis, aneurysms, malformations, vertebral artery syndrome);
- Strokes;
- Demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis), other autoimmune pathologies of the central nervous system;
- Degenerative-dystrophic processes in the cervical spine;
- Herniated intervertebral discs in the cervical spine;
- Neck injuries;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland (cysts, tumors, nodes);
- Other pathologies of the head and neck.
Symptoms for which it is recommended not to delay an MRI examination of the head and neck:
- Headache;
- Pain in the neck;
- Dizziness, tinnitus;
- Unsteadiness of gait;
- Decreased hearing, vision;
- Deterioration of memory, ability to concentrate;
- High blood pressure;
- Convulsive syndrome;
- Feeling of crawling, numbness and burning of the skin;
- Impaired tactile sensitivity;
- Impaired or limited mobility of the spine in the cervical region, crunching when rotating, tilting the head;
- Enlarged lymph nodes, foreign tumors, lumps in the neck (thyroid gland) and head, which are determined visually or by touch.
When is an MRI of the brain with contrast prescribed?
The main reasons to do a contrast brain tomography are:
- suspicion of infection or malignancy
- oncosearch;
- search for metastases and cancer staging;
- control study after brain surgery;
- determination of multiple sclerosis activity;
- in the differential diagnosis of benign brain tumors.
The contrast method of examination is most often used when a tumor is suspected. After the introduction of a contrast composition based on the rare earth metal gadolinium, tumor foci of even very small sizes, for example, metastases, are better visualized, and by the type of accumulation and release of the contrast agent, the doctor can judge the malignant potential of the tumor.
A contrast agent may also be needed if specific hyperintense lesions are detected along nerve fibers in the brain or spinal cord, which may be consistent with multiple sclerosis. In this case, the contrast makes it possible to determine the activity of the demyelination process.
The dosage of contrast agent depends on the patient's weight. The contrast agent is administered through a vein. The composition itself is hypoallergenic and is excreted from the body naturally without any effort on the part of the patient within 24 hours after diagnosis.
Previous Next
MRI of the brain: preparation for the study
The essence of MRI is the use of a magnetic field that affects water dipoles in the body's cells. The intensity of the response directly depends on the moisture saturation of the tissues. The examination takes about 30 minutes; when using a contrast agent, the duration of the procedure increases to 45 minutes.
The patient lies down on a mobile table, his head is fixed with restraints. The magnetic field generator and sensors that read information are located in the wide part of the tomograph, which has the shape of a pipe. The table with the patient moves to the annular section of the device, where the brain is scanned in sagittal, frontal and axial projections.
To improve the quality of the examination, a gadolinium-based contrast solution is used. The drug is administered intravenously, it has no toxic effect and is eliminated from the body within 1-2 days. The contrast illuminates the vascular system of the brain and visualizes the slightest changes in the area of soft tissue, veins and arteries.
During the procedure, the tomograph creates a lot of noise, so the patient is recommended to use special headphones provided by the clinic. Communication with medical personnel is maintained using an intercom. During magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor and technicians are located in an adjacent room, separated by a partition. The data obtained as a result of the study is received on a computer monitor in the form of layer-by-layer images.
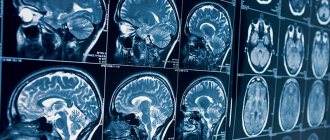
Layered MRI photographs of the brain printed on film, axial projection
A tomogram visualizes the condition of internal organs and helps diagnose the following diseases:
- neoplasms in the head area;
- vascular development abnormalities;
- pituitary diseases;
- consequences of head injuries;
- pathologies associated with impaired blood supply to the brain;
- inflammatory changes in cerebral structures and membranes, cranial nerves;
- congenital pathologies.
MRI of the brain does not require complex preparation. The patient should consult a doctor and exclude the presence of factors that are absolute contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging. These include:
- the presence in the body of the subject of metal products used for medical purposes (pins, dental crowns, implants, dentures, knitting needles, etc.);
- the presence of implanted electromagnetic devices (pacemaker, insulin pump, etc.);
- the presence on the patient’s skin of tattoos made with paints with a high metal content.
If contrast is used, the patient must warn the doctor about the tendency to allergic reactions, the presence of renal and liver failure, diseases of the cardiovascular system and other previously diagnosed pathologies. Any medications taken immediately prior to the MRI should be reported. Patients suffering from claustrophobia should also warn their doctor. A specialist will help you avoid panic attacks during the procedure.
Women are not recommended to undergo an MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the insufficiently studied effect of a magnet on the embryo during the formation of vital organs. Nursing mothers should express milk for the next 2 feedings, which will avoid getting gadolinium salts during contrast MRI into the baby's food.
The subject prepares for the scan in advance: removes uncomfortable clothes, jewelry, accessories, and piercings. The patient then takes a horizontal position on the table and follows the doctor’s recommendations during the procedure.
MRI of the brain in a child, images in a sagittal projection
Contraindications
Brain tomography has two main contraindications:
- the presence of ferromagnetic metal in the body, for example, steel prostheses, iron bullets, shrapnel, Ilizarov apparatus;
- the presence of pacemakers whose passports do not contain a mark indicating compatibility with MRI.
Dental implants and crowns are not a contraindication to the examination. You should inform your doctor about their presence, as some of them can sometimes produce light artifacts on images. The magnetic field itself does not negatively affect the composition and material of dental implants and does not lead to cracks, chips or movement. Most braces will also not be a limitation to magnetic resonance imaging. However, it may happen that the light effect from them will be so strong that the quality of diagnosis will decrease, and the doctor will not be able to make a high-quality description of the tomograms. For some, tattoos and permanent makeup can cause discomfort. If pigments containing metal were used during tattooing, the patient may experience a feeling of intense heating of the skin or even a burning sensation in the areas where the ink was injected subcutaneously. If the subject has undergone surgery to install vascular clips, MR examination should be postponed for 6 months after surgery. If you are unsure whether you can have an MRI, always consult your doctor.
Indications for MRI of the brain in adults
Indications for MRI examination of the brain in adults are:
- traumatic brain injuries (in the acute period - if diffuse axonal damage is suspected, in the later stages - to assess the degree of brain matter atrophy, before reconstructive surgery on the skull);
- endocrine disorders (for abnormal weight fluctuations, hormonal imbalances, infertility, sexual dysfunction, etc., an MRI of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland is necessary);
- hydrocephalus;
- chronic diseases of the nasal sinuses (sinusitis, sphenoiditis, etc.);
- suspected intracranial tumors;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the brain (abscesses, arachnoiditis, meningitis, encephalitis, etc.);
- epilepsy and epileptic syndrome;
- defects in brain development;
- anomalies and pathologies of the cerebral vascular system (aneurysms, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, vasculitis, etc.);
- post-stroke and post-infarction conditions (to assess the extent of brain damage);
- arterial hypertension;
- demyelinating and degenerative diseases (Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, etc.);
- organic brain damage (encephalopathy, etc.).
MRI of the head (sagittal plane). The arrow indicates a neoplasm of the thalamic region on the left
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed to monitor the effectiveness of therapy for identified diseases after operations. For prevention, MRI diagnostics is recommended for people with bad habits (due to the high risk of vascular pathologies), those who constantly experience intense physical activity or play sports associated with blows to the head (boxing, wrestling, volleyball, basketball).
Preparation
MRI of the brain does not require special preparation. Before the procedure itself, the person will be asked to remove all metal objects: watches, chains, various jewelry, hairpins, jewelry, removable dentures, hearing aids, clothing with metal elements. You will definitely need to inform your doctor about the presence and location of any metal inside the body. These could be prostheses, valves, implants, braces, etc. Remember - all this can directly affect not only the quality of the pictures, but also your health!
Preparatory stage
The doctor, based on the test results, determines whether to perform a tomography with or without the introduction of a contrast agent. If the first option is chosen, then the patient does not take food or liquid 5 hours before the diagnosis. Before the procedure, you must remove all jewelry and accessories, watches and objects with metal elements.
During a consultation with a doctor, the patient reports the presence of chronic diseases, allergies to medications, claustrophobia, and pregnancy.
When preparing a child for a head tomography, it is not recommended to give him anything to drink or eat 3 hours before the diagnosis. If an MRI is performed with the administration of contrast, the examination is performed on an empty stomach. Before the procedure, the child should be shown to an allergist to check for an allergic reaction to the injected substance.
How is tomography performed?
The tomography procedure is quite simple. It does not require prior preparation of the patient. It can be done at any time of the day or night by appointment. Before the examination, the patient will be asked to come to the MRI center 10 minutes before the scheduled appointment and fill out medical documents. Then I will take him to the examination preparation room. There you will need to leave all items that contain metal and electronic devices - phones, tablets, watches. In the MRI room, the patient will be helped to sit comfortably on the tomography table, and a special signal-amplifying coil in the form of a plastic helmet will be placed on his head. Then slide the table inside the scanning part of the tomograph, and screening will begin.
The patient will understand that the tomograph is taking pictures by a series of noisy signals and tapping sounds, reminiscent of machine gun fire. There is no need to be afraid. If these noises are annoying, you can always ask to wear special noise-canceling headphones.
The average duration of the examination is:
- 15-20 minutes - native version of the examination
- 40-50 minutes - contrast version of the examination.
The damage to diagnostics with contrast tomography is doubled due to the fact that the patient is first given a series of non-contrast images, and then a series of contrast-enhanced images.
Once the scan is completed, the patient has the option of waiting for the results in the clinic or receiving them by email or upon a return visit to the diagnostic center.
MRI of the brain on an open tomograph
Diagnostic centers can be equipped with open and closed type tomographs. Closed devices are installations in the form of a cylindrical tube, where the patient’s body is placed during the scan. Open tomographs are a structure where the magnet is located in the form of a canopy.
This design allows examinations to be carried out in comfortable conditions, even for patients with a fear of confined spaces. For confidence and greater comfort, the examinee can invite a loved one to stay with him. Parents can be with the child during the scanning session. If, however, any circumstances arise that prevent the patient from continuing the study, the MRI machine is equipped with a call button that allows you to give an audible signal to the staff. In this case, the diagnosis will be suspended, and a doctor will approach the patient, who will find out and eliminate the causes of concern.
| OPEN TYPE MRI | SEMI-OPEN MRI | CLOSED MRI |
Decoding
It will take about an hour to prepare the tomography results. The patient can spend this time in the waiting room. After processing the results, the person receives pictures, a disc with a video recording of the procedure, and a radiologist’s report.
A series of MRIs of the brain, weighted by T2-WI, T1-WI and FLAIR-IP, performed in the axial, coronal and sagittal planes, images of the sub- and supratentorial sections were obtained.
In the left frontal lobe, periventricular to the anterior horn of the left lateral ventricle, an area of altered MR signal measuring 0.7x0.6x0.5 cm is visualized, a hyperintense signal on T2-WI, hypointense with a hyperintense signal along the periphery on FLAIR-IP, hypointense on T1-WI. VI – zone of cystic-glial changes, consequences of a stroke of ischemic type (left MCA basin).
In the white matter of the frontal lobes, a few foci are identified subcortically and periventricularly, with fairly clear, uneven contours, hyperintense on T2-WI and FLAIR-IP, measuring up to 0.2-0.4 cm (most likely foci of vascular origin).
Zones of gliosis are identified periventricular to the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles.
At the level of the semioval centers in the supraventricular white matter and in the projection of the basal ganglia, expanded perivascular spaces are determined along the penetrating vessels.
The grooves of the subarachnoid space along the convexital surface of the frontal and parietal lobes are moderately unevenly expanded.
A cyst of the transparent septum is determined, measuring 5.4x0.7 cm.
The lateral ventricles are asymmetrical (D>S), not dilated - within the age normometry.
III, IV ventricles without features.
The chiasmal-sellar region is not changed.
The cerebellar tonsils are located at the level of the foramen magnum.
Pneumatization of the paranasal sinuses is not impaired.
Conclusion:
MR picture of a previous lacunar stroke of ischemic type in the LSMA basin. MRI signs of a few foci in the white matter of the frontal lobes (most likely foci of vascular origin). MRI signs of expansion of external liquor spaces of a replacement nature.
Author: Shogenov Ramish Kurbanovich
Neurologist with 10 years of experience
What does the cost depend on?
The main factor determining the cost of MRI of the brain is the power of the tomograph. The higher the induction capabilities of the device’s magnet, the more expensive it is to perform tomography on it. However, the quality of the examination and diagnostic value will also increase.
The price of a brain MRI usually includes preparation, examination and interpretation of the tomograms. Additionally, the patient will need to pay the cost of contrast if the doctor ordered an MRI of the head with contrast. The decision to use contrast enhancement is made either by the attending physician or by the radiologist if, during a non-contrast scan, he detects signs of diseases that are validated during brain MRI with contrast. The cost of administering the drug depends on the patient's weight. On average, with a weight of 70 kg, 10 ml of contrast agent will be required, and the price of the contrast agent will be about 3,000 rubles.
MRI of the brain is the cheapest at night, when the maximum discounts apply. In addition, some medical centers provide additional benefits to people with disabilities, pensioners, and students. You can find out about such discount programs when making an appointment for an MRI.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the brain | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (arteries) / MR angiography of cerebral vessels | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland (without contrast) | 3500 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast | from 6500 rub. | not implemented | from 6900 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland and brain | 7800 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9590 rub. | 10890 rub. |
| Comprehensive head diagnostics (MRI of the brain, MRI of cerebral vessels, ultrasound of neck vessels, consultation with a neurologist) | 10900 rub. | 7500 rub. | |
| Contrast administration (based on patient weight) | from 4000 to 6000 rub. | from 4000 to 6000 rub. |
What determines the cost of tomography?
Tomograph power
Applying Contrast
Personnel qualifications
Promotions and discounts
MRI of the brain: how is the procedure performed?
For diagnostics, it is better to choose spacious clothing made from natural fabrics without zippers or buttons.
The patient arrives at the clinic according to a prior appointment. Items that can cause blur in the photo (keys, key fobs, cell phone, jewelry, magnetic cards, etc.) must be deposited.
The medical staff clarifies that there are no contraindications to the diagnostic procedure:
- metal components in the body - prostheses, hemostatic vascular clips, stents, fragments, etc.;
- mechanical or electrical equipment - pumps for supplying drugs, neuro-, myo-, pacemaker, artificial heart valves, permanent hearing prosthesis;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- claustrophobia, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy.
Contrast is not available if you have had an allergic reaction to gadolinium in the past or have end-stage renal failure (glomerular filtration rate less than 30 ml/min).
The x-ray technician explains the rules of behavior and the essence of the diagnostic procedure. The patient is placed on the tomograph table, a special radiofrequency coil is placed above his head to enhance the magnetic field, and a series of images are taken. After completing the study, there are no obstacles to normal activities.
How is an MRI of the brain performed with contrast?
Indications for enhanced scanning are:
- suspicion of a large tumor;
- staging of the tumor process;
- clarification of the structure of the focus or zone of the pathological MR signal obtained on native MRI photos;
- the need to determine hemodynamic features for differential diagnosis;
- monitoring changes after surgery to remove intracranial (intracranial) space-occupying formations;
- determining the phase of the disease (acute or chronic);
- counting the exact number of pathological foci.
During a planned MRI with contrast, a catheter is installed in a vein: during the necessary phases of the study, an amplifier drug will be delivered into the body using a special injector. The duration of the diagnostic procedure increases by about a third and takes about 50-60 minutes. After turning off the unit, the catheter is removed from the vein and an aseptic dressing is applied.