Ventriculomegaly is a pathology that affects the ventricles of the brain. The function of these parts of the organs is to maintain intracranial pressure and ensure normal blood circulation to the human cerebral cortex.
Most often, the disease occurs in unborn babies, less often in children of preschool and school age. Ventriculomegaly in adults develops in exceptional cases, since the disease is congenital.
Let's take a closer look at what ventriculomegaly is, the causes of its occurrence and how it is treated.
Causes and prerequisites for the development of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
According to medical research, ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles occurs due to the following reasons:
- Hereditary prerequisites. If any of the child’s close relatives (mother, father, siblings/cousins) suffered from a similar disease, the likelihood of its occurrence in the newborn increases to 25% compared to a baby in whom no one in the family had such a disease;
- Ventriculomegaly in the fetus often develops as a side disease along with another disease, such as Down syndrome;
- Pathology is provoked by intrauterine infections, as a result of which the ventricles of the brain enlarge.
Prerequisites for the development of ventriculomegaly
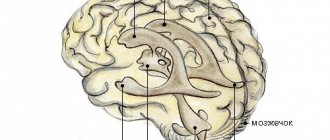
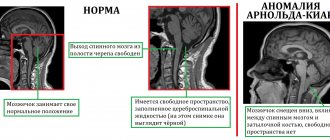
Normally, each person has four cerebral ventricles. Two of them - ventriculi laterales (telencephalon) - are located in the thickness of the white matter: below the corpus callosum, symmetrically on both sides of the midline. Communication with the third of the ventricles - ventriculus tertius (diencephalon) - is carried out through the Monroe (or interventricular) foramina.
The third of the ventricles is located between the visual thalamus, it has the shape of a ring, and in its walls, formed by the gray matter of the brain, there are subcortical autonomic centers. Through the cerebral aqueduct of the midbrain, it communicates with the fourth ventricle - ventriculus quartus (mesencephalon), which is connected to the central canal of the spinal cord.
The main function of the ventricles of the brain is the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which then, if there are no malformations, enters the subarachnoid (or subarachnoid) space. Impaired cerebrospinal fluid outflow provokes the development of ventriculomegaly.
The course of fetal ventriculomegaly in pregnant women after 35 years
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus most often develops if the child’s mother is over 35 years old. This happens for the following reasons:
- The risk of genetic disorders (for example, Down syndrome) increases;
- Intrauterine infections occur more often;
- A pregnant woman over 35 years of age is susceptible to complications while bearing a child.
Thus, if the mother is under 35 years old, ventriculomegaly in the child occurs only in exceptional cases.
Diagnosis of lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain
Ultrasound procedure of a child’s brain
Depending on the age of the patient, various methods for diagnosing pathology are used:
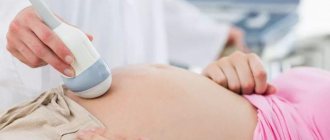
- The disease can be detected in the fetus starting from the 17th week of pregnancy. For diagnosis, the doctor performs an ultrasound of the mother’s abdominal cavity;
- Ventriculomegaly in an infant is confirmed after an ultrasound of the head;
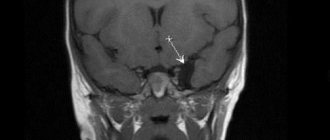
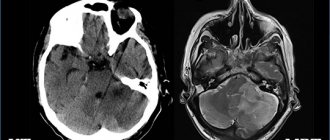
- To diagnose an adult, an MRI of the brain is prescribed.
All procedures are aimed at examining the ventricles of the brain and identifying lateroventriculoasymmetry (violation of ventricular symmetry).
Treatment of ventriculomegaly
Treatment of ventriculomegaly is aimed at preventing the negative consequences of the pathology, including various serious diseases of the brain and central nervous system.
When the cause of the disease is infection, the goal of the prescribed therapy is to eliminate it. If the manifestations of the pathology are mild or moderate in nature, specific treatment, as a rule, is not required, since such a condition rarely causes disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus.
If drug treatment of ventriculomegaly is still indicated, pregnant women are prescribed:
- Diuretics;
- Antihypoxants;
- Vitamins.
Ventriculomegaly therapy is supplemented with massage and a set of physical therapy exercises that involve static loads on the pelvic floor muscles.
Severity of ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles
Doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of pathology:
- First: an increase in the ventricles of the brain to 11-12 mm. Patients are diagnosed with “ventriculodilation” - a slight expansion of the ventricles of the brain in newborns and preschool children;
- Second: enlargement of the ventricles up to 15 mm. Against this background, asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain and impaired blood flow to the affected areas are often observed;
- Third: enlargement of the ventricles up to 20 mm. At this stage, irreversible changes occur in the structure of the brain.
In addition, the child may be diagnosed with “borderline ventriculomegaly,” which means an increase in the lateral ventricles by no more than 9 mm.
Ventriculomegaly 1st degree
At the first stage of development of the disease, there are no pronounced symptoms. Only a neurologist can detect it after diagnosis. Most parents notice that the child becomes excitable and irritable. Unfortunately, no other symptoms appear.
Moderate ventriculomegaly
The second stage of the disease is also called “moderate ventriculomegaly.” As a rule, it is combined with other ailments, for example, ventriculomegaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum often occur together. Also in this case, lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain (asymmetry of the ventricles) occurs. The following symptoms are also observed:
- Periodic convulsions, similar to epileptic seizures;
- Increase in head size;
- The presence of bulging veins on the forehead;
- Slow physical development;
- Mental retardation.
Severe ventriculomegaly
In addition to abnormal expansion of the ventricles of the brain, the following symptoms are present:
- Increased intracranial pressure due to the asymmetric shape of the ventricles;
- Recurrent headaches;
- Speech disorders.
Additional diseases are often added to the pathology: cerebral palsy, Down syndrome or hydrocephalus.
Ventriculomegaly in a child: what is it, causes, treatment
Ventriculomegaly is a pathology that affects the ventricles of the brain. The function of these parts of the organs is to maintain intracranial pressure and ensure normal blood circulation to the human cerebral cortex.
Most often, the disease occurs in unborn babies, less often in children of preschool and school age. Ventriculomegaly in adults develops in exceptional cases, since the disease is congenital.
Let's take a closer look at what ventriculomegaly is, the causes of its occurrence and how it is treated.
Classification of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain
Ventriculomegaly in a newborn is of two types:
- Idiopathic - the factor causing the pathology is unknown, the pregnant woman did not have any complications or health problems;
- Symptomatic – during pregnancy, there were prerequisites for the onset of the disease, for example, the woman suffered an infectious disease, drank alcohol, or suffered a severe stressful situation.
Causes and prerequisites for the development of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
According to medical research, ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles occurs due to the following reasons:
- Hereditary prerequisites. If any of the child’s close relatives (mother, father, siblings/cousins) suffered from a similar disease, the likelihood of its occurrence in the newborn increases to 25% compared to a baby in whom no one in the family had such a disease;
- Ventriculomegaly in the fetus often develops as a side disease along with another disease, such as Down syndrome;
- Pathology is provoked by intrauterine infections, as a result of which the ventricles of the brain enlarge.
The course of fetal ventriculomegaly in pregnant women after 35 years
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus most often develops if the child’s mother is over 35 years old. This happens for the following reasons:
- The risk of genetic disorders (for example, Down syndrome) increases;
- Intrauterine infections occur more often;
- A pregnant woman over 35 years of age is susceptible to complications while bearing a child.
Thus, if the mother is under 35 years old, ventriculomegaly in the child occurs only in exceptional cases.
Diagnosis of lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain
Ultrasound procedure of a child’s brain
Depending on the age of the patient, various methods for diagnosing pathology are used:
- The disease can be detected in the fetus starting from the 17th week of pregnancy. For diagnosis, the doctor performs an ultrasound of the mother’s abdominal cavity;
- Ventriculomegaly in an infant is confirmed after an ultrasound of the head;
- To diagnose an adult, an MRI of the brain is prescribed.
All procedures are aimed at examining the ventricles of the brain and identifying lateroventriculoasymmetry (violation of ventricular symmetry).
Severity of ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles
Doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of pathology:
- First: an increase in the ventricles of the brain to 11-12 mm. Patients are diagnosed with “ventriculodilation” - a slight expansion of the ventricles of the brain in newborns and preschool children;
- Second: enlargement of the ventricles up to 15 mm. Against this background, asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain and impaired blood flow to the affected areas are often observed;
- Third: enlargement of the ventricles up to 20 mm. At this stage, irreversible changes occur in the structure of the brain.
In addition, the child may be diagnosed with “borderline ventriculomegaly,” which means an increase in the lateral ventricles by no more than 9 mm.
Ventriculomegaly 1st degree
At the first stage of development of the disease, there are no pronounced symptoms. Only a neurologist can detect it after diagnosis. Most parents notice that the child becomes excitable and irritable. Unfortunately, no other symptoms appear.
Moderate ventriculomegaly
The second stage of the disease is also called “moderate ventriculomegaly.” As a rule, it is combined with other ailments, for example, ventriculomegaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum often occur together. Also in this case, lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain (asymmetry of the ventricles) occurs. The following symptoms are also observed:
- Periodic convulsions, similar to epileptic seizures;
- Increase in head size;
- The presence of bulging veins on the forehead;
- Slow physical development;
- Mental retardation.
Severe ventriculomegaly
In addition to abnormal expansion of the ventricles of the brain, the following symptoms are present:
- Increased intracranial pressure due to the asymmetric shape of the ventricles;
- Recurrent headaches;
- Speech disorders.
Additional diseases are often added to the pathology: cerebral palsy, Down syndrome or hydrocephalus.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
The disease is most often congenital, so it can be detected even before the birth of the child. To do this, the expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, based on the results of which the degree of pathology is determined. In the third degree, the woman is offered an abortion, since the risk of miscarriage is high.
In other cases, doctors begin searching for the cause of the pathology:
- A woman must be tested for infectious diseases;
- The fetus is checked for the presence of congenital pathologies (cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, etc.);
- If no abnormalities are found, the pregnant woman is prescribed potassium tablets. It saturates the fetus with oxygen, which improves its condition.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in a newborn
With a mild degree of pathology, no therapy is prescribed: the mother only needs to carefully monitor the child’s condition and, at the slightest deviation from the norm, contact a neurologist.
The second stage is treated with medication: the child is prescribed drugs that accelerate processes in the brain:
- Vitamin B tablets;
- Diuretics are drugs that remove excess fluid from the body;
- Medicines to improve blood circulation.
To enhance the effect, it is recommended to walk with your child in the fresh air more often and perform minimal physical exercise with him.
Surgery
The third degree of pathology is treated surgically, since taking medications will not give any results. The asymmetric shape of the ventricles is corrected by performing ventriculo-peritoneal shunting.
This is an operation during which shunts are installed to remove excess fluid. After surgery, children recover quite quickly: insomnia disappears and appetite returns.
Possible complications of ventriculomegaly in a newborn
According to statistics, fetal ventriculomegaly in combination with other genetic abnormalities leads to death in 5% of all cases of the disease.
In 25% of cases, with the successful birth of a child, he may later develop diseases such as cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, etc. But, as practice shows, with timely therapy and shunt surgery (if necessary), the baby’s health condition can be significantly improved or the signs of the disease can be completely eliminated.
Causes and treatment of ventriculomegaly in the fetus Link to main publication
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
The disease is most often congenital, so it can be detected even before the birth of the child. To do this, the expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, based on the results of which the degree of pathology is determined. In the third degree, the woman is offered an abortion, since the risk of miscarriage is high.
In other cases, doctors begin searching for the cause of the pathology:
- A woman must be tested for infectious diseases;
- The fetus is checked for the presence of congenital pathologies (cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, etc.);
- If no abnormalities are found, the pregnant woman is prescribed potassium tablets. It saturates the fetus with oxygen, which improves its condition.
With ventriculomegaly in the fetus, the consequences depend on the promptness of treatment at the stage of pregnancy.
Treatment
Ventriculomegaly in infants, if the disease is mild, cannot be treated. If the ventricles are slightly enlarged, it is necessary to monitor the child, and if there is the slightest deviation, contact a neurologist.
In case of moderate severity, medications are prescribed that will speed up processes in the pituitary gland, remove excess fluid, and are also prescribed to improve blood circulation.
Frequent walks in the fresh air and light exercise are recommended.
When a severe degree of illness is detected in a child, an operation is performed, since therapeutic measures will not bring any effect. During surgery, ventriculoperitoneal shunting is performed, which corrects ventricular asymmetry.
If the child is still in the womb, then for mild to moderate pathology, drug treatment is prescribed with potassium, vitamins and drugs to improve blood circulation. When the cause of the disease is related to infection, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. If a severe degree is diagnosed, the pregnancy is terminated only if the timing allows this to be done without harm to the mother’s health.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in a newborn
With a mild degree of pathology, no therapy is prescribed: the mother only needs to carefully monitor the child’s condition and, at the slightest deviation from the norm, contact a neurologist.
The second stage is treated with medication: the child is prescribed drugs that accelerate processes in the brain:
- Vitamin B tablets;
- Diuretics are drugs that remove excess fluid from the body;
- Medicines to improve blood circulation.
To enhance the effect, it is recommended to walk with your child in the fresh air more often and perform minimal physical exercise with him.
Surgery
The third degree of pathology is treated surgically, since taking medications will not give any results. The asymmetric shape of the ventricles is corrected by performing ventriculo-peritoneal shunting.
This is an operation during which shunts are installed to remove excess fluid. After surgery, children recover quite quickly: insomnia disappears and appetite returns.
Ventriculomegaly in infants
Ventriculomegaly in an infant: what is this diagnosis and what treatment should the child receive?
Ventriculomegaly is a congenital (rather rarely acquired) pathology of the brain caused by its incorrect intrauterine development. The disease is characterized by an increase (dilation) of the lateral ventricles in size, which leads to the formation of various neurological disorders in the newborn.
Normally, the size of the lateral ventricle should not exceed 1...4 millimeters. Ventriculomegaly is confirmed if these indicators increase to 12...20 millimeters.
The causes of this pathology are not known to doctors. But according to statistical data, this disorder is diagnosed much more often in children born to women over 35 years of age than in children born to younger mothers.
Dilation of the lateral ventricles is perceived by many pediatricians not as an independent disease, but as a pathological condition caused by intrauterine developmental defects. Ventriculomegaly can form in response to the prematurity of the child, as well as in children whose mothers suffered a severe infectious disease during pregnancy and suffered an abdominal injury, accompanied by uterine bleeding.
Very often, dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain is diagnosed in conjunction with chromosomal abnormalities, for example, Down syndrome. Non-hereditary developmental defects are no exception.
In healthy infants, pathology can develop as a complication of rickets. In older children, dilation of the ventricular cavities can accompany mental illnesses such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
What are the types of ventricular dilatation?
To assess the development of the fetal brain, a woman undergoes an ultrasound procedure. This is the only reliable method for diagnosing pathology.
There are two types of ventriculomegaly - right-sided and asymmetric.
The next gradation is based on the type of severity of the current.
- Easy pathology format. The expansion of the ventricles does not exceed 12 millimeters.
- Moderate severity. Dilatation reaches 15 millimeters and is accompanied by suffocation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (brain fluid). The child is diagnosed with neurological disorders.
- Severe form. The volume of the cerebral ventricle is increased to 20 millimeters (sometimes more). In this case, severe pathologies of brain development are recorded, in particular, hydrocephalus can be confirmed.
According to location they are distinguished:
- lateral dilatation of the ventricles (left + posterior);
- pathology of the third ventricle (in the area of the visual tuberosities in the front of the forehead);
- fourth ventricle (in the occipital part - in the medulla oblongata and cerebellum).
Symptoms of pathology
The disease can be diagnosed without any problems during an intrauterine ultrasound procedure. But a specialist may miss the pathology if the deviation is small (a mild form of ventriculomegaly, not combined with any other diseases).
If a child is born with this deviation, then it is necessary to carefully monitor the progress of its development. The baby requires specialist advice in the following cases:
- he later sat down and walked (in comparison with his peers);
- the child is silent at a time when it is time to babble and try to pronounce sounds;
- experiences headaches and seizures;
- with a large head size (the difference between the volume of the skull and the baby’s chest exceeds 3 centimeters).
Sometimes the diagnosis is made to children with existing delays in motor and speech development. But as such, ventriculomegaly is absent. Subsequently, such children easily catch up with their peers in development and, of course, we are not talking about any neurological type deviations.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly
After determining the degree of dilatation of the ventricles, the child can be prescribed either treatment or simply observation. In approximately 80% of all diagnosed mild and moderate cases, children develop without any abnormalities. The remaining 20% accounts for the formation of various neurology.
The drug treatment regimen is drawn up by the doctor on an individual basis. Here the severity of the pathology and the characteristics of the course of the disease are taken into account. You need to understand that medications cannot return the ventricle to the “correct” size, but they normalize the processes occurring with “errors”.
The most common appointments are:
- Nootropic drugs that improve blood supply to brain cells.
- Antihypoxants. The drugs increase the body's resistance to hypoxia.
- Diuretics. Medicines help remove excess fluid.
- Potassium-sparing drugs. The drugs slow down the removal of potassium from the child’s body, which prevents the formation of neurological disorders.
- Vitamin complexes.
Therapeutic gymnastics and massage sessions provide good results.
In case of severe pathology, the child may be prescribed surgical treatment. A drainage tube is installed in the baby's skull to drain excess fluid.